Life Science Human Origins
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
Mammals are animals, vertebrates, tetrapods, amniotes
Mammals have hair, mammary glands, warm- blooded, heterodonty(different teeth), body plam, limbs under body
Mammals comes in three main groups
monotremes, marsupials, placental mammals
Marsupials and placental mammals are more closely related to each other than either is to monotremes
Primates’ closest living relatives are
colugos and tree shrews
that shared group(primates-colugos-tree shrews) is closely related to
rodents and rabbits
Convergence occurs among mammals
Primates and their close relatives
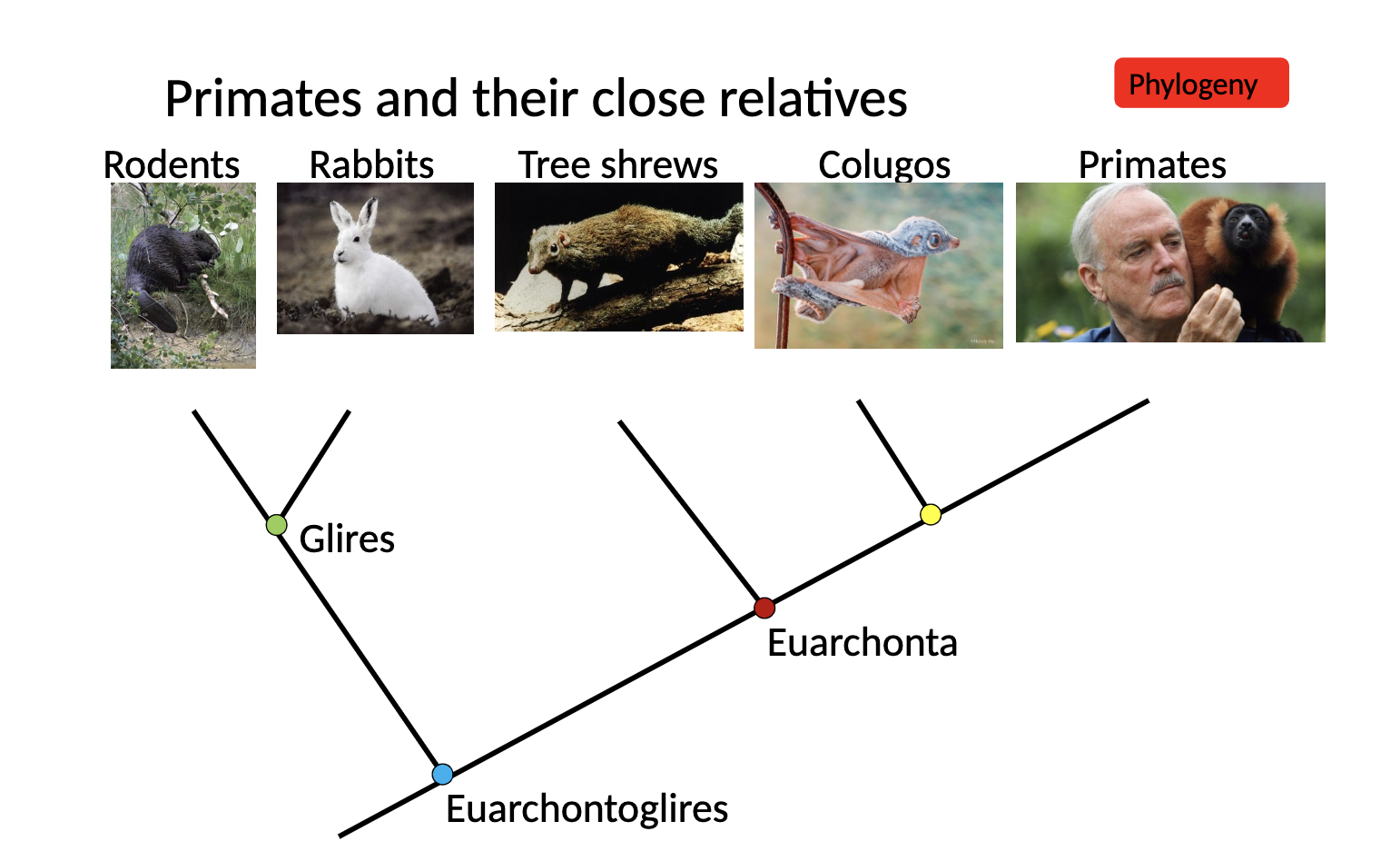
