Electrophilic Carbonyls
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
What does electrophile mean?
A chemical species (atom, ion, or molecule) that is electron-deficient
What does electrophilic carbonyl mean?
Electrophilic carbonyl: the partially positive carbon in a C=O group that is susceptible to nucleophilic attack due to bond polarisation.
How is carbonyl made to be electrophilic?
Oxygen is much more electronegative than carbon
It pulls electron density toward itself
This polarises the C=O bond
So:
Oxygen becomes δ⁻ (partially negative)
Carbon becomes δ⁺ (partially positive)
That δ⁺ carbon is the electrophilic carbonyl carbon.
Electrophile = electron-loving
The carbonyl carbon accepts an electron pair
Nucleophiles (e.g. OH⁻, NH₃, CN⁻) attack the carbonyl carbon
What is a leaving group?
A leaving group is an atom or group of atoms that can detach from a molecule by taking a pair of electrons with it during a reaction.
What makes a good leaving group?
Stable on its own after leaving
Usually weakly basic
Often able to stabilise negative charge
What does “carbonyl without a leaving group” mean?
It means a carbonyl compound where nothing attached to the carbonyl carbon can easily leave.
Aldehydes and ketones are carbonyls without a leaving group
H or alkyl groups cannot act as leaving groups (H- and R- would be extremely unstable)
Carbonyls WITHOUT leaving groups:
Aldehyde
Ketone
What does ketone + water form?
Water adds across the carbonyl (C=O) bond to create a form a hydrate
Is ketone + water a nucleophilic addition or substitution reaction?
Nucleophilic addition
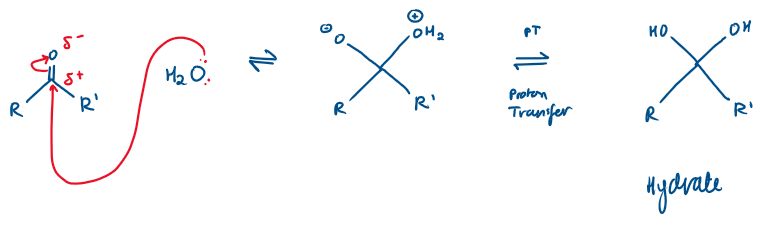
Ketones/Aldehydes reaction with H2O Mechanism:
H2O is a weak nucleophile, so it attacks the electrophilic carbonyl carbon
It forms a tetrahedral intermediate
Proton transfer takes place. Proton transfers from the +vely charged OH2+ group to the negatively charged O- , neutralising charges, stabilising the molecule
Because there is no leaving group, the intermediate cannot collapse by expelling a group, so the reaction stops at addition, not substitution
This reaction is all in equilibrium
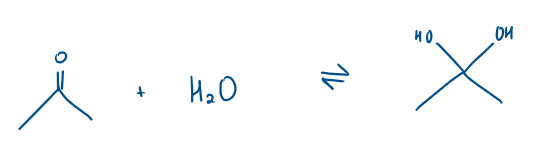
Which is the major and minor product?
The equilibrium is heavily based to the left
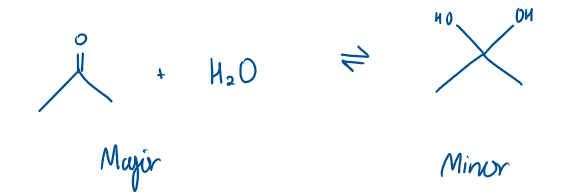
Formaldehyde
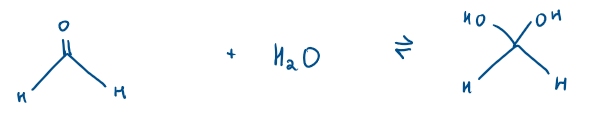
Formaldehyde + H2O
Which is the major and minor product?
There is no inductive effect here (because H is neither electron withdrawing or donating), so formaldehyde is very reactive due to its carbonyl C being very electrophilic and the water attacks it, and so the equilibrium lies to the right.
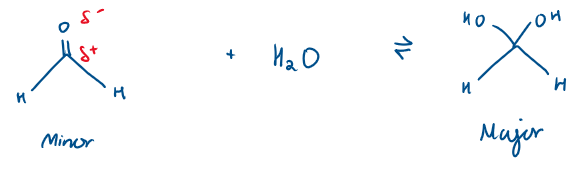
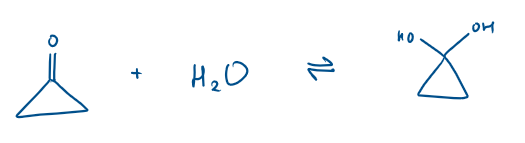
Cyclic ketone + H2O
Which is the major and minor product?
This is due to sterics
The 3C ring is a triangle shape. The angle in a 3C ring is 60°. There is very high ring strain therefore in the cyclic ketone, as the sp2 angle is 120°.
In the product, the sp3 angle is now 109° which is closer to 60°, so there is reduced ring strain. The molecule wants to be in the hydrated form because it is “happier”
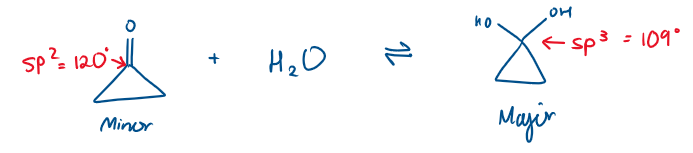
When considering why a reaction occurs, what 2 points do you have to consider?
Steric argument
Electronic argument
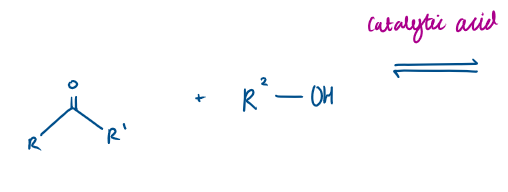
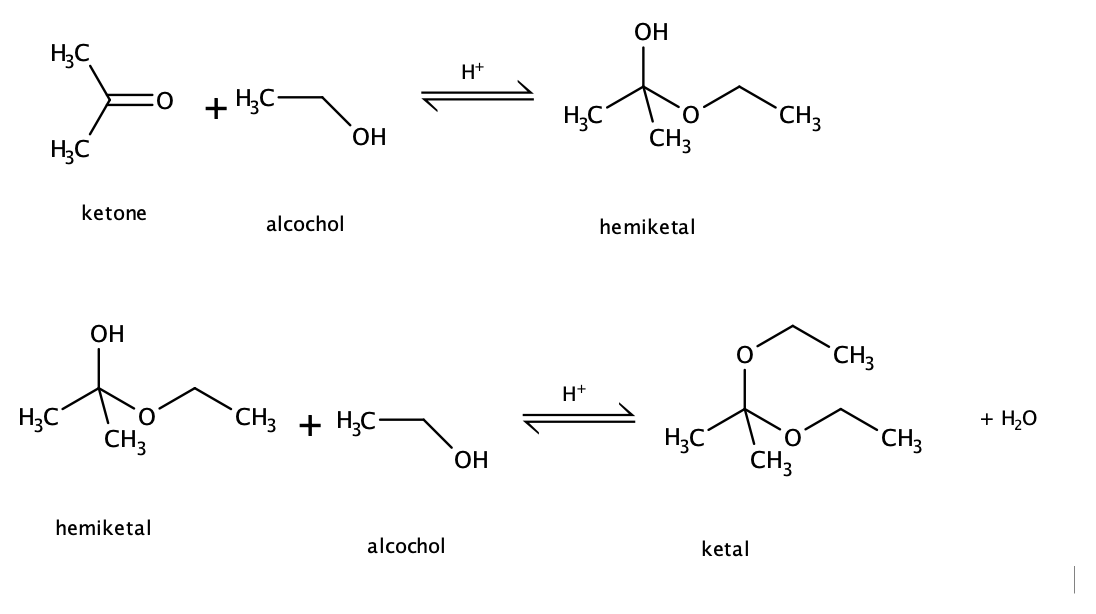
Carbonyl + Alcohol Reaction Mechanism → Draw it out
The H in R-OH (alcohol) protonates the O in C=O
This makes the C=O C more electrophilic, so is very δ+
Therefore the lone pair of electrons on the O in R-OH (alcohol) moves via curly arrow to the electrophilic C.
Making a bond, leads to bond breaking in C=O
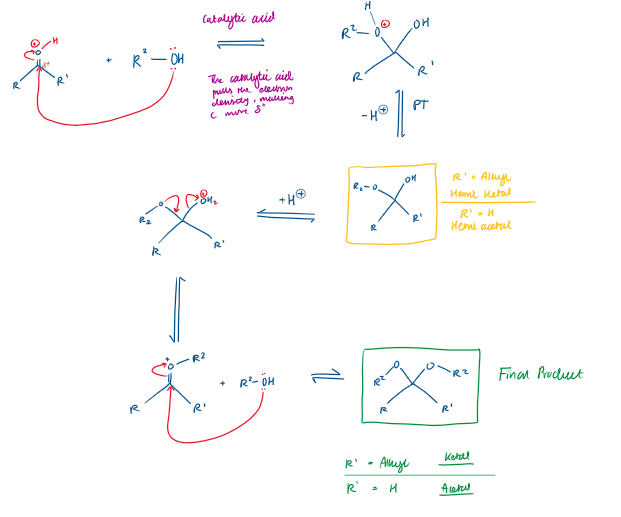
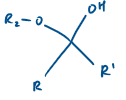
If R1 = Alkyl, what is this known as?
