ALL HARD CHEM QQ
1/155
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
156 Terms





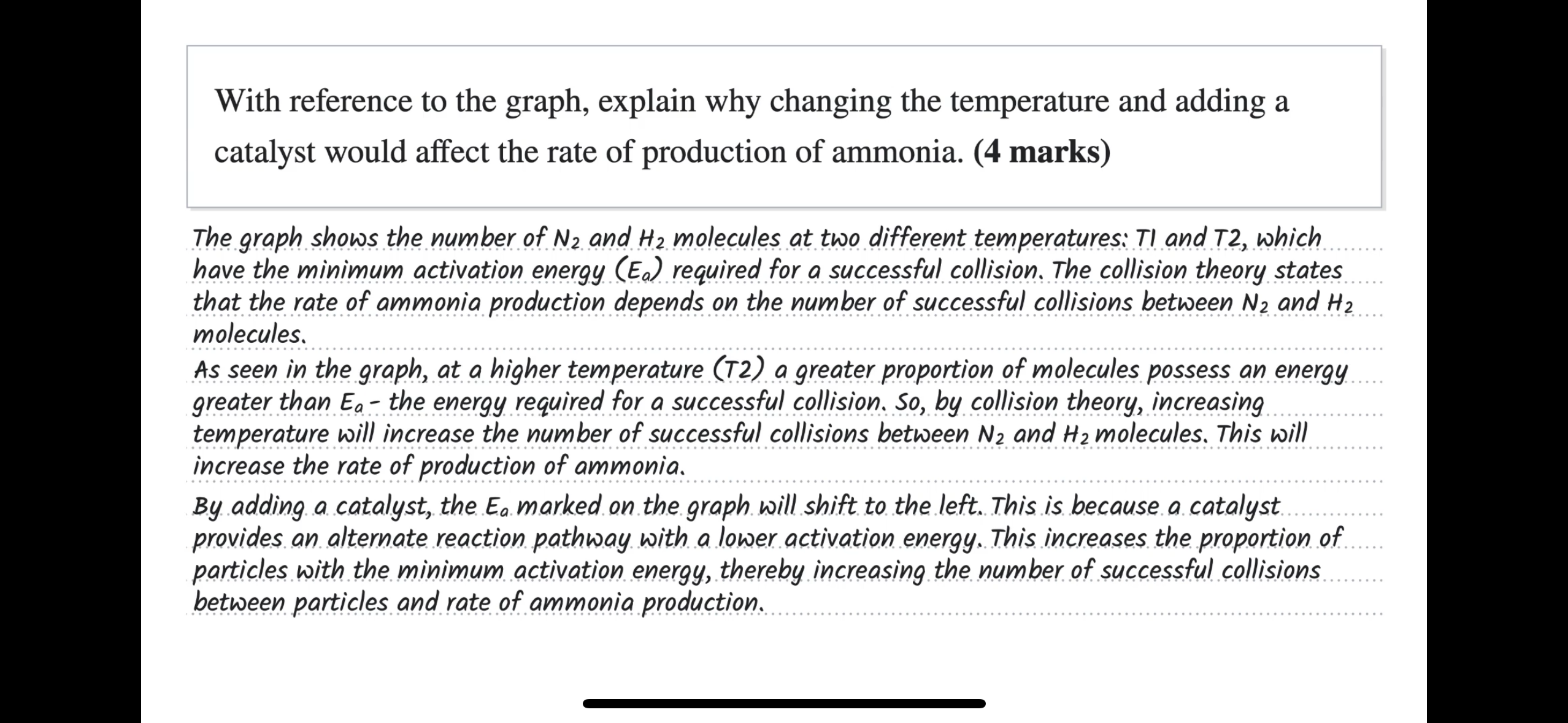
Outline how you could use a pH probe to determine the ka of benzoic acid, if you gave access to pure benzoic acid powder (formula C6H5COOH, solubility 3.44g per L)



two first-hand investigations are carried out. one demonstrates the use of sulfuric acid as an oxidising agent and the other demonstrates the use of sulfuric acid as a dehydrating agent. Explain the observations that could be made in these investigations. Include relevant equations














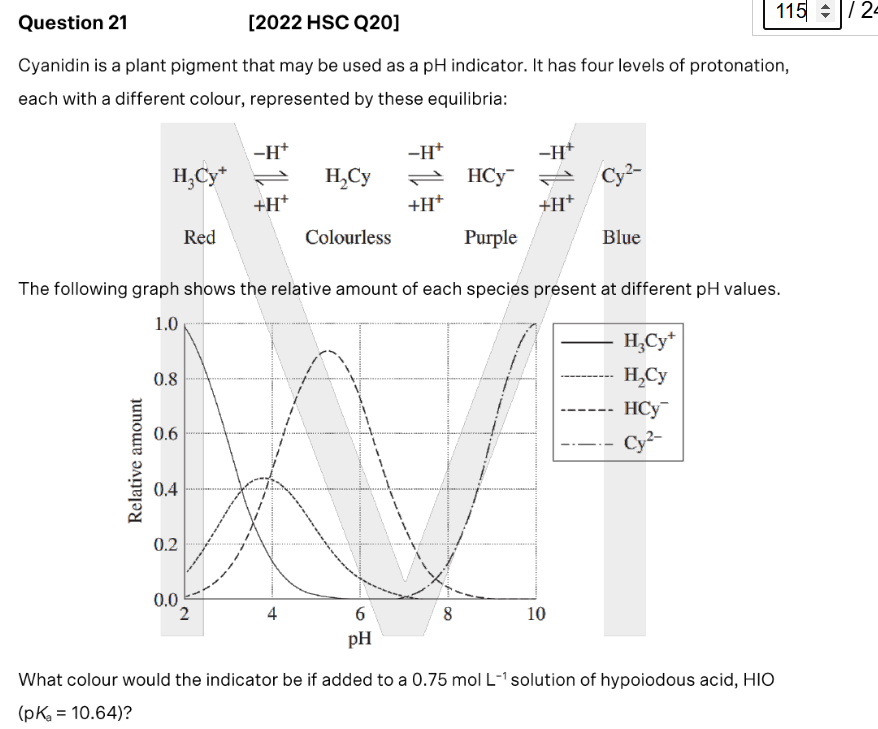
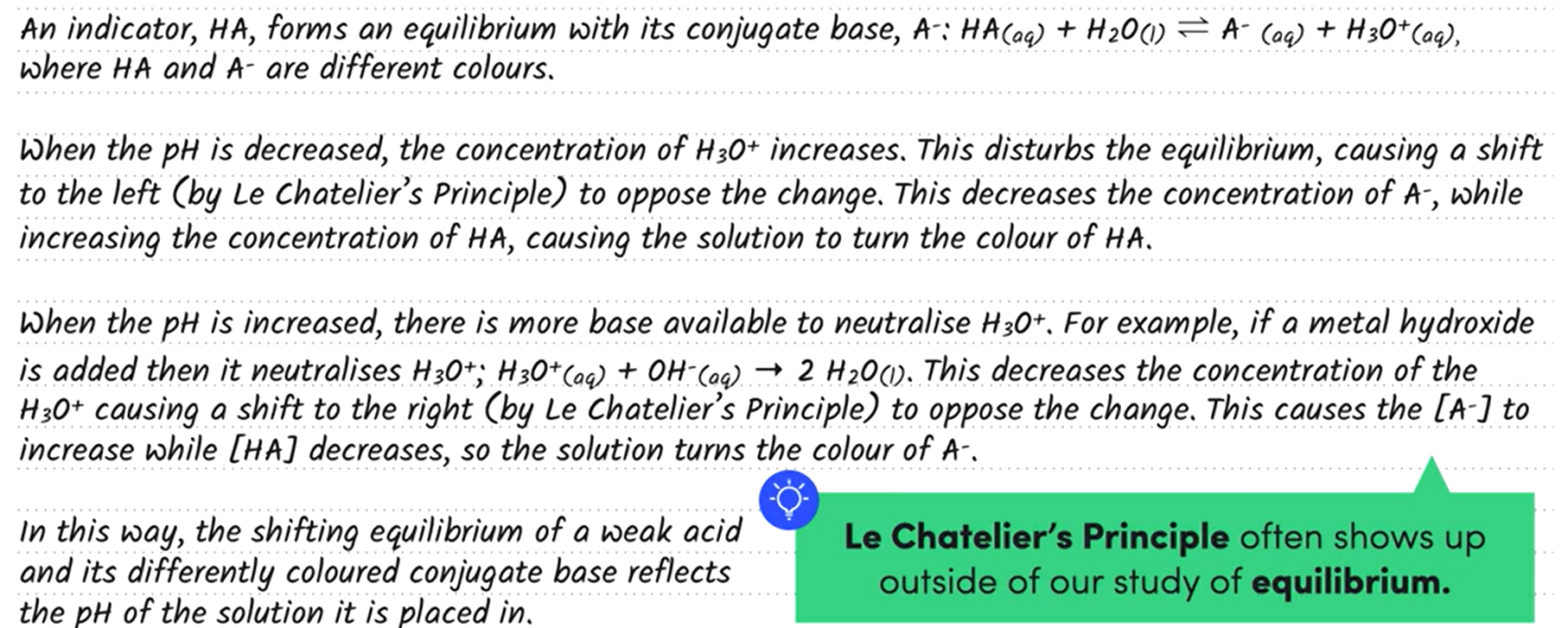
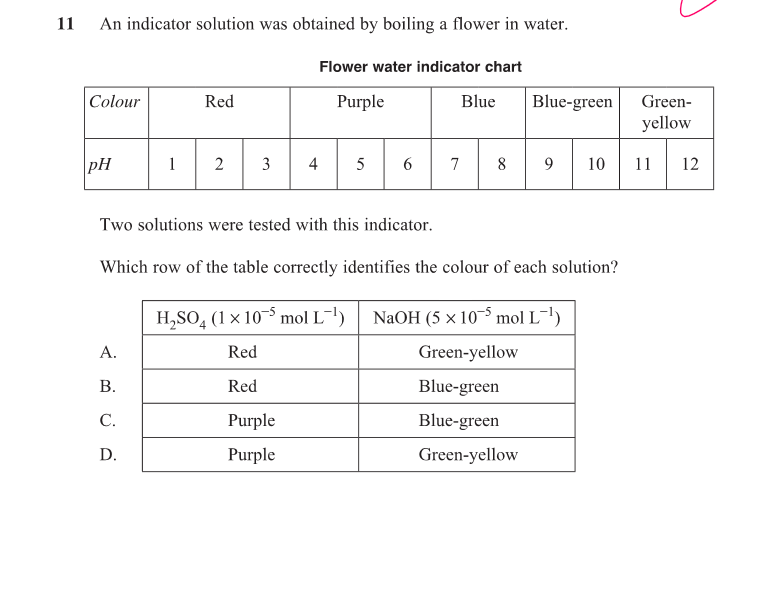
purple
Go find H+ concentration
Then pH
Then look at graph


