Econometrics Chapters 1-6 Cumulative Review
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
Jack and Jill have a quiz for their statistics class on Monday. Jack studies for quizzes 30% of the time and his friend Jill studies 40% of the time. The probability that at least one of Jack or Jill studies for a quiz is 58%. Are the students study habits statistically independent?
Yes, their study habits are statistically independent.
Should have found out by either
- P(J) dependent on P(L)
or
- P(J)P(L) = P(J intersect L)
A professor notices that 40% of students attend every class. The professor also notes that of students who attend every class, 80% receive a B or higher on the final exam. Of the students who do not attend every class, only 10% receive a B or higher on the final exam. What is the probability that a randomly selected student does not receive a B or higher on the final exam?
P(B compliment) = 0.62
Six students will be competing in the annual spelling contest. You are required to predict, in order, the students that will become the top 3 contestant.
a) Ignore the possibility of ties, calculate the number of different predictions you could make.
b) What is the probability of making the correct prediction by chance?
a) 120
b) 1/120
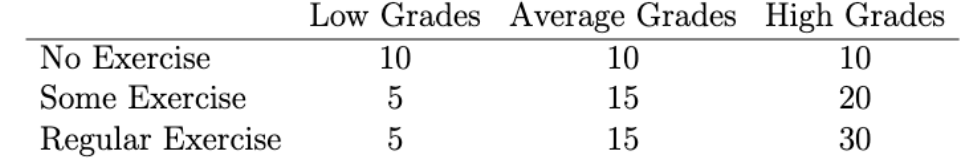
A study looked at the relationship between exercise and school performance among 120 students. The table below gives the results. Suppose one student is chosen at random.
a) What is the probability that the student does no exercise?
b) What is the probability that the student has high grades?
c) Given the student has high grades, what is the probability that they do regular exercise?
d) Given the student does no exercise, what is the probability that they have at least average grades?
a) ¼
b) ½
c) ½
d) 2/3
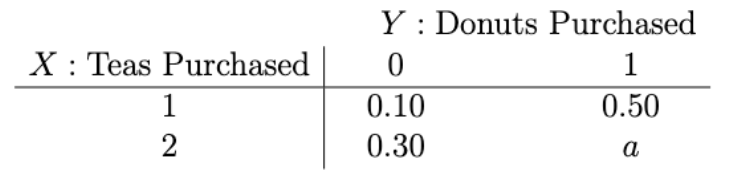
A study examined the relationship between tea purchases (X) and donut purchases (Y). The table below provides the joint PMF P(x,y).
a) What value of a in the table above makes the joint PMF P(x, y) consistent with the postulates of probability? Use the value that you calculate for a to answer (b) to (d).
b) What is the expected value of X?
c) What is the variance of X?
d) What is the covariance of X and Y?
a) 0.10
b) 1.40
c) 0.24
d) -0.14
Three students are running a marathon. The probability that a student finishes the race is ½, and whether a student finishes does not depend on whether the other students finish. Let X be the random variable representing the number of students who finish the race.
a) Write out the PMF for the variable X in a table
b) What is the expected value of X?
c) What is the variance of X?
a)
0 = 1/8
1 = 3/8
2 = 3/8
3= 1/8
b) 3/2
c) 3/4
Sandra is selling coffees at the farmers’ market. She earns $10 for every coffee she sells and receives a $4 bonus if she sells at least 4 coffees in a given day. The probability of any student buying a coffee is 1/4 and their purchase decisions are independent. If 4 students shop at the farmers’ market today, how much money does Sandra expect to earn?
10 + 1/64
Vikram works at a store and has noticed that customers visit the store 5 times per day on average. Assuming customers’ shopping visits occur independently, what is the probability that customers visit the store at least 3 times today? What is the variance in the number of visits per day
1 - 18.5e^-5
We know the smash burger weights at a local eatery are normally distributed with a standard deviation of 4 ounces. What is the probability that a sample of 64 smash burgers has an average weight between 6 and 8 ounces, if the true mean is 7 ounce?
0.9544
A group of 1,000 runners is training for a 10 km race. The average training time per week for all runners is unknown, but the population standard deviation is known to be 12 minutes. A random sample of 36 runners is selected, and their weekly training times are recorded. What is the probability that the sample mean exceeds the population mean by more than 4 minutes?
0.0228
On a 6-mile hiking trail, tourists are equally likely to stop at any point to take photos – so stops are uniformly spread along the trail. Let X be the distance (in miles) from the start of the trail (mile 0) where a randomly selected tourist stops.
a) Draw the PDF of the variable X in a figure.
b) What is the expected value of X?
c) What is the variance of X?
a) straight line at 1/6
b) 3
c) 3
The random variable X has probability density function f (x) = 3/7 x^2 for
1 ≤ x ≤ 2 and 0 otherwise.
a) What is the CDF?
b) What is the probability that x is between 1 and 2?
a) antiderivative of pdf
b) 1