Hemi ketal
Hemi ketal derives from a…
ketone
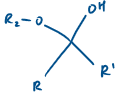
If R1 is H, what is this molecule known as?
Hemi acetal
Hemi acetal derives from an…
aldehyde
Ketone + Alcohol
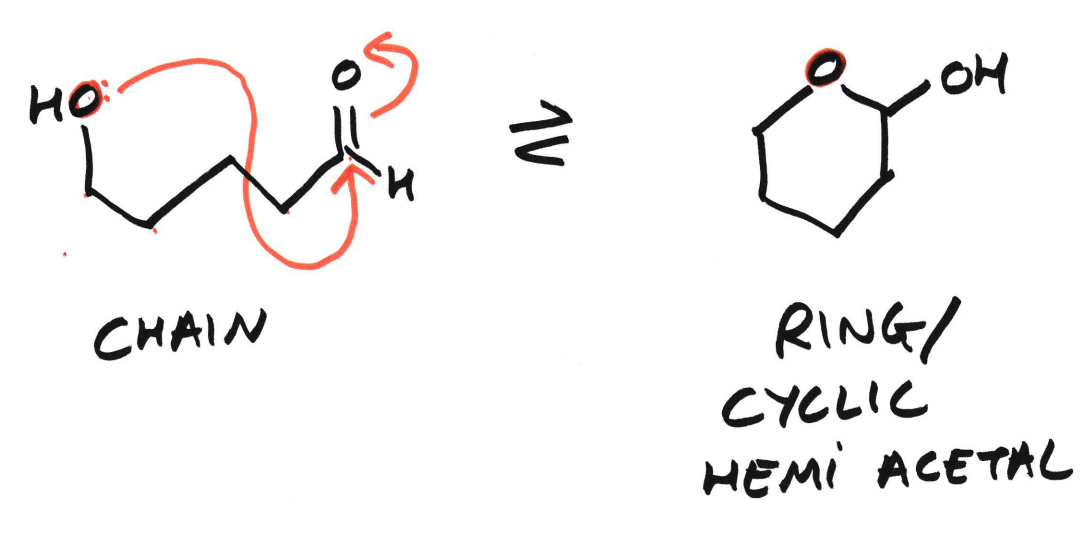
How is a cyclic hemi acetal formed?
It forms when an alcohol group within the same molecule reacts with its aldehyde group.
(A cyclic hemi ketal can form from the same molecule reacting with its ketone group)
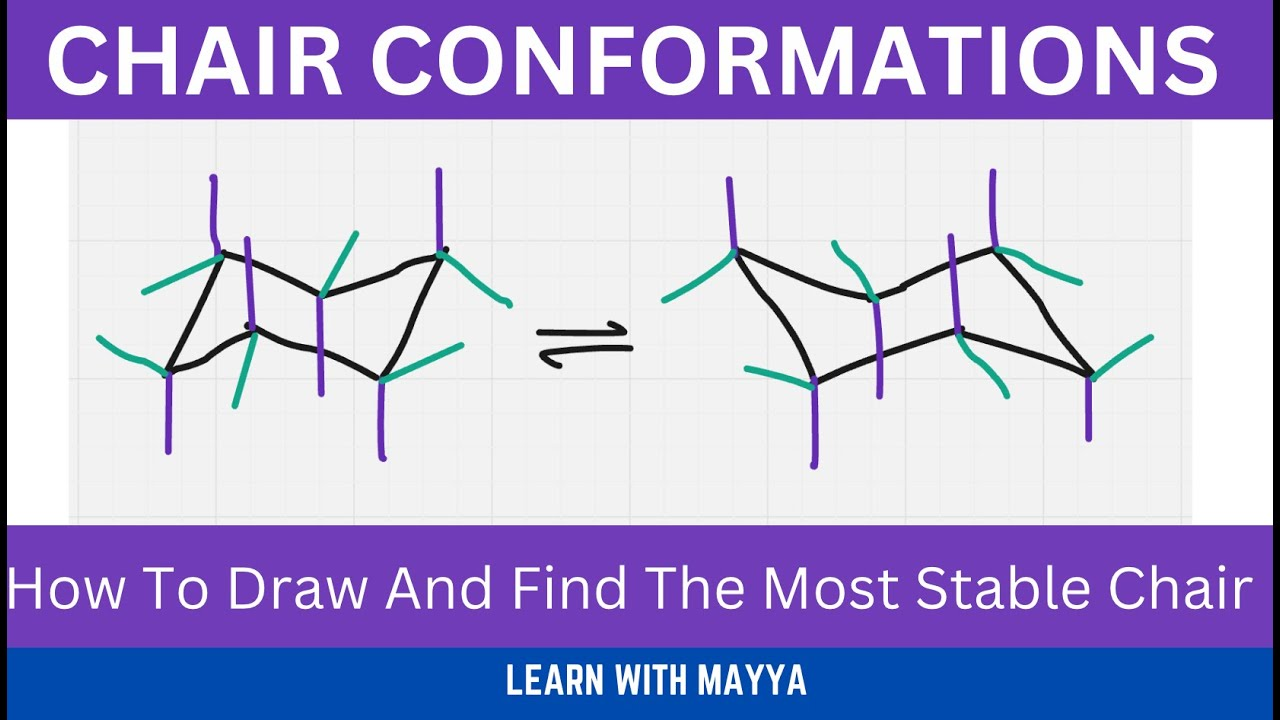
What are chair conformations?
Six-membered rings are not flat
They adopt a chair shape to minimise strain
Substituents can be:
Axial (straight up or down)
Equatorial (around the “equator” of the ring)
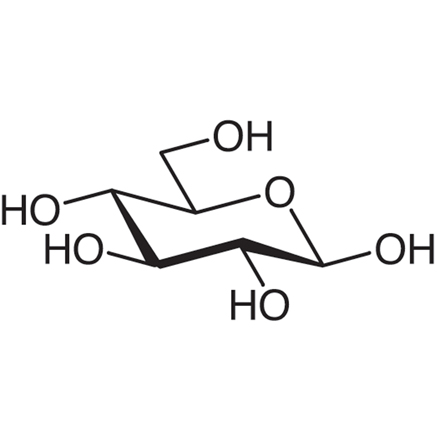
For β-D-glucose, almost all OH groups are equatorial. What does this mean
Minimal 1,3-diaxial interactions
Minimal steric hindrance
Very stable
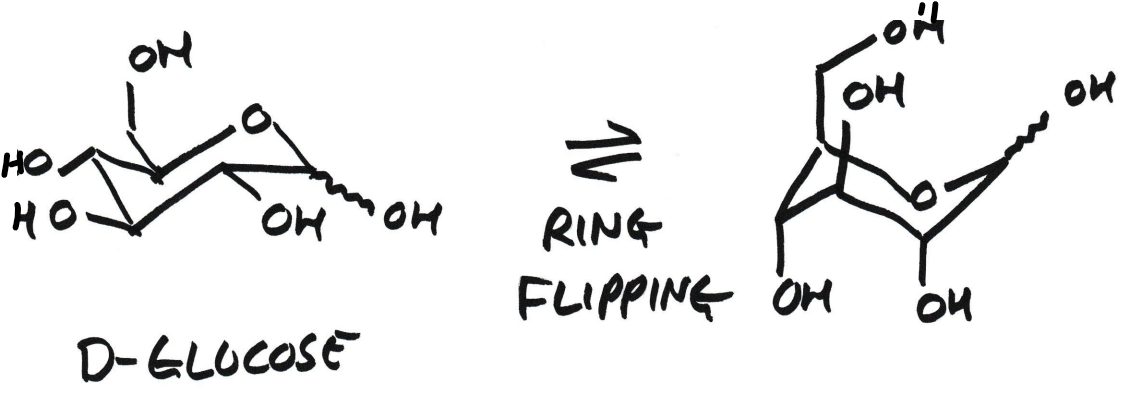
What does ring flipping do?