Convergence in mammals
Evolutionary convergence between marsupial and placental mammals (aka homoplasy)
Evolutionary convergence within placental mammals
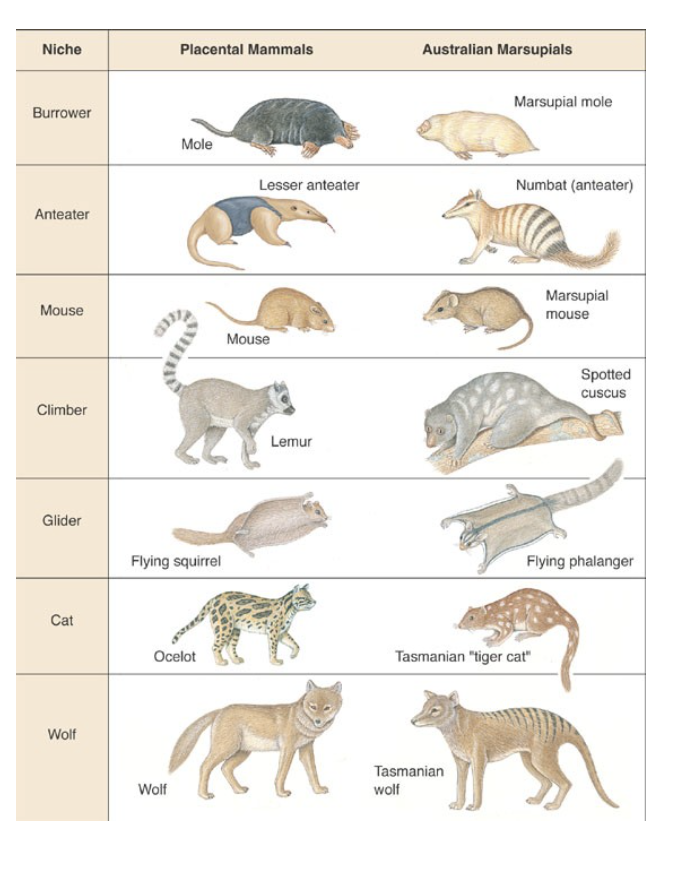
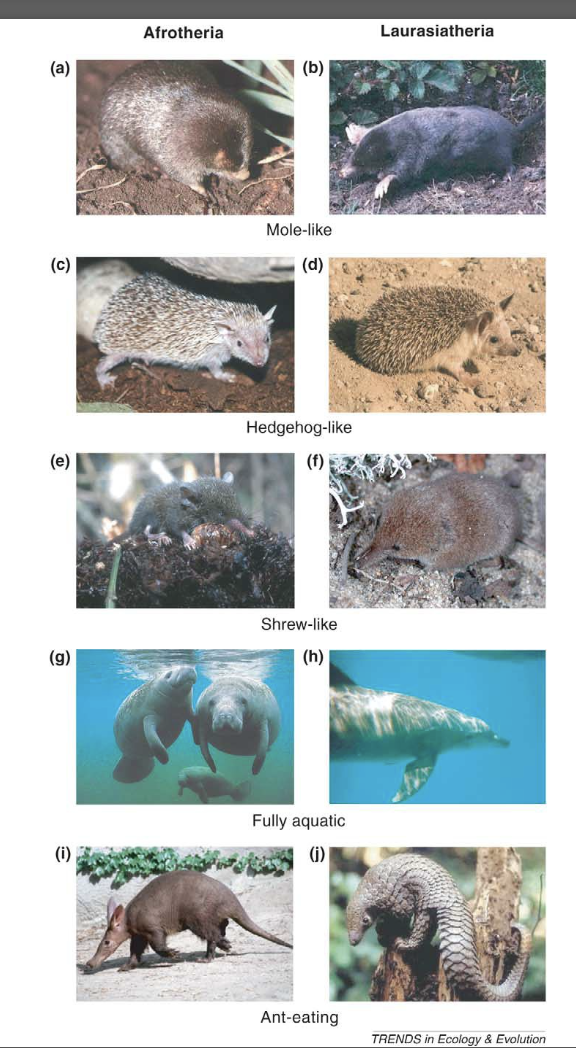
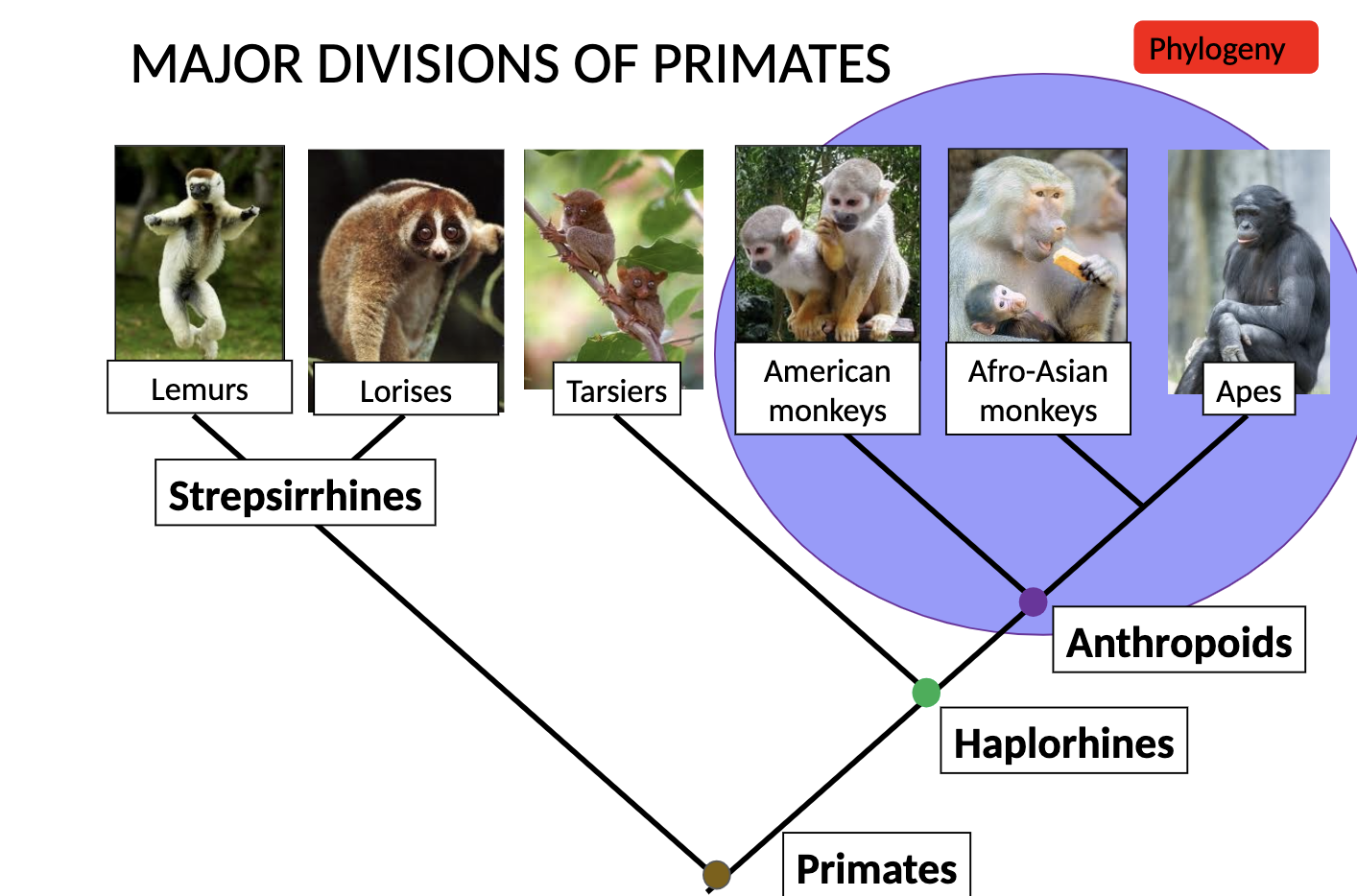
What is a Primate? Two sub orders of Primate?
