Sportsmed past test questions
1/91
Earn XP
Description and Tags
use for midterm study
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
92 Terms
protein
Needed for growth, maintenance, and repair of all body tissues. Needed to make enzymes, hormones, and antibodies to fight infection. Amino acids are the building blocks.
mineral
Function to generate energy, form strong bones and teeth, activate enzymes, and maintain water balance
vitamin
Regulate body processes. Needed in smaller amounts than other nutrients
water
Most essential nutrient needed for energy production, digestion, and maintaining proper environment in and out of the cells. Makes up 60% of the body
carbohydrate
The body's most efficient source of energy
lipid
Minimal amount needed for growth and development. Most concentrated form of energy
the 3 macronutrients are
lipids, carbohydrates, proteins
the 3 micronutrients are
water, minerals, vitamins
What is the relationship between micro and macro nutrients in terms of providing and using energy?
Macronutrients supply energy. Micronutrients do not supply energy but without them, macronutrients cannot be absorbed.
complex carbohydrates
Digest more slowly and provide long-lasting energy
unsaturated fat is
healthy fat
What makes an amino acid essential?
It must be obtained through the diet
Electrolytes are important during exercise because they
Help maintain fluid balance and muscle function
Which statement correctly compares fat-soluble and water-soluble vitamins?
Excess water-soluble vitamins are excreted in urine, while excess fat-soluble vitamins can build up and become toxic
Purposes of sports medicine
performance enhancement
injury care and management
professions of performance enhancement
Exercise Physiology
Biomechanics
Sports Nutrition
Strength & Conditioning
Personal Training
Coaching
Physical Education
professions of injury and care management
Practice of Medicine (Physicians, Physician’s Assistants)
Athletic Training
Sports Physical Therapy
Sports Massage Therapy
Sports Dentistry
Osteopathic Medicine
Orthotists/Prosthetics
Sports Chiropractic
Sports Podiatry
Emergency Medical Technicians
Paramedics
Which of the following is not a component of the preparticipation health examination?
cardiovascular screening
orthopedic screening
maturity assessment
nutritional performance screening
medication assessment
mental health screening
balance and agility assessment
wellness screening
nutritional performance screening
balance and agility assessment
Which law protects students’ educational records?
FERPA
Which law protects students’ medical records?
HIPPA
Injury reports must be kept for how many years?
3 years
A personal information card should include all of the following EXCEPT
daily nutrition log
Name responsibilities of the athletic administrator
budgeting
hiring personnel
making: risk management procedures, policies, and emergency action plans
Which of the following is NOT typically a responsibility of an Athletic Trainer Certified (ATC)?
Performing surgical procedures on injured athletes
In their role of prevention, ATCs are responsible for all of the following EXCEPT:
prescribing medications for injury prevention
Purpose of Performance Enhancement
Maintain and improve functional capacity for physical labor, exercise, and sports
Purpose of Injury care and management
Prevention and treatment of diseases and injuries related to exercise and sports
Whats the difference between organized and recreational sports teams?
There are different levels of sport involvement and therefore different levels of treatment and involvement from healthcare professionals
What is the purpose of a preparticipation health examination (PPE)?
To identify past or existing medical problems
For a muscle to improve in strength, it must be forced to work at a higher level than it is accustomed. What is this called
overload
Endurance muscles are usually a higher ratio of ____-twitch muscles.
slow
Is squatting at a smith machine an open or closed kinetic chain exercise?
closed

Increased intensity at lower reps builds what?
strength
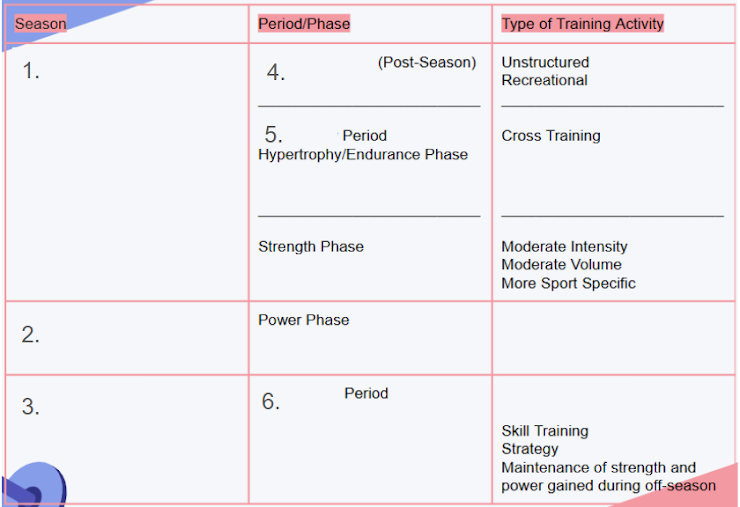
fill out blanks
1. Off-Season
2. Pre-Season
3. In-Season
4. Transition Period
5. Preparatory Period
6. Competition Period
Which of the following is an example of an isometric exercise?
wall sit
Which of the following best describes the difference between active and passive motion?