Converts axial → equatorial
Converts equatorial → axial
Does not change:
Connectivity
Stereochemistry (up/down remains the same)
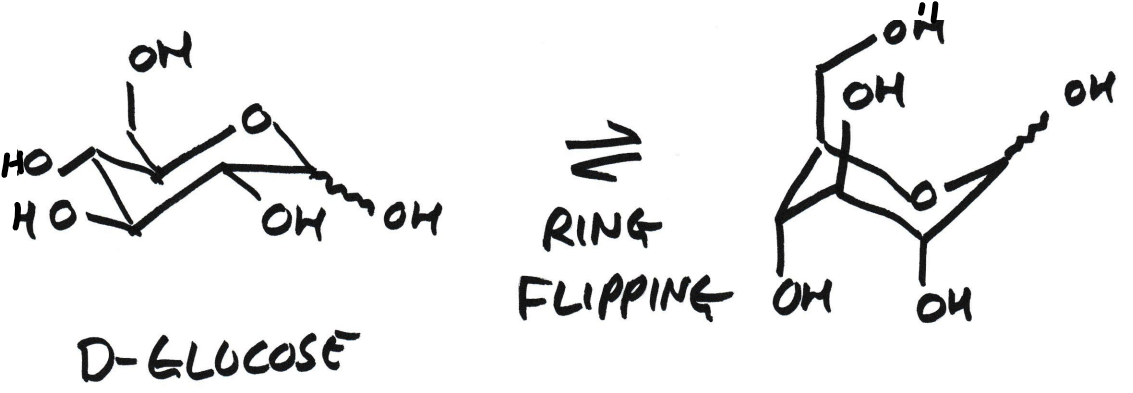
Ring flipping β-D-glucose causes all equatorial OH groups to become axial. What does this mean?
All previously equatorial OH groups become axial
Many 1,3-diaxial steric clashes
Much higher energy
Therefore minor conformation
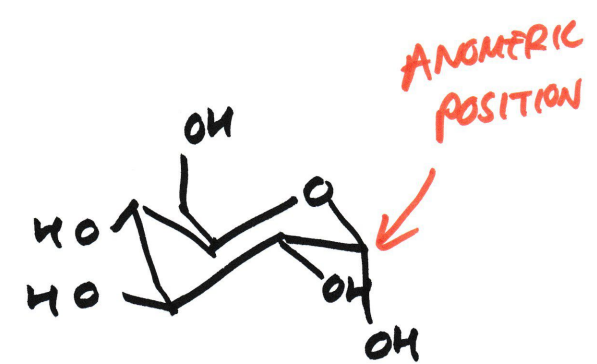
What is an anomeric carbon?
The carbonyl carbon of glucose before ring formation

What happens to the anomeric carbon after cyclisation?
It becomes the new stereogenic centre, and has an -OH and an -OR (ring oxygen) attached
What does the anomeric carbon define?
Whether it is an α or β anomer
α/β anomer
These are not ring flips. They differ in configuration at the anomeric carbon (C1) only

α-anomer
The hydroxyl (-OH) group on the anomeric carbon (C1) is on the opposite side (trans) of the ring from the CH₂OH group (on C5)
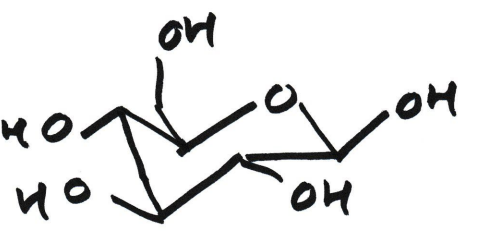
β-anomer
A beta (β) anomer is a specific stereoisomer of a cyclic sugar where the hydroxyl (-OH) group on the anomeric carbon (C1 in aldoses) points to the same side (cis) as the CH₂OH group attached to the highest-numbered carbon (like C5 in glucose) in the ring
Are α/β anomer epimers?
Yes
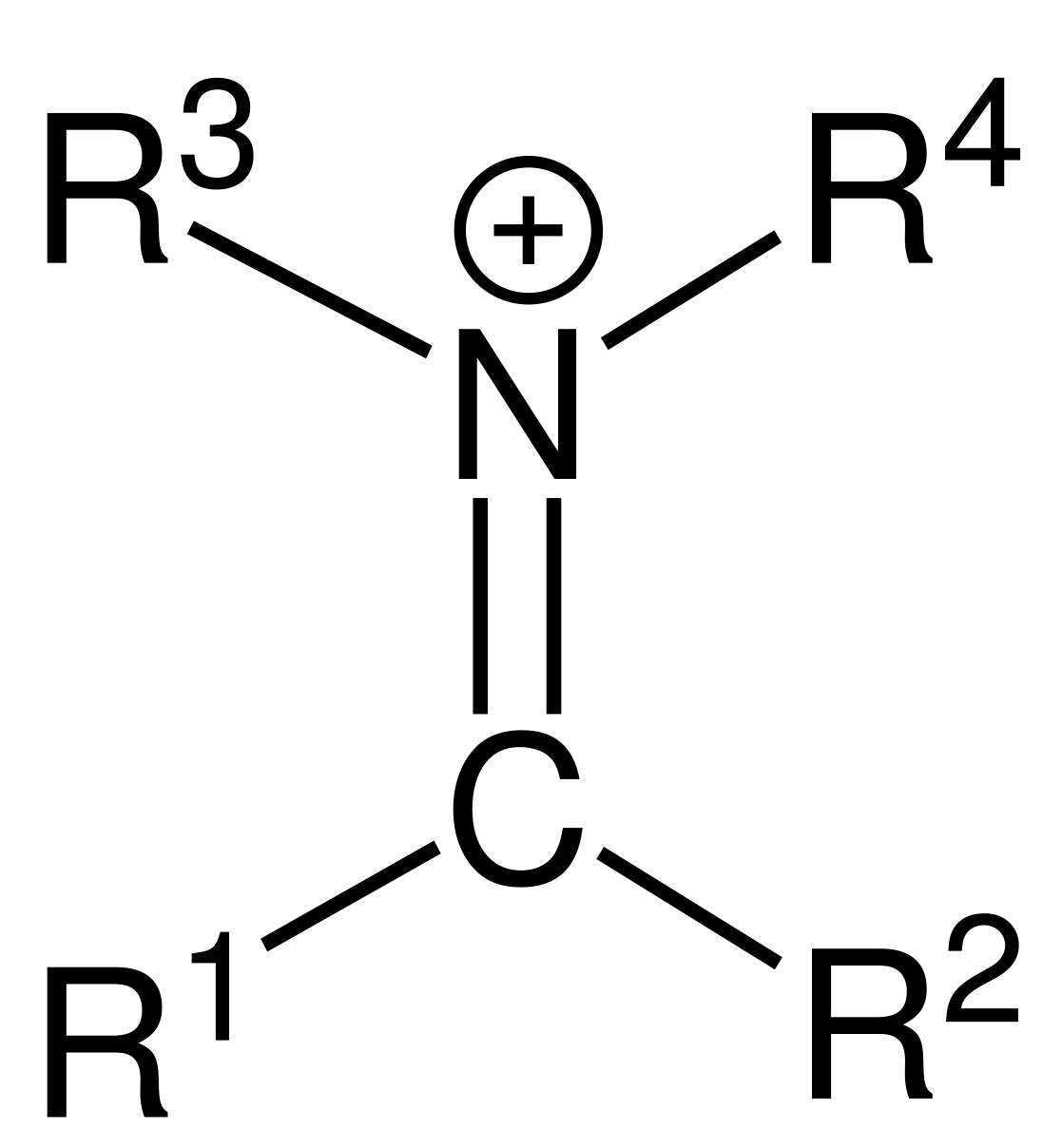
Iminium
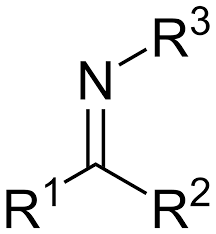
Imine
Imine is the N analogue of a carbonyl group.
