AQA A-Level Biology Mitosis and Cell Division
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
what are the phases of the cell cycle?
interphase
mitosis
cytokinesis
which phases make up interphase?
G1 (growth) phase
S (synthesis) phase
G2 (growth) phase
which phase makes up the majority of the cell cycle?
interphase
what happens in G1 phase?
cells grow
new organelles and proteins are made
what happens in S phase?
DNA replication occurs
completed as quickly as possible to prevent exposed bases being exposed to mutagens - chromatids now
what happens in G2 phase?
microtubules produced
lots of protein synthesis occurs to increase organelle numbers
more ATP produced
define mitosis
process of cell division
in which two identical daughter cells are produced
why is mitosis required?
needed for growth of multicellular organisms
repair of tissues
what are the stages of mitosis?
prophase
metaphase
anaphase
telophase
describe what happens in prophase
chromatin condenses into visible chromosomes, each made up of two chromatids (identical)
centrioles move towards poles of the cell
this forms a network of protein fibres across cell called spindle fibres
nuclear envelope breaks down
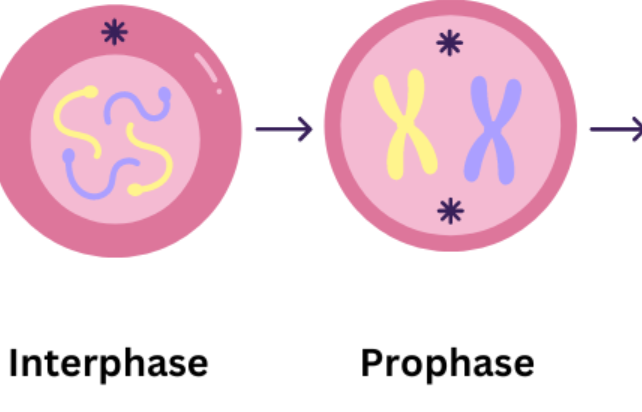
describe what happens in metaphase
chromosomes line up in the centre of the cell
centromeres attach to the spindle
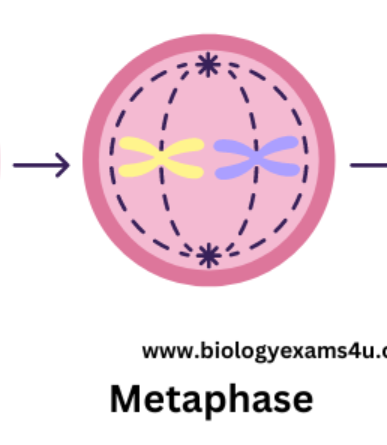
describe what happens in anaphase
centromeres divide which separates sister chromatids
spindle fibres contract
pulls sister chromatids to opposite poles of the cell - ensures genetically identical
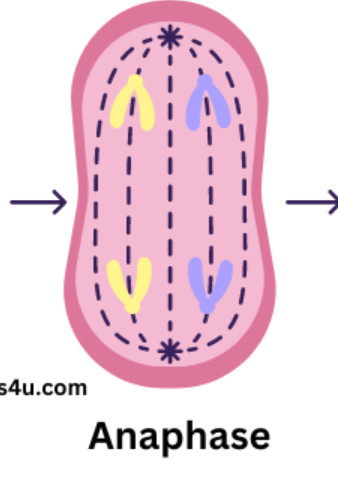
describe what happens in telophase
separated chromatids group together at opposite ends of the cell
chromosomes unwind and become indistinct
spindle fibres disappear
nuclear membrane reforms
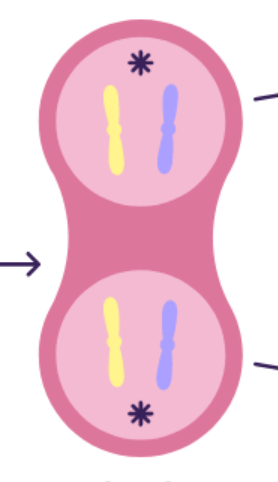
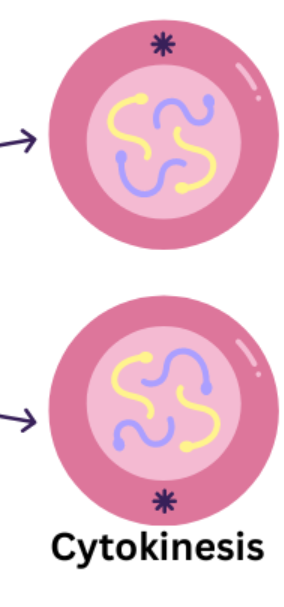
