Neurology for Exam 2 Reduced Version
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
66 Terms
what protects and supports the brain (3)
1) skull (cranium)
2) epidural space
3) meningeal layers
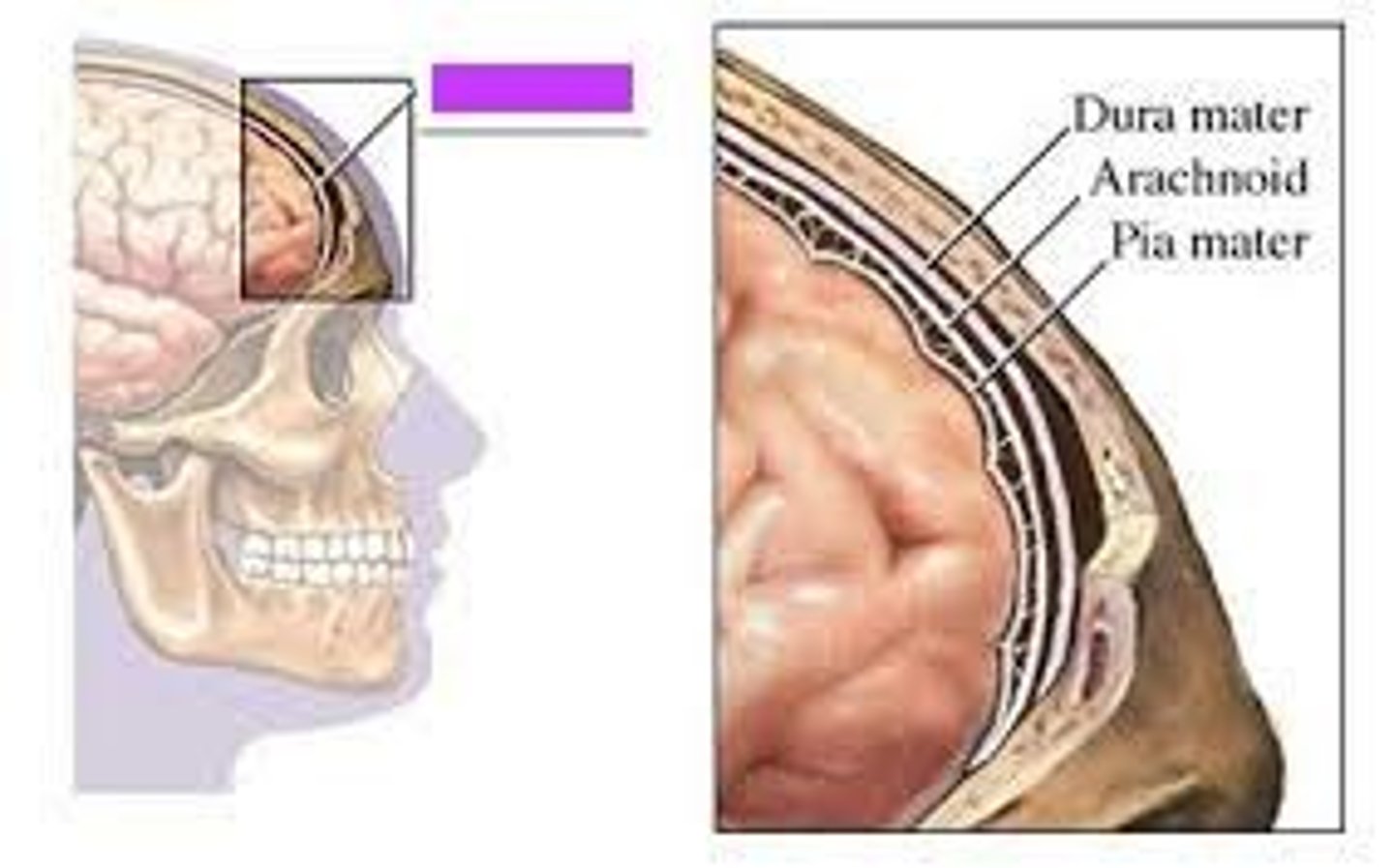
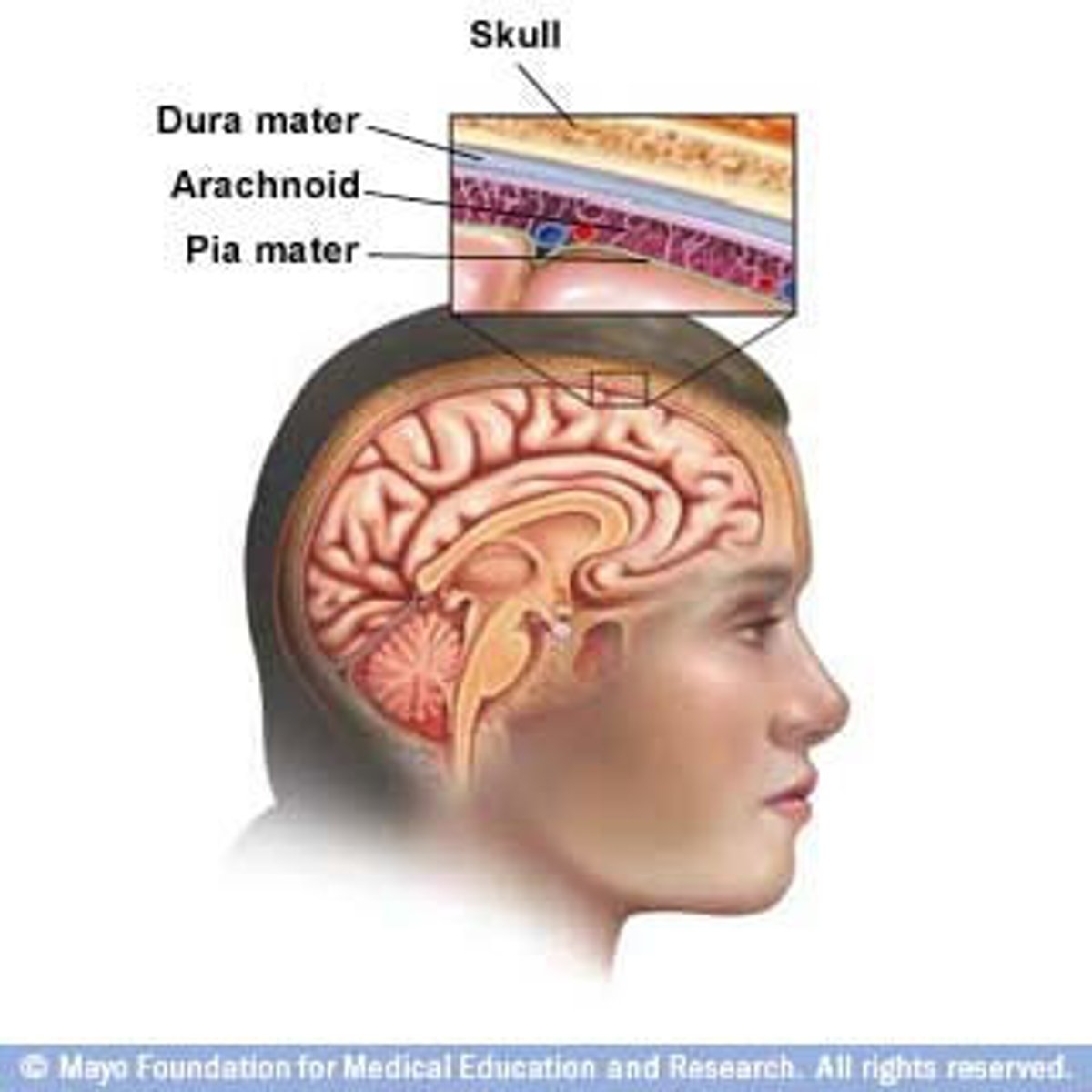
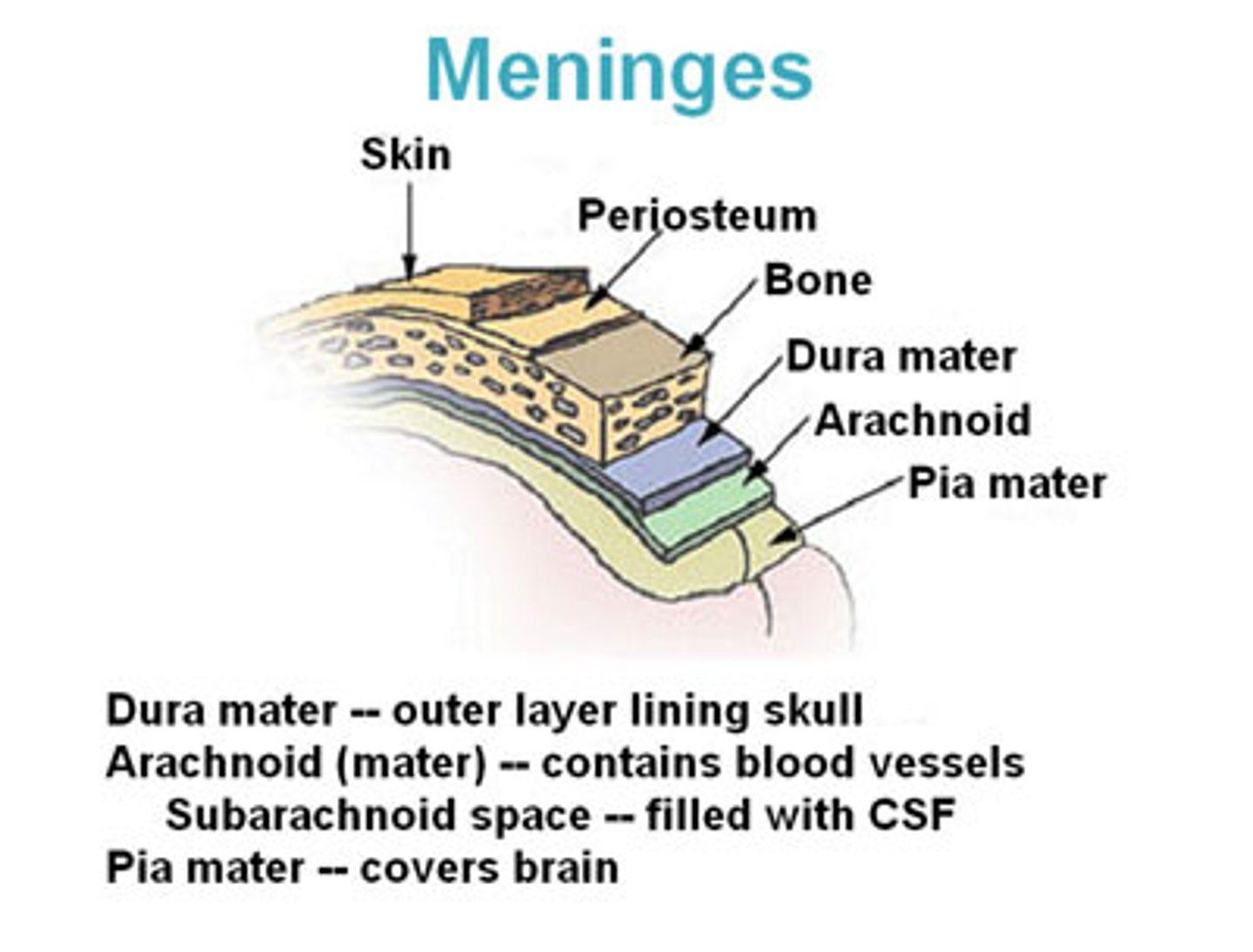
what are the specific names of the meningeal layers
1) dura mater
2) subdural space
3) arachnoid mater (where the subarachnoid space is)
4) pia mater
how many bones make up the skull
22
what is the three purposes of the skulll
protects the brain
provides muscle and tendon attachment
contains sinuses to accommodate changes in air pressure
where is the epidural space