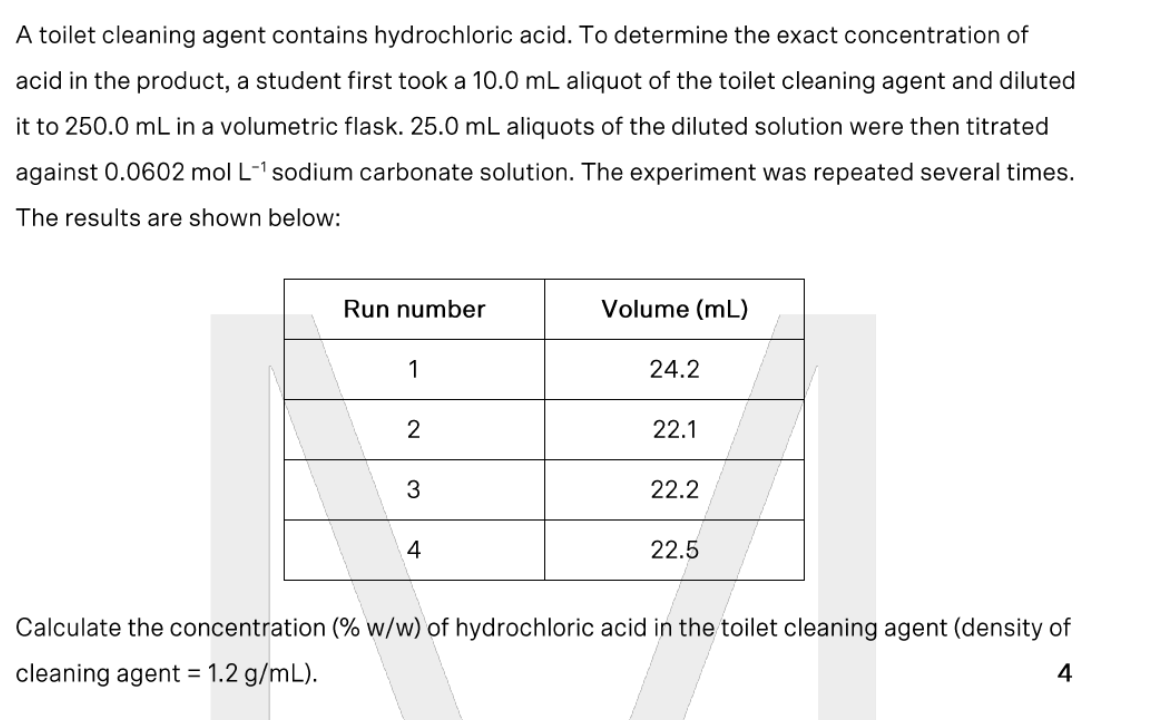
A sample containing approximately 0.5 g sodium carbonate is to be analysed via a back titration. Which of the following would NOT be suitable as the excess reagent?
(a) 25.0 mL of 0.50 M nitric acid
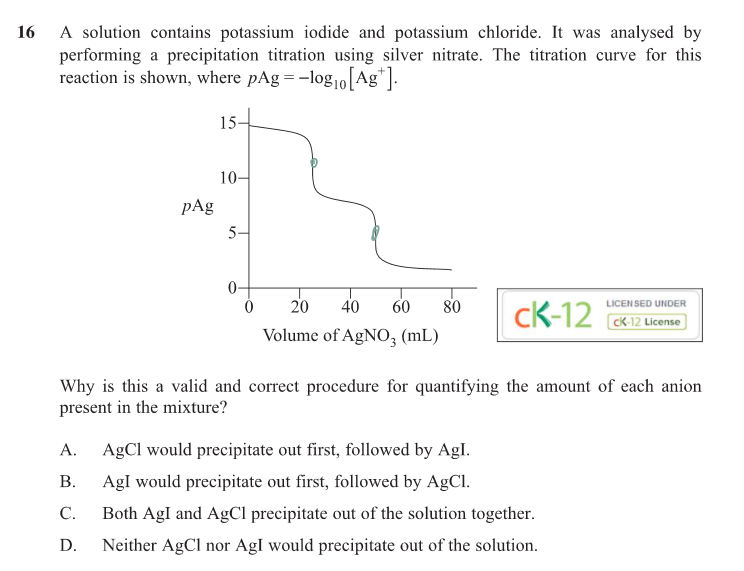
(b) 50.0 mL of 0.12 M hydrochloric acid
(c) 100.0 mL of 0.050 M sulfuric acid
(d) All of the above are suitable





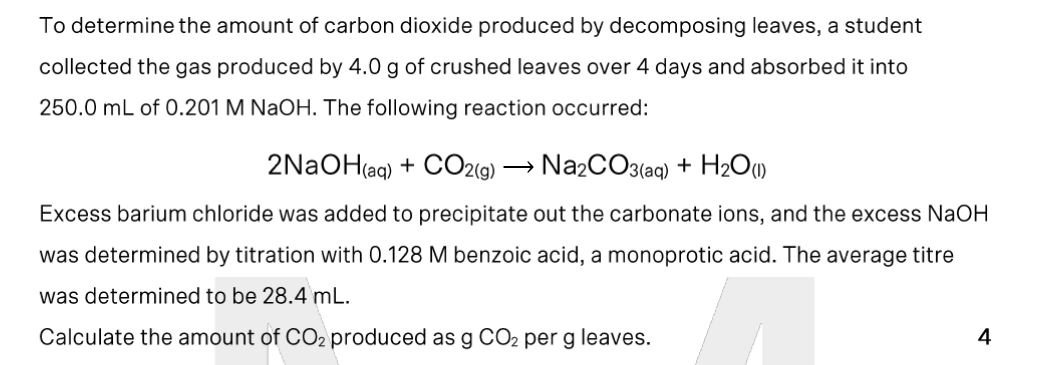

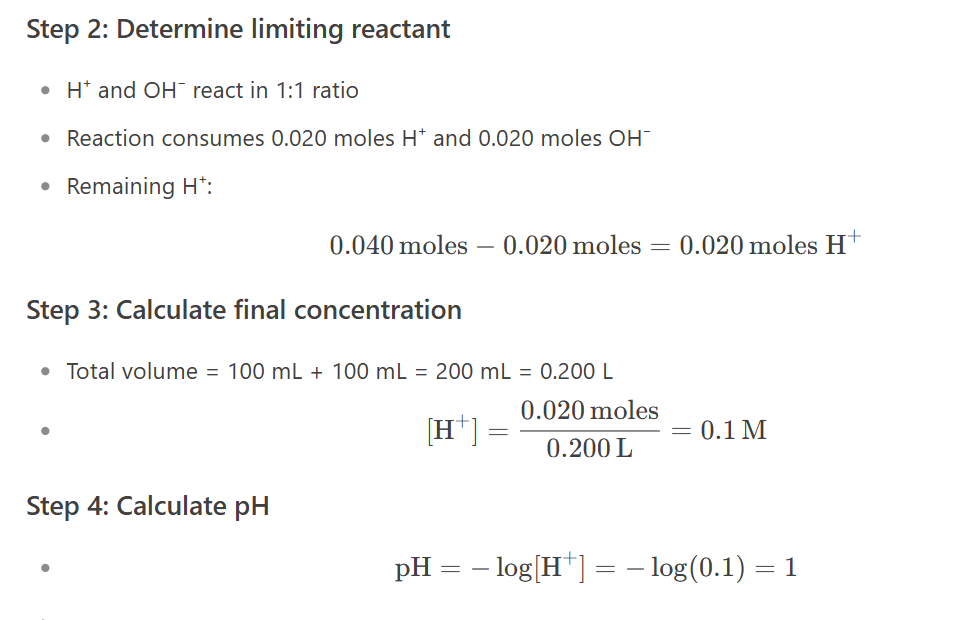
100ml of 0.4M nitric acid is added to 100mL of 0.1 barium hydroxide. the Ph of the resulting solution is
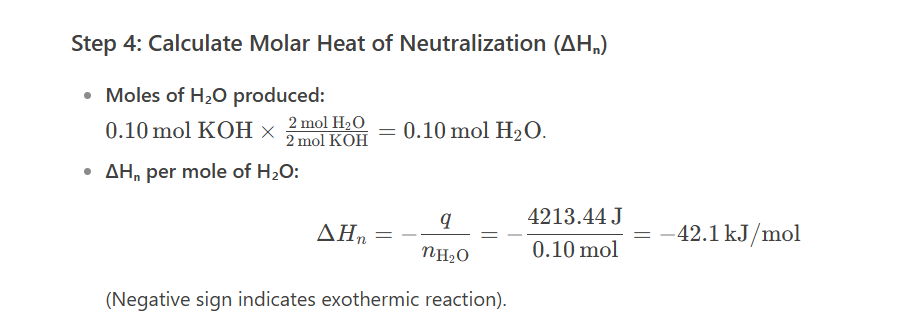
a student mixes 20ml of 5M sulfuric acid with an equal volume of 5M potassium hydroxide in a calorimeter. the temp rose from 22.9degrees to 48.1degrees. What is the experimental molar heat of neutralisation for this rxn
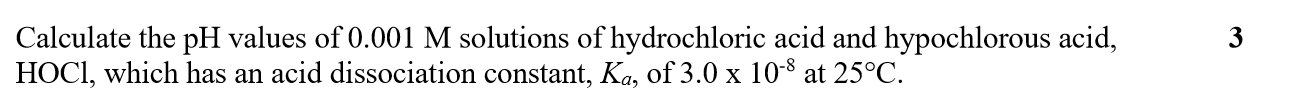



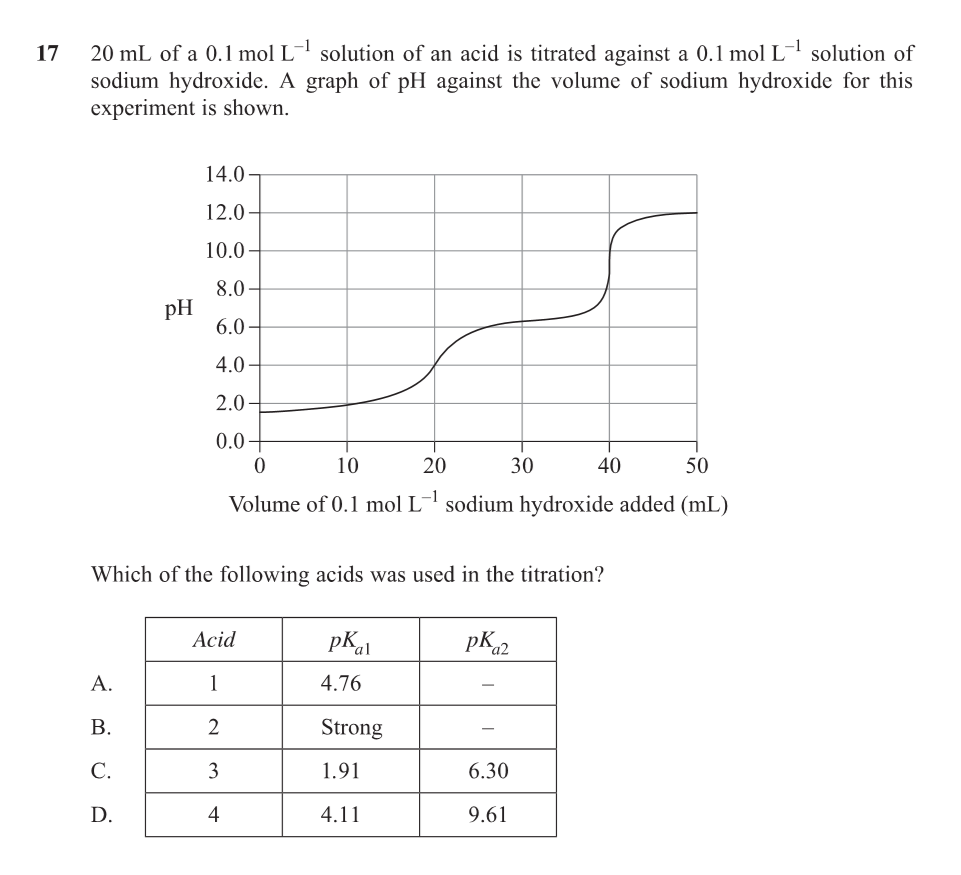
At each buffer region (flat part), the pH equals the pKa of that acidic proton being titrated.
That’s why the pH value at the centre of a buffer region = pKa.


