4B alkenes
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
.
.
Single bonds have free rotations and are constantly rotating around binds true or false
True
C=C bonds have restricted rotation. They are unable to move
this results in stereoisomers existing for some alkenes true or false
Definition of stereoisomers
Molecules with the same structural formula but a different arrangement of atoms in 3d space
How are bonds formed in alkenes
When orbitals on two different atoms overlap
A single bond is called what
A sigma bond
What is a double bond called
Pi bond
consequences of pi bonding
geometric isomerism = two points overlap prevent C=C bond from rotating
Reactivity = electrons in pi bonds are more accessible for reactions
How do pi bonds form
the sideways overlap of p-orbitals above and below plane of atoms
Diagram of how pi bonds form
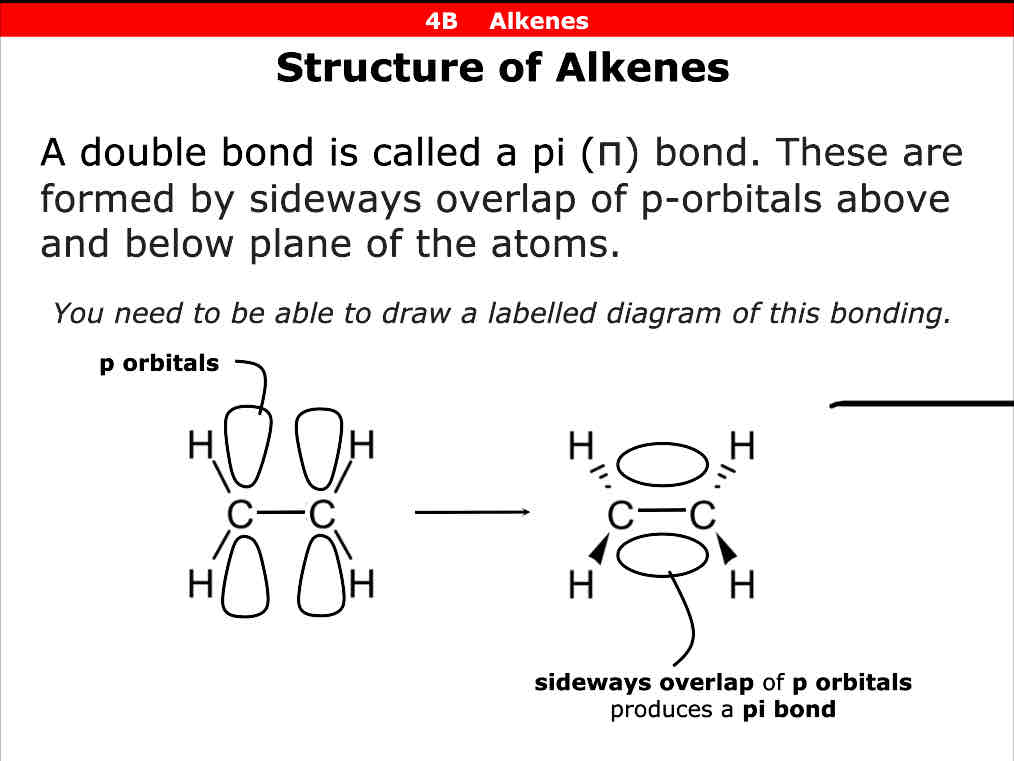
Which bond is stronger sigma or pi bond
sigma bond
When do E/Z isomers exist
When carbon of C=C bond has 2 different groups
How do you name E/Z isomers
•Check each C of C=C is joined to 2 different groups if so E/Z isomers exist •Draw a dashed line down vertically C=C •List atoms joined directly to each C of C=C and circle atoms with highest atomic number (they have the higher priority) •If both priority groups are on the same side of dashed line it i Z isomer
What do you do if two atoms have the same atomic number
List the atomic number of atom one bond further out and whichever one has the highest atomic number has higher priority
How do you know when to use cis or trans isomerism
Need the same group attached to both sides of C=C bond If the same groups are on the Same side it's cis If opposite side it's trans
E isomers pack more closely together meaning more contact area and stronger London forces true or false
True
Alkenes can undergo what reactions
Addition reactions
What is an addition reaction
A reactant is added to an unsaturated molecule to make one saturated molecule.