above the dura mater
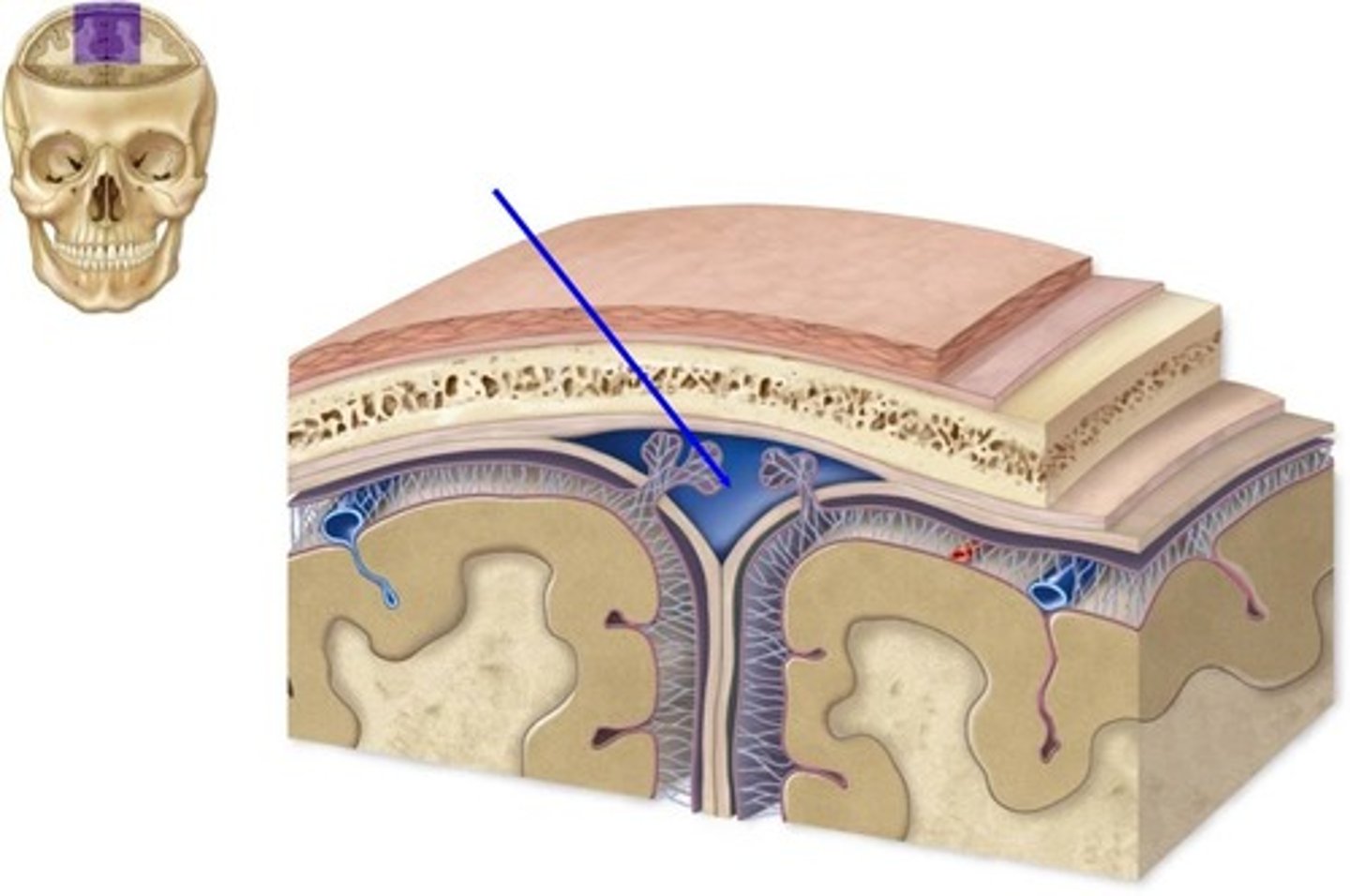
what does the epidural space contain
arteries and veins to sustain the meningeal layers
does the epidural space always exist
no, it only exits when there is a problem (pathologically)
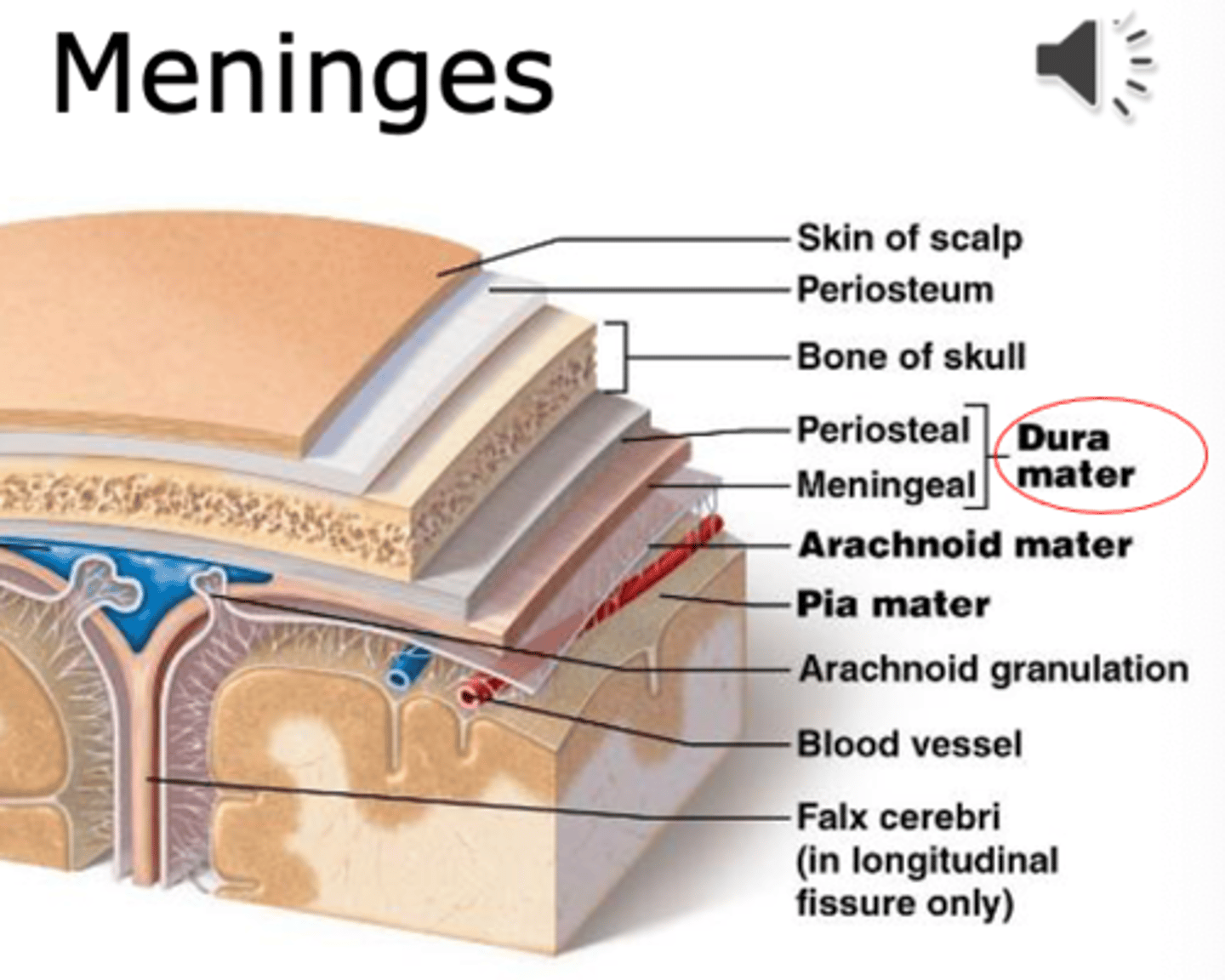
dura mater
thick, outermost layer of the meninges surrounding and protecting the brain and spinal cord (also called tough mother)
what two layers make up the dura mater
1. periosteal layer
2. meningeal layer
(contains some of the venous system between the layers)
subdural space
space between dura mater
exsits pathologically (only when there is a problem)
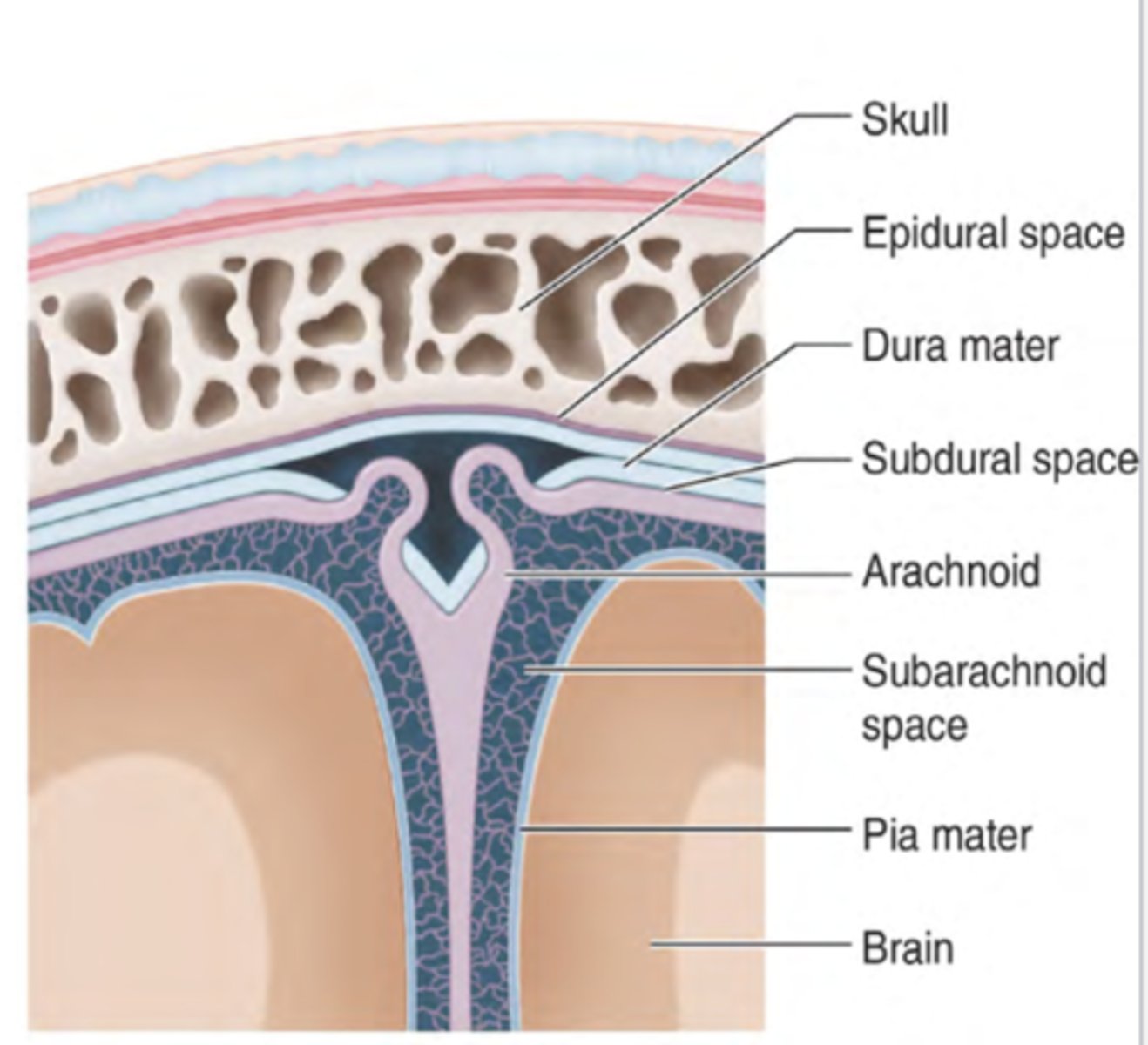
arachnoid layer
middle layers
thin, transparent membrane
what is within the arachnoid layers
the CSF (where the CSF enters the venous system)
subarachnoid space
filled with CSF; contains major arteries of the brain
exists independently of pathology (meaning we have this space even if we are healthy)
pia mater
deepest layer of the meninges, thinest layer, provides a covering for blood vessels
how does the brain get energy
glucose, however it is unable to store it, so it needs a constant supply
arteries
carry blood away from the heart
carry oxygen to the body
flow is pulses (as the heart pulses)
thick walls with muscle tissue
no valves
under high pressure
vein
A blood vessel that carries blood back to the heart.