This means that an imine is structurally and chemically analogous to a carbonyl, but with N replacing O
Electrophilic carbonyls reacting with amine
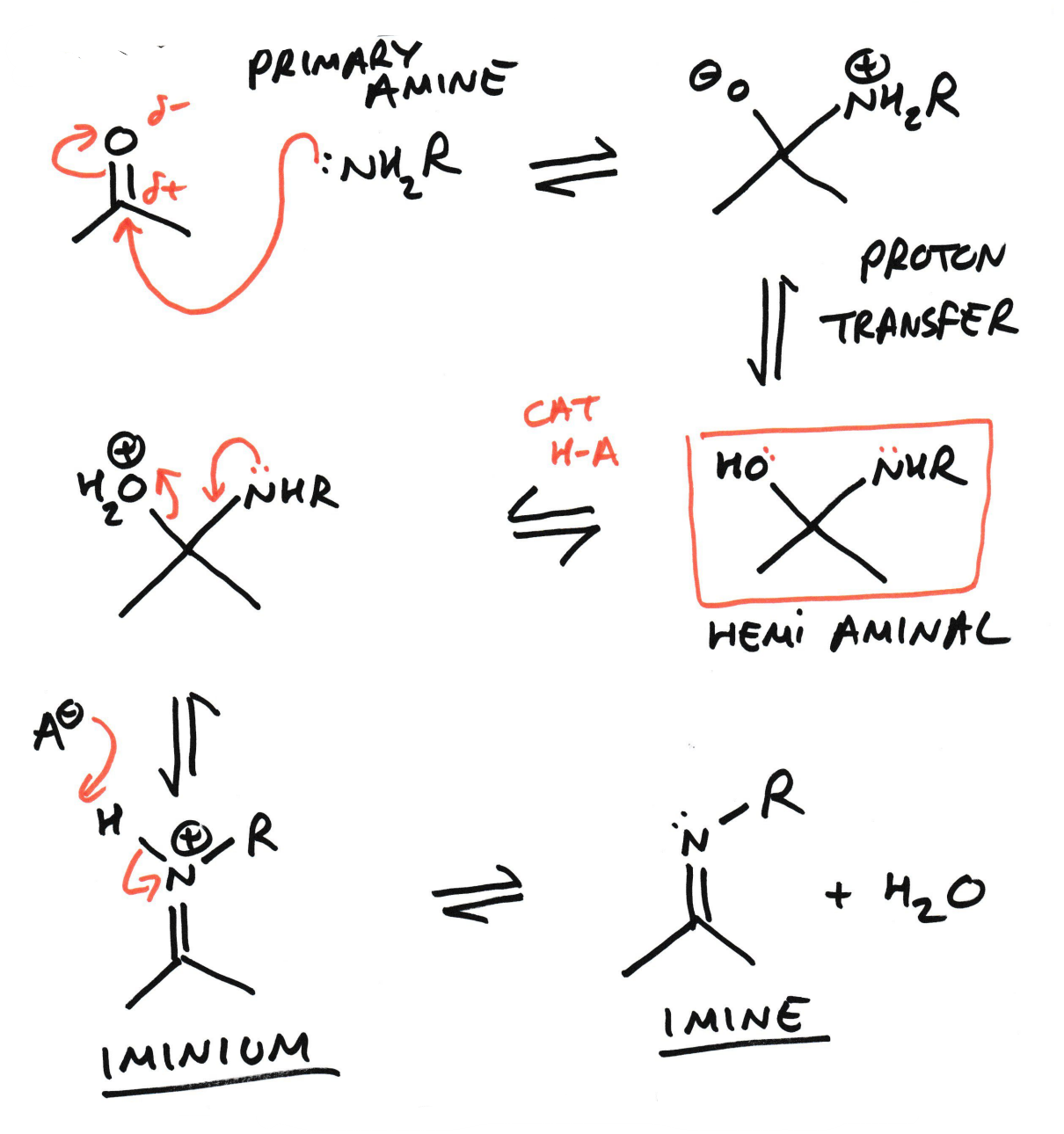
Condensation reaction
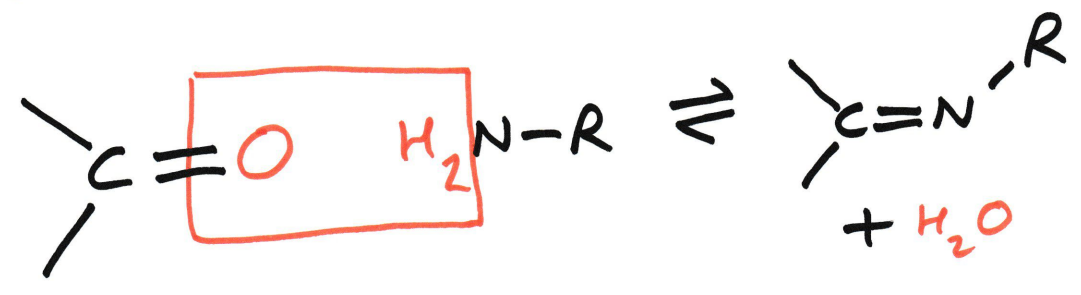
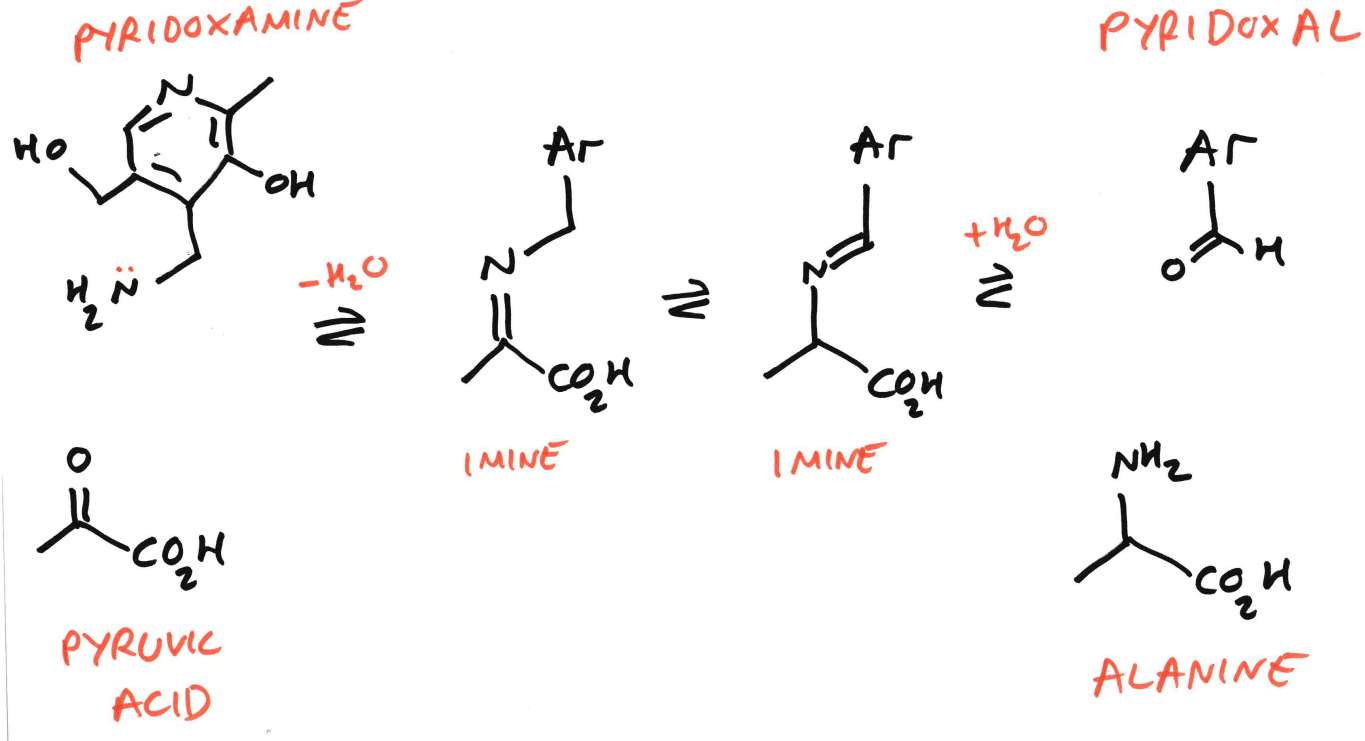
Biosynthesis of Amino Acids
An (here: pyruvic acid)
Is converted into an α-amino acid (here: alanine)
Using vitamin B₆ cofactors:
Pyridoxamine (PMP)
Pyridoxal (PLP)
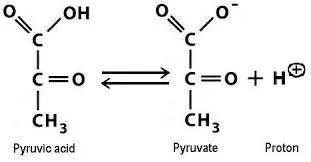
Pyruvic acid Vs Pyruvate
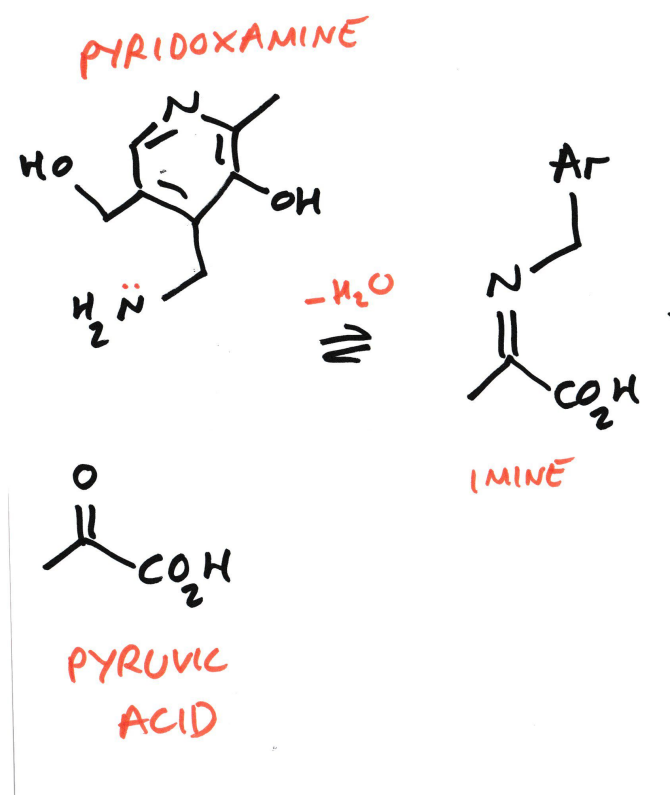
Pyridoxamine donates an NH2 group, acting as an amine donor
Pyruvic acid is an α-keto acid. This carbon skeleton will become alanine.