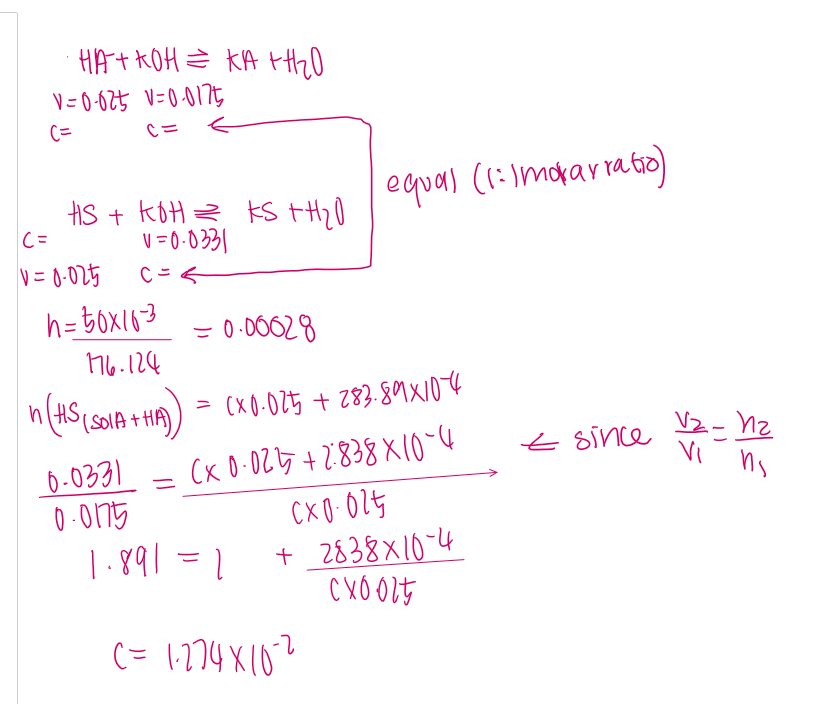






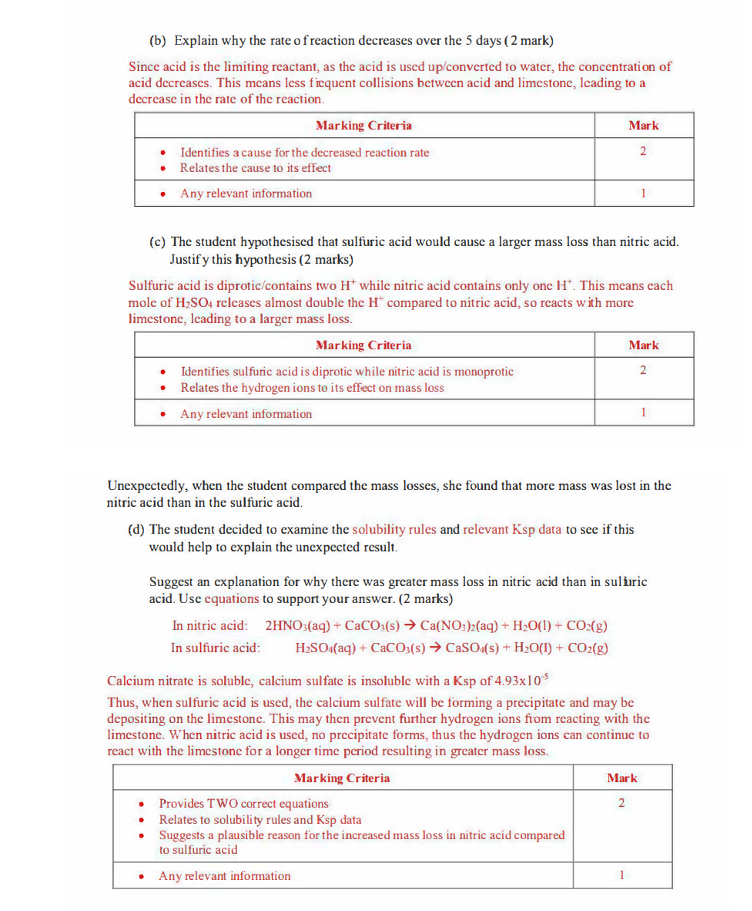
calculate mass of ammonium ions
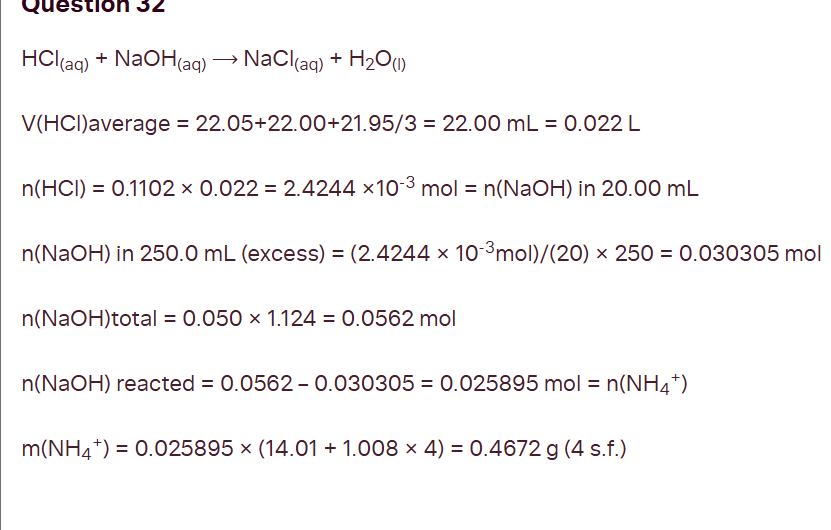



b) Explain how your answer in A would be different if the carbon dioxide was not removed from the soft drink




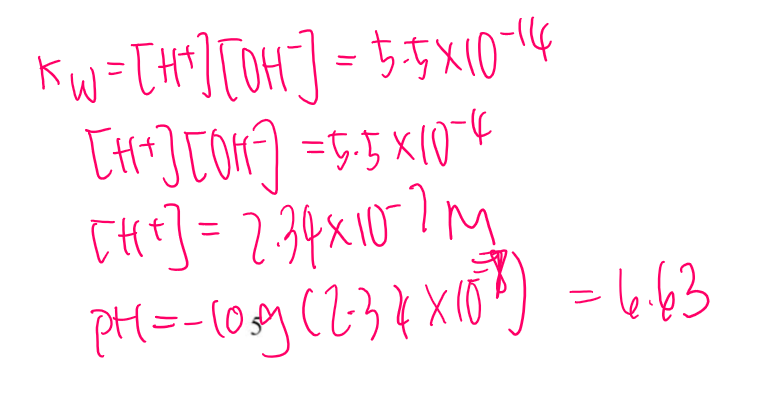

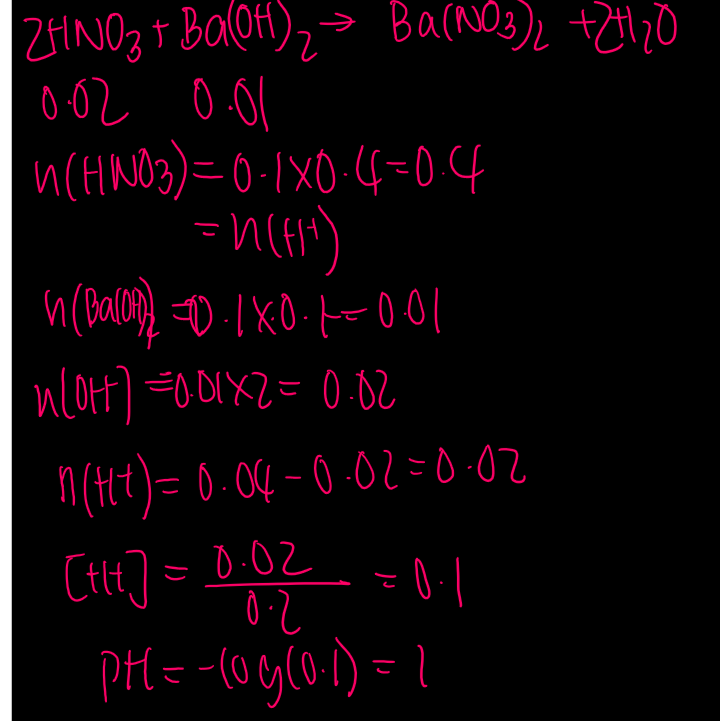

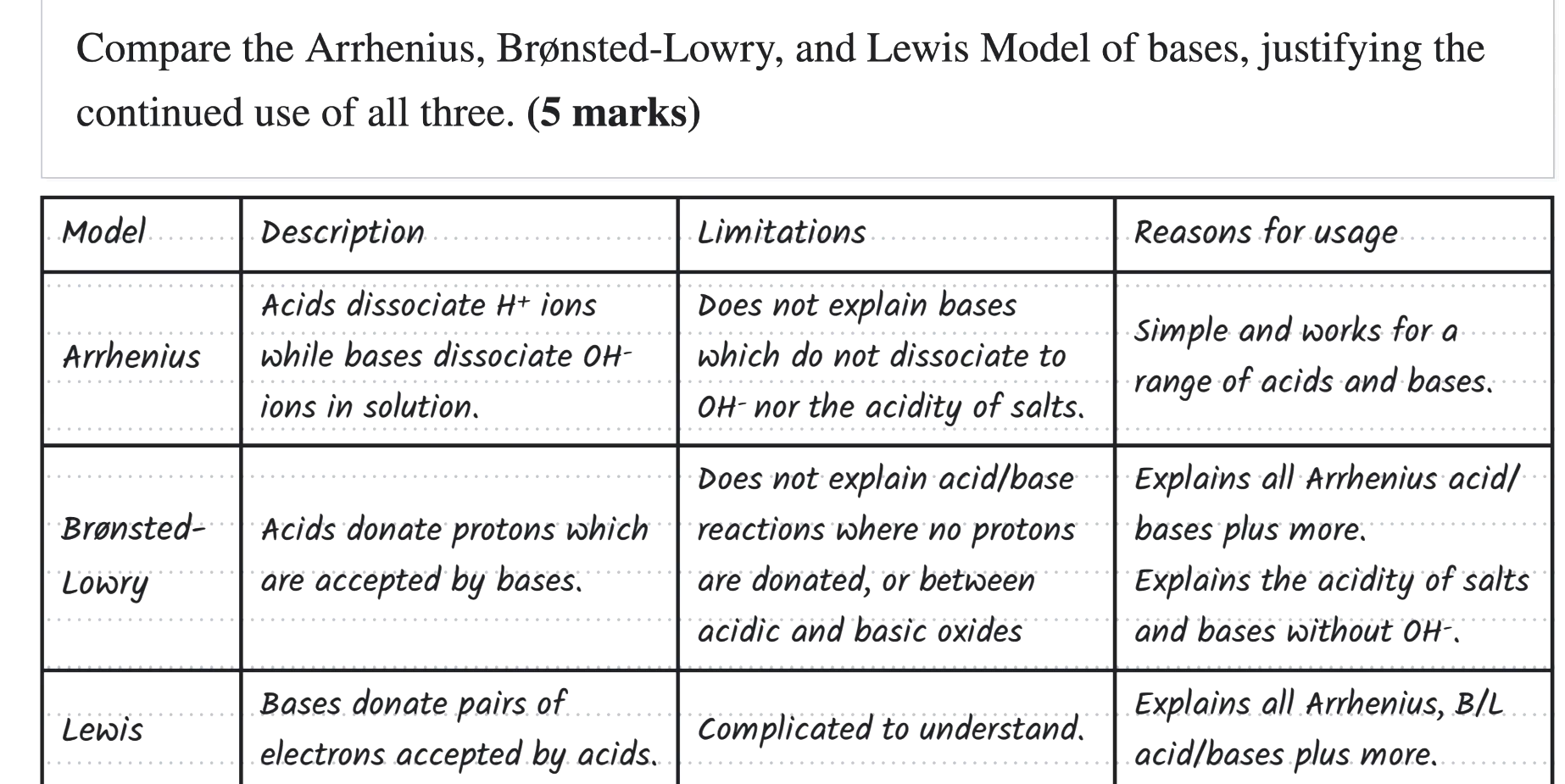
A



Explain the difference between a steady state and dynamic equilibrium
Steady state = the properties of a system remain constant over time, despite ongoing processes.
Dynamic equilibrium occurs when the forward and reverse reactions in a system happen at equal rates, resulting in no net change in the concentrations of reactants and products.
Describe what you would observe in a system at equilibrium
No observable changes at dynamic as concentration and observable properties are constant


