4.15. Advanced VPC Routing - PART2
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
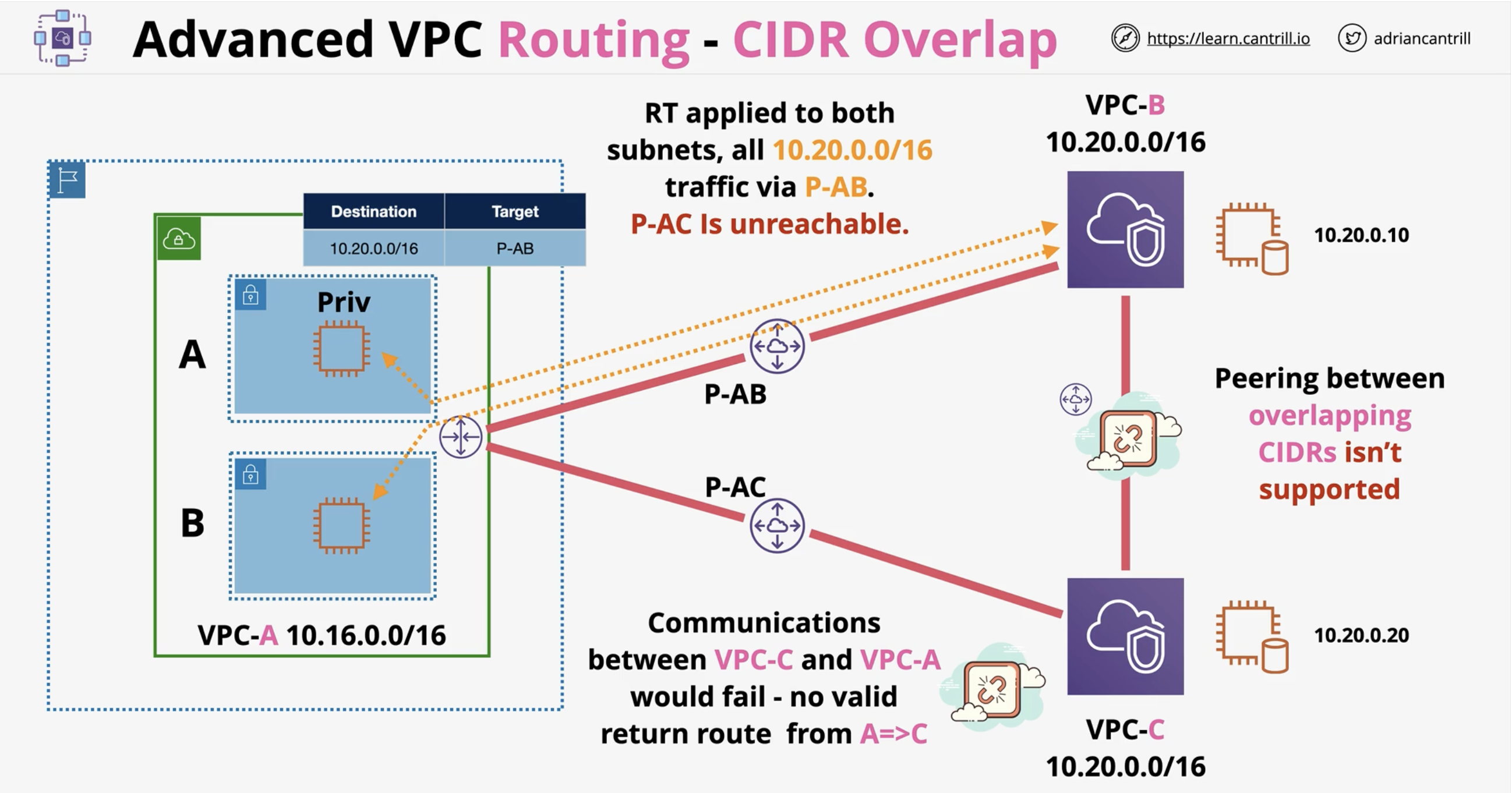
What is a common issue that prevents VPC peering between two VPCs?
Overlapping CIDR ranges.
Can a VPC have peering connections to multiple VPCs that use the same CIDR block?
No, overlapping CIDRs block peering.