Flows smoothly,
thin walls,
has valves to prevent backflow,
under low pressure
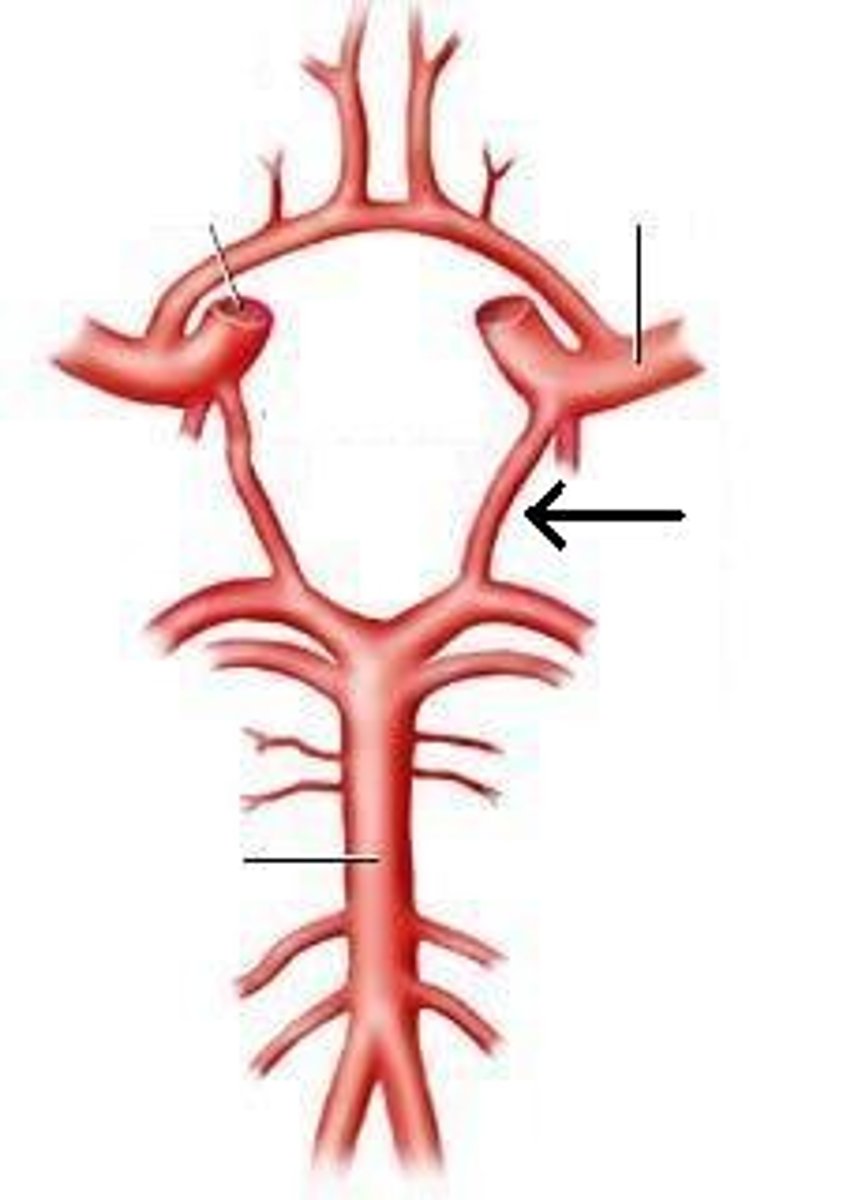
what are the 4 arteries that go to the brain and skull
1) right verterbral artery
2) right common carotid artery
3) left common carotid artery
4) left verterbral artery
external carotid artery
Artery that supplies blood to the anterior (front) parts of the scalp, face, dura mater
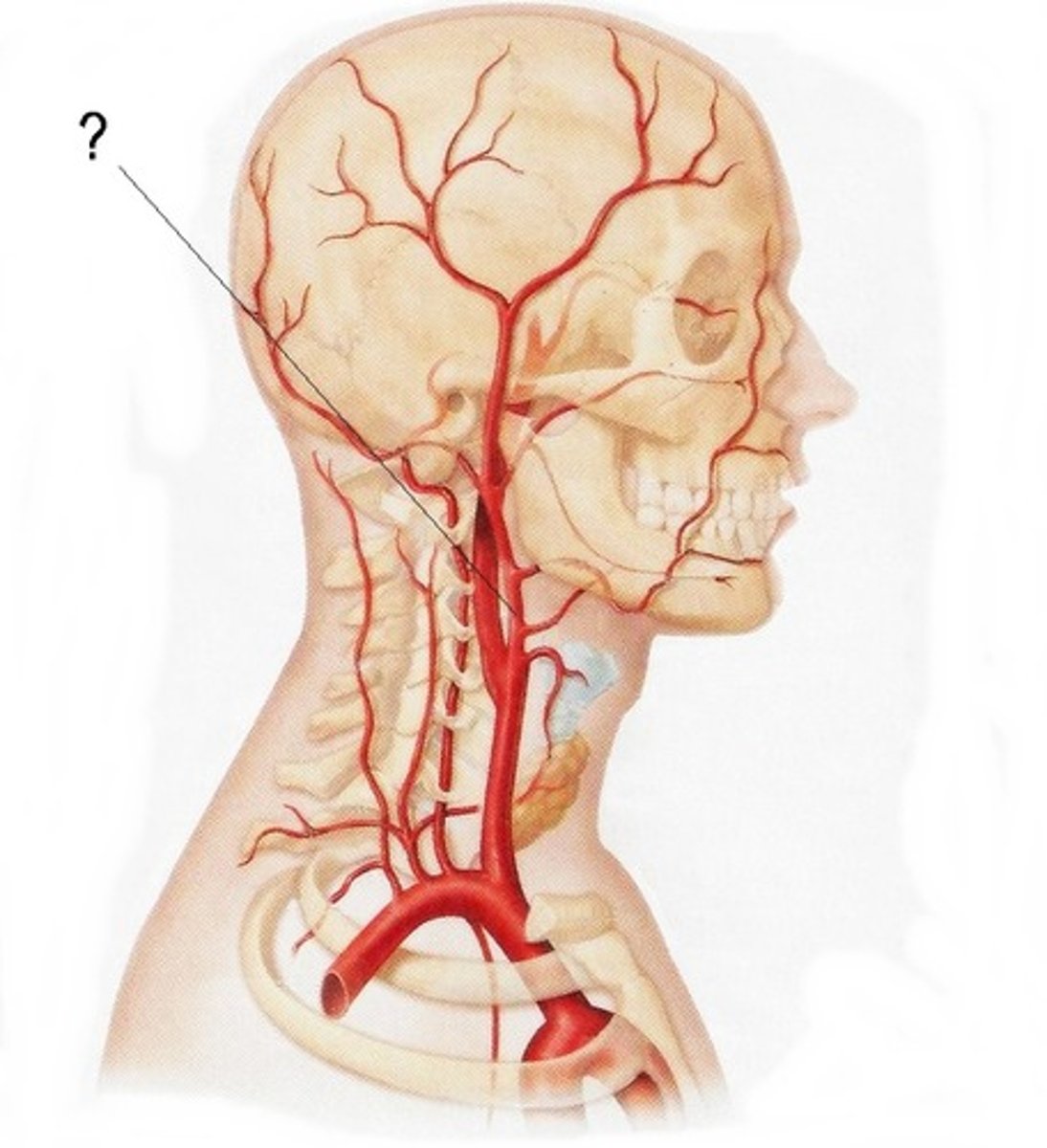
internal carotid artery
blood to the brain cells
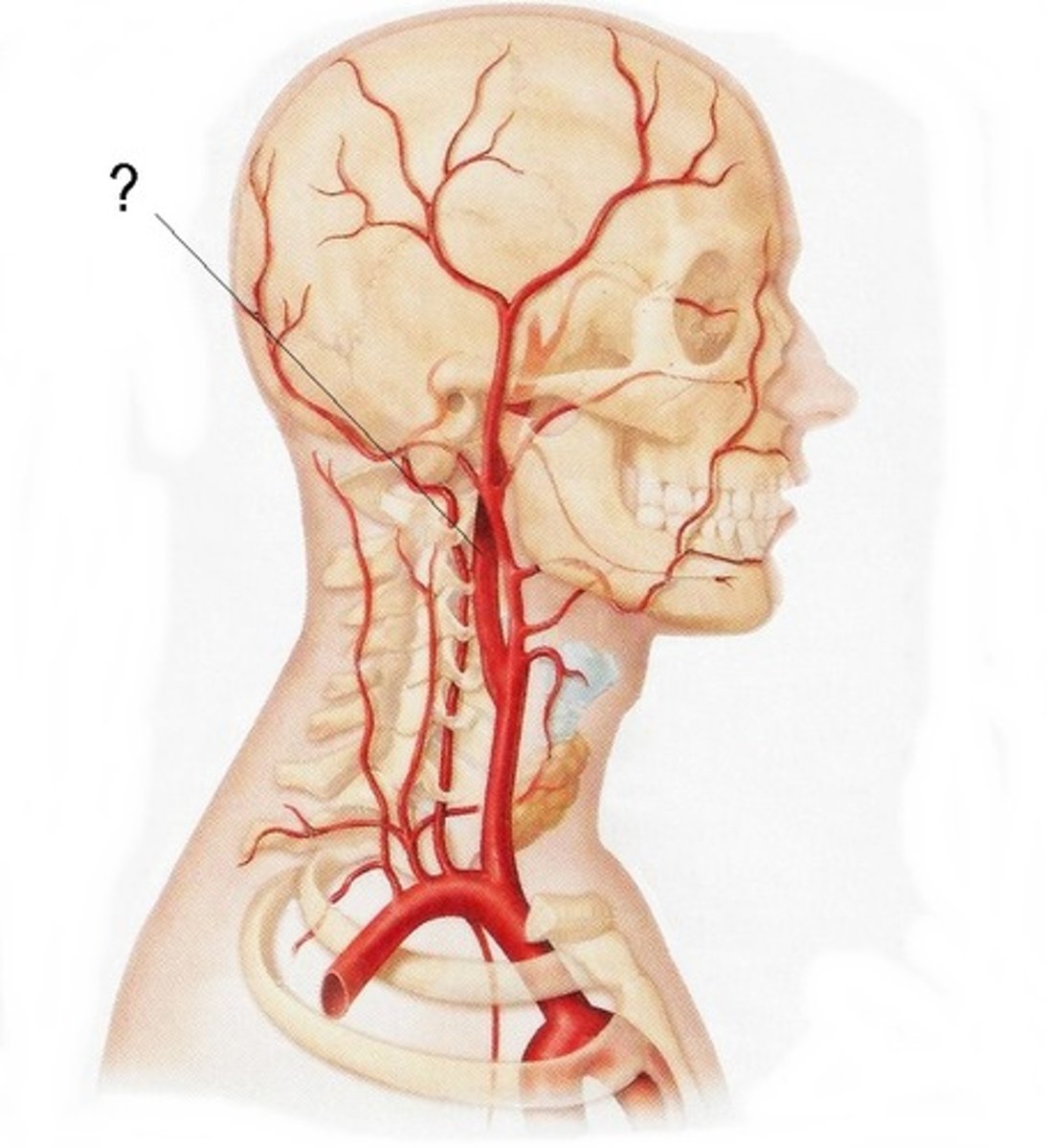
what are the 3 branches of the internal carotid artery