The amine from pyridoxamine reacts with the carbonyl carbon of pyruvate
Water is eliminated (−H₂O)
An imine (C=N) is formed
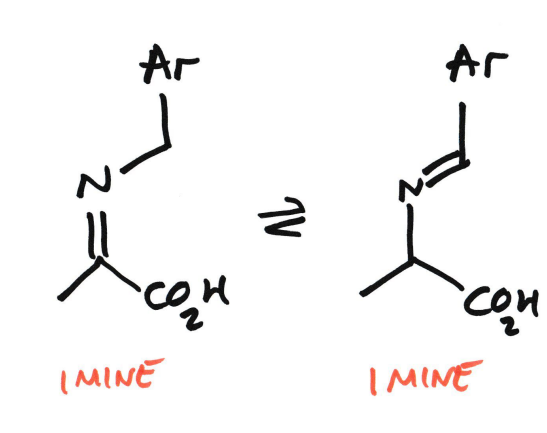
The two imine drawings represent:
Electron rearrangement
Proton shifts
Stabilisation by the PLP/PMP system
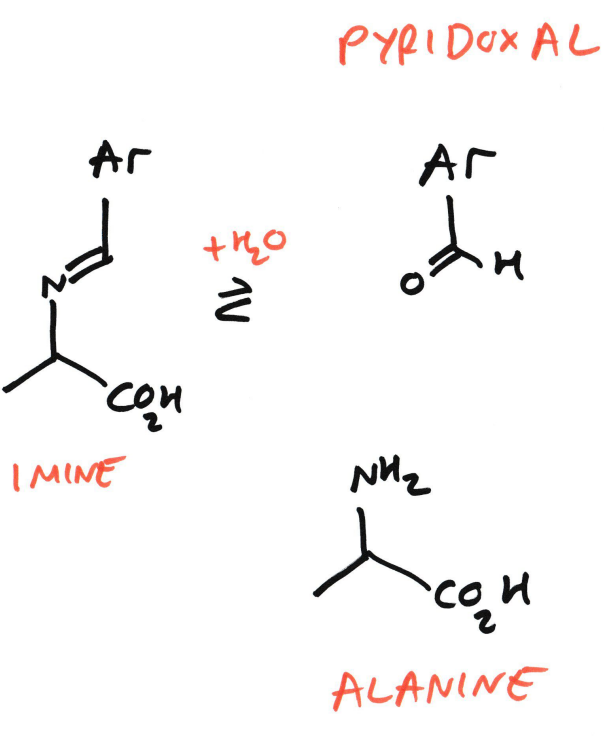
Water adds back in
The imine is hydrolysed
This splits the intermediate into:
Alanine (now has –NH₂)
Pyridoxal (PLP) (now without the amine)
So:
PMP → PLP
Pyruvate → Alanine
Electrophilic carbonyls reacting with a secondary amine
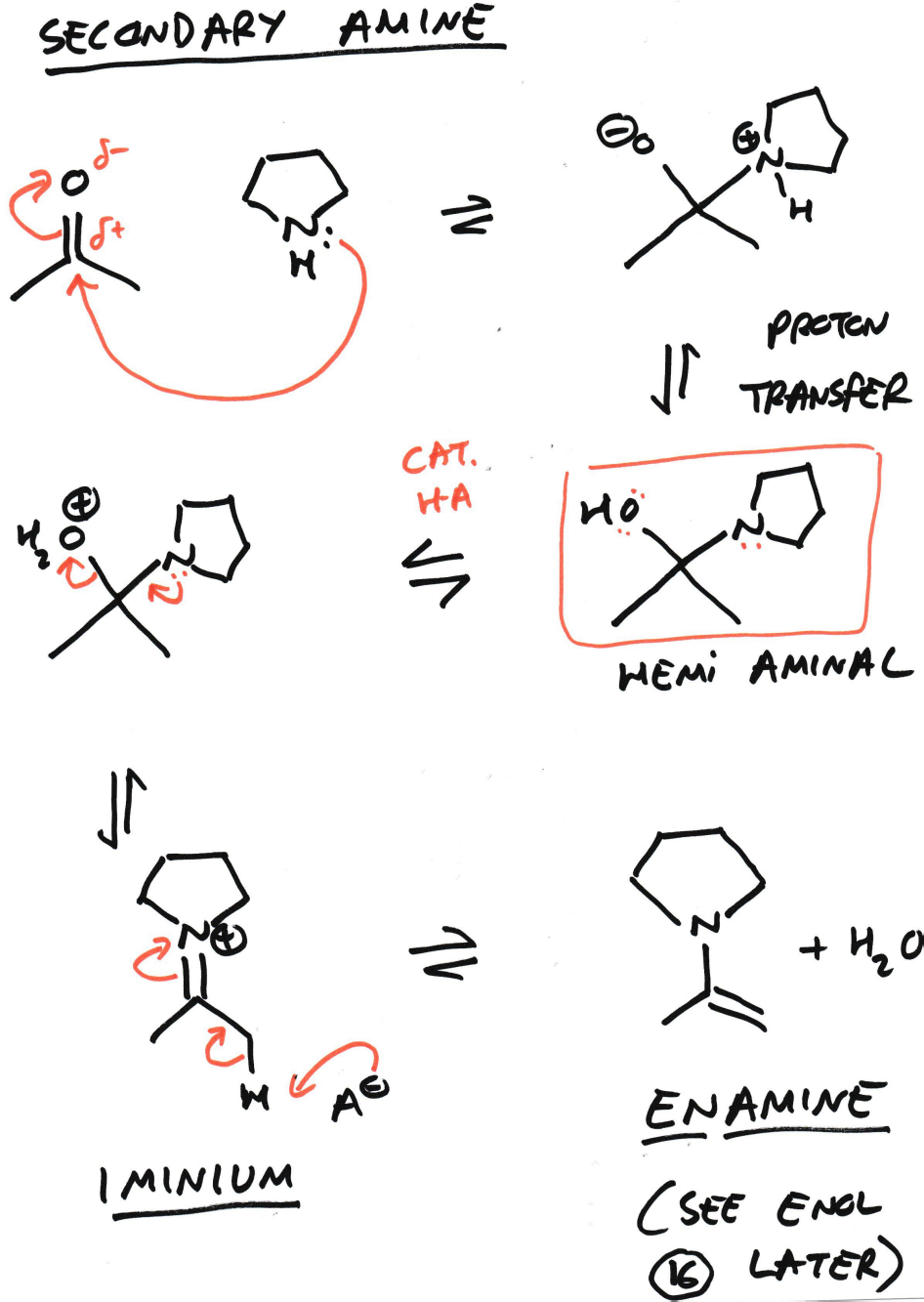
What is enamine?
