Lung Cancer
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
What are the risk factors that can put a patient at an increased risk of lung cancer?
· Occupational hazards ( miners, heavy metal workers)
· Smoking/tobacco
· Second-hand smoke
· Family history
· Radon gas
· Aging
· Other illnesses ( COPD, tuberculosis, etc.)
· Pollution
· Exposure to radiation
What is the major cost of lung cancer that accounts for 80% of lung cancer deaths in the US?
· Smoking/tobacco use.
What are the local symptoms associated with Lung Cancer?
· Most common: Cough
· Hemoptysis: 50-60%
· Dyspnea
· Chest pain/discomfort ( +/- hemoptysis)
· Bronchitis
· Hoarseness
· Wheezing
· Pneumonitis
· Pleural or pericardial effusion
· Dysphagia
What can be other signs and symptoms of Lung Cancer?
· Bone pain: can see this when the cancer spreads to the bone.
· Fatigue
· Weight loss/ anorexia
· Clubbing
· Paraneoplastic and other syndromes
This type of Lung cancer accounts for 15% of Lung Cancers:
Small-Cell Lung Cancer
How do you stage Small-Cell Lung Cancer?
§ Limited stage ( I-III)
§ Extensive stage (IV)
Pathophysiology of Small-Cell Lung Cancer:
o Has a clear relationship to smoking.
o Likes to metastasize to the Brain.
o Very aggressive and rapidly growing tumors.
This type of Lung Cancer accounts for 85% of Lung Cancers:
Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
What are the types of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancers?
-Adenocarcinoma
-Large Cell Carcinoma
-Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Pathophysiology of Adenocarcinoma:
§ Mostly nonsmokers
§ Happens in the bronchoalveolar.
§ Can metastasize early.
Pathophysiology of Large Cell Carcinoma:
§ Poorly differentiated.
§ Happens in the periphery of lung.
§ Has a poor prognosis.
Pathophysiology of Squamous Cell Carcinoma:
§ Mostly smokers, males.
§ Tends to be centrally occurring.
§ Has a better prognosis.
How do you stage Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer?
§ TNM stages ( I-IV):
· Localized (I-II)
· Regional (II-IIII)
· Distant (IV)
What are the platinum doublet treatment for Lung Cancer?
· Cisplatin:
o Vinorelbine
o Vinblastine
o Etoposide
o Gemcitabine
o Docetaxel
o Pemetrexed
· Carboplatin:
o Paclitaxel
o Gemcitabine
o Pemetrexed
o Etoposide
What is considered platinum sensitive?
o Response to platinum doublet for 6+ months.
What is the first line treatment approach for a patient with advanced stage metastatic non-small cell lung cancer?
· 1st: Assess for targetable genomic alterations:
o This is recommended in squamous cell.
o This is mandatory to do in adenocarcinoma.
· 2nd: After assessing genomic alterations ; you assess PD-L 1 Status (TPS):
o < 1%: negative
o > 1:-49% : positive
o >50%: it is for sure positive.
· 3rd: The Patient is Biomarker negative:
o They can only use a platinum-based regimen.
EGFR TKI medications:
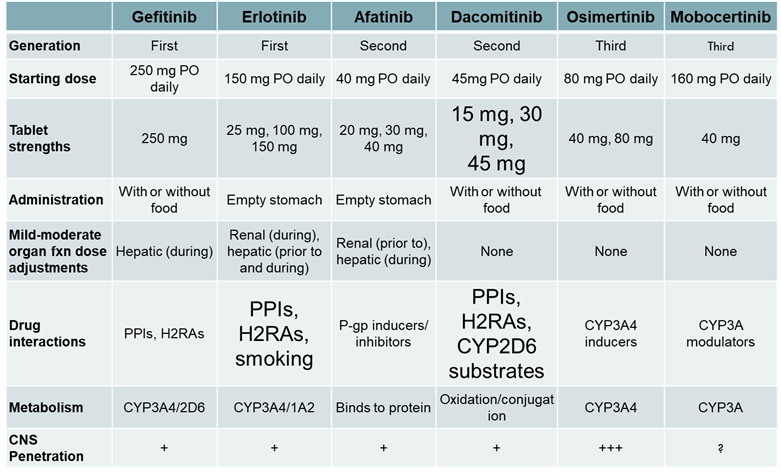
Amivantimab:
o This is a Bi-specific antibody to EGFR and MET.
o This medication is an antagonist to EGFR mutations.
It also prevents receptor crosstalk with MET.