1) anterior cerebral artery
2) middle cerebral artery
3) posterior communicating artery
Anterior cerebral artery
medial surface, blood to foot and leg area of motor strip
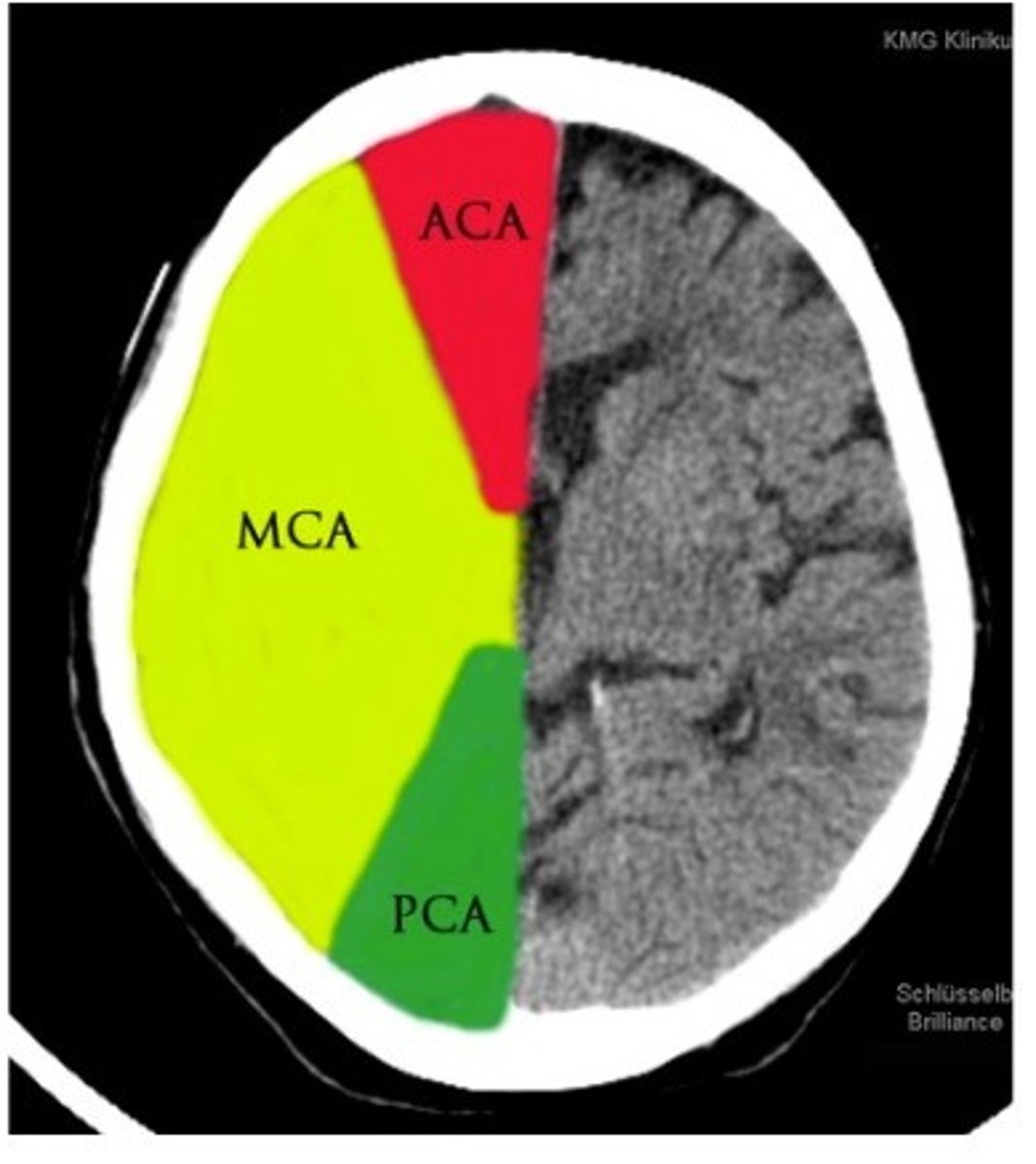
middle cerebral artery
very common area for stroke
impacts brochas and werinkies area (depending on where stroke is)
outside of brain
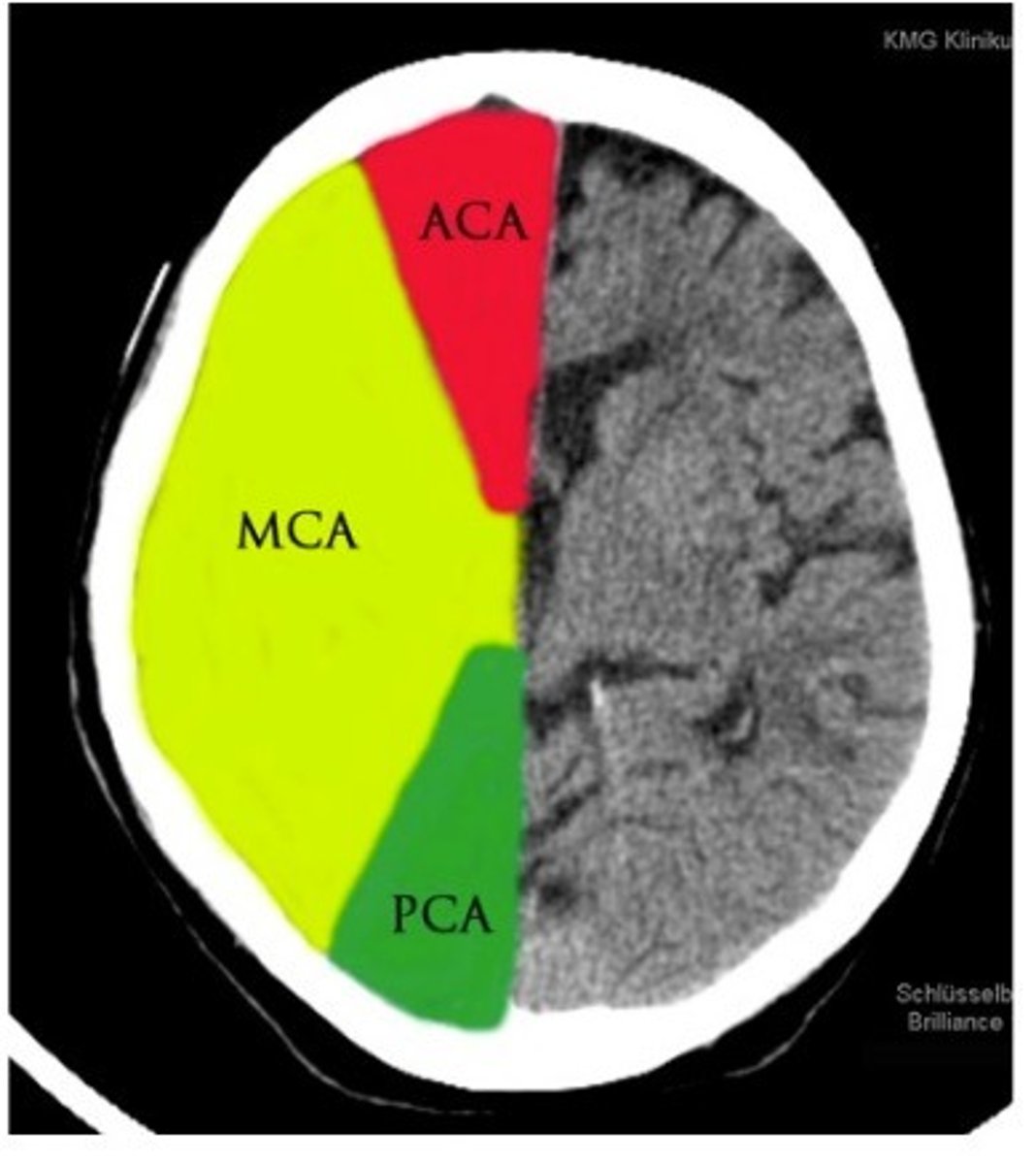
posterior communicating artery
The artery that connects the basilar artery to the circle of willis. Supplies occipital lobe, branches off of posterior cerebral artery.