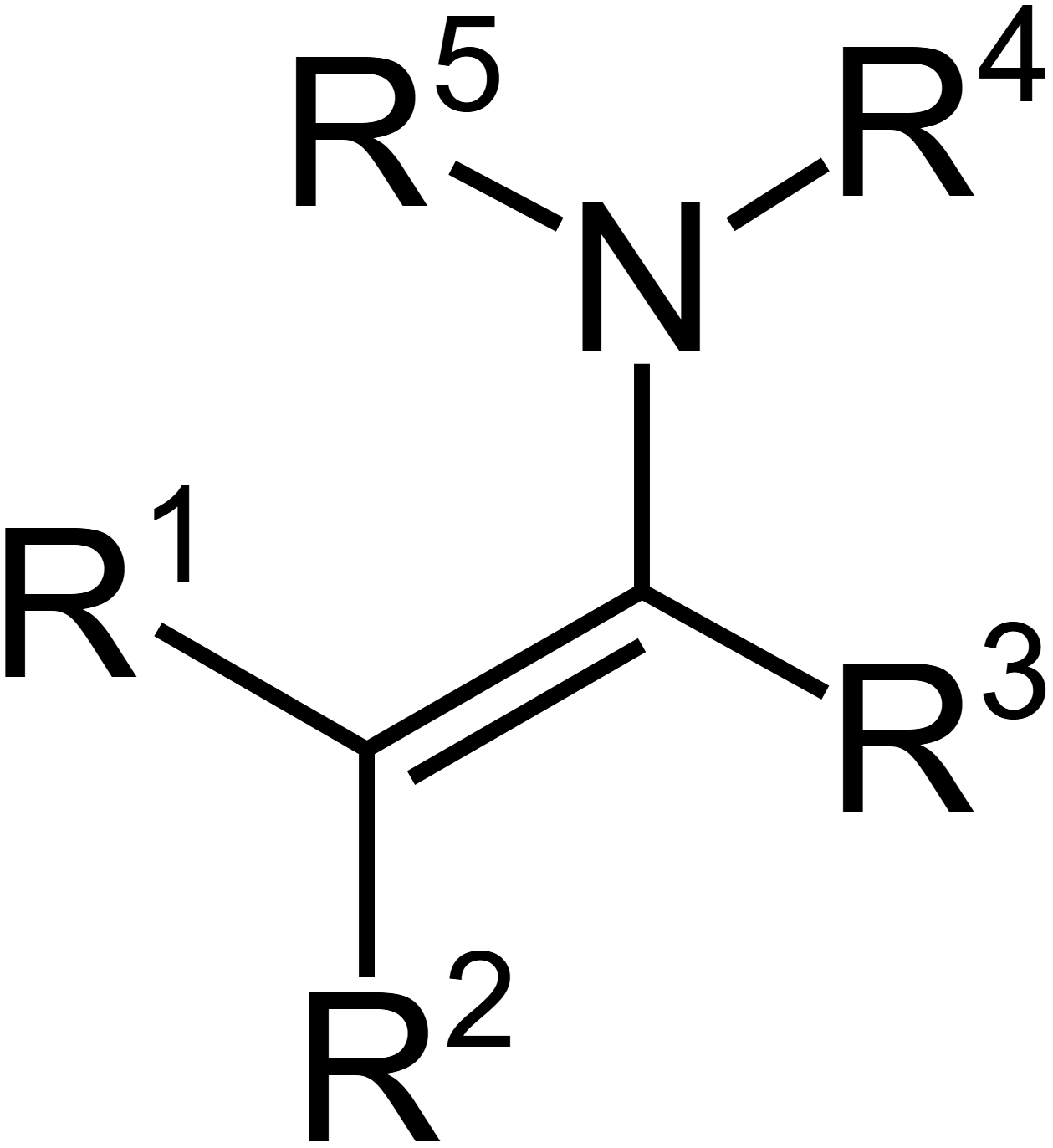
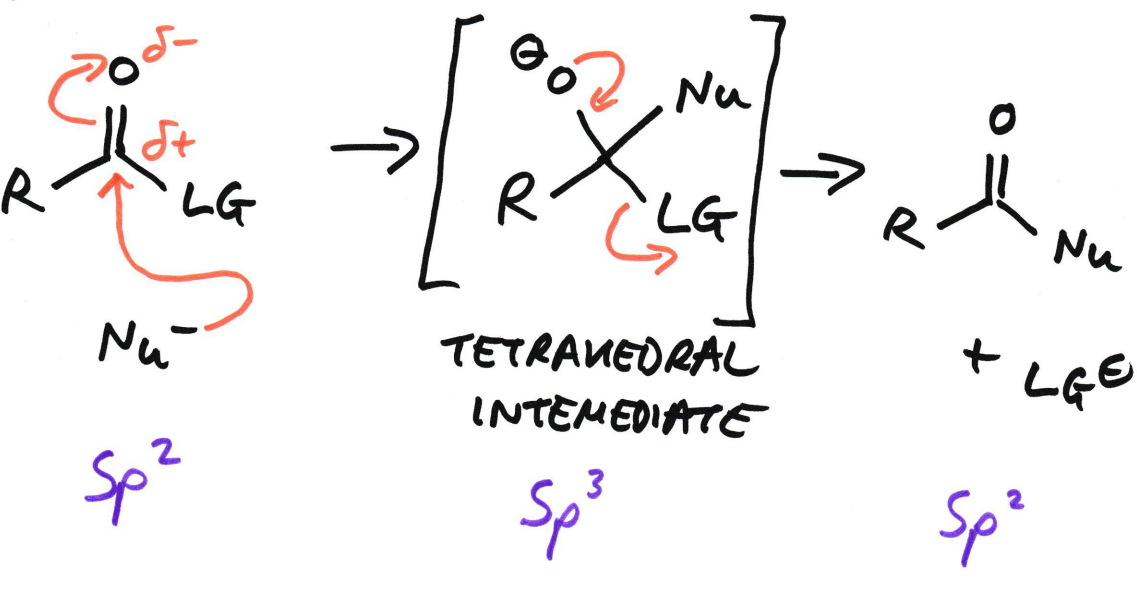
If carbonyls have a leaving group, what does the mechanism look like?
Nucleophile attacks the carbonyl C
A tetrahedral intermediate forms
The nucleophile substitutes the LG
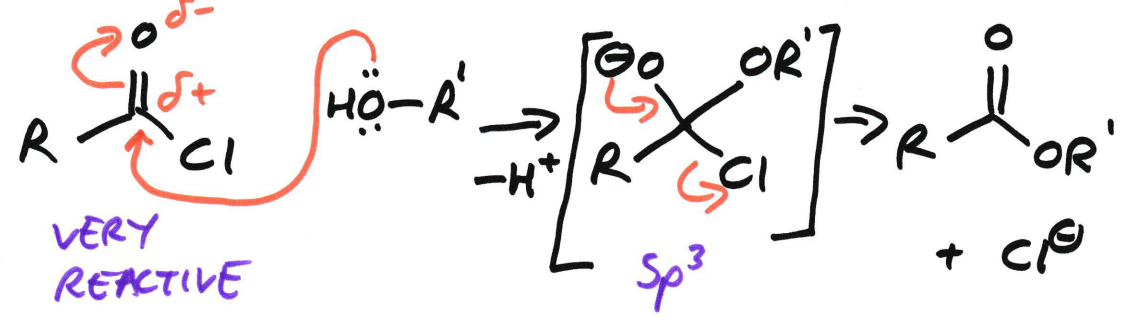
Acyl chloride → Ester
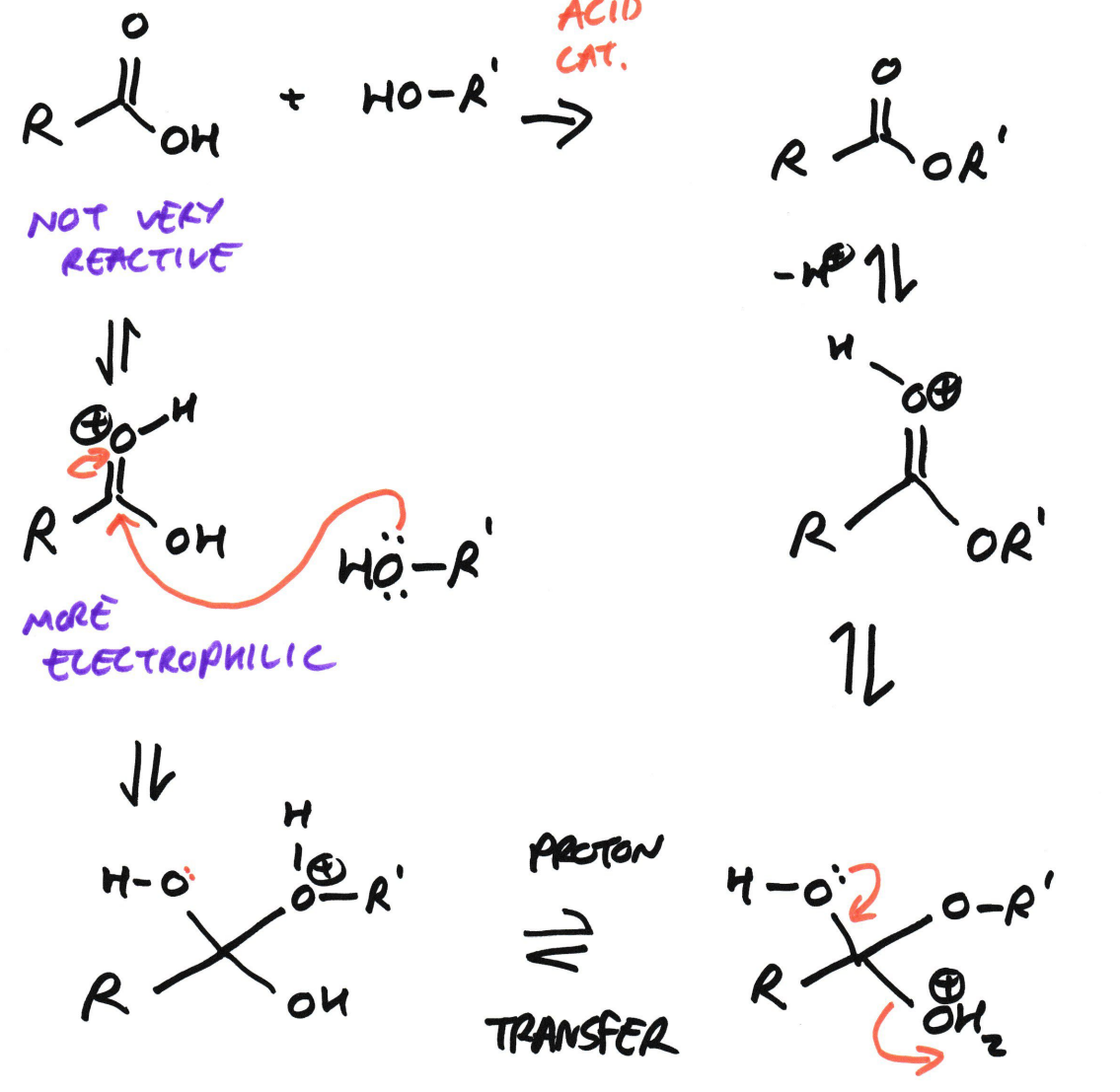
Carboxylic acid → Ester
Requires an acid catalyst since carboxylic acid is not very reactive on its own. This is because the carbonyl carbon in the COOH is not very electrophilic (the -OH donates electron density by resonance, making for a poor LG)
The acid catalyst protonates the carbonyl O and increases the δ⁺ on the carbonyl carbon, making it more electrophilic
Now that the carbonyl carbon is activated:
The alcohol HO–R′ attacks the carbonyl carbon
Forms a tetrahedral intermediate
You now have:
Two –OH groups
One –OR′ group
One of the oxygens is protonated
4. Proton transfer (key rearrangement step)
At this stage:
There is a bad leaving group (–OH)
We need to convert it into a good leaving group
So a proton transfer occurs:
A proton moves from one oxygen to another
Converts –OH into –OH₂⁺
This step:
Does not change connectivity
Just rearranges protons
Makes the next step possible
5. Loss of water (leaving group step)
Now:
H₂O is a good leaving group
Water leaves
The tetrahedral intermediate collapses
C=O reforms
This gives a protonated ester.
