Trauma of upper limb
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
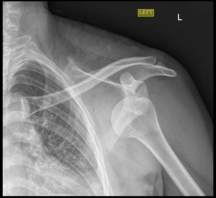
What findings are present in this image?
A. dislocated shoulder
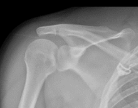
What findings are present in this image?
P. dislocated shoulder
What is the Hill-Sachs sign, and how does it occur?
The Hill-Sachs sign is a deformity of the superior, posterior border of the humeral head. It typically occurs due to impaction of the anterior inferior surface of the glenoid labrum on the posterolateral aspect of the humeral head during dislocation.
What is a Bankart lesion, and what is its association with shoulder dislocation?
A Bankart lesion is a fracture of the glenoid cavity that accompanies anterior dislocation of the humeral head. It involves a small sliver of bone being elevated, and the labrum may be completely detached.
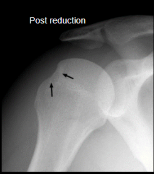
What are the two arrows pointing too, and what does it suggest?
Hill-Sachs sign
Prior A. disslocation
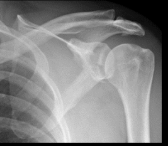
What findings are present in this image, and what does it suggest?
Bankart lesion
Injury to the glenoid labrum/rim (anterior-inferior)
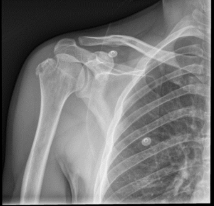
What findings are present in this image?
Fractured greater tubercle of humeras
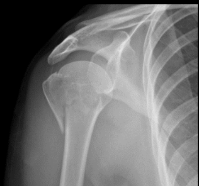
What findings are present in this image?
Fracture of proximal humerus resulting in tubercle separation
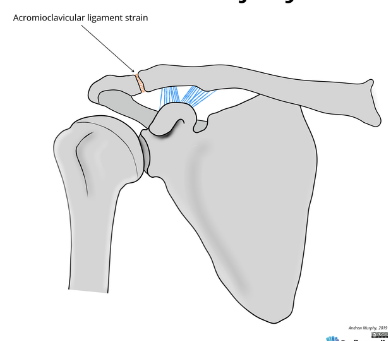
Based off Rockwood classification of acromioclavicular joint injury, what grade would this be?
1
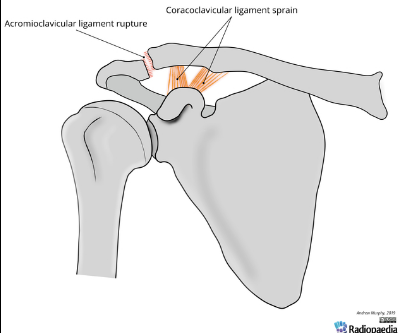
Based off Rockwood classification of acromioclavicular joint injury, what grade would this be?
2
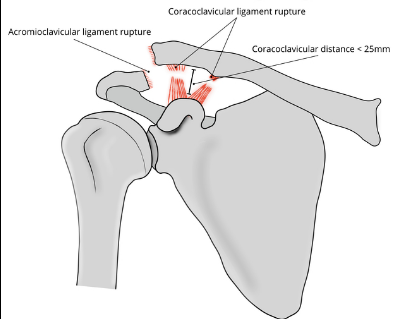
Based off Rockwood classification of acromioclavicular joint injury, what grade would this be?
3
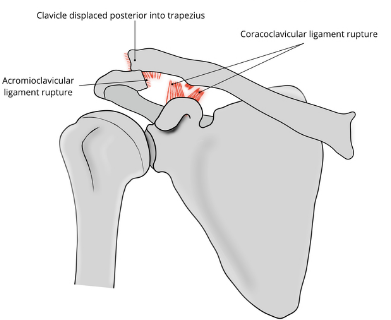
Based off Rockwood classification of acromioclavicular joint injury, what grade would this be?
4
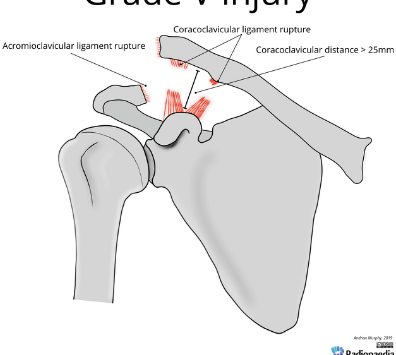
Based off Rockwood classification of acromioclavicular joint injury, what grade would this be?
5
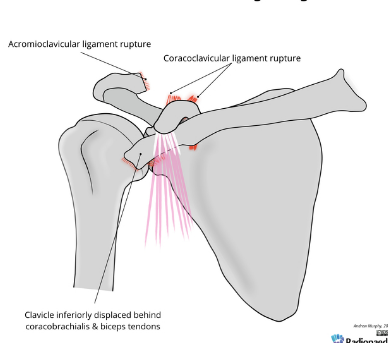
Based off Rockwood classification of acromioclavicular joint injury, what grade would this be?