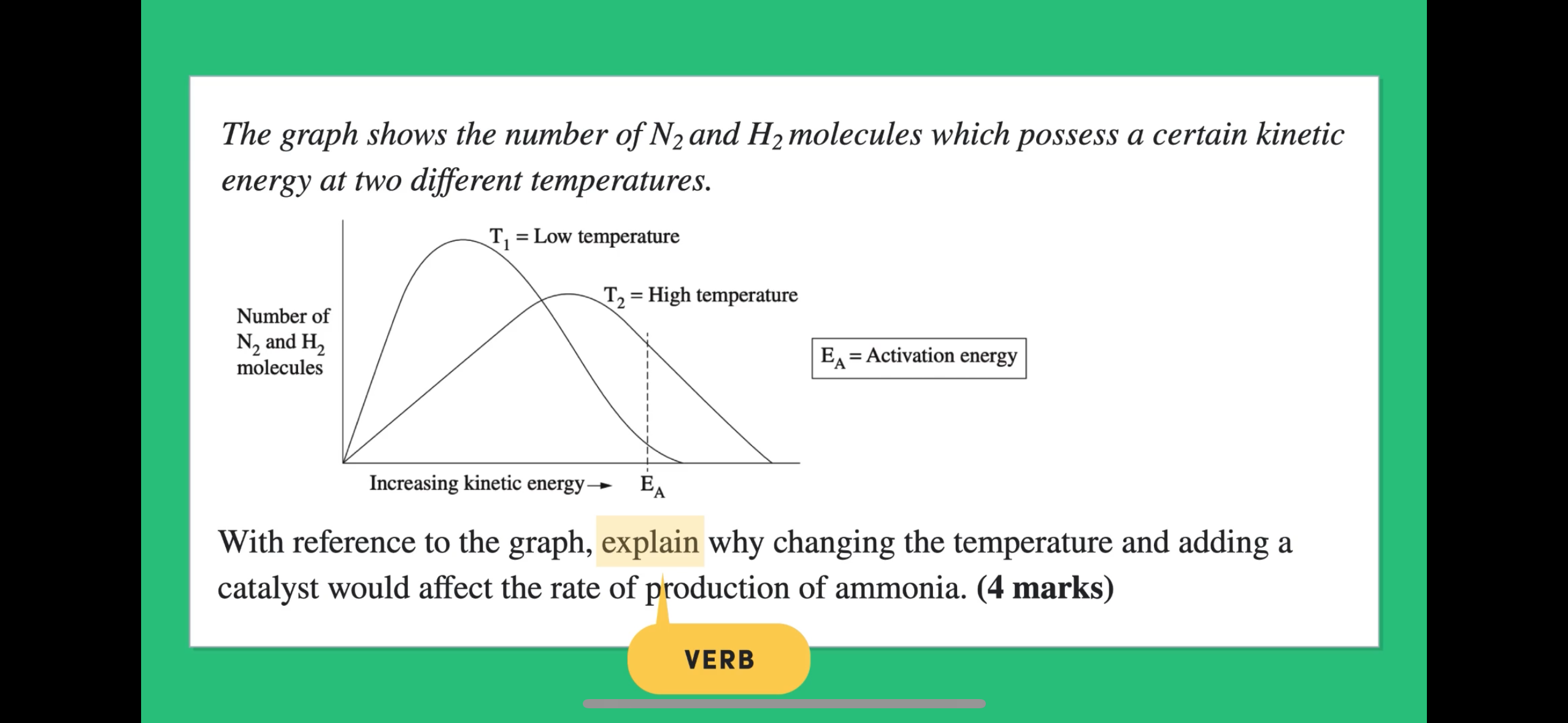
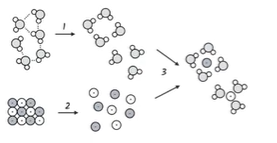
Explain the changes in enthalpy and entropy that occur when an ionic substance dissolves in water. Support your answer with a diagram (5 marks).
Dissolution of ionic substances occurs in 3 steps:
Separation of water molecules. This involves breaking hydrogen bonds to create spaces between water molecules for ions. This absorbed energy (H>0) and increases the order of the solvent (S<0).
Separation of the ions from the lattice. This breaks ionic bonds, so also absorbs energy (H>0), and causes the system to become more disordered (S>0).
Formation of ion-dipole bonds between the water molecules and separated ions. In this step, bonds are formed, which releases energy (H<0), and the system becomes more order (S<0).
An ionic substance will dissolve if Gibbs free energy, has a negative value. This requires either the change in enthalpy to be negative and/or the change in entropy to be positive.




C




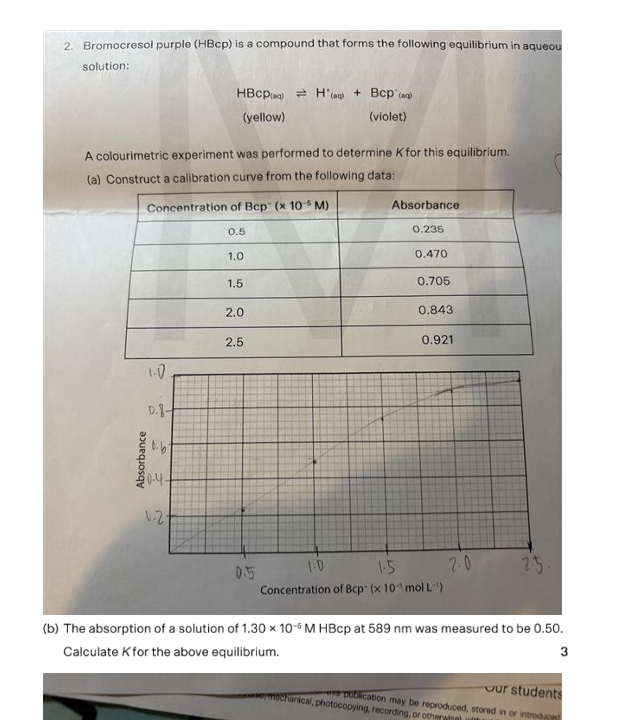
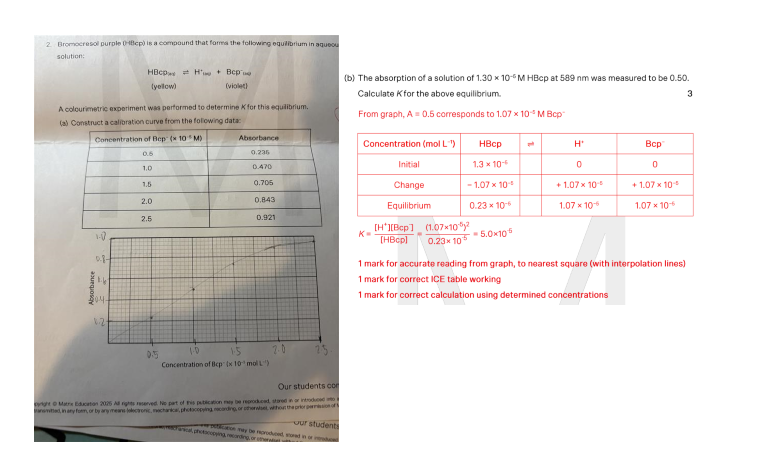
Would to the solubility of calcium sulfate in a 0.01 mol/L solution of sodium sulfate be different from its solubility in water? Give a reason for your answer.