Active motion is performed by the athlete using their own muscles, while passive motion is performed with assistance from another person or external force
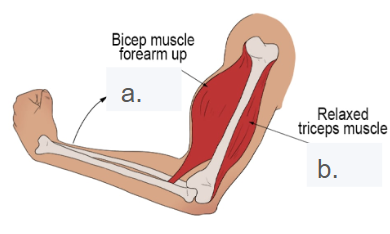
This person is doing a bicep curl. Which muscle is the "agonist" and which is the "antagonist"? What is the difference?
Agonist (A) contracts to move the muscle while the antagonist (B) is relaxed, but offering control to the agonist.
What is cross-training?
Alternative activities that have carry-over value to specific sports to prevent boredom while maintaining fitness.
What is the difference between static and dynamic warm up?
Give one benefit of each.
How long after warming up should activity begin?
Static is passive stretching compared to dynamic which moved through a controlled full range of motion.
- Static can be useful for less mobile people. Dynamic is more functional for athletes.
- 15 Minutes
What is progressive resistance training? There are three different ways to perform them. What's the difference?
Strengthen muscles through isotonic exercises that overcome resistance from equipment.
Can use free weights, machine weights, or exercise bands
Free weights focus on neuromuscular control. Machine weights can lift heavier. Bands are more functional for sports.
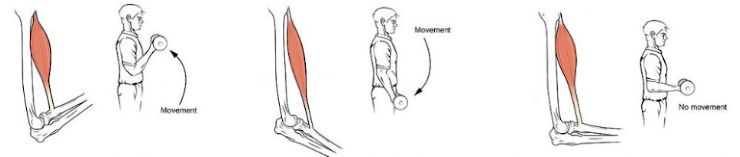
Explain the type of movement in each image (left, middle, and right). Is it isometric, concentric, or eccentric?
1.concentric 2. eccentric 3. isometric
What is it cardiorespiratory fitness and what is the general pathway
The body’s ability to transport and use oxygen efficiently to improve performance and reduce fatigue while performing whole body, large-muscle activities for extended periods. The general pathway starts from the mouth, through the heart, out into the lungs (for carbon dioxide), and goes back into the heart.
Periodization training should change from (1. high, low) volume, (2. high, low) intensity, (3. sport-specific, non-sport-specific) activity to (4. high, low) volume, (5. high, low) intensity, (6. sport-specific, non-sport-specific) activity.
1) high
2) low
3) non-sport-specific
4) low
5) high
6) sport-specific
SAID Principle states that
The body will overcome imposed demands of stress and overload
Anaerobic vs Aerobic
Short bursts is anaerobic. Endurance is aerobic. Aerobic uses oxygen. Anaerobic uses sugar and ATP via glycolysis.
A gluten-free diet is primarily necessary for individuals with:
Celiac disease or gluten sensitivity
What is the formula for caloric balance? Which would lead to weight gain? Which would lead to weight lose?
Caloric Balance= Number of calories consumed - number of calories expended
If the balance is positive (consumed is greater than expended), weight gain.
If balance is negative (expended is greater than consumed), weight loss.
The purpose of carbohydrate loading before endurance events is to:
Maximize glycogen stores in muscles
what does the glycemic index (GI) measure?
How quickly a carbohydrate-containing food raises blood sugar levels
Which of the following is not one of the three main ways the body expends calories?
Protein synthesis
Why is it important for athletes to maintain a healthy body fat percentage
Going too low can cause hormone imbalances and reduce organ protection
How long do you have to bring someone's core temperature down, before heat stroke becomes life threatening?
30 minutes
How does humidity impact an athlete’s ability to dissipate heat?
Humidity of 65% severely impairs evaporation, and 75% nearly stops it, increasing the risk of heat illness even in moderate or cool temperatures.