posterior cerebral Artery
supplies occipital lobe
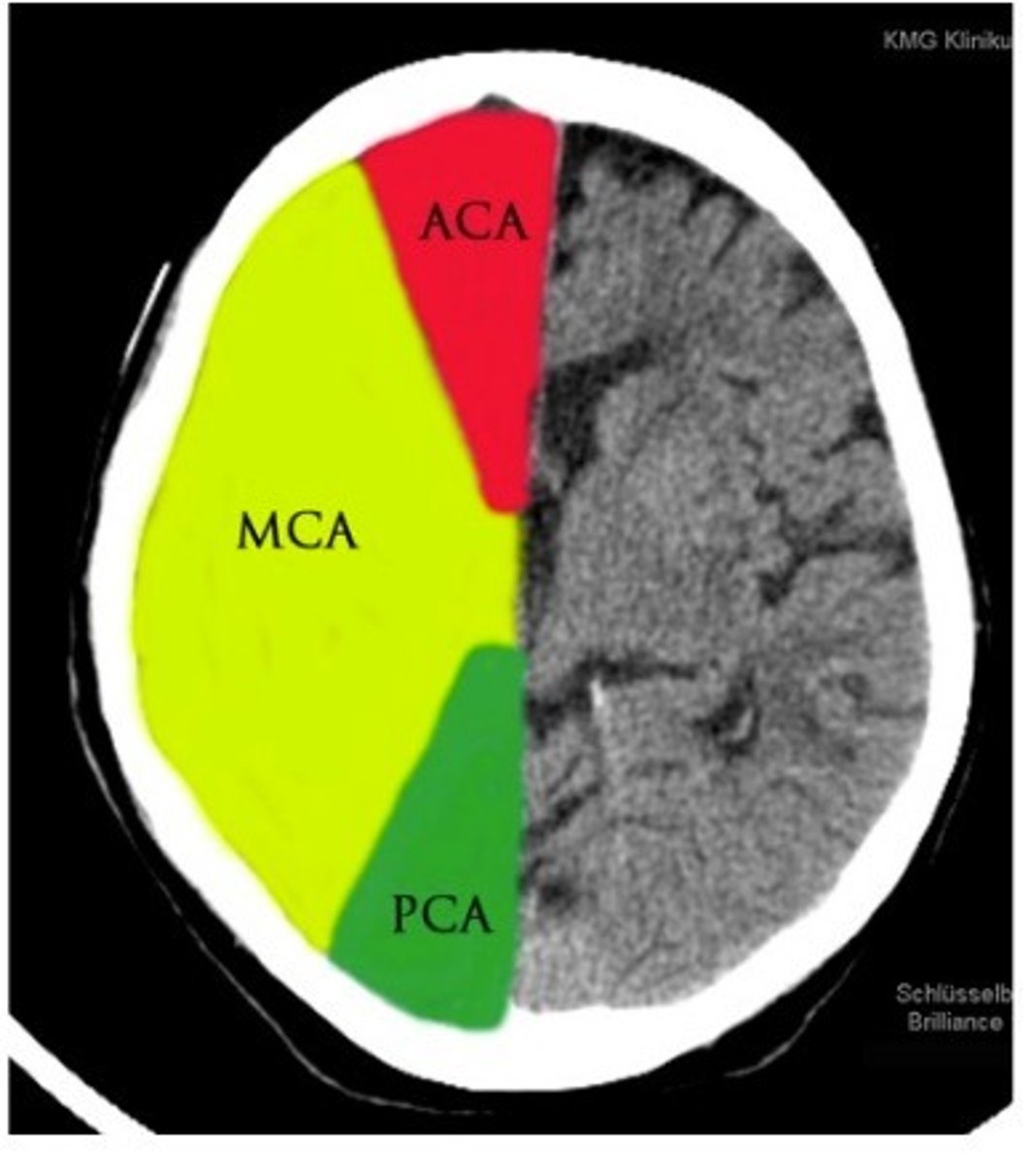
veterbral regions (controlled by veterbral arteries)
spinal cord
Cervical Musculature and Cerebellum
basilar regions (basilar arteries)
pons
portion of the cerebellum
thalamus
midbrain
Anterior Cerebral Artery (ACA) infraction
foot and leg dragging
Middle Cerebral Artery (MCA) infraction
broca's/wernikies aphasia
posterior cerebral artery (PCA) infraction
loss of sight and smell
vertebrobasilar infraction
brainstem and spinal cord issue
cerebellar infraction
balance, smooth and accurate movements become a problem
deep subcortical infraction
sensory and motor information and not accessable
what is the purpose of the veterbral and basilar regions
to have a redundancy of blood flow to the body
what is the accronm for a stroke
F-face drooping
A-arm weakness
S-speech difficulty
T-time
what are other signs of a stroke
numbness
confusion
trouble seeing
trouble walking
headache
Transient Ischemic Attack (TIA)
brief period of neurological change
usually less than one hour in length
not lasting changes
a short blockage. Vascular cause
what are the two types of ischemic strokes
thrombotic, embolic
thrombosis
artery closure from plaque at a specific location
arteriral dissection
a break in an artery, forms a clot
Emboli
debri from else where in the body that blocks an artery
ischemic stroke medical intervention
tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) or Tenecteplase (TKN)-breaks down blood clot and promotes blood flow
clot retrieval-pulling the blood clot out of you (thrombectimy)
tissue plasminogen activator (tPA)
promotes blood flow, cannot be used if someone has a bleed, can only be given if the stoke has occured in the past 3 hours is not given if a brain bleed is happening.
what is a hemorrhagic stroke
A stroke caused by bleeding into the brain due to a ruptured blood vessel
what are the two groups of hemorrhagic strokes
intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH) and subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH)
what is a ICH stroke
bleeding in the brain
what is a SAH stroke and what is the main symtpom of them
bleeding of the subarachnoid space
thunderclap headache
what % of strokes are SAH and ICH
20% SAH
10% ICH
what is the leading cause for hemorrhagic strokes
hypertension (high blood pressure)
ruptured aneurysm and treatment
Subarachnoid hemorrhage (most common)
coiling and clipping
what is bad about arteriorvenous malformation (AVM)
the abnormal connection between the artery and veins can cause high blood pressure and puts pressure on the blood walls causing bleeding (causes hemorrhages)
what are the 3 different types of traumatic bleeding
epidural hemorrhage
subdural hematoma
subarachnoid hemorrhage
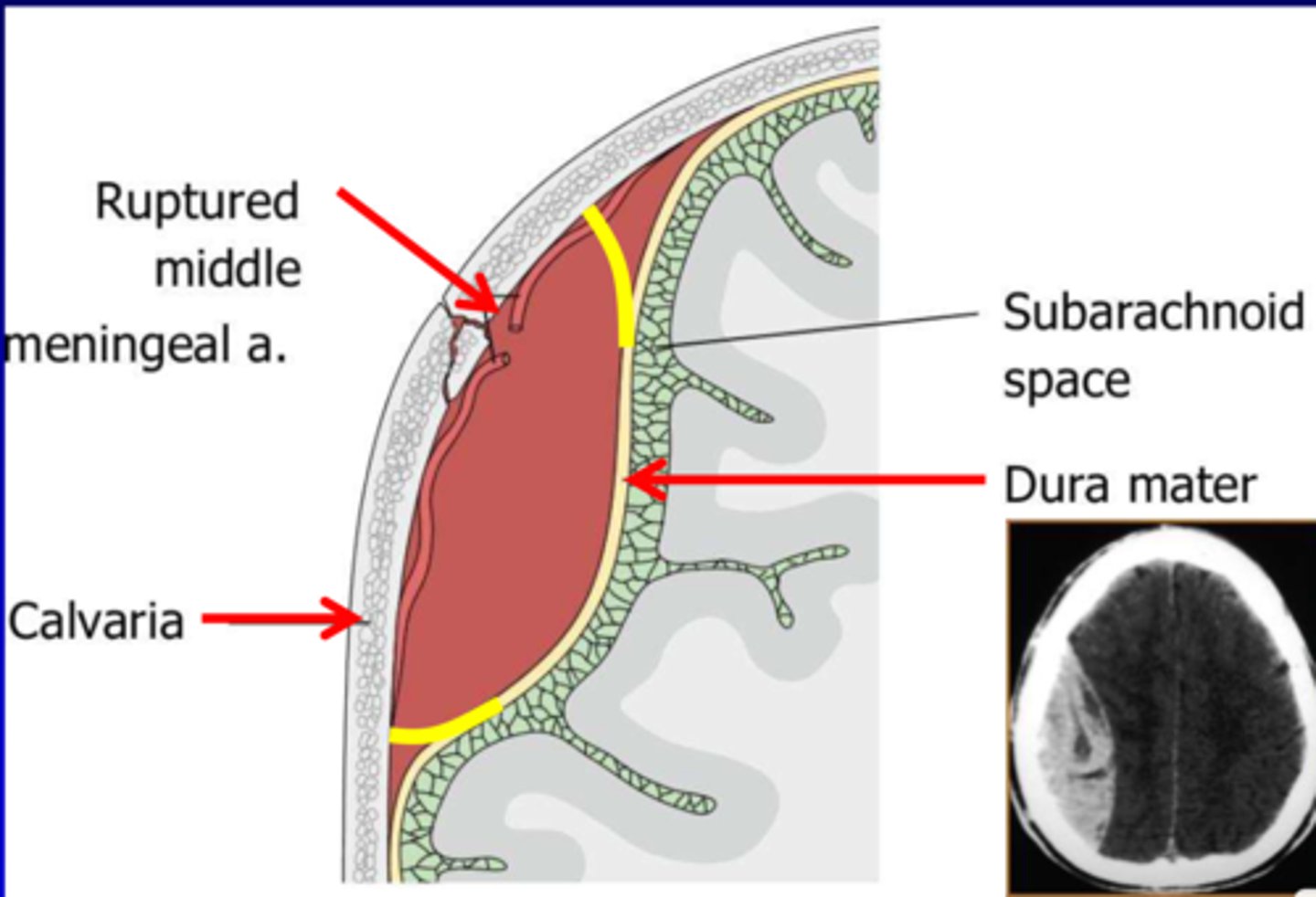
epidural hemorrhage
A hemorrhage that occurs between the dura mater and the skull, usually of traumatic origin. Wake up, talk, die syndrom
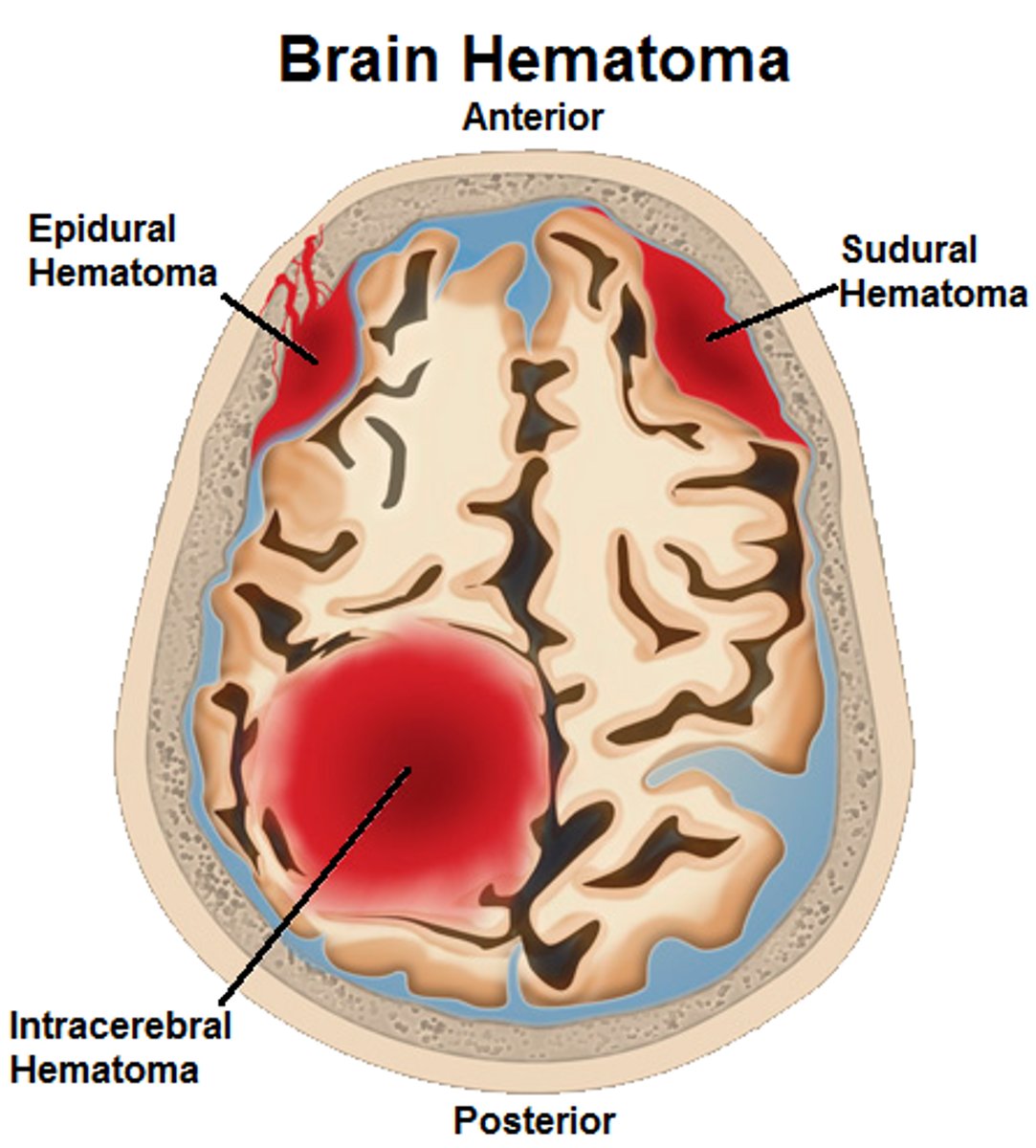
subdural hematoma
pertaining to below the dura mater, tumor of blood in the venus system that drips out slowly
where subarachnoid hemmorage could occur
in all the artires in the brain and into deep brain areas, bleeds fast
where intracerebral hemorrage could occur
deep in brain, blood in brain is toxic if not in vessel
what are the three types of brain tumors and diseases the brain can get
meningioma
gliblastoma multiforme
acoustic neuroma
meningioma
benign tumor of the coverings of the brain (the meninges). Most common CNS tumor
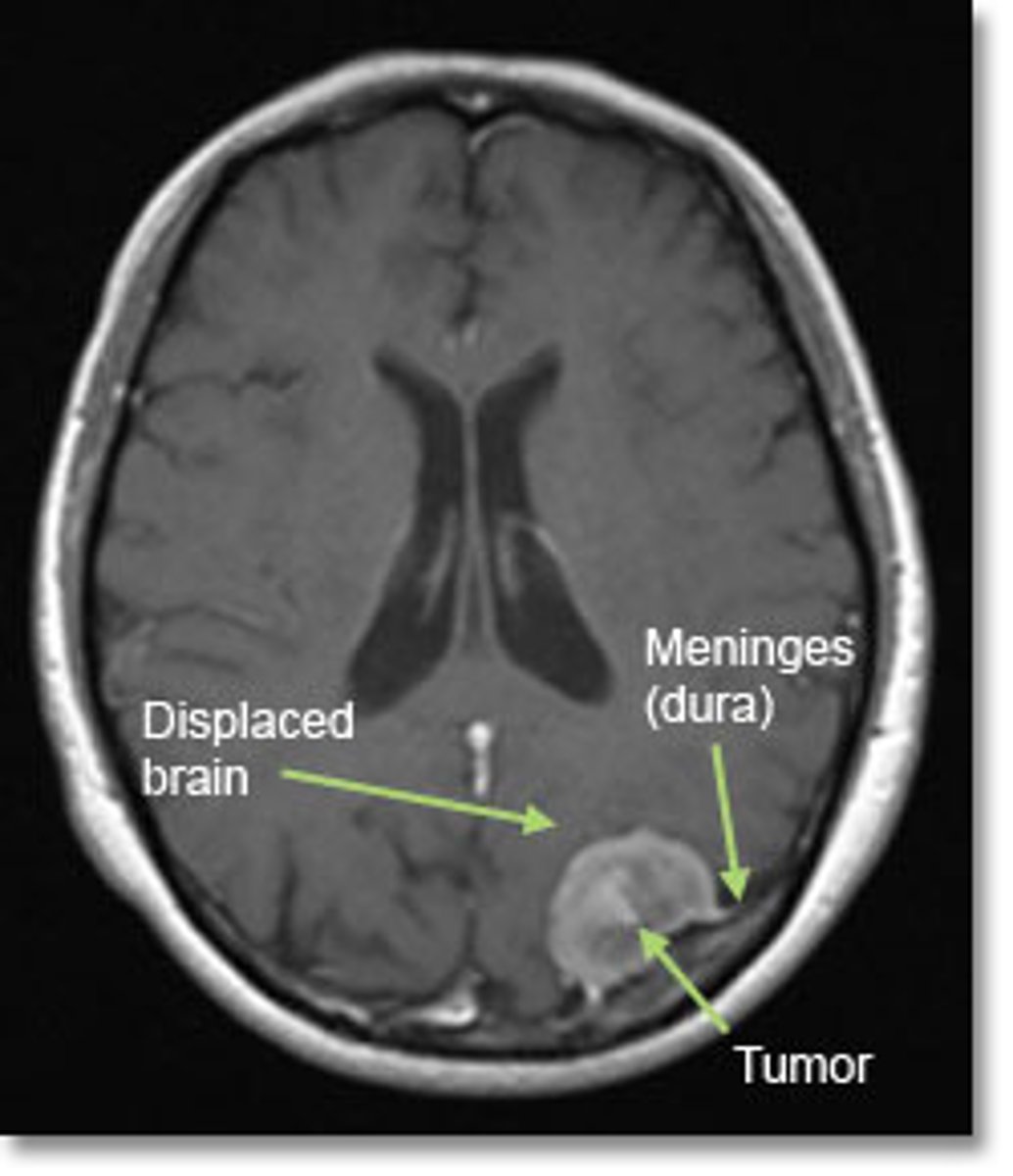
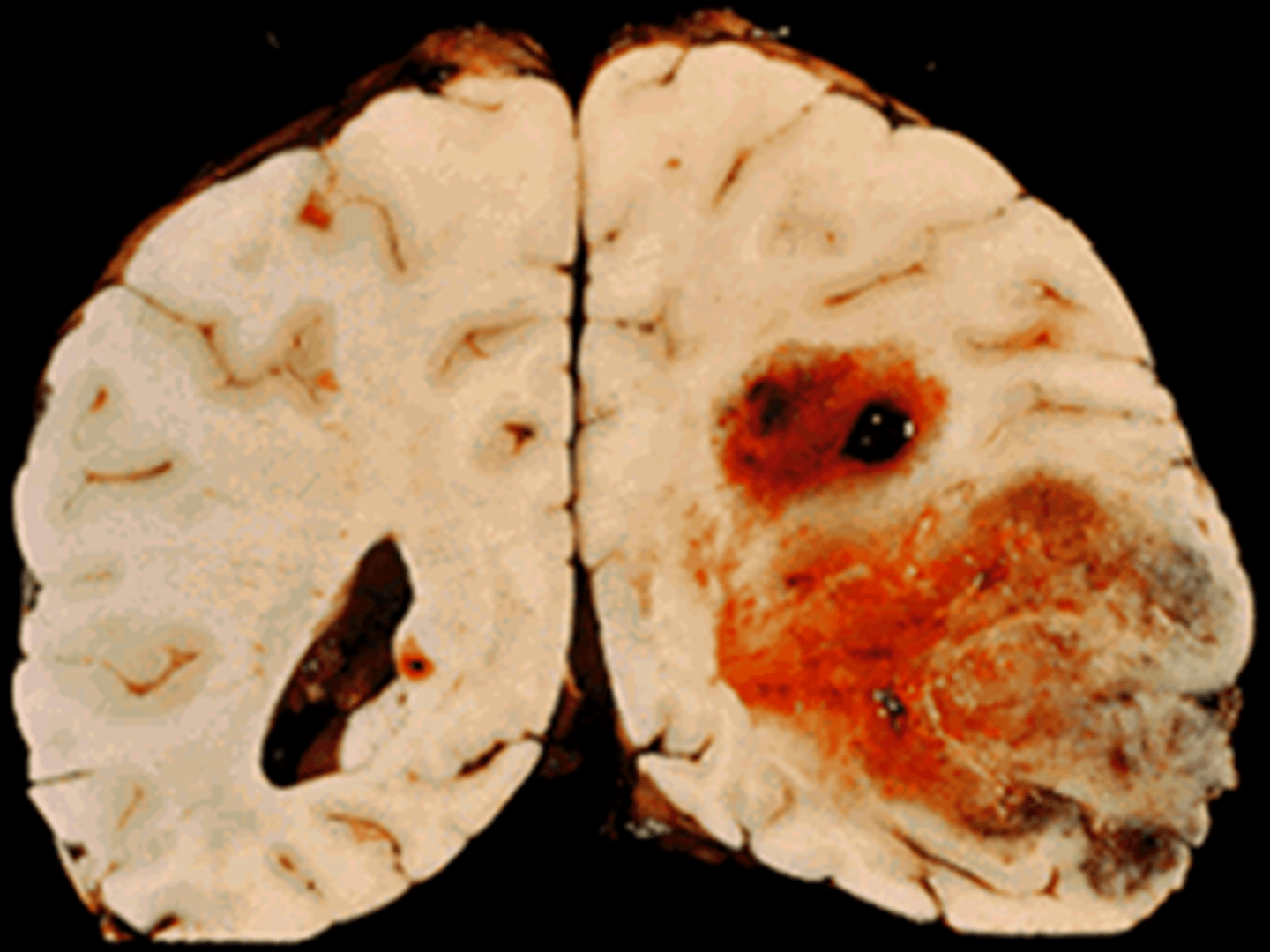
glioblastoma multiforme
most common primany brain tumor in adults
causes motor defecits, speech difficulties, confusion,
life expactancy is 17 months
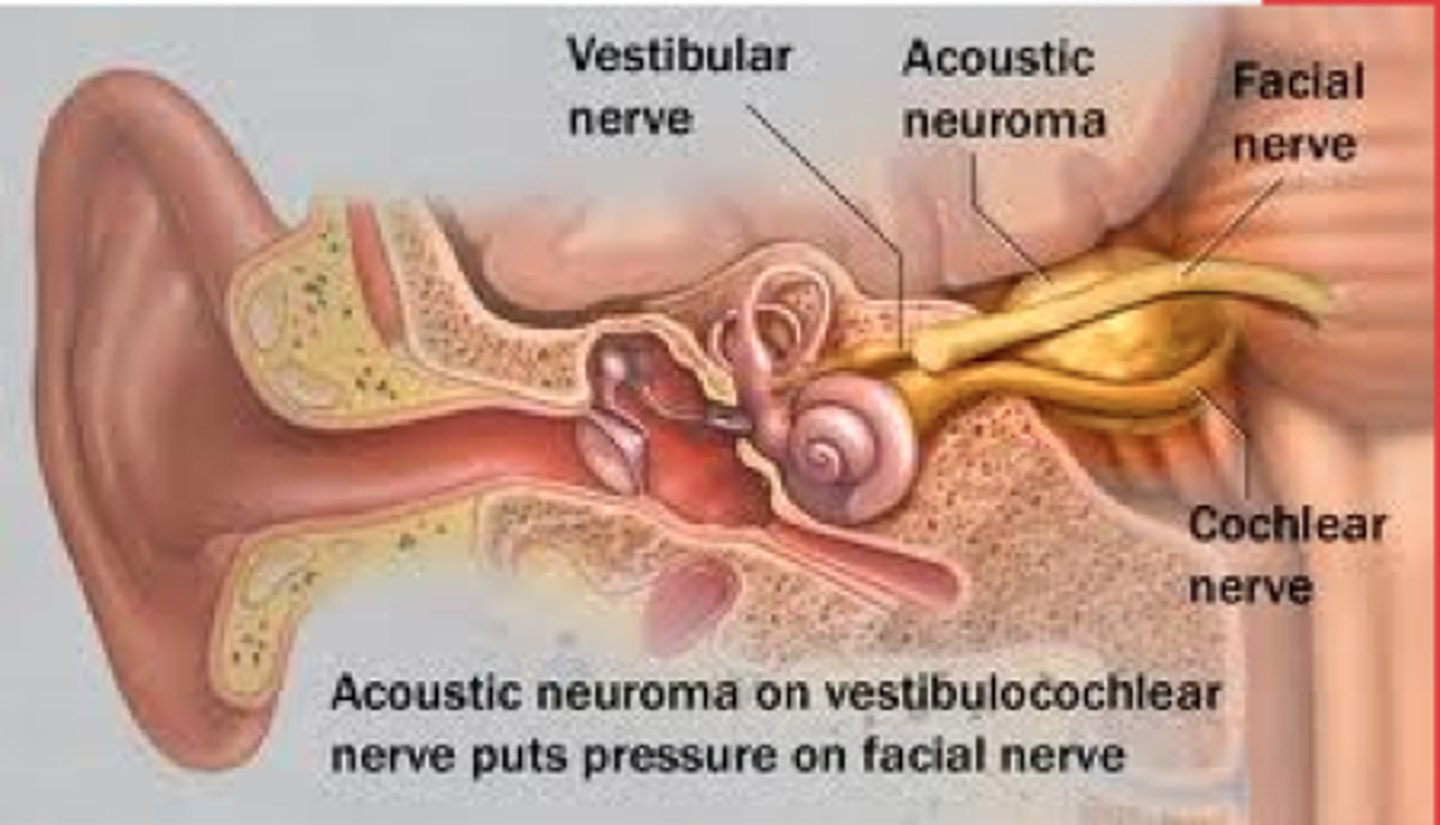
acoustic neuroma
benign tumor on the auditory nerve (8th cranial nerve) that develop from the shealth of schwann cells. Causes vertigo, tinnitus, and hearing loss
