MCB 32- Human Physiology Mod 1-12
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
External environment
parts of the body that are directly connected to the outside (skin, gastrointestinal system, urinary, respiratory, reproductive)
Internal environment
parts of the body not connected to external environment, although external materials can be brought across epithelial cells into blood cells and vice versa
Homeostasis
The body’s ability to maintain a relatively stable internal environment (eg, within the range of 37 °C, near pH 7). uses negative feedback to counteract stimulus
Covalent bond
sharing of electrons (either unequally/ polar or equally/ nonpolar)
Ions
transfer of valence electrons binds two molecules to make them fully charged. they dissolve in water, making them good conductors of electricity, and giving them the name electrolytes.
Acids
Molecules that release H ions in water (either strongly or weakly depending on if they fully lose the H or disassociate)
Bases
molecules that bind protons (H)
4 types of tissue
Epithelial (epidermis, glands, lining of GI tract and other hollow organs), have tight junctions
Connective (fat and other soft padding)
Muscle (skeletal, cardiac, smooth), contract and produce force
Nervous (neurons and their support cells/glia: brain, spinal cord, nerves)
pH
measure of how many H ions are in a solution to quantifiy acidity (<7 is acidic, more H, >7 is basic, less H)
Exocrine glands
secrete chemicals into external environment
endocrine glands
secrete hormones into bloodstream
microtubules
around cell membrane, support cell movement and muscle contraction. found in microvili
microfilaments
large parts of the cytoskeleton that provide track for transporting vesicles
Parameters that affect rate of diffusion
surface area, permeability, distance of diffusion, concentration gradient, size of molecule passing
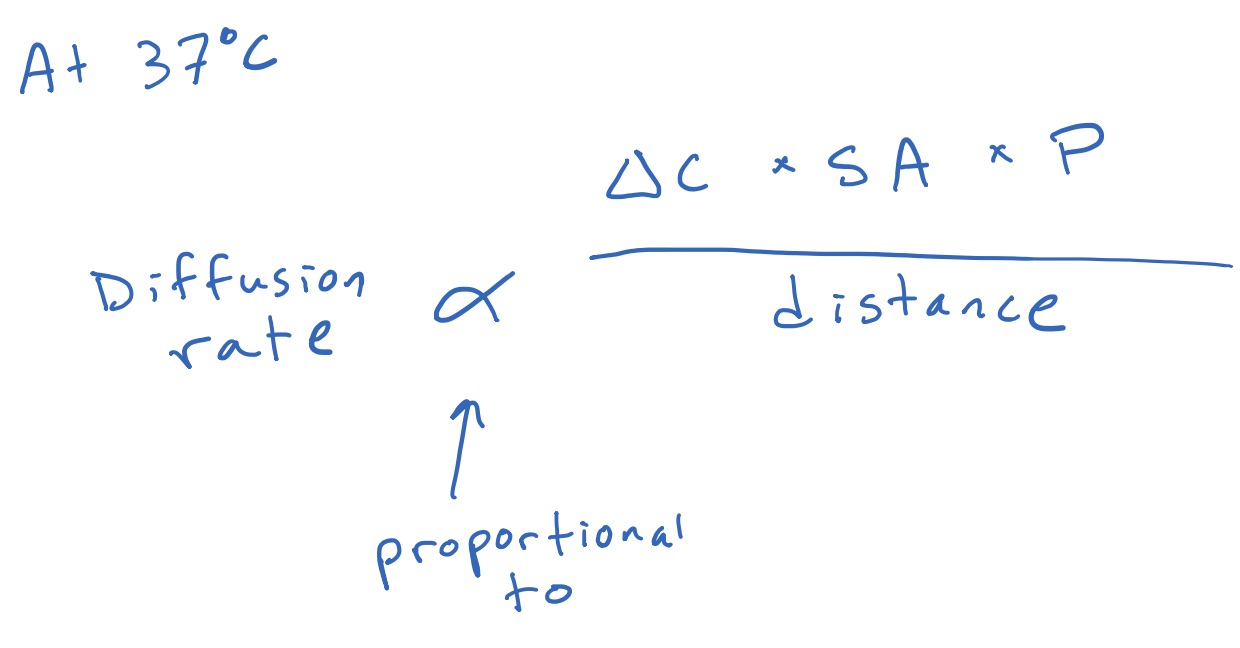
Diffusion rate at body temp
At 37 C, the rate is proportional to the concentration gradient(surface area)(permeability) / distance
Secondary active transport
pump couples the flow of one substance going down gradient with another substance going against it. does not use ATP
Co transport (symport)
transport of two molecules going in same direction
Counter transport (antiport)
transport of two molecules in opposite directions
Paracrine signal
chemical messenger that diffuses locally and acts on a neighboring cell