What is a diuretic?
A medication or substance that increases urine production, helping the body remove excess fluid.
Which treatment is most appropriate for an athlete showing signs of a cold-related illness?
Apply gentle rewarming by breathing on the hands or placing them under the armpits, remove cold/wet/restrictive clothing, and use heating pads or blankets to gradually raise core temperature.
Regarding sunscreen use in athletes, which statement is correct?
SPF stands for Sun Protection Factor; a minimum of waterproof SPF 15 allows an athlete to stay in the sun roughly 15 minutes longer without burning.
After seeing lightning or hearing thunder during athletic activity, how long should play be delayed to ensure safety?
30 minutes from every lightning strike seen or thunder heard.
Why does altitude sickness occur? How does the body adapt to combat altitude sickness?
It occurs because the higher the altitude, the lower the oxygen level. The body combats this by generating more red blood cells which can take 3 days to 3 weeks.
Heat Syncope
Rapid physical fatigue during overexposure to heat that causes dizziness, fainting, and nausea
Heat Stroke
Body loses the ability to dissipate heat through sweating and core temperature increases to 105F. Serious, life-threatening emergency.
Exertional heat exhaustion
Collapse, profuse sweating, pale skin, elevated temperature (101-104 degrees F), etc. caused by dehydration
Exercise-associated hyponatremia
Caused by low sodium intake and increased fluid intake that decreases sodium concentration in blood
Frost Nip
High wind and/or severe cold that causes skin to initially appear firm, cold and numb
Chilblain
Prolonged and constant exposure to cold (50 degrees or less) for more than 60 minutes that disrupts peripheral circulation
Superficial Frostbite
Involves the skin and subcutaneous layer. When rewarming, feels numb at first, then stings and burns
Which of the following strategies is most effective for preventing cold-related illness in athletes?
Wear thin, moisture-wicking layers and perform a proper warm-up.
What is the purpose of the primary survey?
To assess life-threatening conditions
CAB during the primary survey stands for
Circulation, Airway, Breathing
What does the secondary survey assess?
Conditions that are not immediately life-threatening
The Good Samaritan Law protects people who:
Provide emergency care in good faith and within their training
In POLICE, the “P” stands for
Protection
One of the main principles of splinting is:
splint above and below the injury
A vacuum splint is best used for:
Angulated fractures that need molding
Air splints should NOT be used when:
It may change the angle of a fracture deformity
A SAM splint becomes rigid when
It is shaped into curves
SMR stands for
Spinal Motion Restriction
Manual conveyance is used for
Mildly injured athletes who cannot walk long distances
The 3-point gait pattern is used when:
The athlete is non-weight-bearing on one leg
The 4-point gait pattern involves:
Moving both crutches together
The 1-point (cane) gait pattern involves:
Cane and injured leg moving together
What are the risks associated with passing down equipment?
Athletes receiving the equipment are already less coordinated. Now the equipment is worn out and less effective. Risk of injury is compounded.
Why is it important to check the fit of equipment when traveling to different altitudes?
Air pressure changes and pads are pockets of air so they may over or under-inflate during travel.
Name two sports that use hip, buttocks, and coccyx pads
hockey and football
What is the difference between football, hockey, and soccer "helmets"?
Football helmets are made for repetitive impact.
Hockey are made for high velocity projectiles or high mass people hitting them.
Soccer concussion bands are virtually useless.
What is the importance of using polycarbonate lenses in sports eyewear?
To prevent glasses from breaking into sharp shards and causing further injury.
With the use of face masks, why have nose injuries decreased but concussions increased?
Nose has been "breaking the fall" and absorbing impact for the head.
What are the three types of sports bras and their purpose?
Lightweight for low intensity activities
Compressive for high intensity activities
Supportive for athletes with larger chests to have more support and protection from injury
What is the purpose of the heel counter?
to prevent ankle rolling
What considerations are there in determining football shoulder pads?
Position. Running/catching can have fewer and more mobile pads. Blocking and hitting positions need bulkier protection.
How many bars are on face masks and how close together should they be?
There should be a minimum of two bars regardless of sport and they should be close enough to prevent projectiles or sticks (relevant to the specific sport) from entering.
What is the risk of an individual's protective equipment to the sport?
Something that protects one person can be a weapon against another so regulations need to be put in place.
What is the purpose of ear guards?
to prevent cauliflower ear in boxers/wrestlers