6. Deprotonation (regeneration of catalyst)
Finally:
A base (often water or alcohol) removes the proton
Neutral ester is formed
Acid catalyst is regenerated
Acyl chloride → Amide
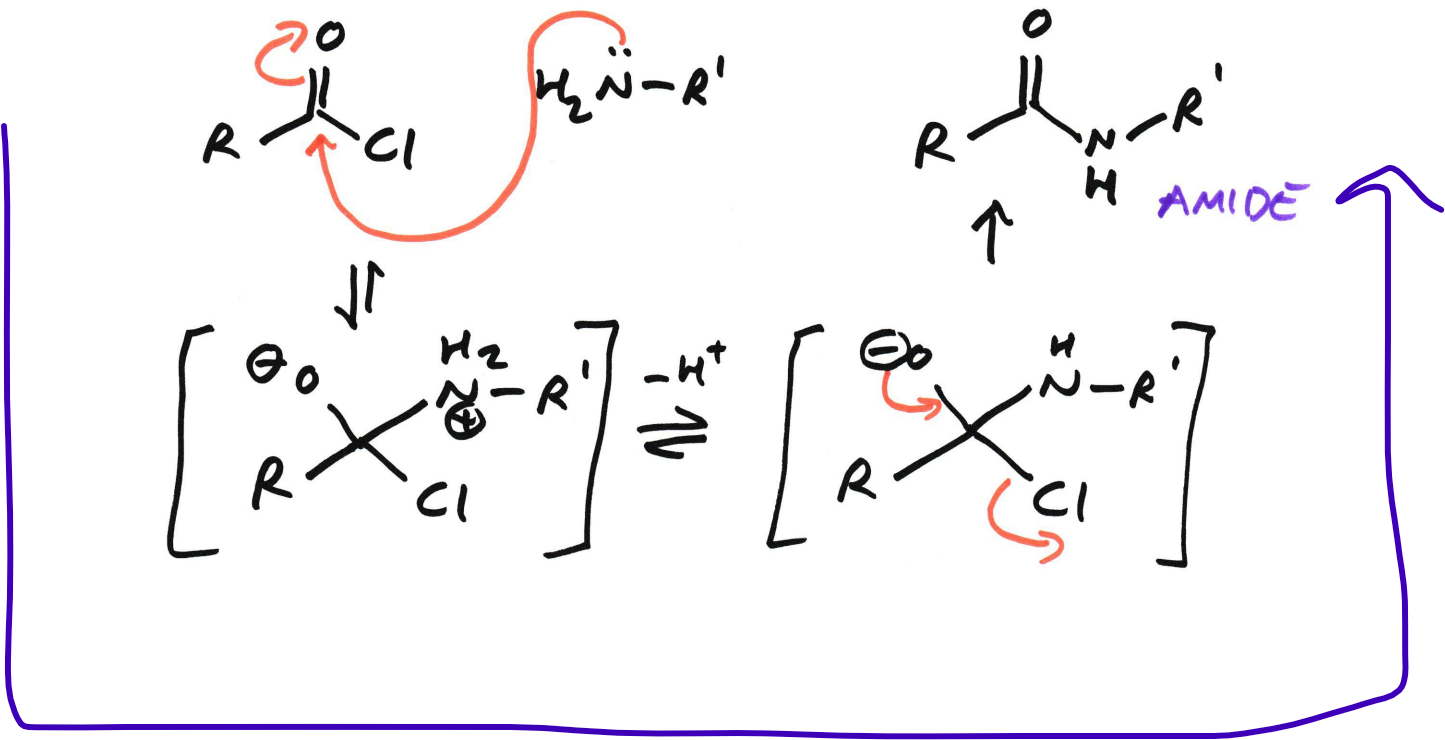
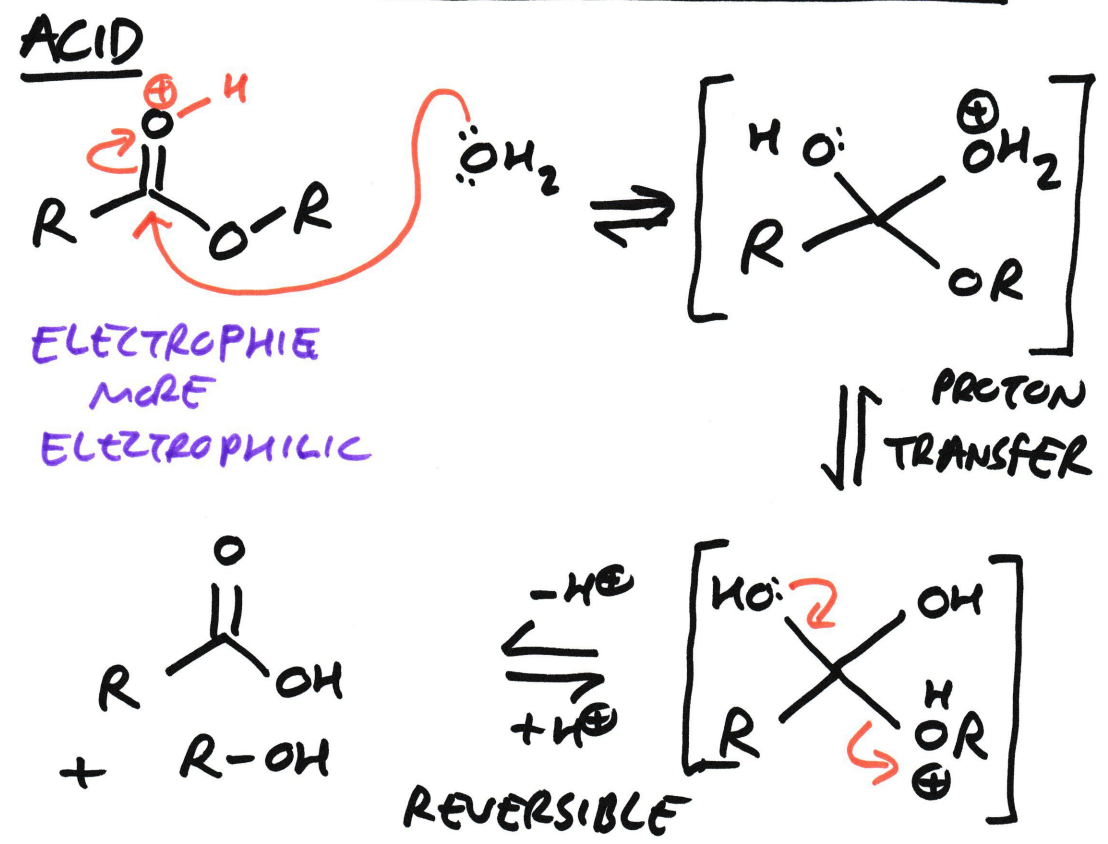
Ester → Carboxylic acid + Alcohol
Using Acid hydrolysis (H2O)