The two new groups of atoms always attach to the carbon in the double bond
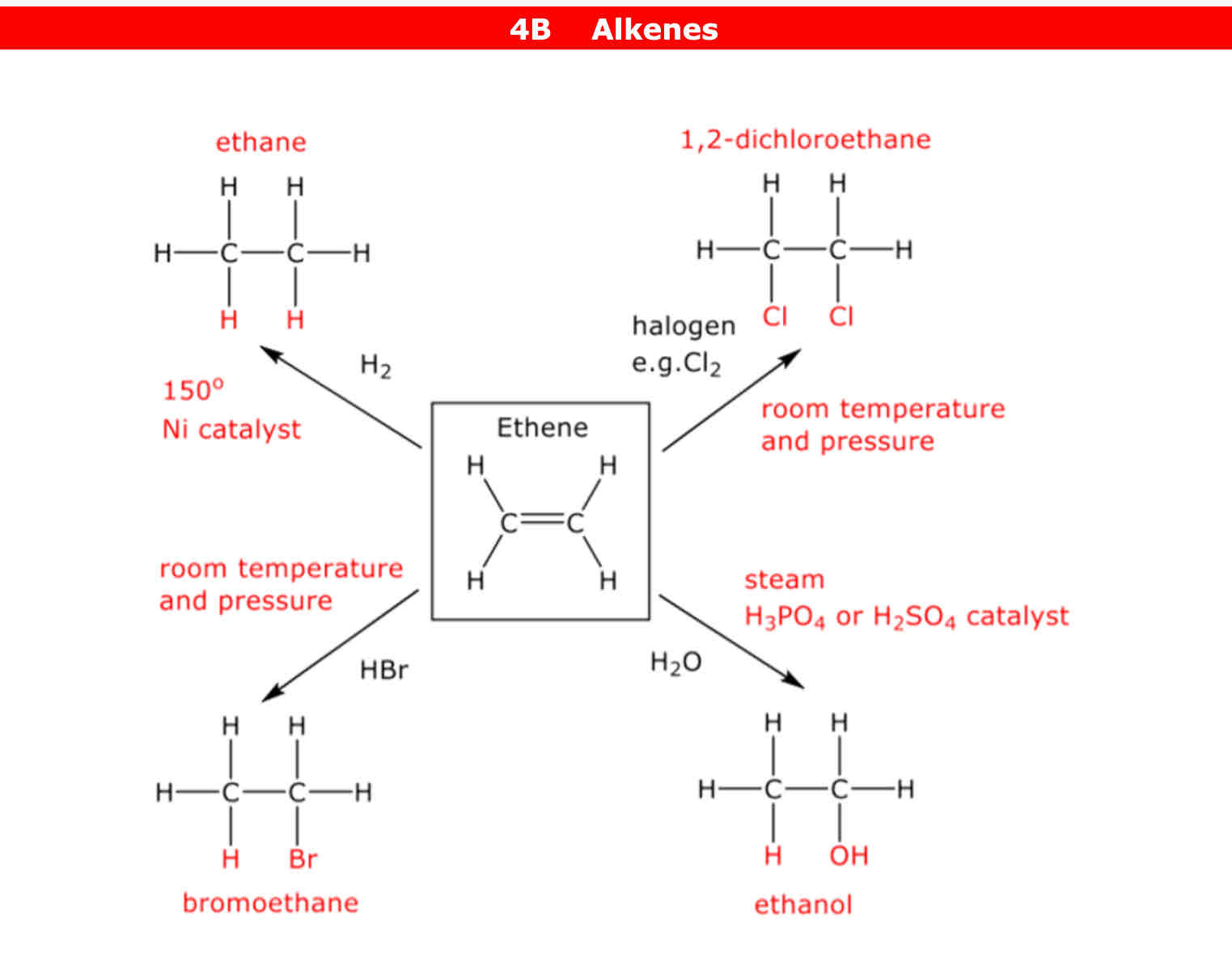
What are the 4 addition reactions and what conditions need to happen for reaction to occur
Alkenes can react with a halogens eg: chlorine but it needs to be at room temperature and pressure
Alkenes can react with water (H2O). The conditions needed are steam (high temperatures) and H3PO4 catalyst or H2SO4 catalyst
Alkenes can react with H2 (hydrogen gas). The conditions needed are 150° and Nickel (Ni) catalyst
