CH12 (Part 1) - Urinalysis
1/64
Earn XP
Description and Tags
i miss her (there is no 'her', i just like saying that) (unless) (?)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
65 Terms
Define “Urinalysis“
The macroscopic, physical, chemical, and microscopic analysis of the urine.
True or False: You can diagnose a patient just by urinalysis test.
True.
What is the renal anatomy and physiology of urine?
It is a fluid composed of the blood’s waste materials; an ultrafiltrate of blood.
What are some functions of our kidneys?
Provides homeostasis
Maintains blood pressure
Eliminates metabolic waste (medications, vitamins, any in/organic substances)
Helps regulate hormones
The function of the hormone Erythropoietin (EPO) is?
Induction of RBC production
The function of the hormone aldosterone is?
Salt and water regulation
Anti-diuretic hormone (ADH) allows for?
Release of less water
If urine output is increased,..
…then ADH secretion is decreased.
If urine output is decreased,..
…then ADH secretion is increased.
ADH is also known as?
Vasopressin
What is a nephron?
The basic functional unit of the kidney
How many nephrons are inside each kidney?
1-1.5 million
What is the map of the kidney? (6)
Glomerulus
Bowman’s Capsule
Proximal Convoluted Tubule
Loop of Henle
Descending Loop of Henle
Ascending Loop of Henle
Distal Convoluted Tubule
Collecting Tubules
What is the Glomerulus, and its function?
A tuft of anastomosing capillaries, inside Bowman's Capsule
When blood exits this, it is called glomerular filtrate
What is Bowman’s Capsule?
Semi-permeable membrane that allows passage of substances with MW of less than 70,000 Daltons
What does the Proximal Convoluted Tubule do?
It reabsorbs majority of essential substances from the glomerular filtrate, like ions and sugars
What is the Loop of Henle?
It is the major exchange site for salt and water.
What is the Descending Loop of Henle for?
It is freely permeable to water, and reabsorbs water
What is Ascending Loop of Henle for?
Exchanges salt.
What is Distal Convoluted Tubule for?
Secretion of aldosterone and ADH
What are the Collecting Tubules for?
Allocation of the final concentration of urine.
What does the bladder do?
Store urine
What does the urethra do?
Expel urine (you pee)
What is responsible for the contraction of the bladder?
Sphincter muscle
What is the percent composition of urine?
96% water. 4% dissolved substances.
Free table on urine!
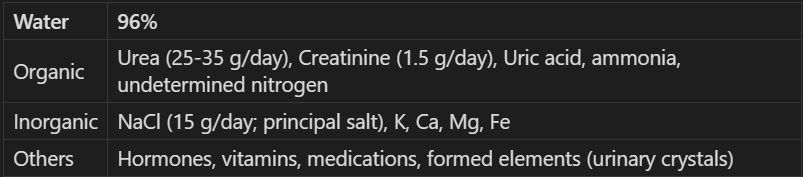
What are some factors that affect urine composition?
Dietary intake (nuts, legumes, red meat)
Physical activity
Body metabolism
Endocrine functions
What are the two most important factors before urine examination?
Patient’s full name
Patient’s date of birth
What does Px mean?
Patient
What does Spx mean?
Specimen
What does Tx mean?
Treatment
What does Dx mean?
Diagnosis
What does DDx mean?
Differential Diagnosis
What is the most commonly received spx in the laboratory?
Single/Random Specimen
What is the ideal screening spx, and the most concentrated?
First Morning Specimen
What are some characteristics regarding the Fasting Specimen (2nd Morning)?
Second voided spx after a period of fasting
In conjunction with fasting blood glucose for blood extraction
Px needs to empty bladder before fasting for 8-10 hours
Fasting spx used for glucose monitoring
What is the 24hr timed spx used for?
Used to measure total amount of solutes in urine, creatinine clearance
What is the 12hr timed spx used for?
Addis count (quantitative), 40% formalin to preserve
What is the 2hr timed spx, Postprandial spx used for?
Glucose testing. Also used to monitor insulin therapy.
Includes insulin dependent, type I diabetes
What is the afternoon (2-4pm) spx used for?
Determines urobilinogen.
The peak concentration for afternoon spx is at 2-4PM due to?
Diurnal activity
What is the Glucose Tolerance spx used for?
To tolerate glucose flow subjected to patient; 75g normal
What is the Mid-Stream Clean Catch spx for?
Most common
What is the Three-Glass Collection for?
Male patients only
Screens prostatic infection
In the three-glass collection specimens, what is the FIRST glass for?
Consists of first voided urine
In the three-glass collection specimens, what is the SECOND glass for?
Mid-stream portion, serves as a control
In the three-glass collection specimens, what is the THIRD glass for?
Consists of prostatic secretions, subjected to microbiology section for bacterial culture
What is the Catheterized spx for?
Bacterial culture.
What does Suprapubic Aspiration include?
Bacterial culture and psychologic studies; anesthetic in bladder, physician uses syringe to puncture bladder
What is the Pediatric Specimen for?
To collect toddlers’ urine sample.
How much mL of urine does the Drug Testing Specimen usually need?
30-45
In some drug testing facilities, how much mL of urine does the Drug Testing Specimen require?
60
What is the temperature range for Drug Testing Specimens?
32.5'C - 37.7'C
What is required regarding Specimen Integrity? (3)
Urine must be delivered to lab and examined within 2 hours
Refrigeration, between 2-8'C, to inhibit bacterial growth and metabolism
Chemical preservative, like 40% formalin, or boric acid
In macroscopic/physical examination, what is the volume of urine needed?
600-2000 mL
In macroscopic/physical examination, what is the color range for urine?
Light yellow (dilute random spx.) to dark yellow (concentrated spx.)
In macroscopic/physical examination, what does it mean when urine is colorless?
Recent fluid consumption (you just had water)
In macroscopic/physical examination, if patient is infected, what color might their urine be?
Green, black, or red
In macroscopic/physical examination, what is the normal transparency of urine?
Clear transparency
In macroscopic/physical examination, if there are any sediments in the urine, to what length can the transparency vary?
Clear, hazy, cloudy, curbid, milky
In macroscopic/physical examination, what is the normal odor?
Faintly aromatic
In macroscopic/physical examination, what could be said if there is a fruity sweet smell?
Presence of ketones, or MSUD (maple syrup urine disease)
In macroscopic/physical examination, what is the range of specific gravity?
1.005 - 1.035
What if there is less specific gravity?
Less concentrated spx.
What if there is more specific gravity?
More concentrated spx.