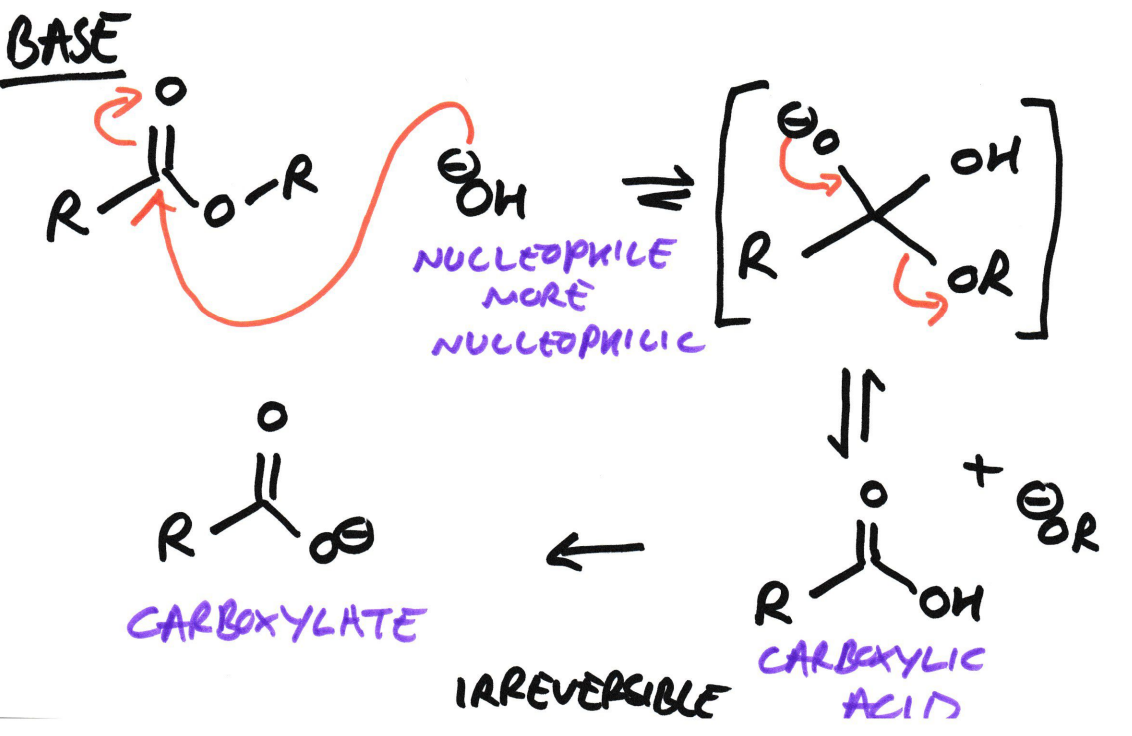
Ester → Carboxylic acid + Alcohol
Using Base/Alkaline hydrolysis (OH-)
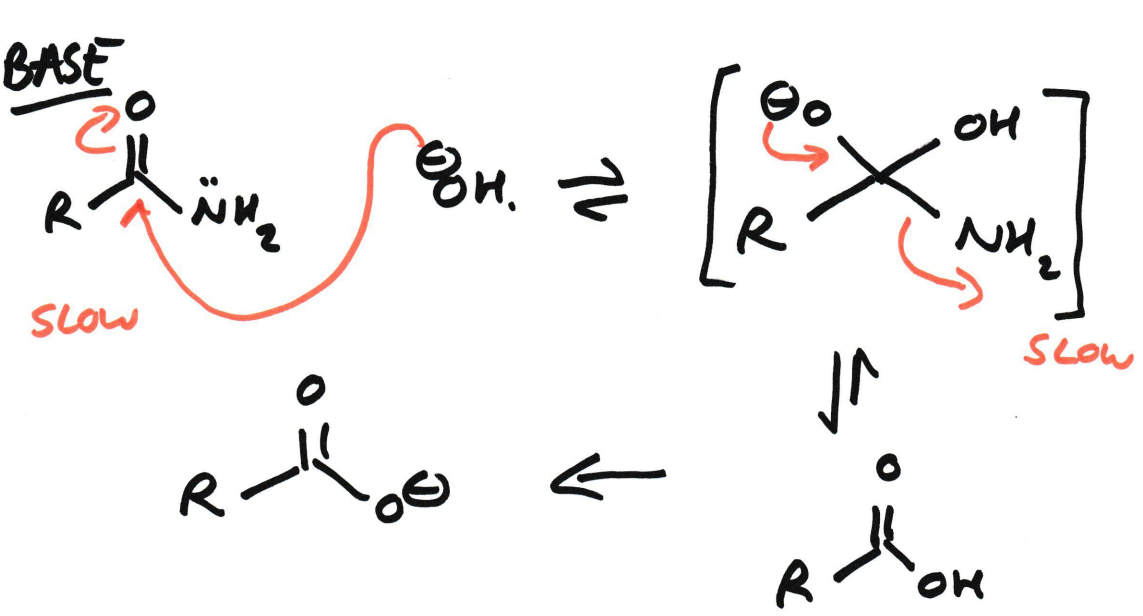
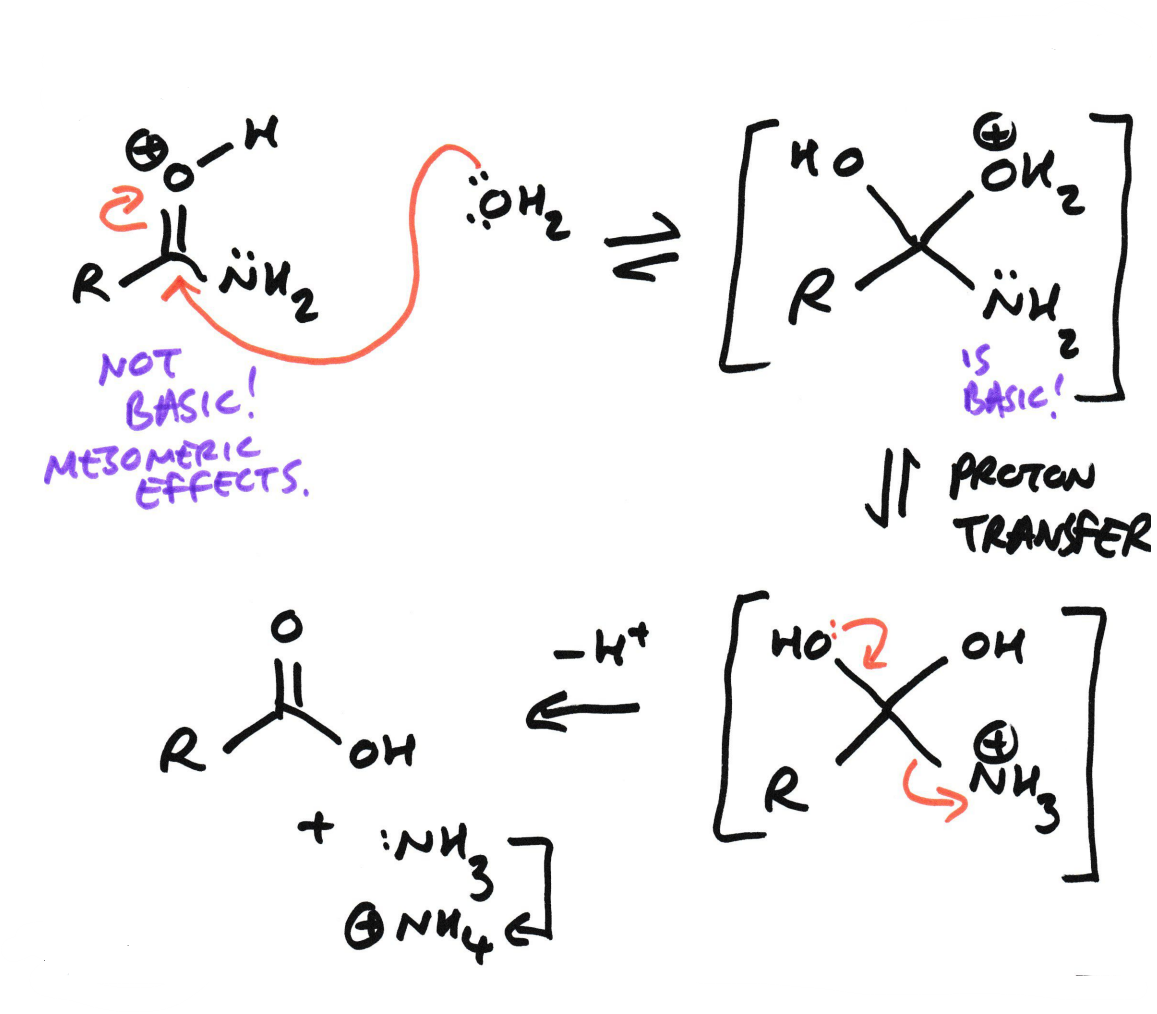
Amide → Carboxylic acid + Ammonium salt
Using Acid hydrolysis
Amide → Carboxylate salt + Ammonia/amine
Using Base/Alkaline hydrolysis (OH-)