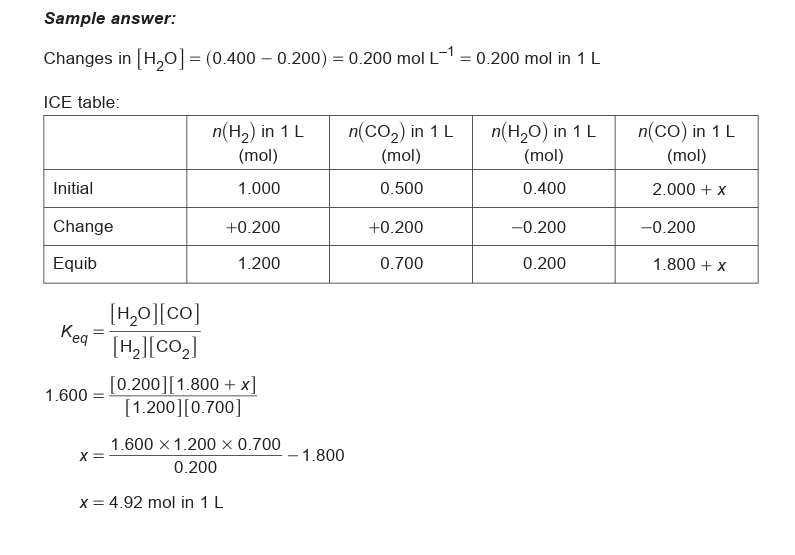
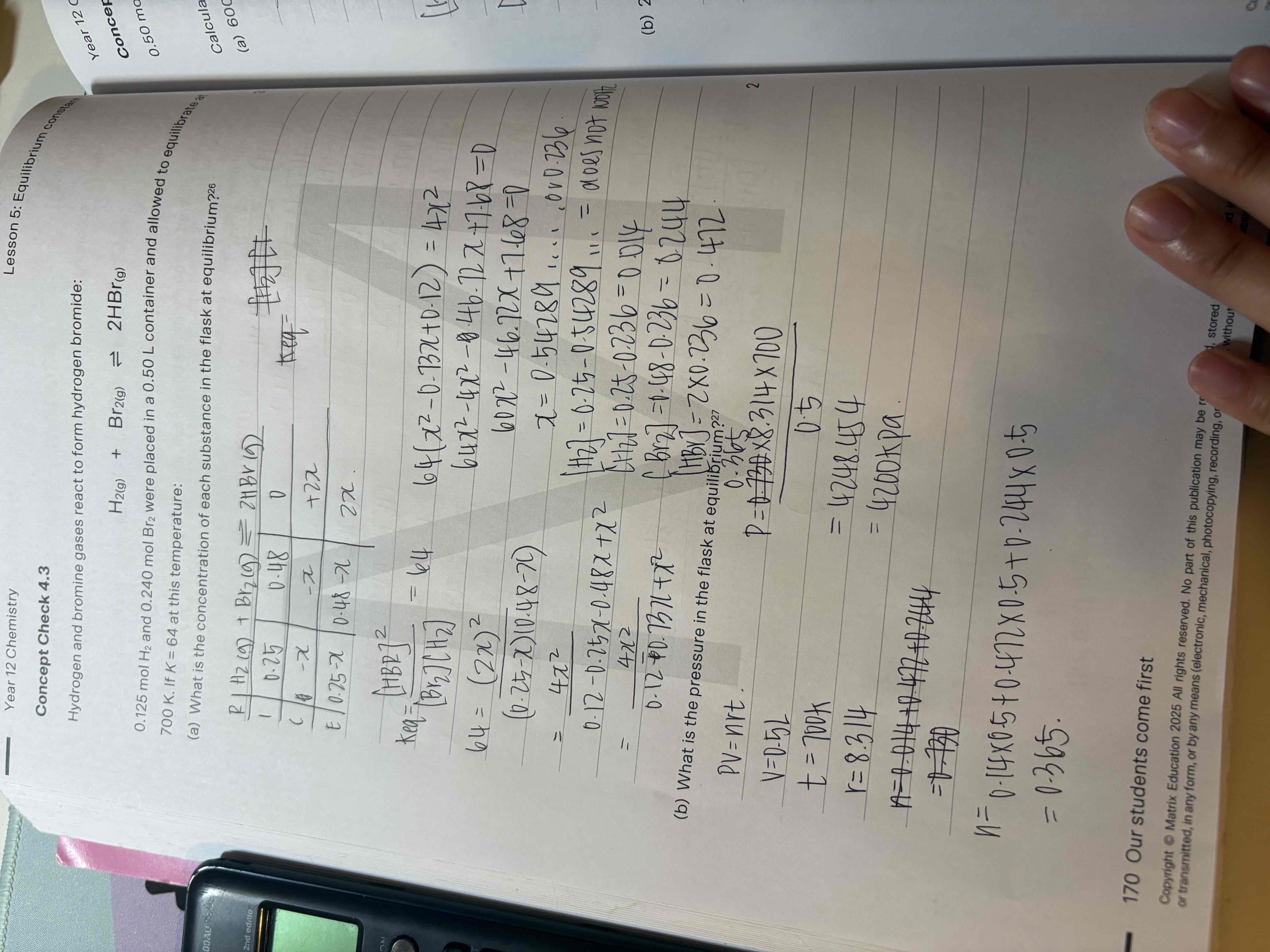
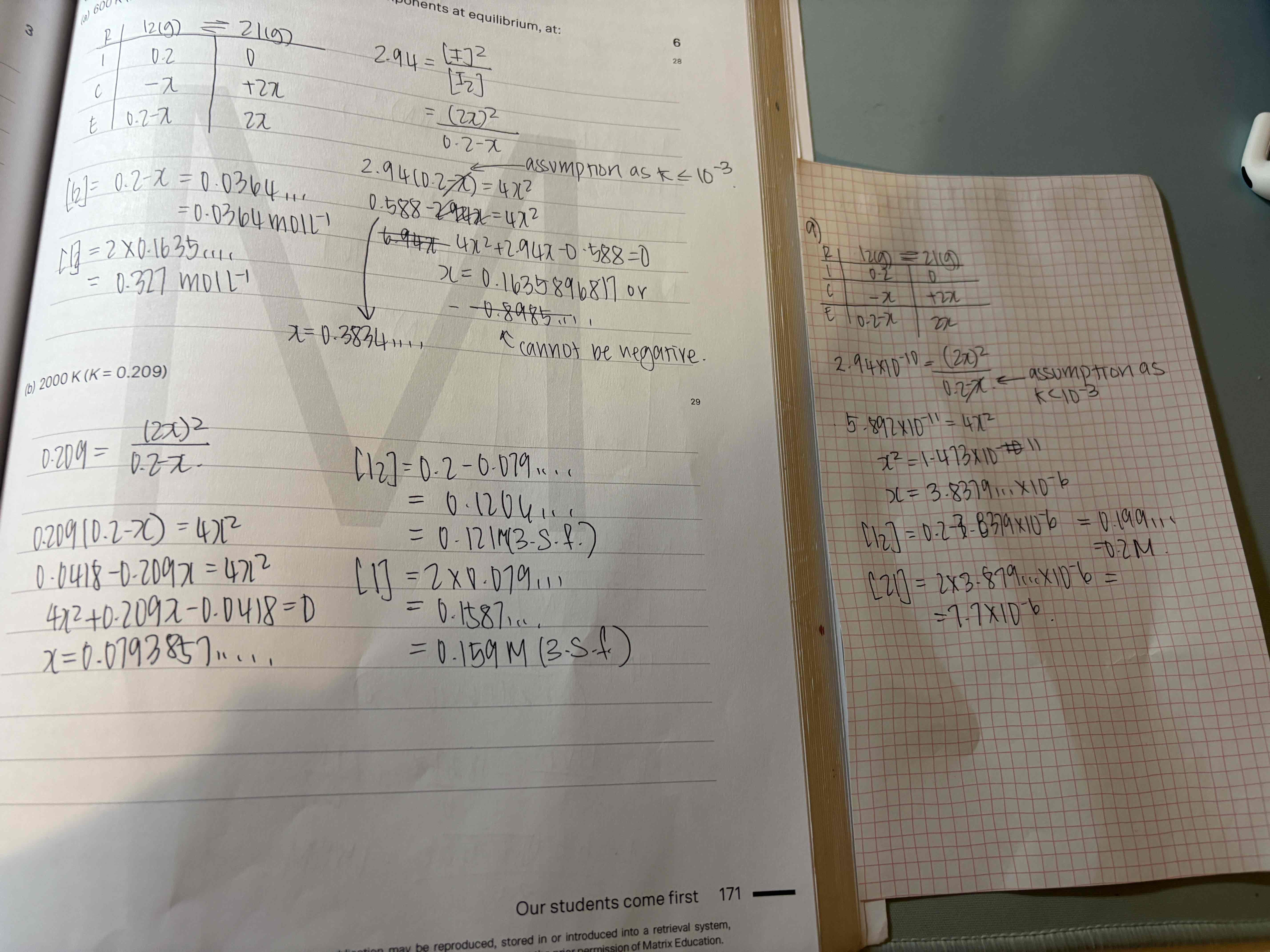
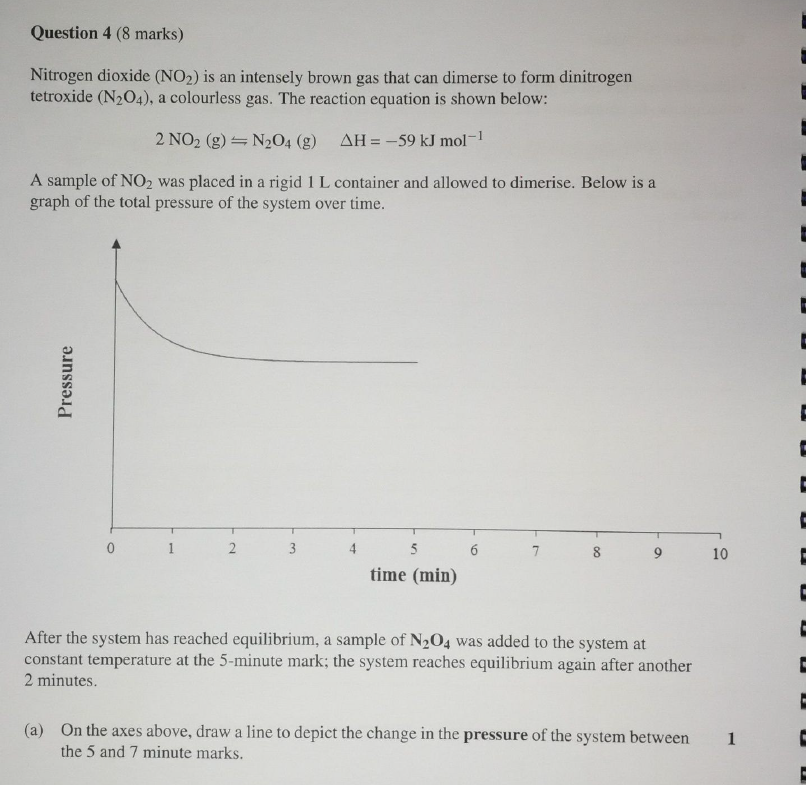
B) what is the pressure in the flask at equilibrium



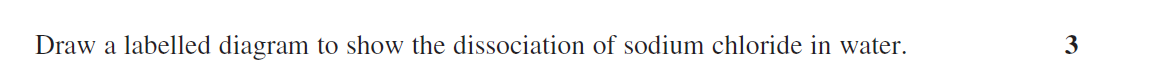


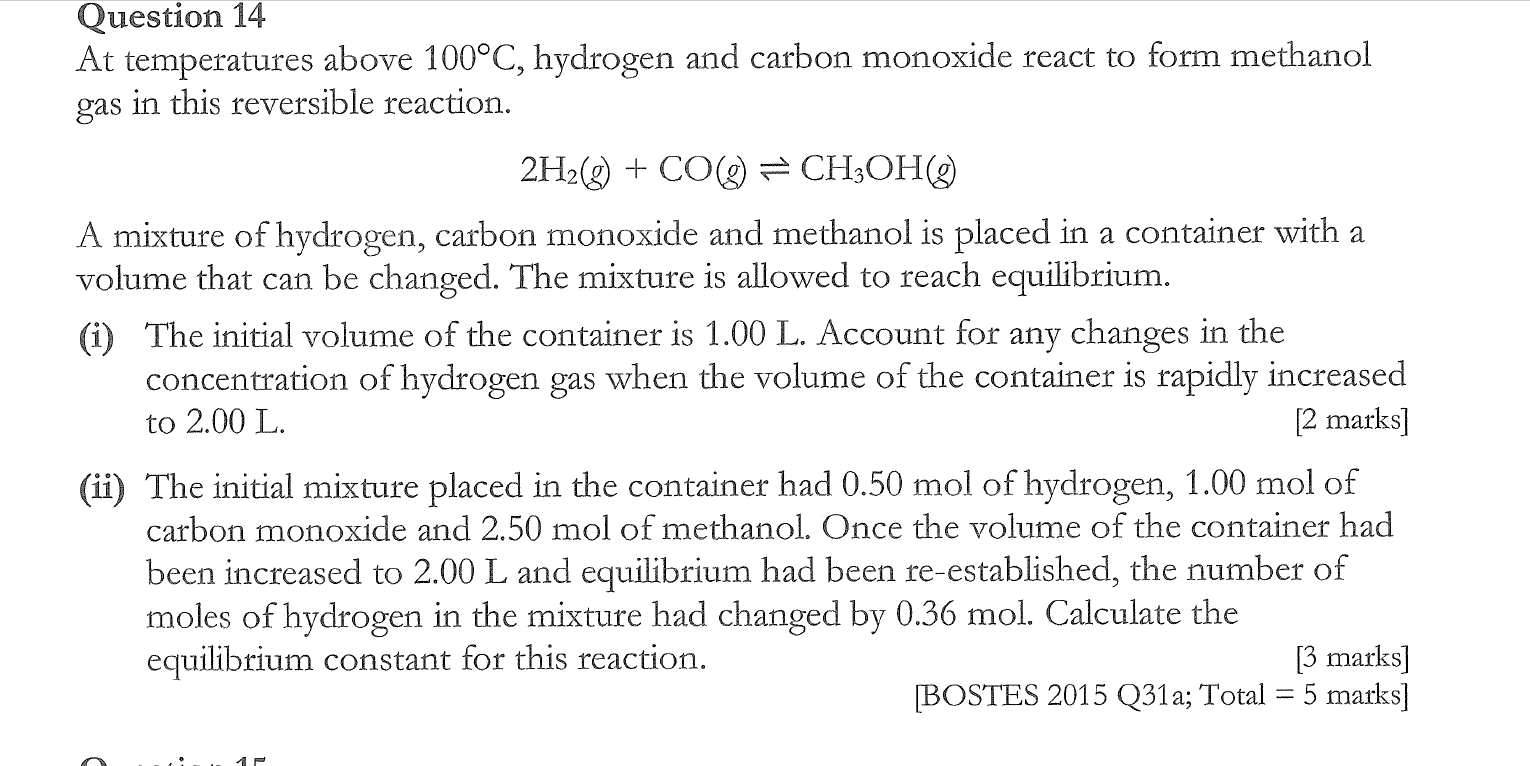
an initial mixture of nitrogen gas and hydrogen gas is reacted in a rigid container at a certain temperature to form nh3. At equilibrium the concentrations of H2 = 5M, N2 = 8M and NH3 = 4M. What were the concentrations of nitrogen gas and hydrogen gas that were reacted initially?