Types of hormones
Peptide (lipophobic- like insulin, oxytocin)
Steroid (lipophilic- like cortisol, aldesterone, testosterone, estrogen, progesterone)
Amine (sometimes both but epinephrine is lipophobic)
Primary endocrine system (main fcn is to secrete hormones)
hypothalamus, anterior pituitary gland, thyroid, thymus, adrenal gland, pancreas
Secondary endocrine system
Heart, liver, stomach, kidney
tropic hormones
Hormones that stimulate the release of other hormones (most released by anterior pituitary gland, peptides (lipophobic))
explain how action potential releases NT
action potential causing VgCach to open, calcium goes down gradient, triggering release of synaptic vesicles with NTs, which bind to receptors in post synaptic cell
Types of membrane receptors in NS
Ionotropic/Ligand-gated ion channels (open and close for specific ion, used for faster, shorter responses)
Metabotropic/GPCRs (activate ion channels or use secondary messengers to activate ion channels. slower, but can change gene expression for longer-lasting effects)
2 types of neural signaling
Electrical (gap junctions, cell to cell)
Chemical (NTs)
How are NTs cleared from synaptic cleft?
Via reuptake channels, transported into glia cells to be reused, or destroyed by enzymes
2 types of graded potentials with examples
depolarizing/excitatory: open Na+ or all cation channels, close K+ channels to increase likelihood of action potential. eg: glutamate
hyperpolarizing/inhibitory: open K+ or Cl- channels to decrease likelihood or reaching threshold. eg: GABA
used for local signaling only (decremental). because graded potentials can summate and have different amplitudes, they can have multiple inputs (synaptic integration, either from two rapid synapses (temporal) or nearby synapses (spatial))
axon hillcock
integrator that adds up arriving signals (excitatory/inhibitory)- where threshold is met
Graded potentials vs action potentials
Graded: localized, variable electrical-strength signals, can sum, excitatory/inhibitory, in dendrites/ cell body (soma)
Action: non-decremental, all-or-none electrical signals triggered by reaching threshold from graded potential, have refractory periods, in axon
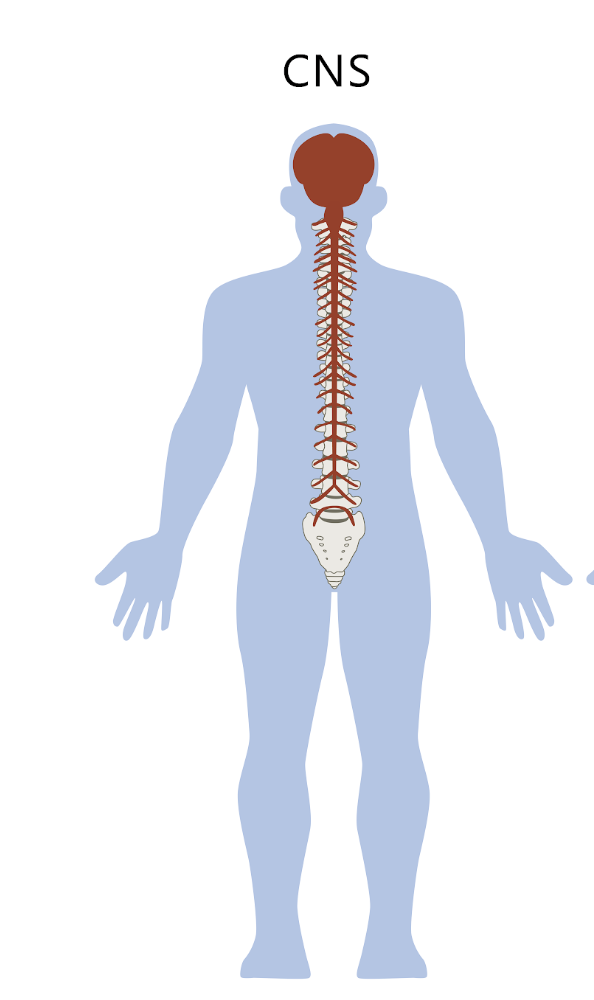
CNS
made of brain and spinal cord, which integrate information and initiate actions
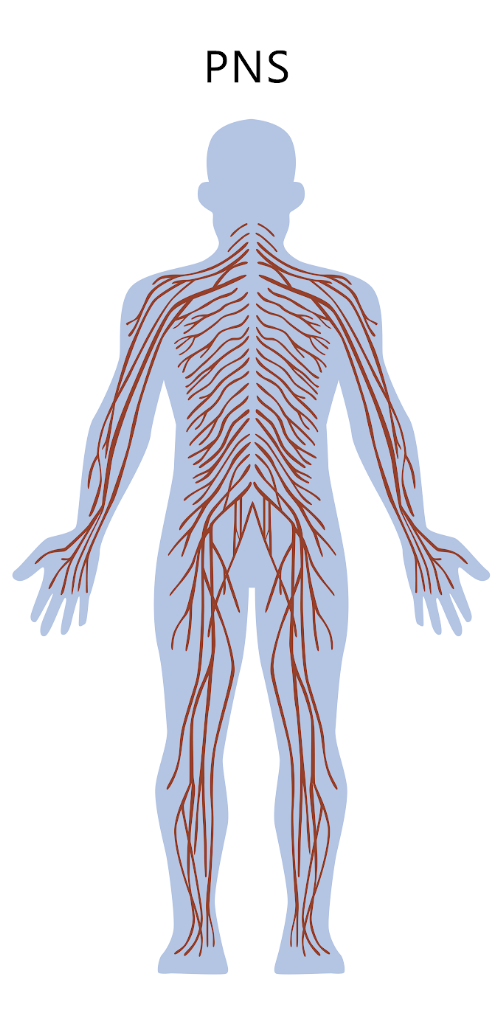
PNS