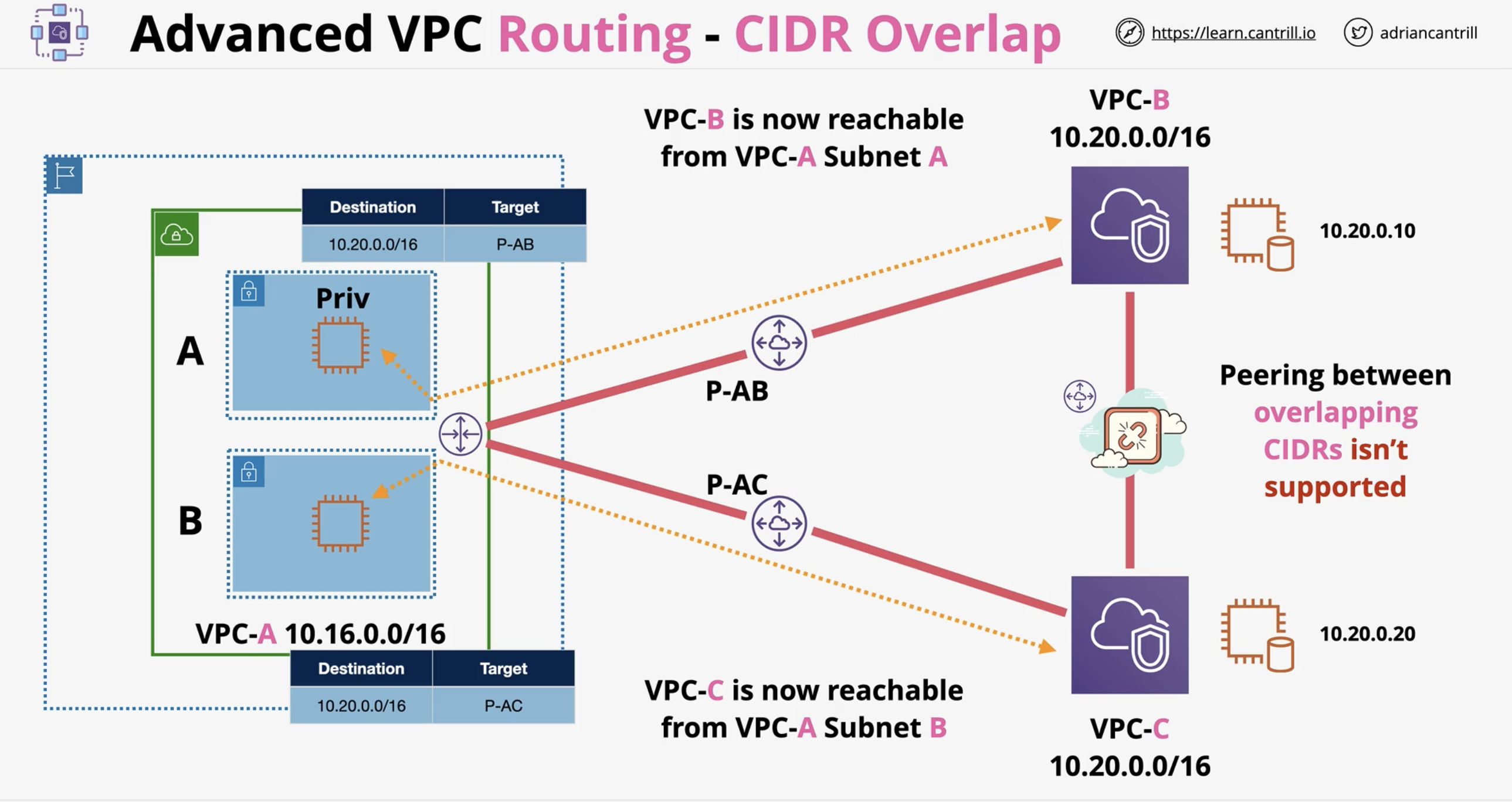
What routing method allows selective communication in overlapping CIDR cases?
Split routing using different route tables per subnet.
How does using multiple route tables help with overlapping CIDRs?
Allows traffic to same CIDR block to route via different peers, isolating traffic.