Alzheimer's Deisease
Progressive form of Dementia (60-80% of all dementias)
Early onset strikes < 65 years old
Begins in hippocampal region
First sign in memory loss for new info, episodic and semantic memory
Disease process spreads throughout brain
Treatments, but no cure
Typically, people live 4-8 years post diagnosis
creutz-feldt jakob disease
Very rare (1 in 1,000,000)
puts holes in brain
Rapid deteration of brain and nerve tissues.
Prion, abnormal forms of proteins
First symptoms include decreased walking, balance, coordination, confusion, memory and descision making difficulties.
Later symptoms include immobility, dysphagia, coma
Sporadic, hereditary, and acquired forms
No treatments, no cures
korsakoff's syndrom and three components of it
Lack of B1; causes damage to brain
1) altered gait
2) bad memory
3) comfabulation (non-sense talk)
Acute form is called Wernicke's Encephalopathy
Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis
Upper and Lower Motor Neuron Disease
Presents initially with limb symptoms or cranial nerve symptoms
Severe impact on speech, swallowing, ambulation, respiration
Most commonly diagnosed between ages 55-75
Sporadic and familial forms
No cure, treatments can slow progression of diease
AAC approaches should begin early (voice banking, message banking)
Parkinson's disease
Progressive disorder impacting movements initially
Arises from depletion of dopamine produced in the substantia nigra (mid brain)
Classic PD signs are: resting tremor, rigidity, bradykinesia, postural instability
Age of onset is early to mid 60s
Treatment: drug, behavioral, deep brain stimulation
what are other neurological diseases of the brain
MS
Lyme disease
dementia with lewy bodies-starts with cognitive dementia then movement problems (starts as dementia, then moves to parkinson's) causes huliciations
Progressive supranuclear palsy
Wilson's disease