Alkenes can react with Hydrogen halide (most of the time it's HBr) but it has to be at room temperature and pressure
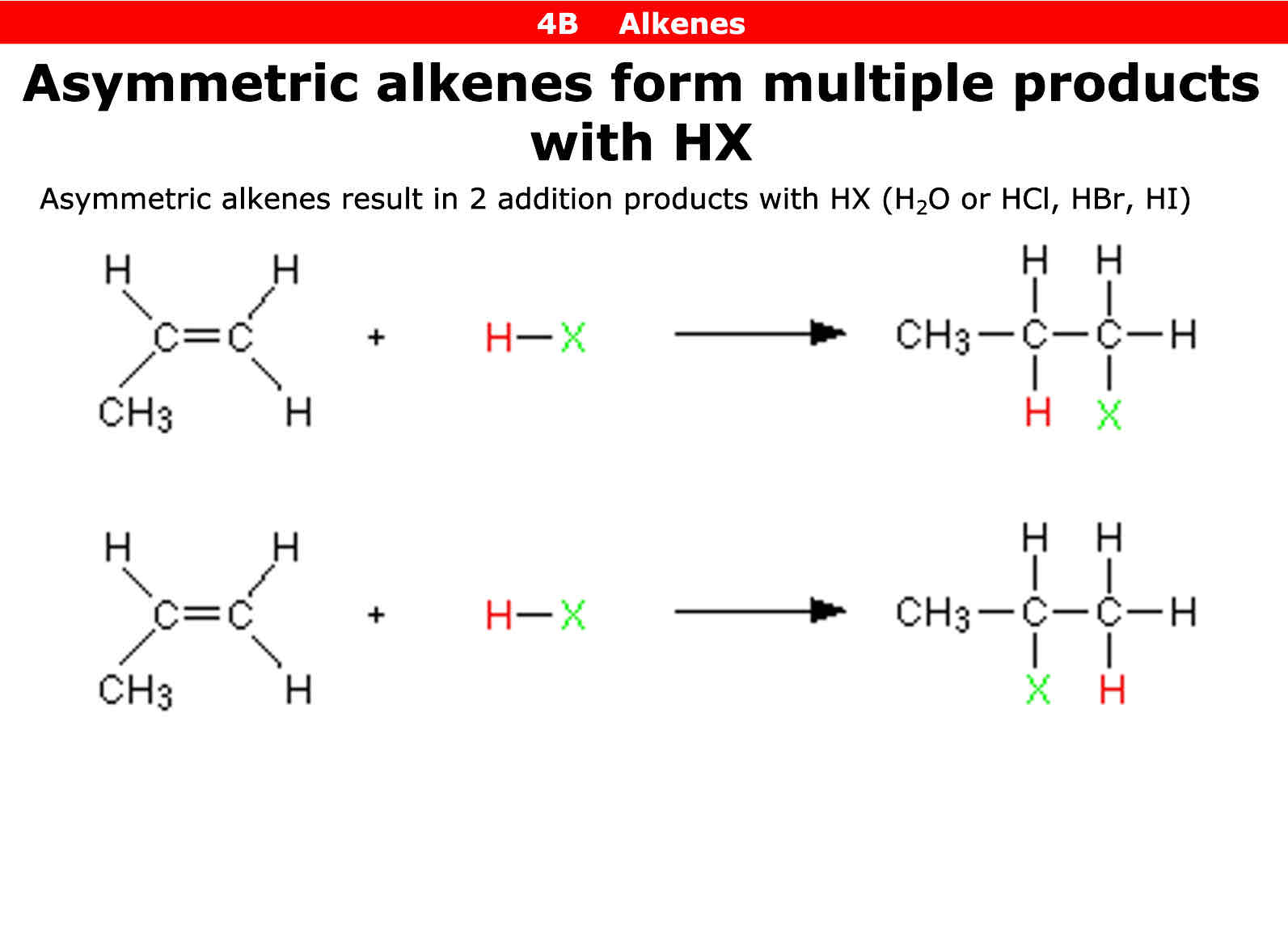
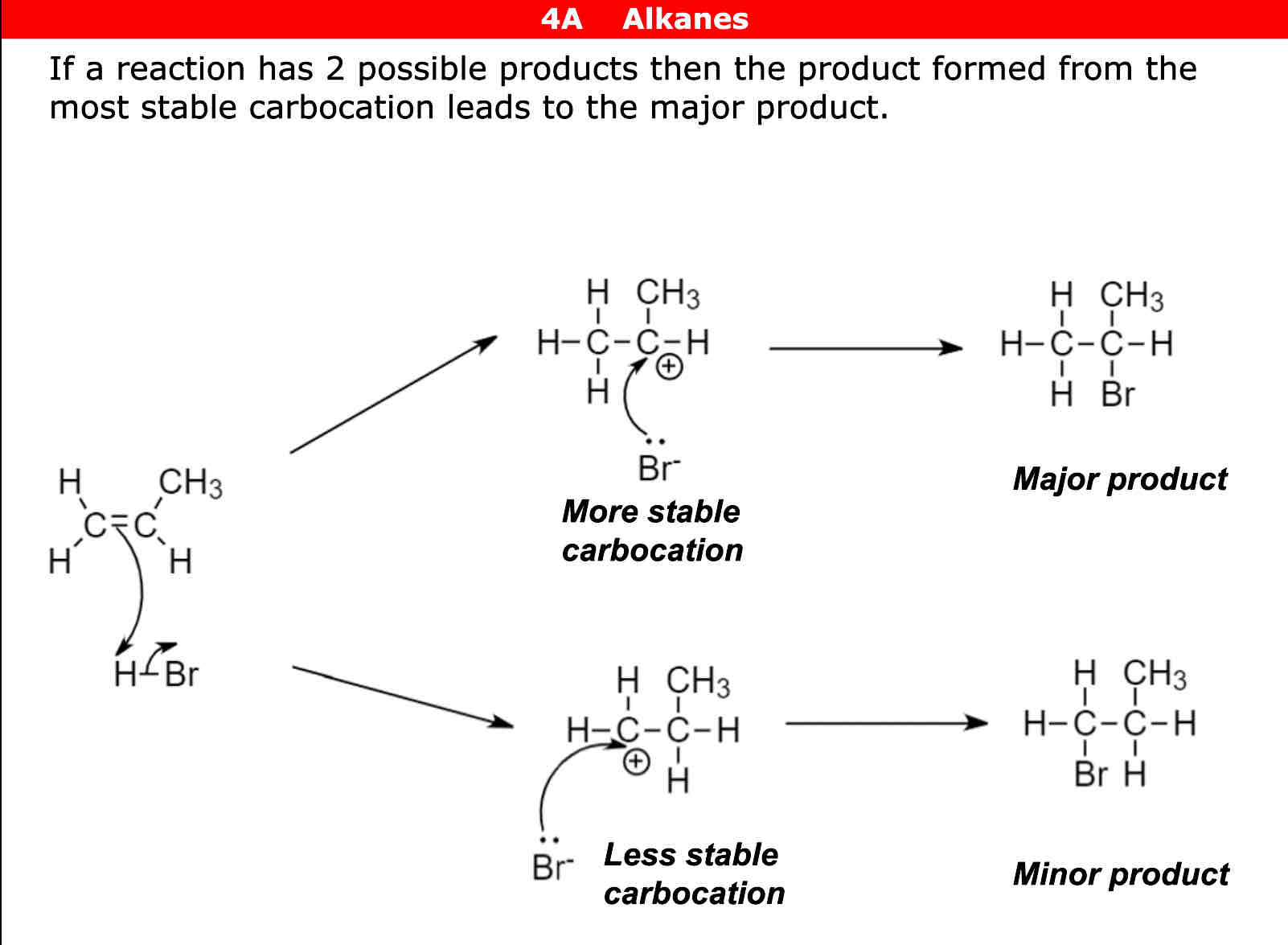
Asymmetric alkenes can react with HX to form 2 addition products true or false
True
How do you tell an alkene is assymetrical
On both sides of carbon double bond there is not the same molecule on the top or bottom half or even opposite