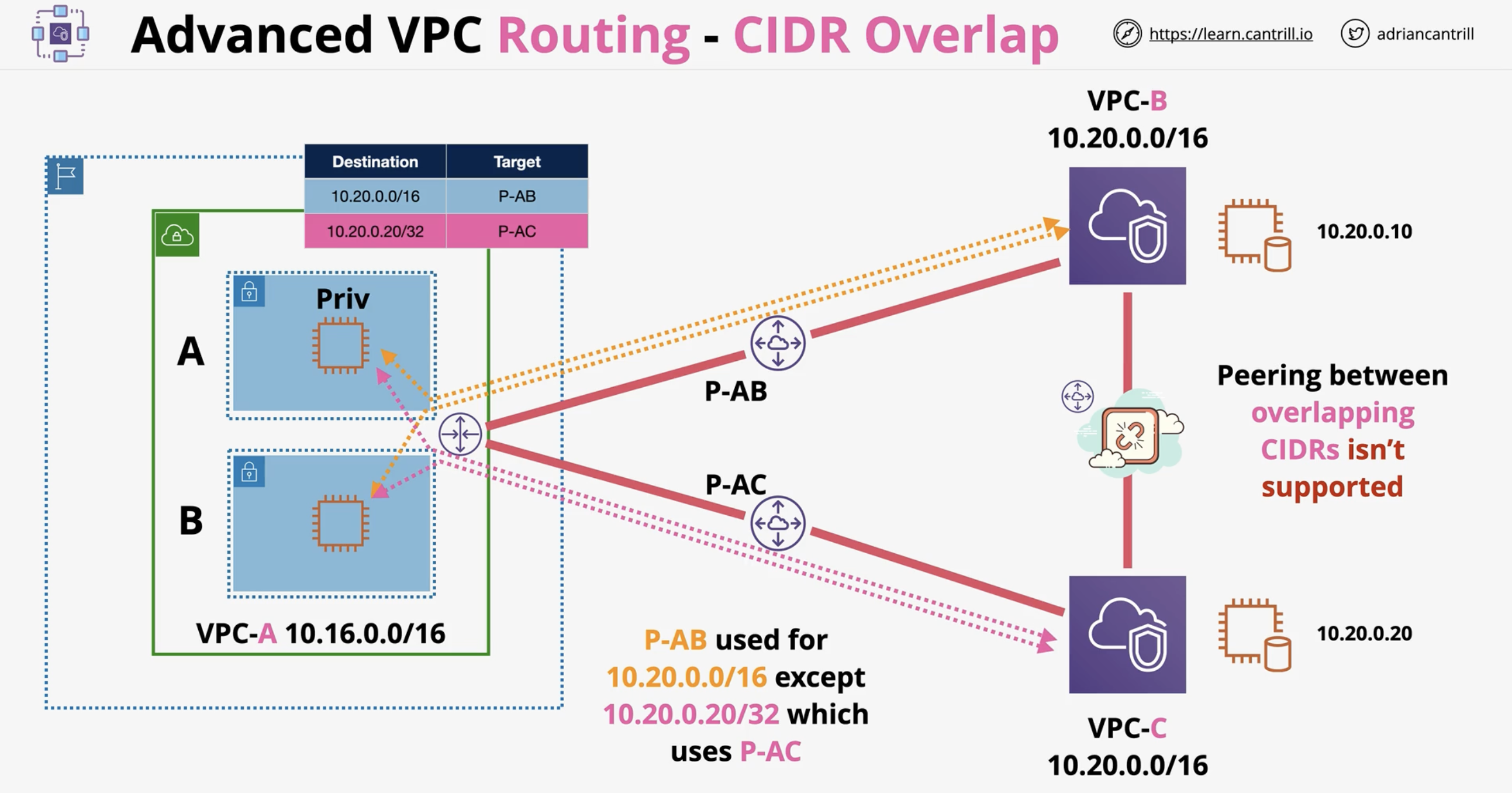
What’s the effect of using a more specific route (e.g., /32) in a route table?
It overrides less specific routes like /16 — longest prefix match wins.
Can you route traffic from a subnet to two VPC peers with the same CIDR?
Yes, using specific /32 routes to override a broader /16 route.
What architectural trade-off does using split route tables introduce?
Instances in each subnet can only reach the target VPC for that route table, limiting flexibility.