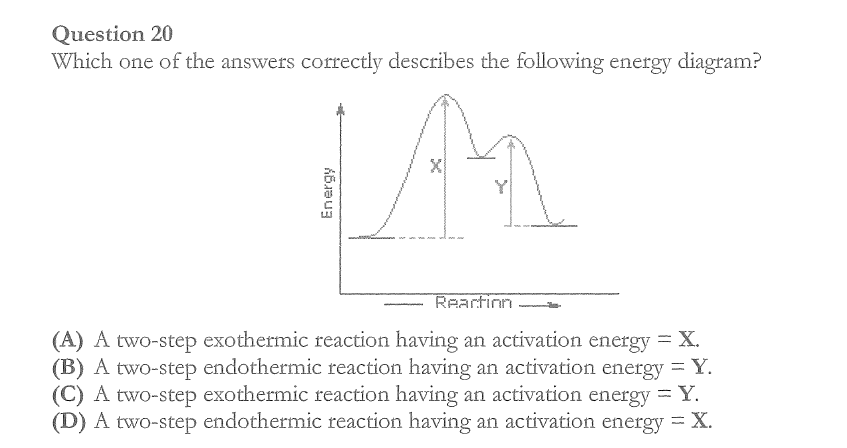
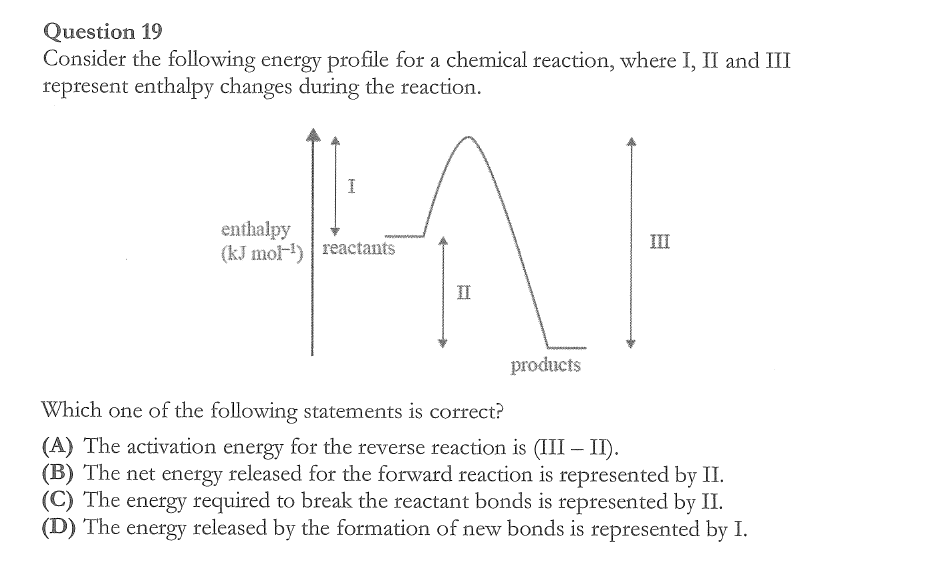

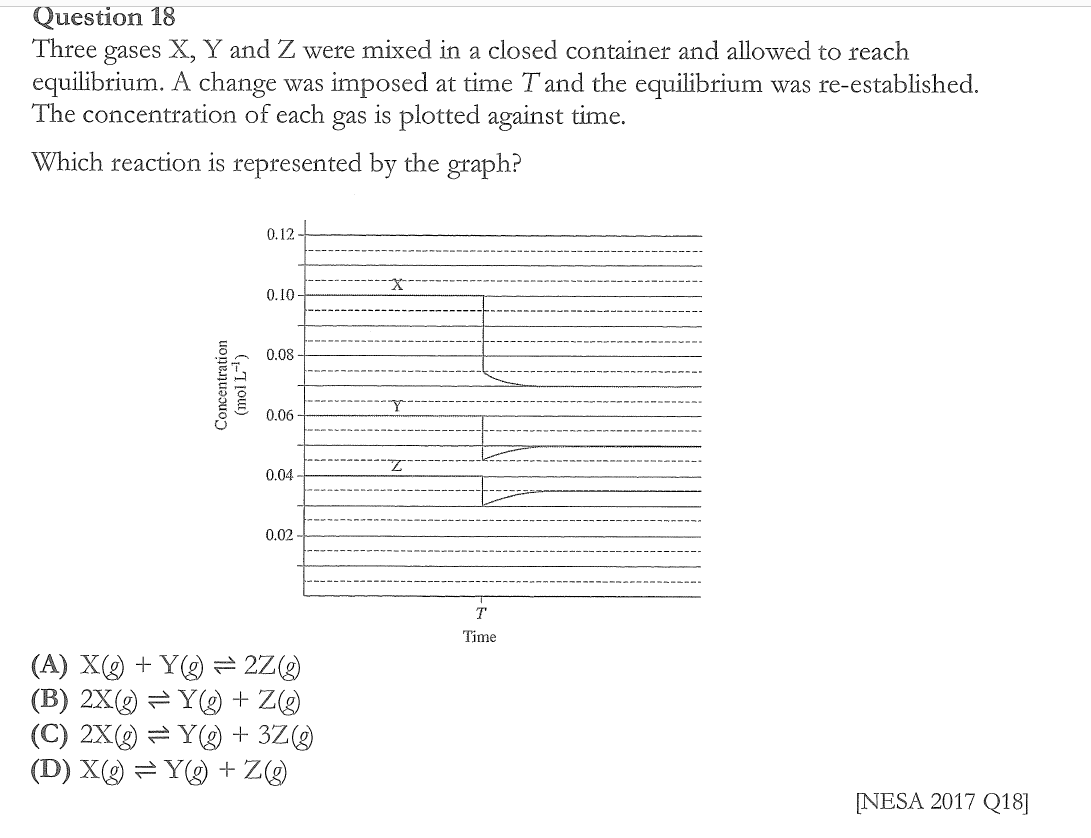
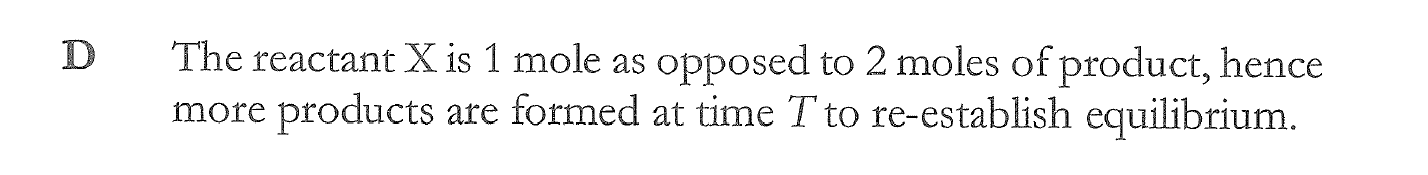