In addition reactions you can have more than one possible product true or false
True
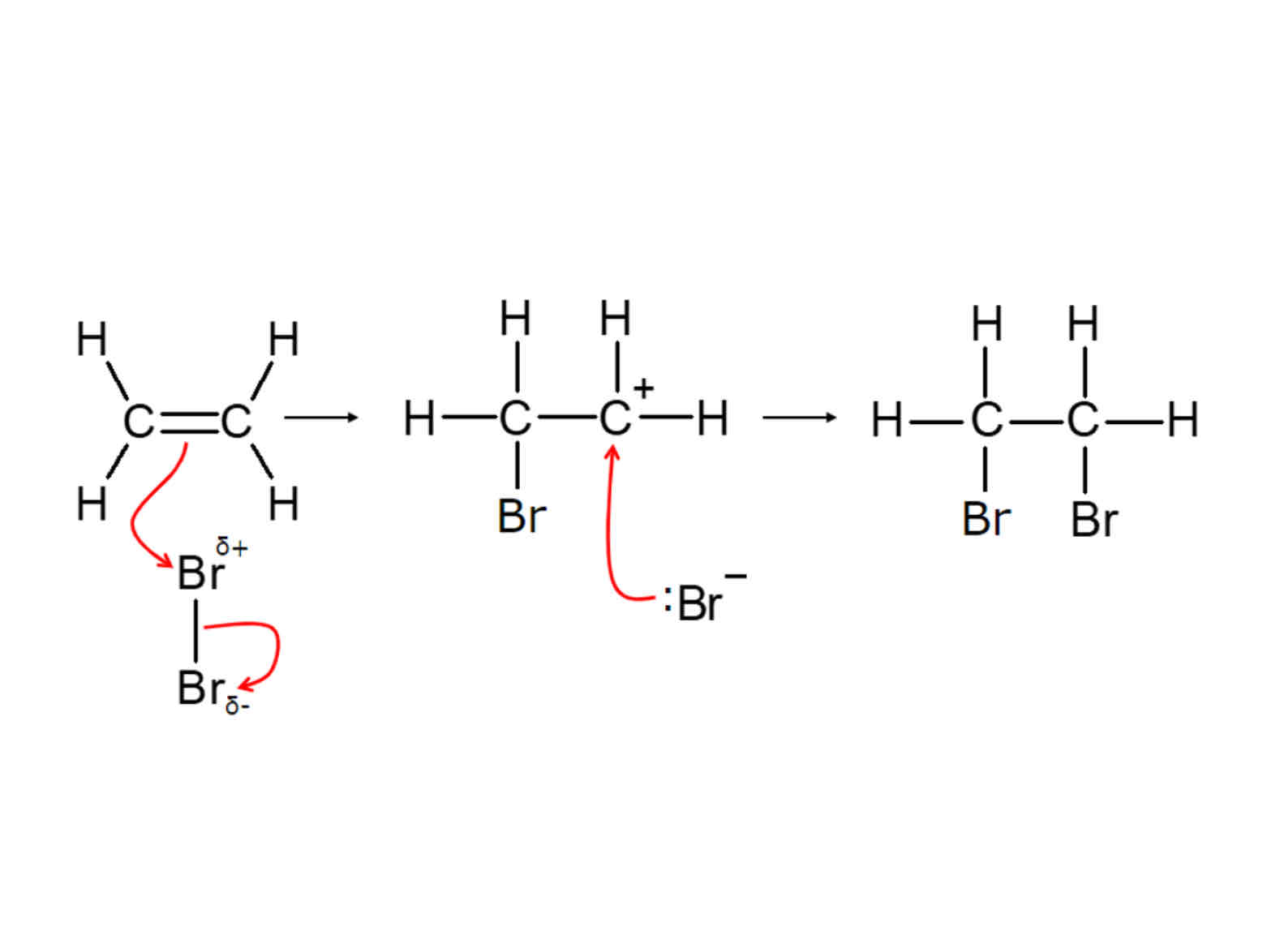
What is electrophillic addiction
Reactions where alkenes react with hydrogen halides, halogens or h20
What is an electrophile
electron pair acceptor
In these reactions what is the electrophile
Hydrogen halides
What is a nucleophile
An electron pair donor
In these reactions what is a nucleophile
Alkene
What does the curly arrow show in electrophilic addition