Strepsirhini (strepsirhines)(lemurs and lorises)
Haplorhini (haplorhines)(tarsiers, monkeys, apes. and humans)
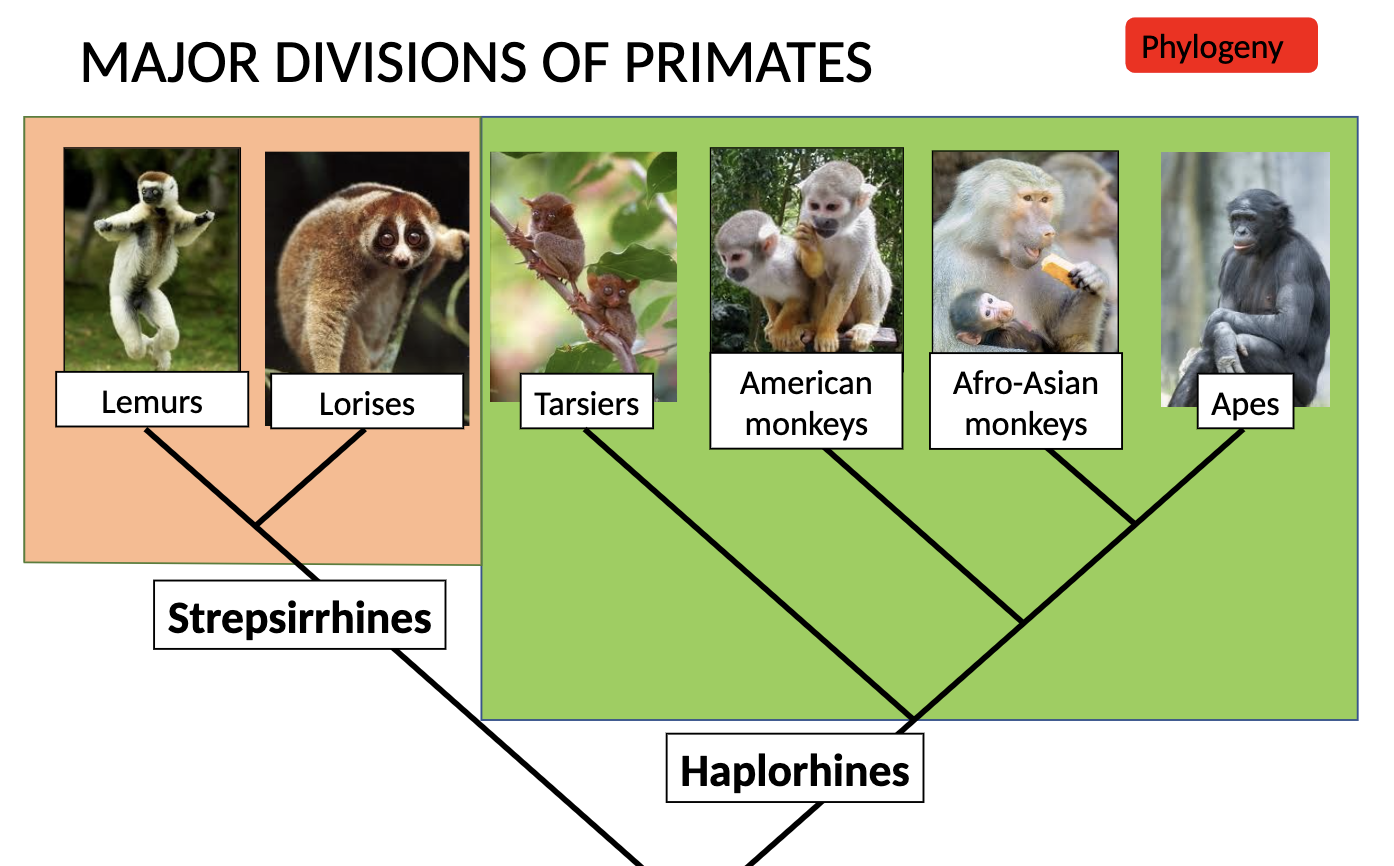
List of primate adaptations
Primates: nails; grasping hands and feet, 1st digit opposability; convergent orbits(stereoscopic vision), postorbital bar; reduced snout and olfactory bulb; increase in overall brain size
Lemur & lorises (streps) retain grooming claw, tapetum lucidum (eye shine); derived:tooth comb
Tarsiers and anthropoids (haps): increased postorbital closure()