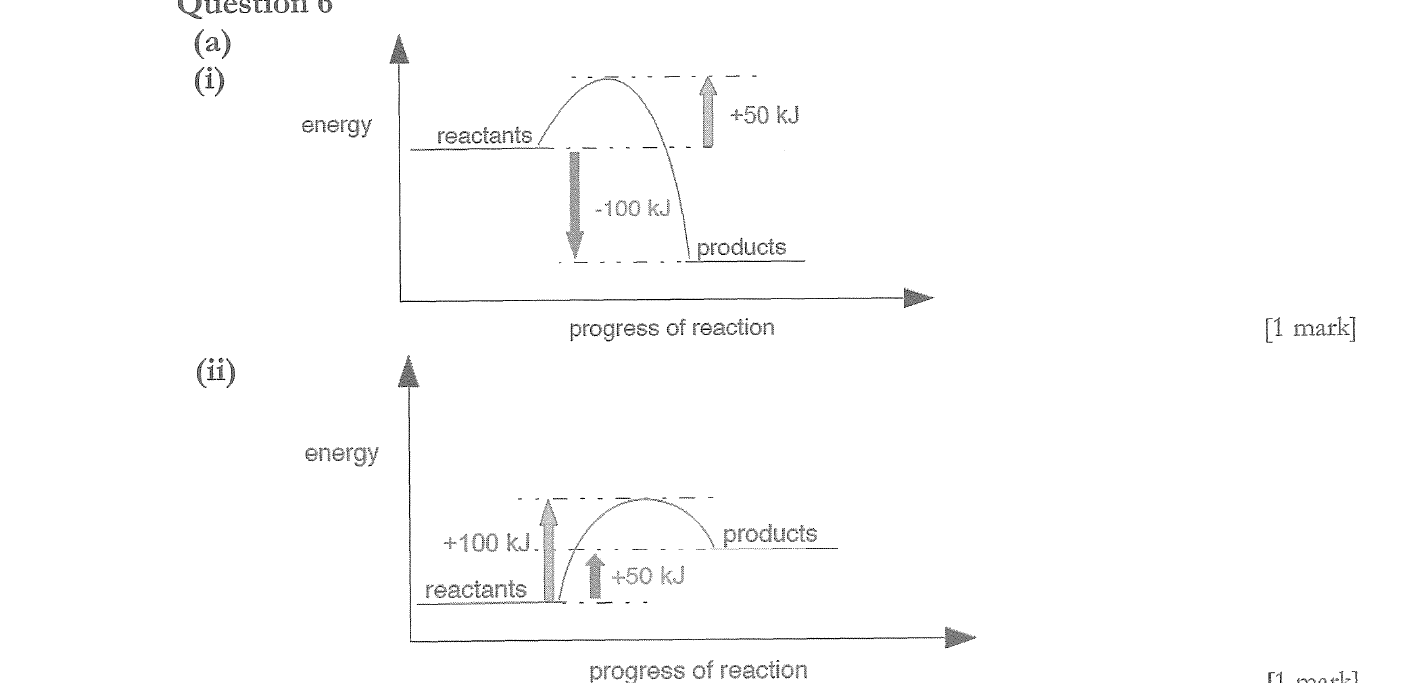

Explain the term homogeneous when it refers to an equilibrium reaction


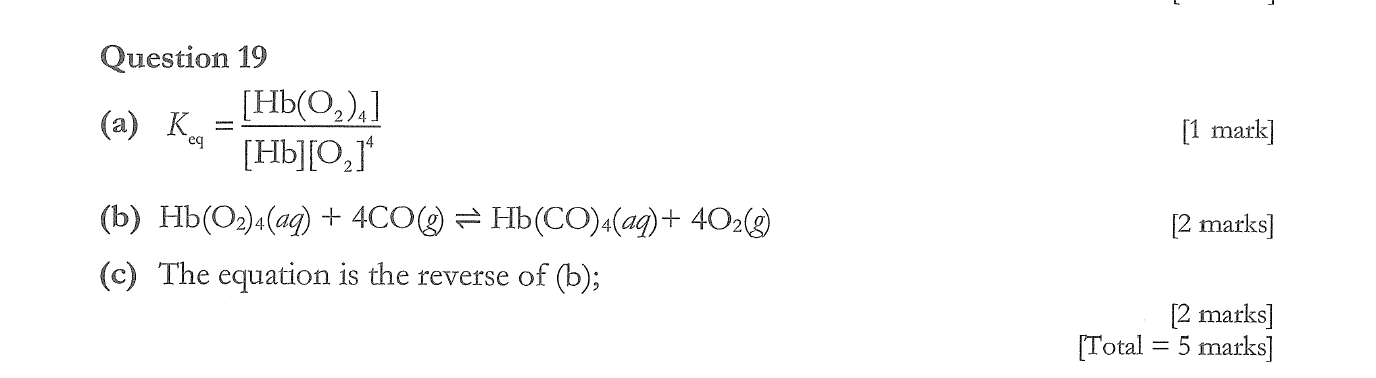
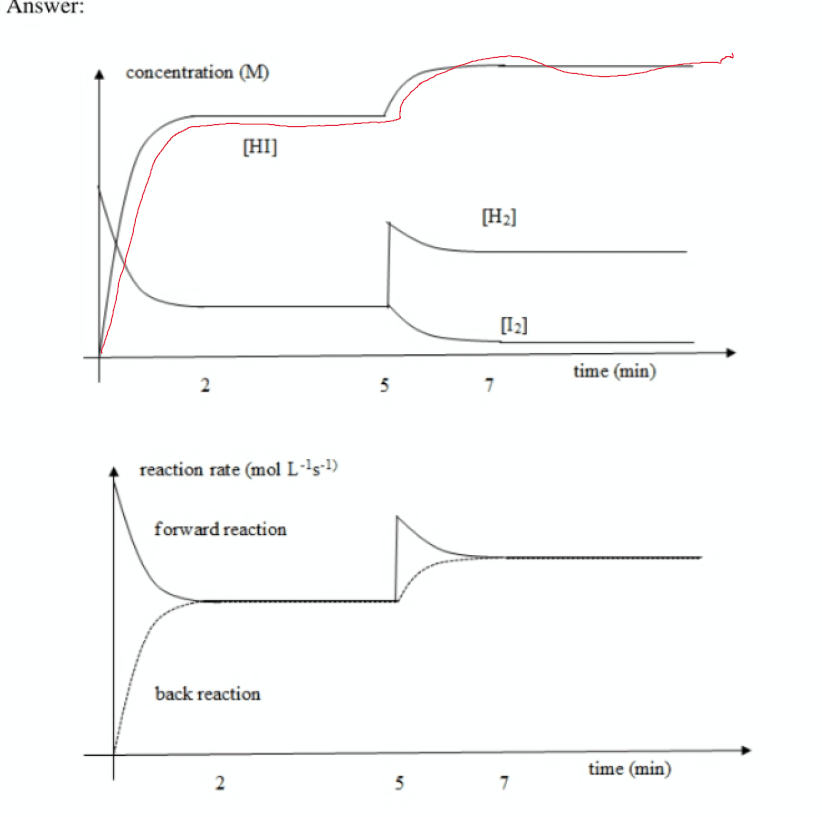
Explain your answer to part a. using LCP
Since n2o4 is being added, the pressure inside the vessel intially increases (PV=nrt). The reverse rxn is then favoured to remove the addition of n204. Since more gas molecules mean higher pressure, the graph shows a gradual upward slope until the system reaches a new equilibrium.
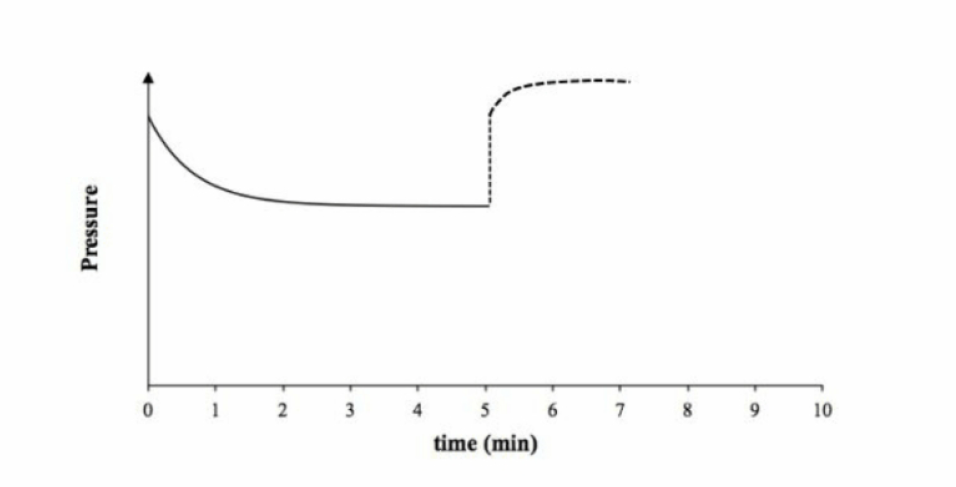









C
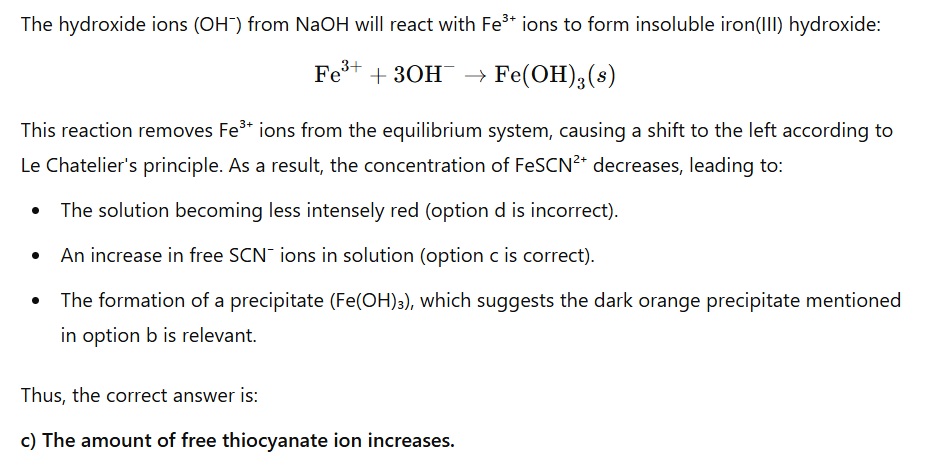
state two observations that could be made to indicate that the system has reached equilibrium
Colour remains constant since concentration does not change.
Temperature remains constant since heat is produced at the same rate as it is consumed
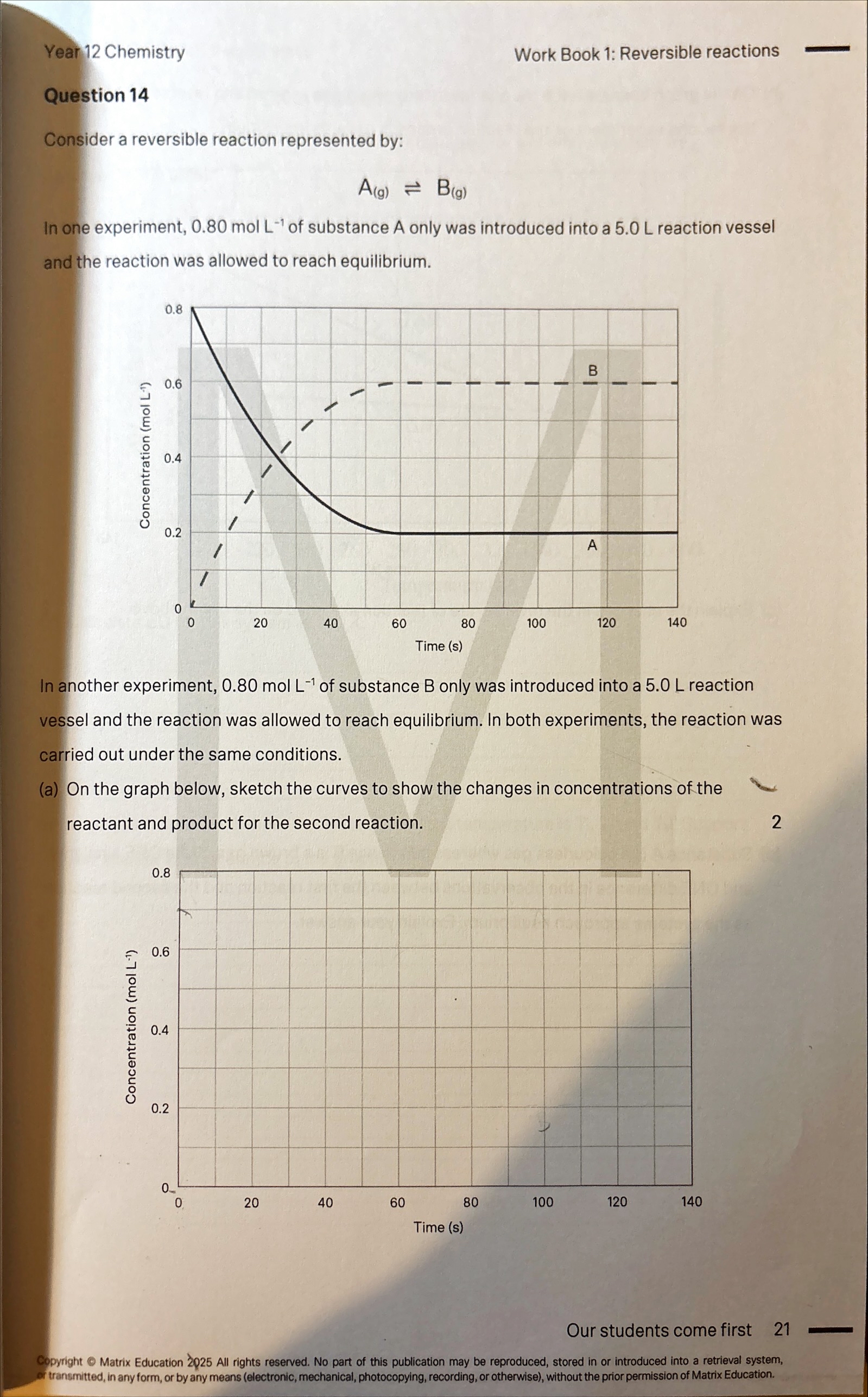
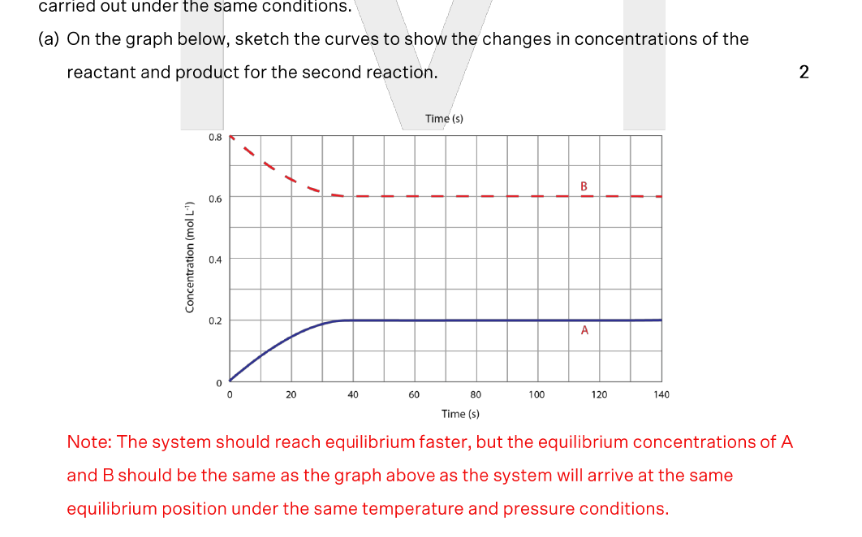
Substance A is a colourless gas whereas substance B is a brown gas. State ONE similarity and ONE difference in the observations between the first reaction and the second reaction as the systems approach equilibrium
Difference: In the first rxn, the flask will become more intensely coloured as the system approaches equilibrium since the concentration of B gas increases. However, in the second rxn, the colour will fade as the system approaches equilbrium since the concentration of B gas decreases
Similarly: Both reactions will have the same colour at equilibrium since the concentrations are the same
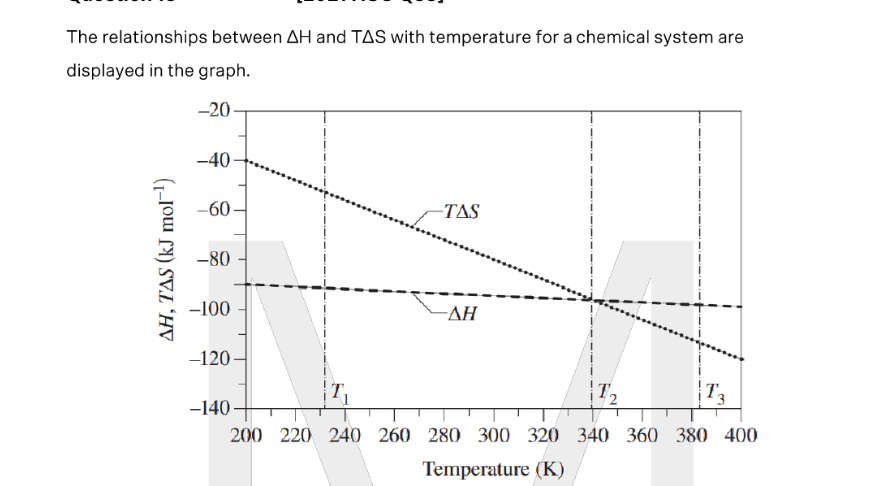
What can be deduced about the system when the temperature is T1, T2, T3? Support your answer with reference to the graph