describe what happens in cytokinesis
cytoplasm of cell divides
two new cells formed
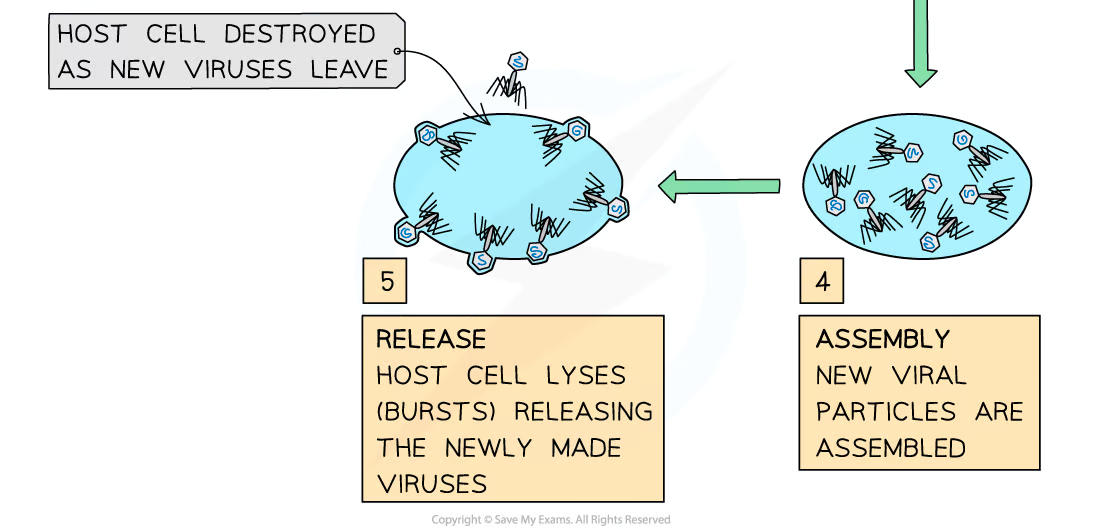
describe the process of viral replication
attachment proteins on the virus bind to complementary receptors on the host cell
viral DNA/RNA is injected into the host cell
host cell uses ribosomes to synthesize viral proteins and nucleic acids
new viral particles are assembled
the viral particles are released from the cell by cell lysis/budding
budding - cell membrane is converted to viral envelope
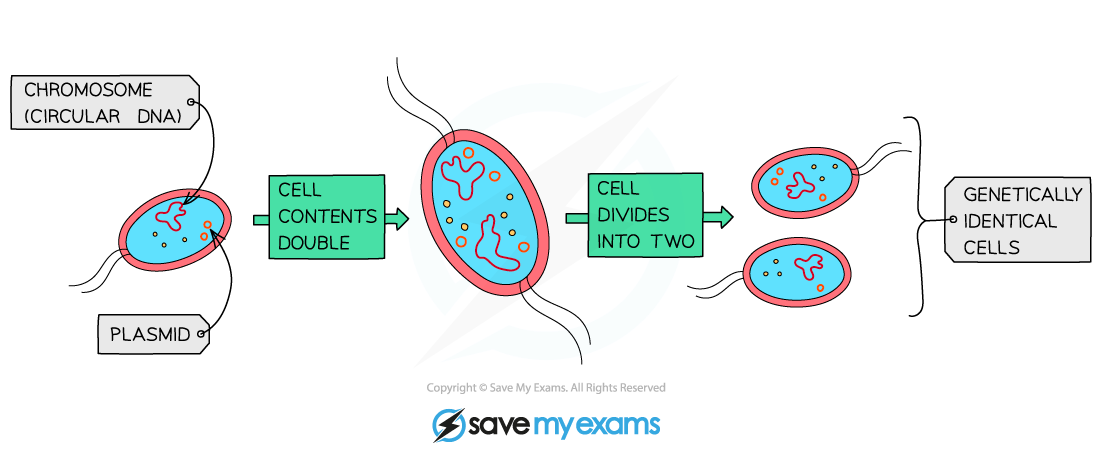
how do bacteria divide?
by binary fission
describe the process of binary fission
cell elongates and DNA is replicated (circular and plasmids)
cell wall and plasma membrane constrict
cytoplasm divides between 2 daughter cells
cell wall and membrane close around 2 daughter cells forming 2 new cells
cells can divide up to every 20 mins
how is cancer caused?
caused when there are mutations in genes that control cell division
causes cells to divide uncontrollably, forming a tumour, invading nearby tissues
how do cancer treatments work?
aimed at controlling rate of cell division - either affect G1 or S phase
G1 - prevent synthesis of enzymes needed for DNA replication, prevents S phase, causes cell death
S - drugs damage DNA, during replication DNA is checked for damage, if severe damage is detected, the cell dies
describe the mitosis root tip practical
cut off root tip of garlic bulb
place in 1moldm-3 HCl for 5 mins
swirl in distilled water briefly
use a scalpel to cut off the yellowish very tip - meristem region - of the root tip
place on a slide, squish it, add a few drops of ascetic stain
leave for 2 mins then slowly place a coverslip on top, using it to gently squash cells
use filter paper to absorb any excess stain
look at cells under microscope
how would you calculate mitotic index?
cells in mitotis/all cells