Shows movement of a pair of electrons
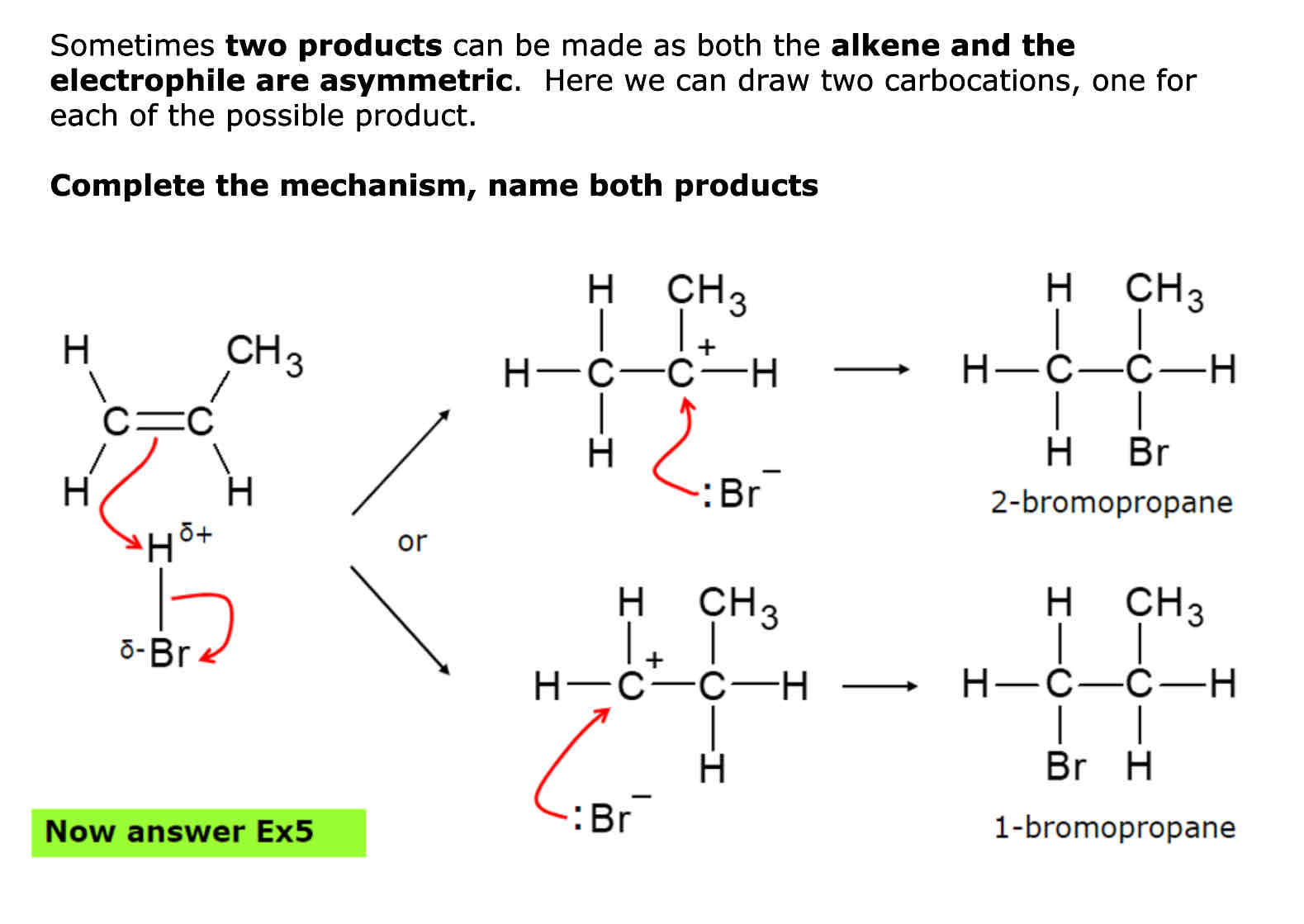
Steps of electrophillic addition
1.)Double bond in alkene attracts electrophiles 2.) pi bond of C=C breaks. The pair of electrons from the pi bond make a new bond with delta + atom of electrophile 3.) delta + atom has too many bonds. The polar bond in electrophile breaks and the electrons move onto the delta - atom as a lone pair 4.) The bond is broken by heterolytic fission forming two ions
.