Acid rain containing sulfuric acid attacks a marble statue according to the following reaction:
CaCO3 (s) + H2SO4 (aq) → CaSO4 (s) + CO2 (g) + H2O (l)
Dscribe how the equilirium is affected in the abov scenario by the fact that co2 is gaseous
The gaseous CO2 diffuses away from the reaction site thus removing the product from the equilibrium mixture, the reaction never reaches equilibrium.
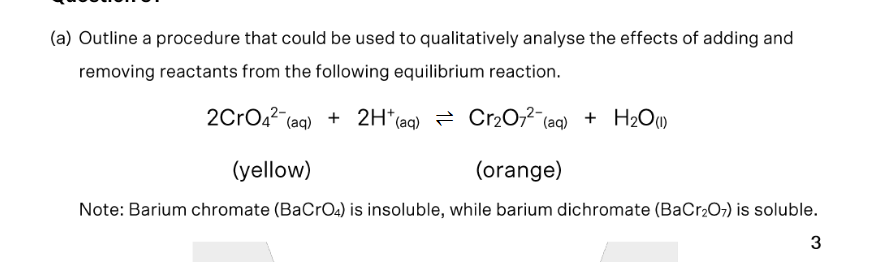
state the expected observations from the method outlined in (a)



b) What effect will increasing the partial pressure of oxygen have on the equilibrium constant?
c) Why is it easier to liquefy methanol than methane?




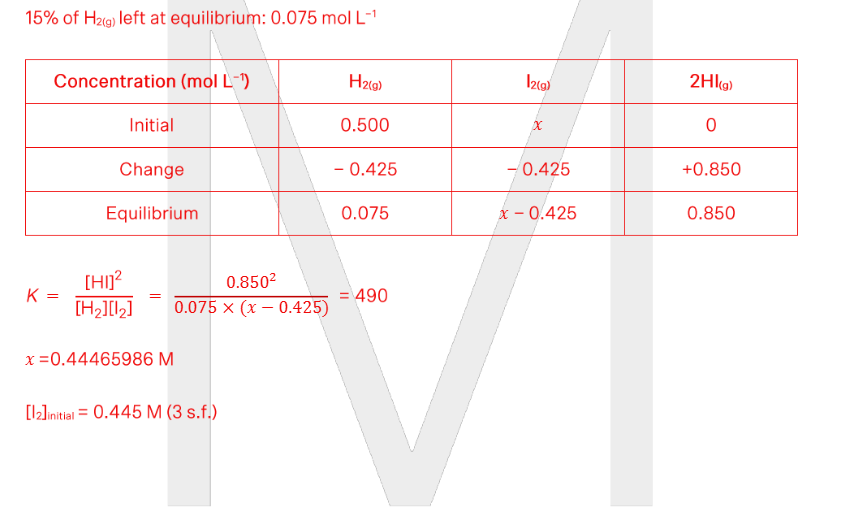
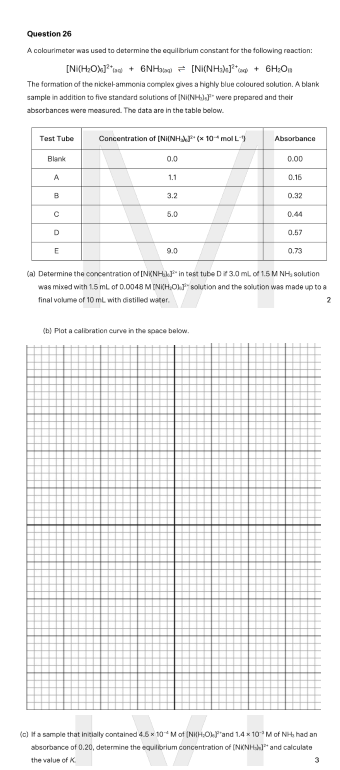
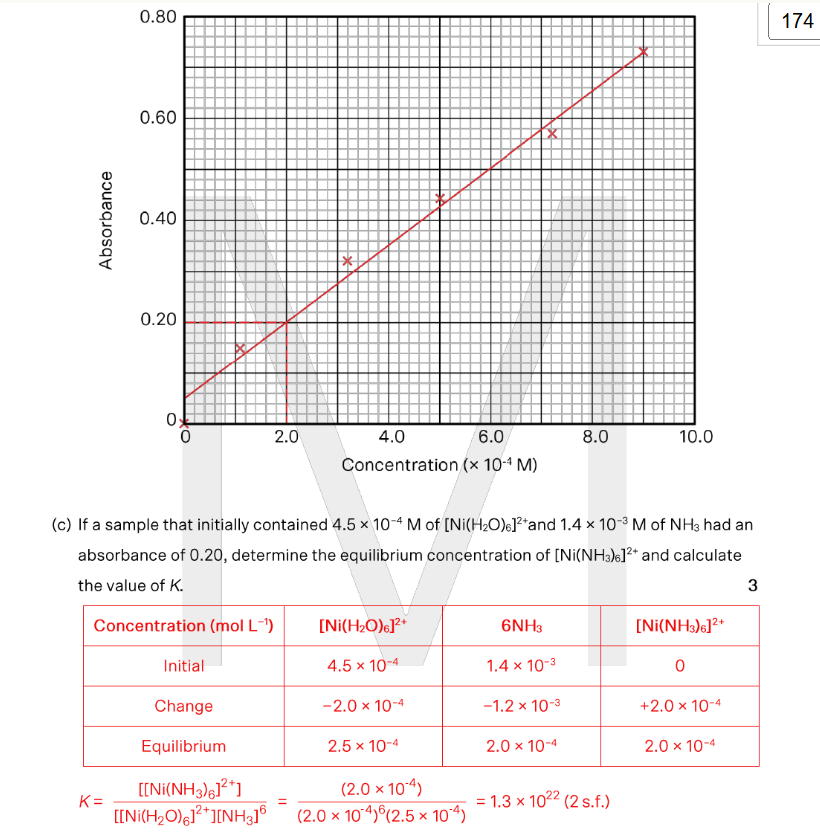






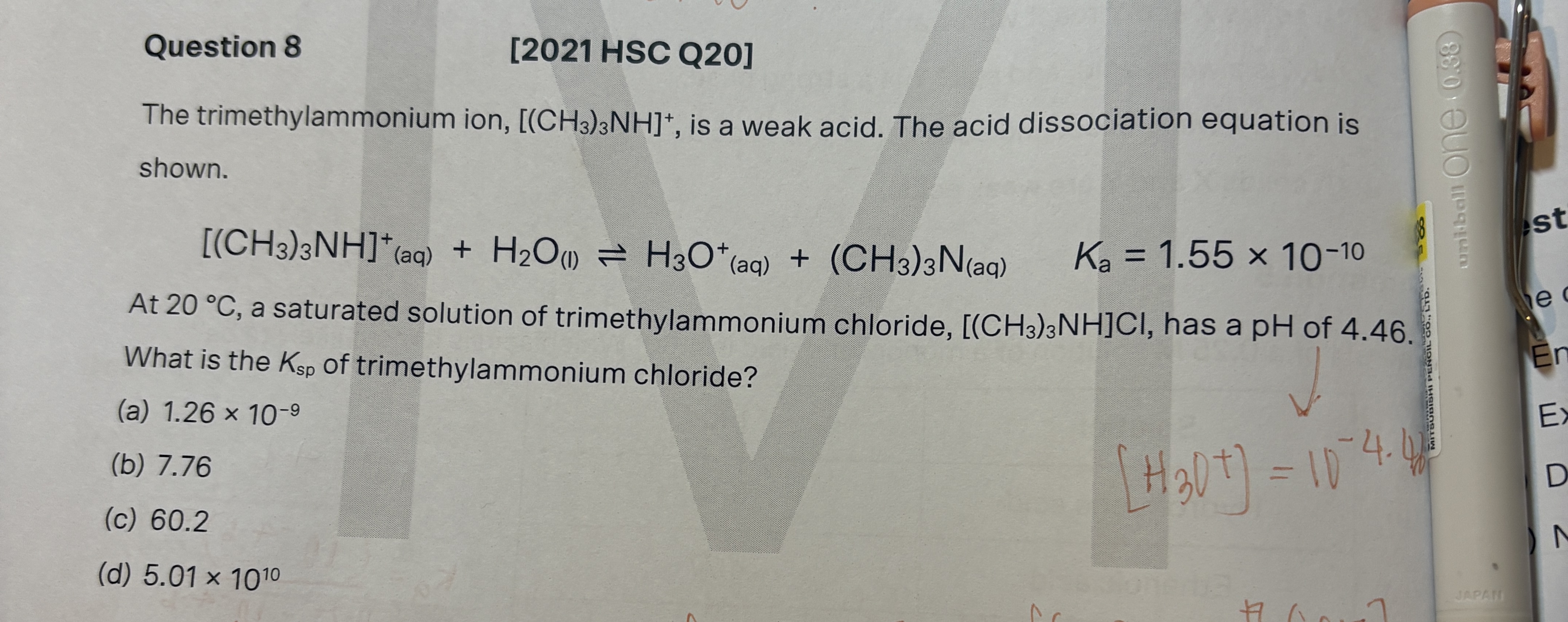
A
Solids do not affect eqm