KRAS G12 Inhibitors:
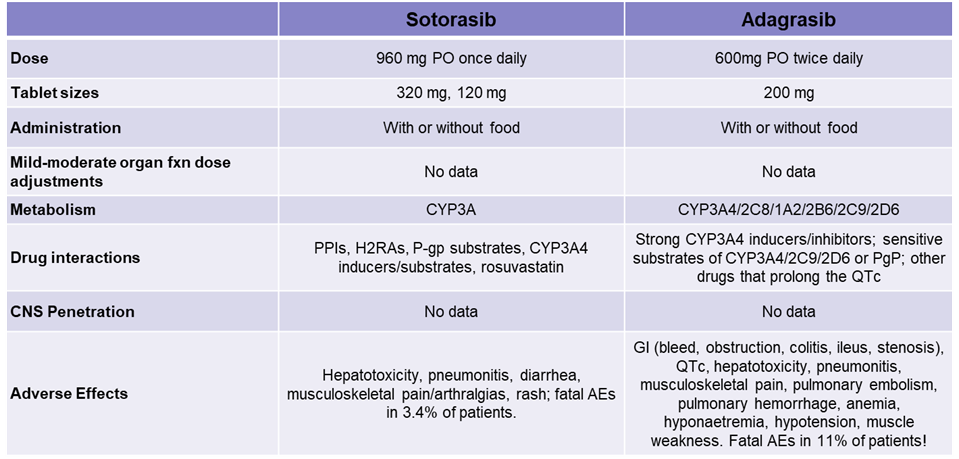
What are some KRAS G12 phenotypes?
o Adenocarcinoma
o Smokers
o Resistance to EGFR TKIs
ALK Inhibitors
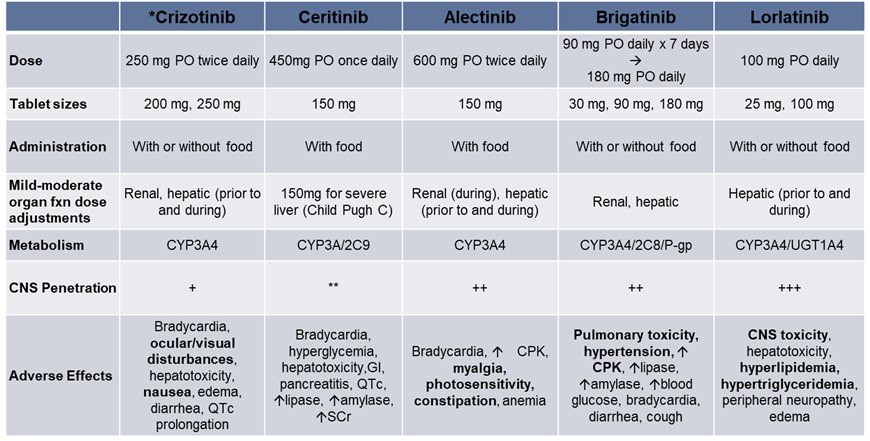
What are some ALK phenotypes?
o Adenocarcinoma
o Younger patients ( med. Age= 52)
o Nonsmokers or former light smokers
o More likely to present with brain Mets.
Genomic Alteration Negative treatment plan:
No targetable genomic alterations ( PD-L1 testing) | ||
PD-L 1 > 50% | PD-L 1 (1%-49%) | |
Pembrolizumab alone Atezolizumab alone Cemiplimab-rwlc alone or Platinum/pemetrexed + pembrolizumab | Adenocarcinoma large cell ( other non-squamous): Platinum/pemetrexed + pembrolizumab | Squamous cell: carboplatin _ nab-paclitaxel + pembrolizumab |
What are the side effects of the EGFR inhibitors?
-acneiform rash
-diarrhea
-stomatitis
If a patient has Grade 1 rash, what would be the treatment?
§ Topical steroids or topical antibiotics
If a patient has a Grade 2 rash, what would be the treatment?
§ Topical steroids + oral antibiotics.
If a patient has a Grade 3 rash, what would be the treatment?
§ Temporarily discontinue + ( grade 2 treatment)
If a patient has a Grade 4 rash, what would be the treatment?
§ Discontinue medication permanently.
How would you treat a patient who experiences diarrhea from their EGFR Inhibitor?
§ Loperamide
§ IV fluids
§ Electrolyte replacement
How would you treat a patient who gets stomatitis from their EGFR inhibitor?
§ Triamcinolone dental paste
§ Oral erythromycin
§ Magic mouth wash
§ Clobetasol ointment