Sometimes electrophile is not polar and you can do electrophillic addition with molevules like Br2 or H2 true or false
True
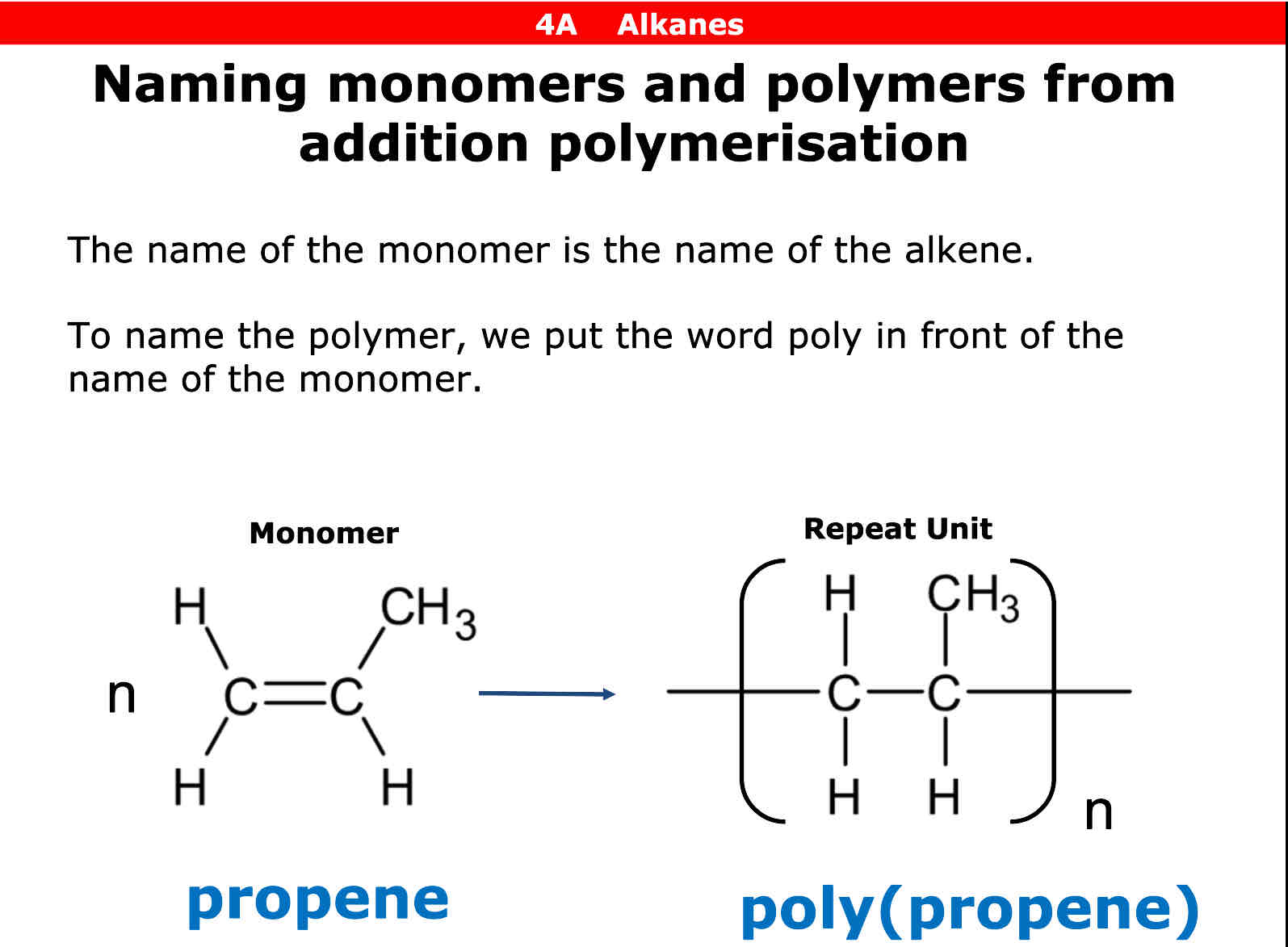
What is addition polymerisation
Joining together of many alkene monomers to form a polymer
When an alkene molecule has the square brackets and letter n what word do you put infront of the molecule
Poly
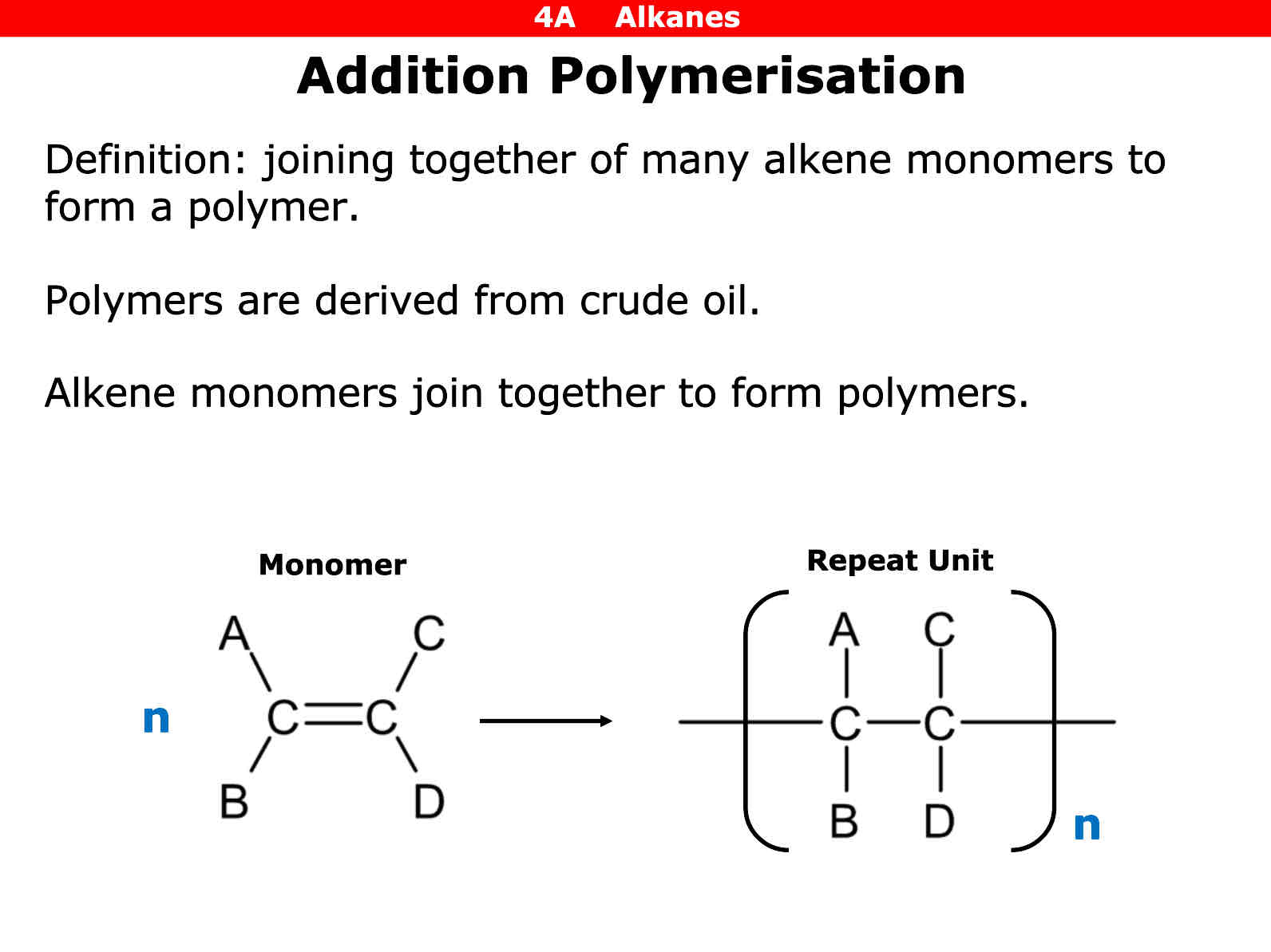
Polymers are derived from what
Crude oil
Alkene monomers join to form what
Polymers
How can we dispose plastics