made of neurons going into afferent/sensory neurons our out of efferent neurons
Afferent nuerons
Sense (aka sensory neurons) external environment and signal CNS
Efferent neurons
‘Exit’- transmit information out of CNS to peripheral neurons
Interneurons
only in CNS, do most of processing
blood brain barrier
separates blood from CSF to protect CNS from harmful substances in blood, made up of glia cells called astrocytes. these have tight junctions for extra protection to prevent crossing.
meninges
connective tissue that protects NS
Cerebrospinal Fluid
CSF: fills space between meninges and in cavities in the brain called ventricles to protect the brain from hitting the skull. CSF also serves as a reservoir for the brain’s interstitial fluid, so it has correct extracellular ionic concentrations and provides neural cells with essential nutrients via the circulatory system.
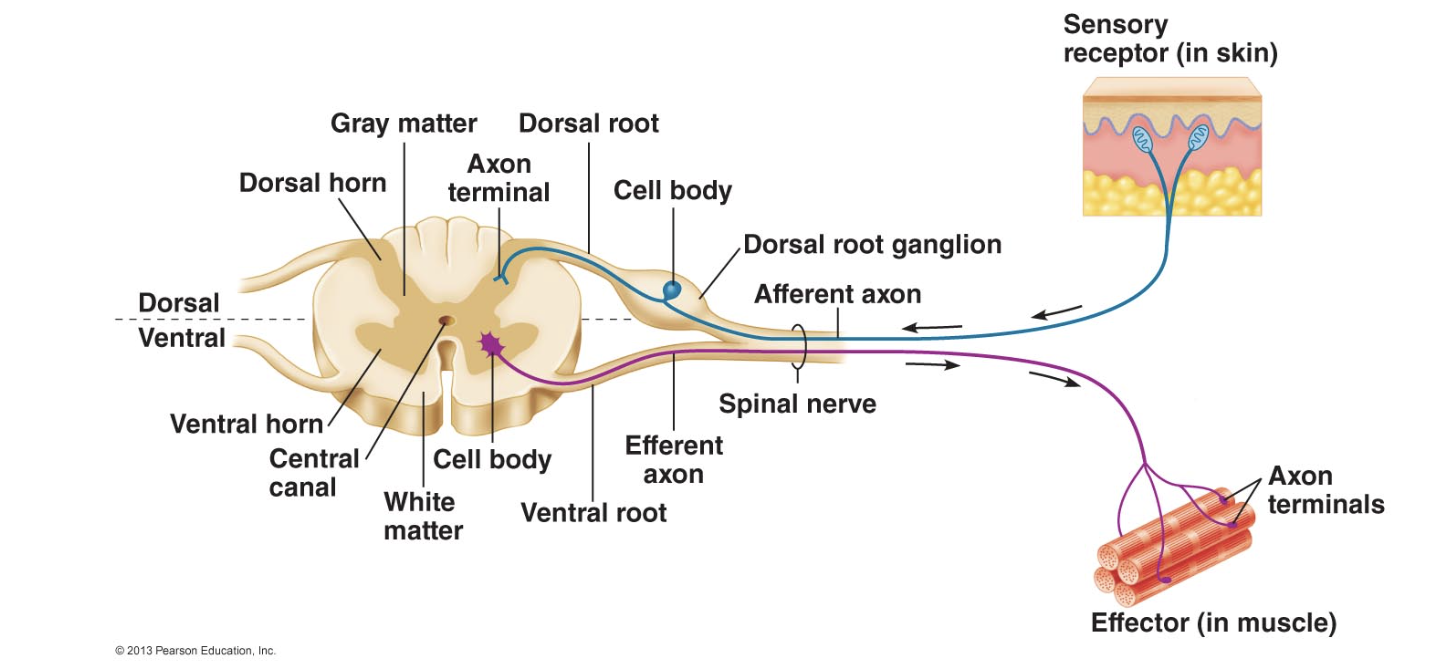
Dorsal/ventral
dorsal= side facing back half of body
ventral= side facing front/belly
dorsal root ganglion
collection of sensory neuron cell bodies outside of spinal cord
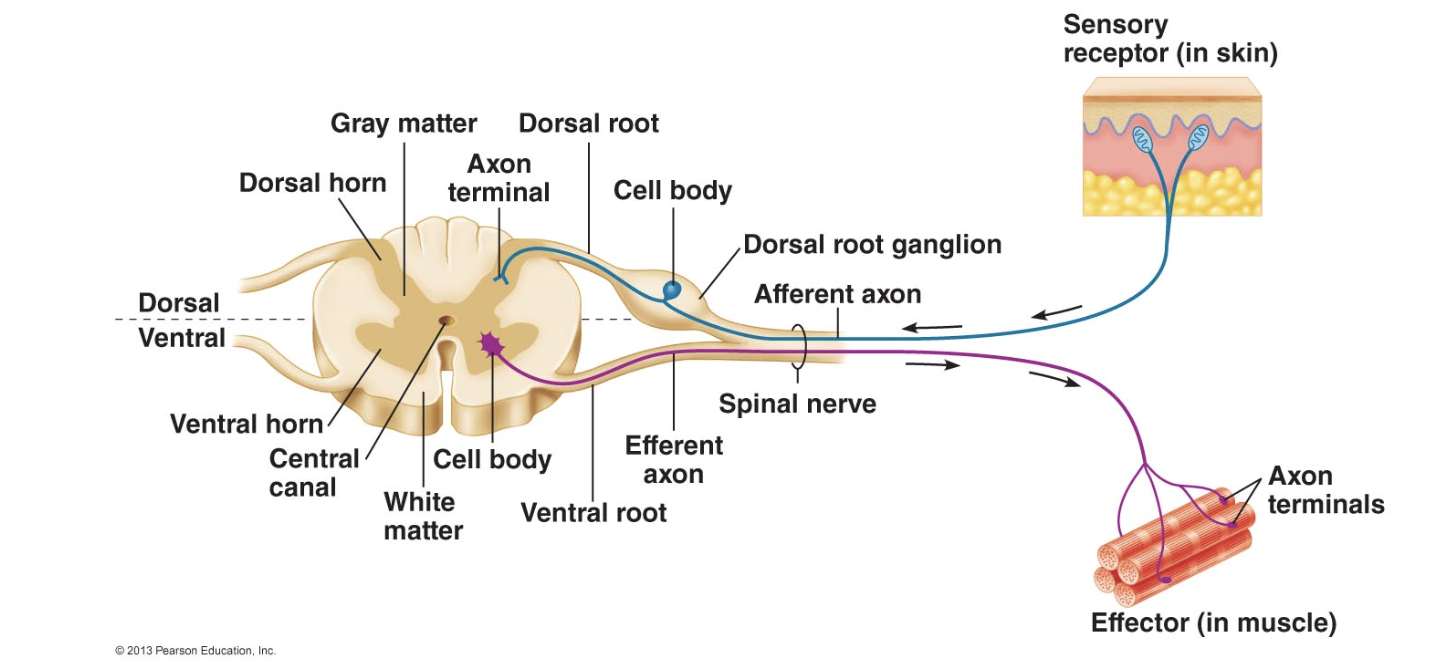
dorsal/ventral root
Sensory neuron axons (afferent) enter the spinal cord via the dorsal root and the motor neuron axons (efferent) leave via the ventral root
