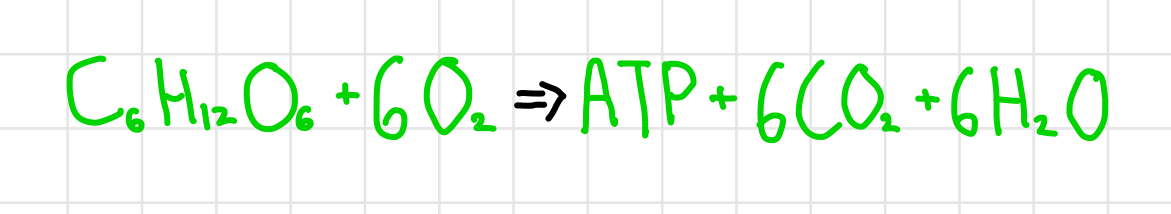
Life Hierarchy Homeostasis/Metrics
1/35
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
SPONCH
Sulfur, Phosphorous, Oxygen, Nitrogen, Carbon, Hydrogen. The major elements of life.
The four primary tissue types in the human body
Epithelial, Connective, Muscle, and Nervous
Cell
Smallest living unit in the body
Tissue
Group of cells that perform a common function
Organ
Group of two or more tissue types
Homeostasis
The maintenance of a relatively stable internal environment.
Extracellular Fluid (ECF)
The fluid environment where the cells live, or the fluid outside the cells
Plasma
The liquid portion of blood
Interstitual Fluid (ICF)
The fluid contained within all body cells
How does the Nervous System maintain homeostasis?
Neurons within this system control rapid responses to changes from the external environment
How does the Endocrine System maintain Homeostasis?
Glands within this system regulate bodily functions that require duration, like concentration of internal volumes and electrolytes
Ideal blood pressure
120/80 mmHg
Ideal blood volume
4-5 liters
Ideal human body temperature
37 degrees celsius
Ideal body pH
7.35-7.45
Intrinsic Controls
Local controls inherently existing within an organ that makes corrections or autregulates to benefit the organ
Extrinsic Controls
Regulartory mechansisms initiated outside an organ by the nervous and endocrine systems to benefit the organism
Feedforward
System that makes responses made in anticipation of a change, like the smell of food causing gastric secretion
Negative Feedback Loop (NFbL)
Type of feedback loop that attempts to re-regulate something when the change moves a value away from its reference value, like the lowering of insulin when glucose (blood sugar) is too high.
Positive Feedback Loop (PFbL)
Type of feedback loop that enhances a change that moves away from its reference value and intensifies the original stimulus, like the stretching of the uterine walls causes contractions to stretch futher until birth.
Stimulus
The first step in a feedback system where a change occurs
Receptor
The second step in feedback system where the structures that monitor detect the change.
Afferent Pathway
The third step in the feedback system where info is communicated about the change through neurons or blood.
Control Center (Integration Center)
The fourth step in the feedback system where the CNS or Endocrine system determines the next action
Efferent Pathway
The fifth step in the feedback system where the signals are sent from the integration center to the effector organ
Effector
The sixth step in the feedback system where the organ or tissue that received the directions from the control center produces it
PFbL Response
The output that increases the original stimulus
NFbL Response
The output that removes the original stimulus
kilo (k)
10³
deci (d)
10-1
centi (c)
10-2
milli (m)
10-3
micro (mc) (μ)
10-6
nano (n)
10-9
gram, liter, meter
100
Foundation of all living things