Recycle them Can be put in landfill Can be burned to produce energy Can be broken down into monomers and used as a feedstock for organic reactions
Biodegradable polymers are broken down by what
Microorganisms
Photodegradable polymers are broken down by what
UV light
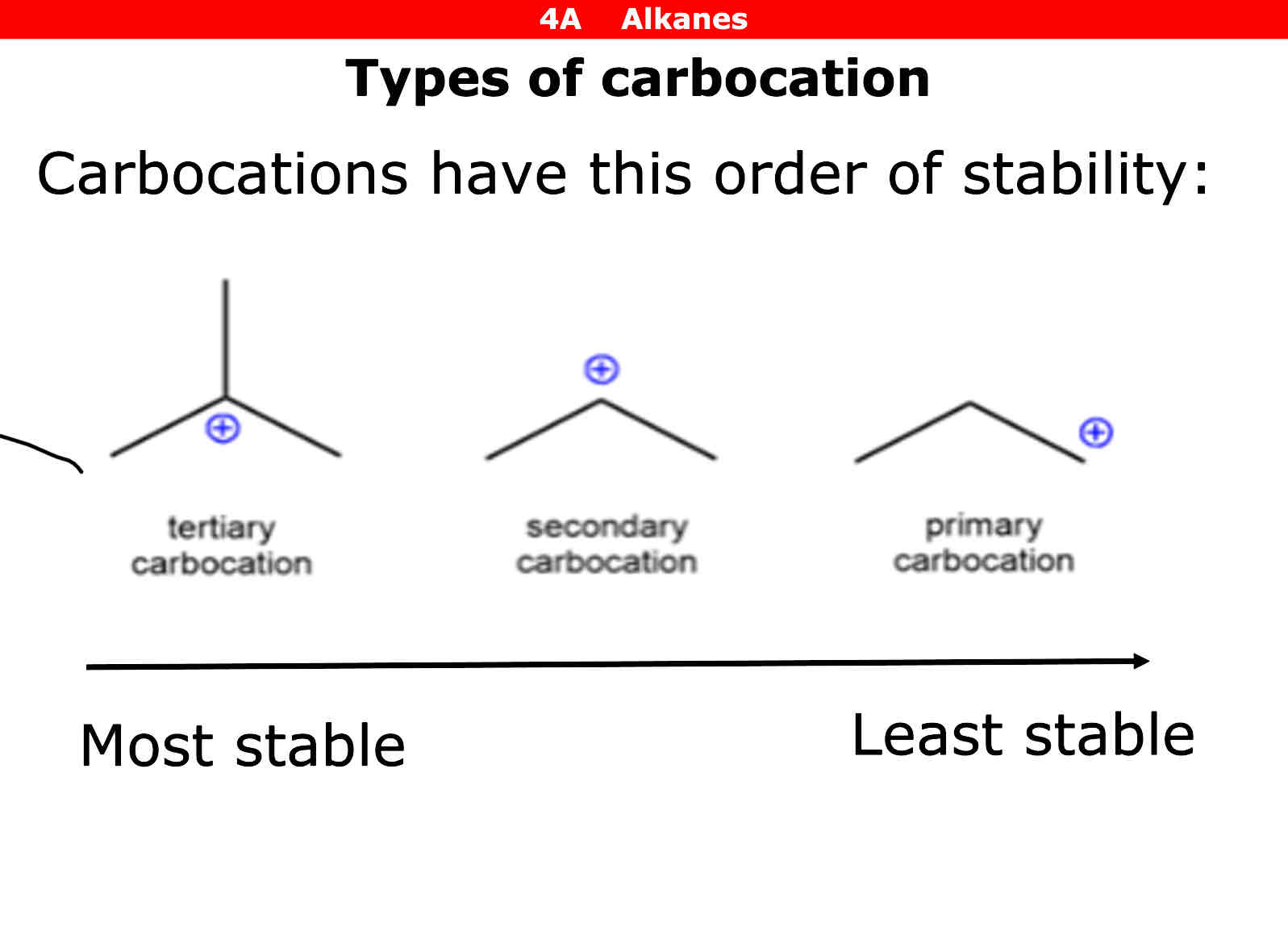
Types of Carbocations
Tiertiary (a carbon joined to 3 other carbons) Secondary (a carbon joined to 2 other carbons) Primary ( a carbon joined to 1 carbon)
Which carbocation is the most and least stable
Tiertiary = most Secondary = second most Primary = least
When in electrophillic addition when 2 products form the carbocation that is most stable forms what
Major product
When in electrophillic addition when 2 products form the carbocation that is least stable forms what
Minor product
Formula for atom economy
Total Mr of useful products/ Total Mr of all products x 100
Big numbers are involved as well
Formula for percentage yield
Actual mass of product / theoretical maximum mass of product x 100
How to calculate theoretical maximum mass of product
Calculate moles of reactant used Calculate maximum amount of moles by seeing ratio Calculate mass with moles and mr
.