Corpus callosum
axons that connect the left and right sides of cerebral cortex (white matter bundle) in the center of the brain between the cerebral hemispheres
diencephalon (thalamus and hypothalamus)
Thalamus: relay station for sensory information
Hypothalamus: maintaining homeostasis
Brainstem and its parts
Brainstem: connects to spinal cord, regulates ANS, other unconscious functions
Midbrain: controls eye movement, orienting head to sound/sight
Pons: controls sleep, breathing, swallowing, etc
Medulla oblongata: controls blood pressure, breathing, etc
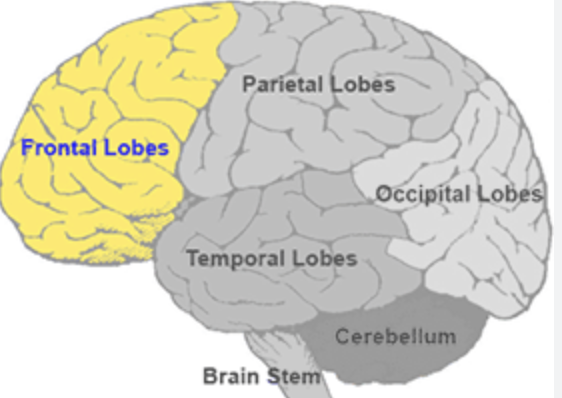
Frontal lobe
Executive function, decision-making, problem-solving, personality, motor control
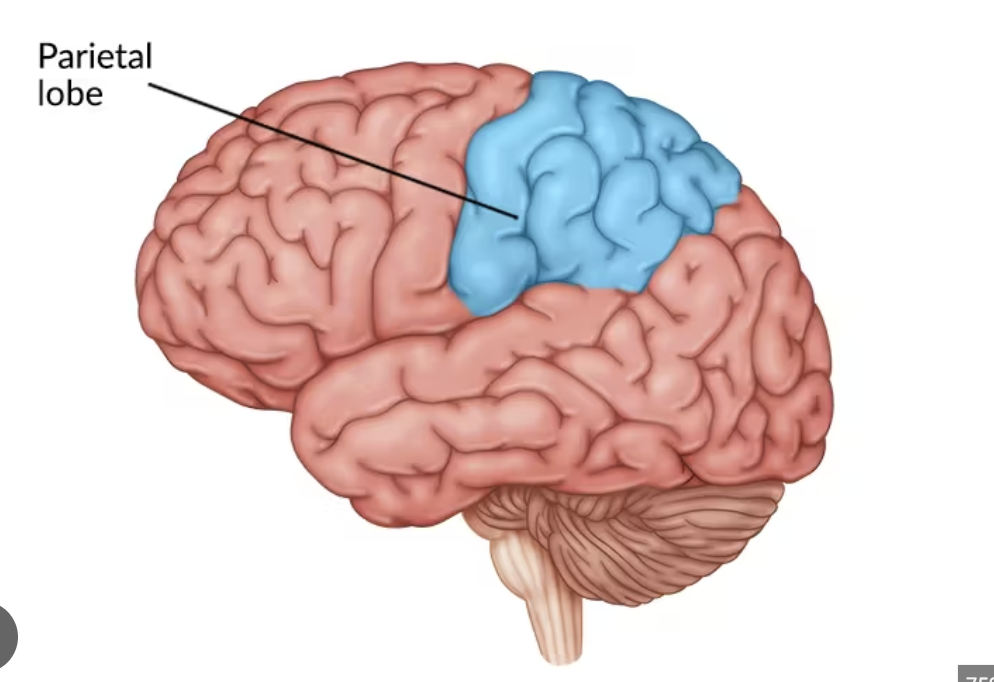
Parietal lobe
Sensory perception (touch, pain, temp), spatial awareness, attention
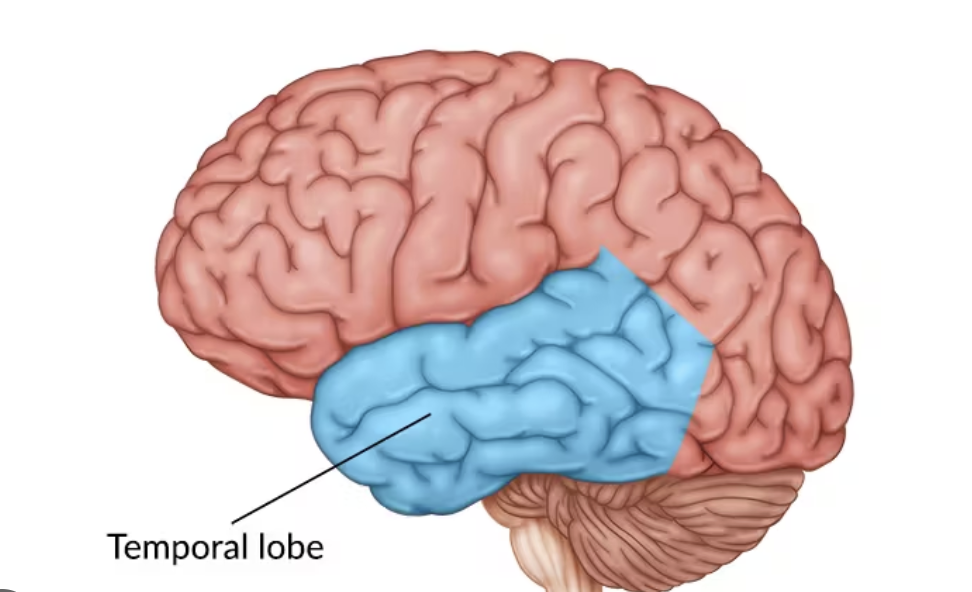
Temporal Lobe
Auditory processing, memory, language comprehension, emotion
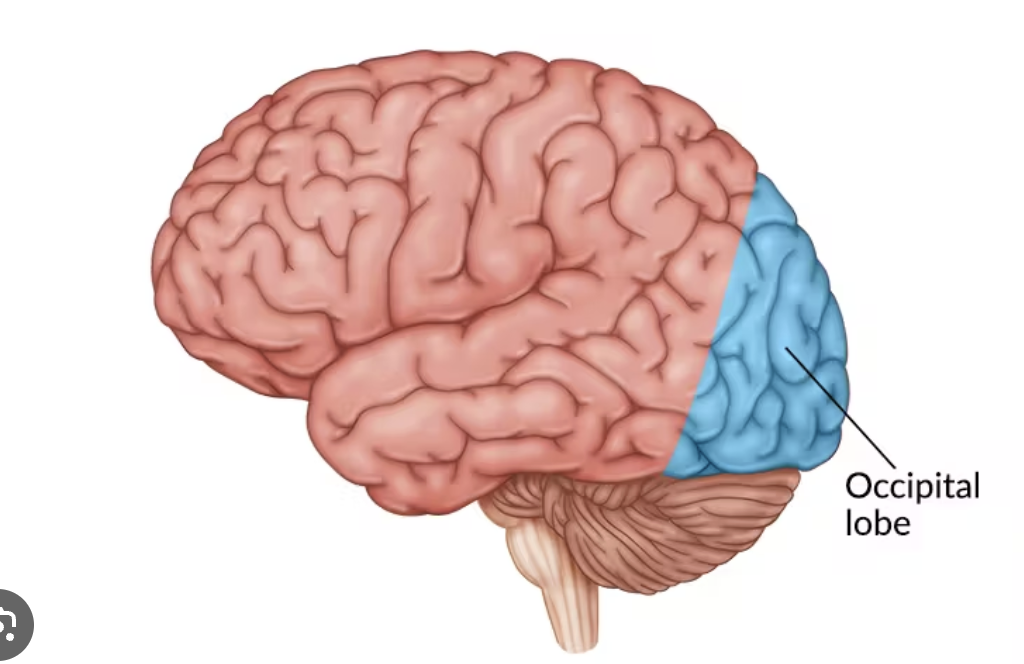
Occipital Lobe
Visual Processing
Agonist/antagonist drugs
Agonists act similar to neurotransmitters and cause the same effects, antagonists block the receptor so the NT cannot bind.