6
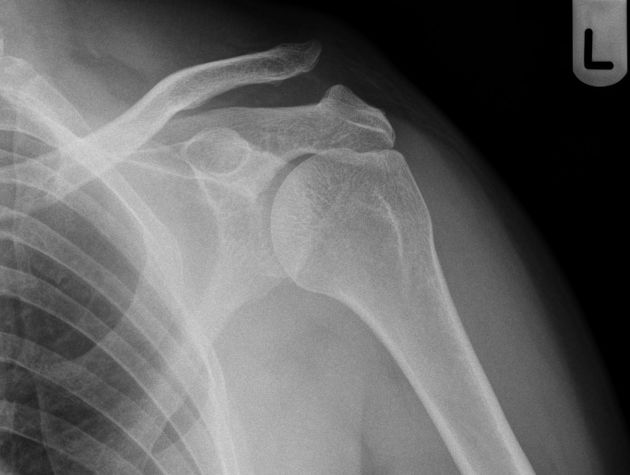
Based off Rockwood classification of acromioclavicular joint injury, what grade would this be?
3
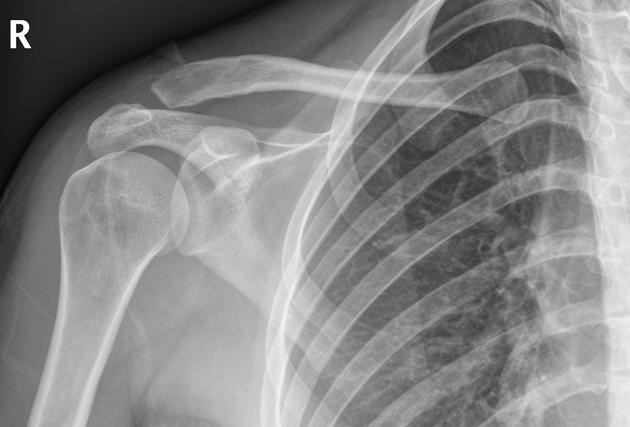
Whats wrong in this image?
Rockwood classification of acromioclavicular joint injury, type 1
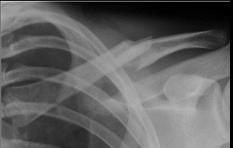
What findings are present?
Clavical fracture
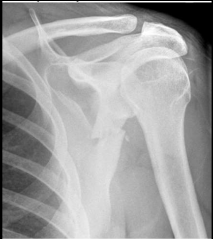
What findings are present?
Fracture of scapular
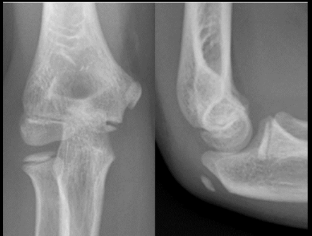
What findings are present?
None- Normal pediatrics elbow
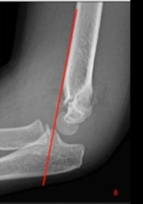
What findings are present?
A distal humerus fracture (e.g., supracondylar fracture in children or intercondylar fracture in adults) with posterior displacement of the distal fragment. This is a critical finding in trauma evaluations.
What does it mean when the elbow fat pads are visible?
bleeding! Likely due to a fracture.
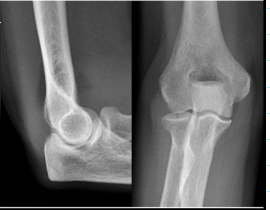
What findings are present?
Fat pad signs- Fracture of radial head
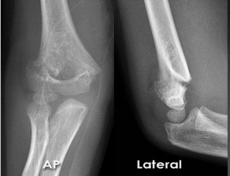
What findings are present?
Fx of distal humerus
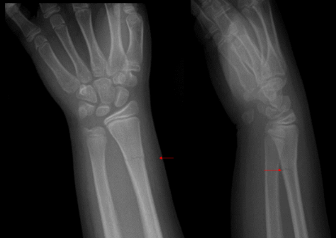
What findings are present?
Greenstick Fx
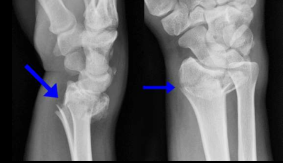
What findings are present?
Colle’s Fx
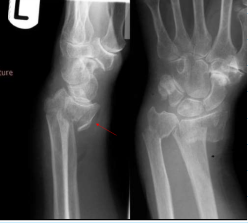
What findings are present?
Smiths Fx
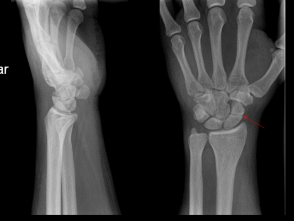
What is the red arrow pointing too?
Scaphoid Fx
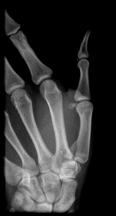
What findings are present?
Bennett’s Fx
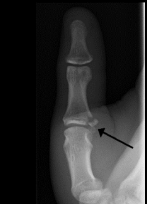
What findings are present?
Gamekeepers thumb