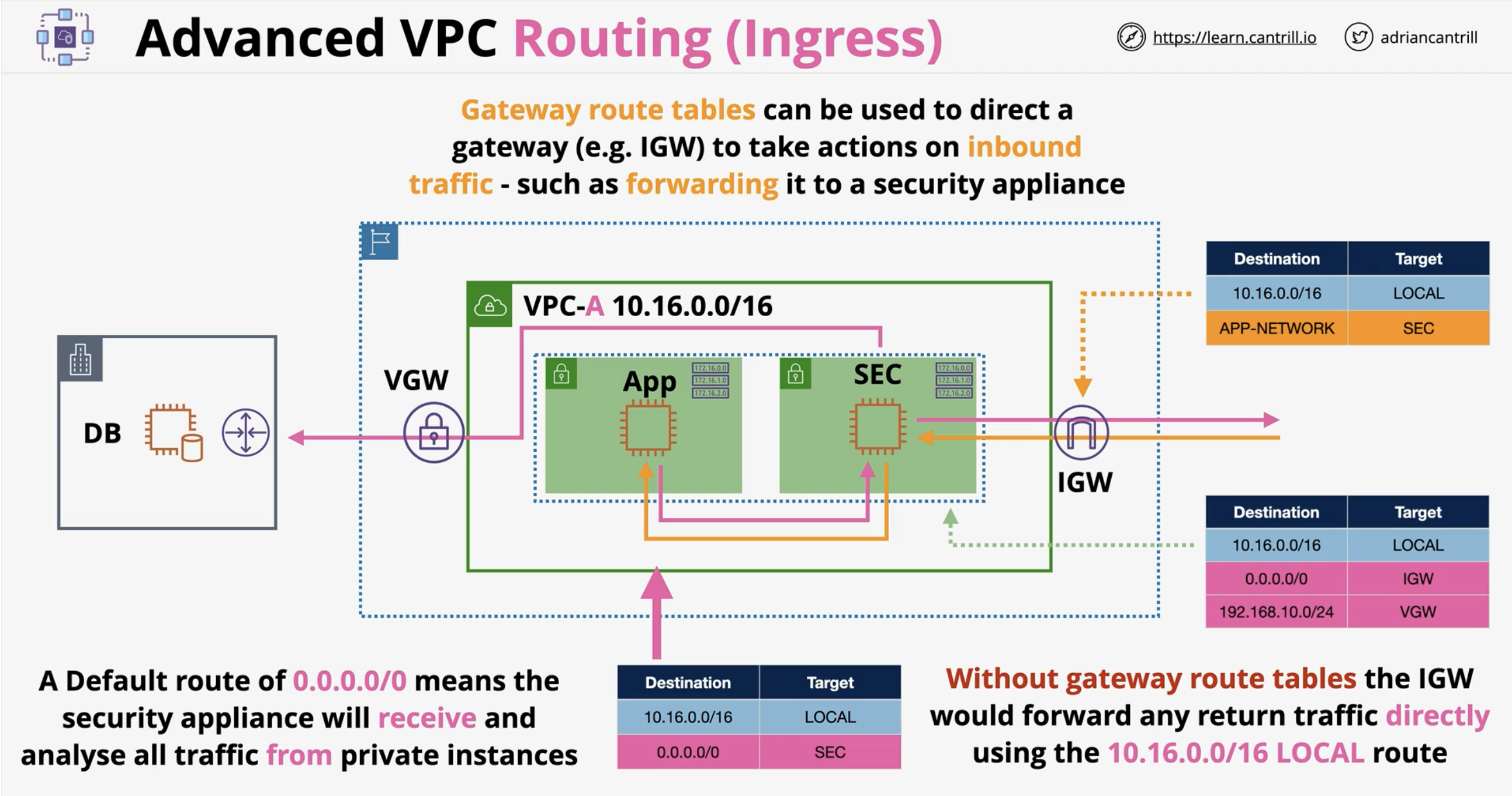
What is ingress routing in AWS VPCs?
A method using gateway route tables to control incoming traffic at an Internet Gateway or Virtual Private Gateway.
What is the default behavior of traffic entering via an IGW?
It is routed directly to its destination subnet, without inspection.
What problem does ingress routing solve?
Enables inspection or redirection of inbound traffic before it reaches its destination.
How is a gateway route table different from a standard route table?
Gateway route tables are attached to a gateway (IGW/VGW), not a subnet, and apply to incoming traffic.
What traffic can gateway route tables influence?
Inbound traffic entering the VPC via an Internet Gateway or Virtual Private Gateway.
Can you inspect both egress and ingress traffic with this method?
Yes, combining subnet route tables (egress) with gateway route tables (ingress) enables bidirectional inspection.
What target is typically used to inspect traffic before final delivery?
A security appliance, like a firewall or proxy in a public subnet.
What happens if two routes match and one is /16 and the other /32?
The /32 route is selected because it’s more specific.
How can you route specific IPs in overlapping CIDRs to different VPCs?
Use /32 static routes pointing to different VPC peers.
Is it possible to override peer routes dynamically in peered VPCs?
No, peer routing is static and must be manually defined in route tables.
Why should you avoid overlapping CIDRs in AWS environments?
They complicate routing, especially for peering and hybrid networks.
What does a subnet route table control?
Outgoing traffic (egress) from that subnet.
What does a gateway route table control?
Incoming traffic (ingress) at the IGW or VGW level.
[Diagram] CIDR Overlap Unsupported (One Route Table)
[Diagram] CIDR Overlap - Split between Subnets (Multiple Route Tables)
[Diagram] CIDR Overlap - Route Precedence for Split Routing (One Route Table)
[Diagram] Ingress Routing