Respiratory System - Anatomy
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
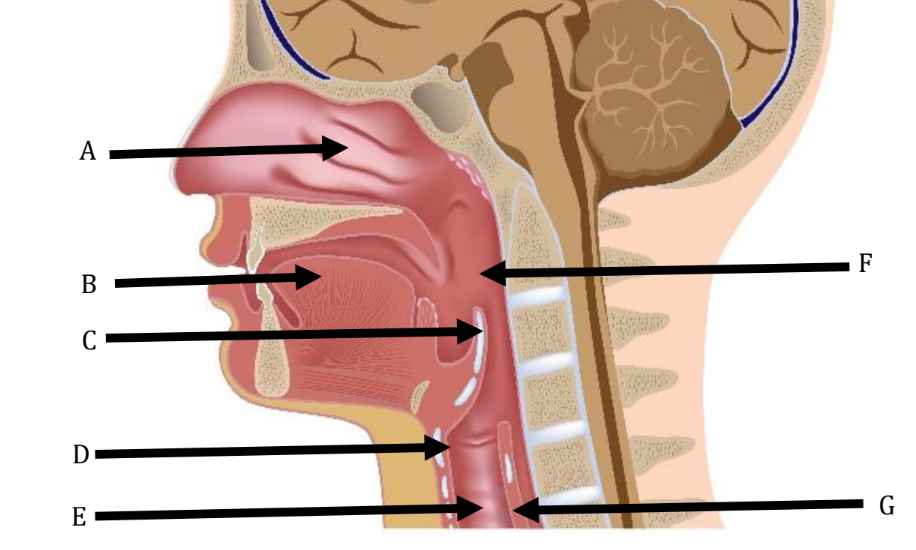
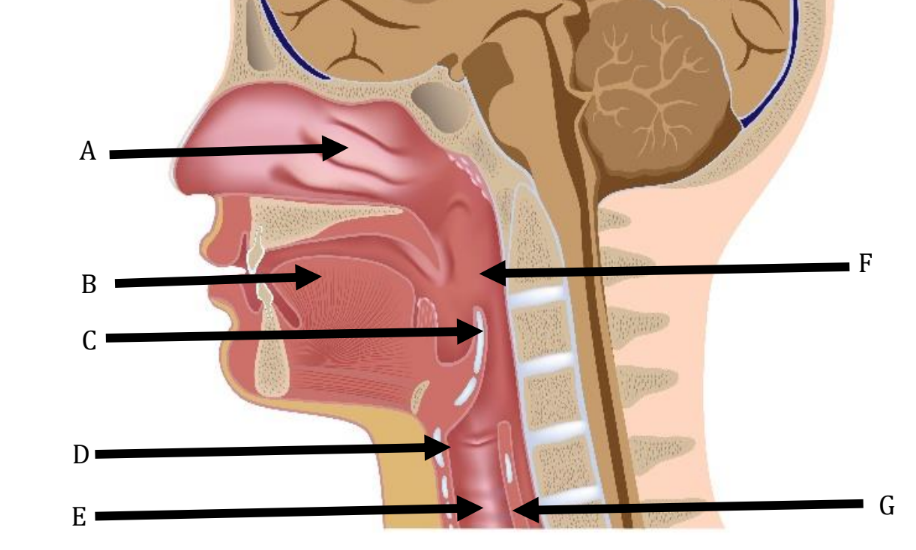
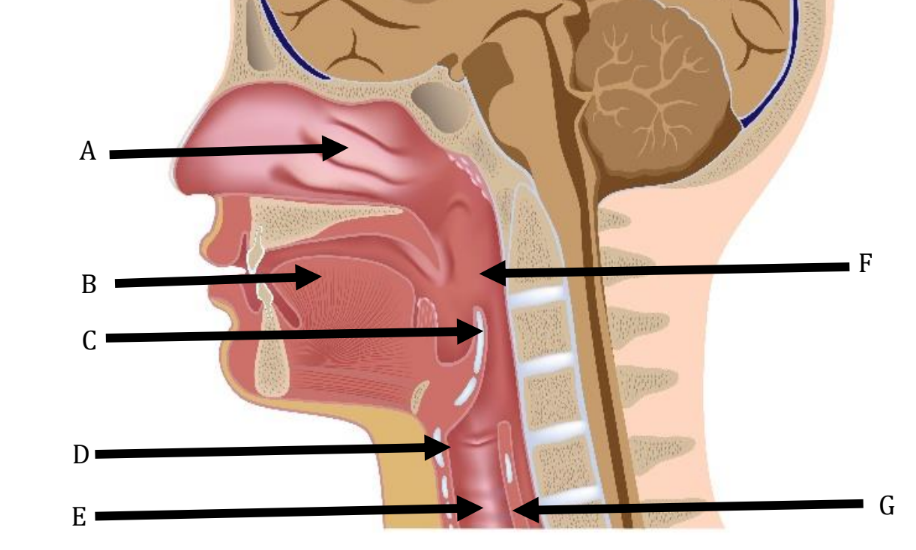
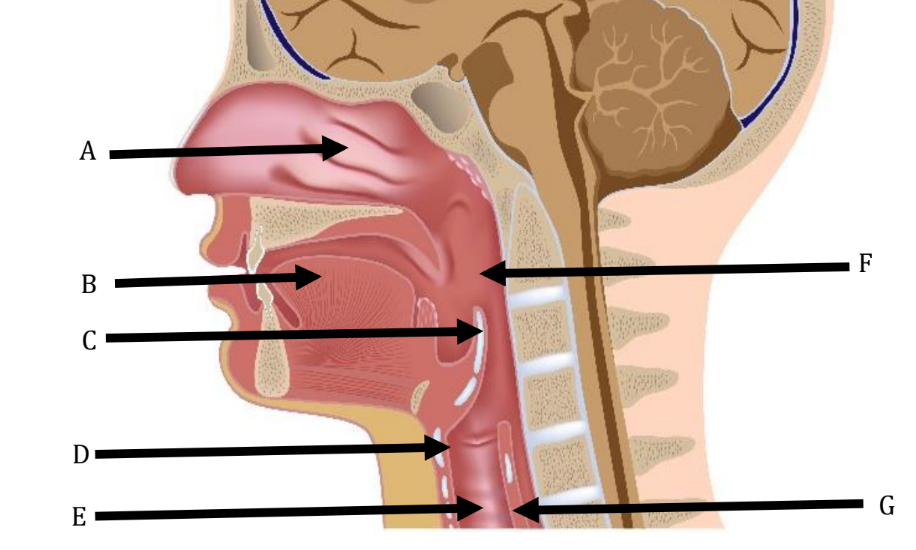
A
Nasal Cavity
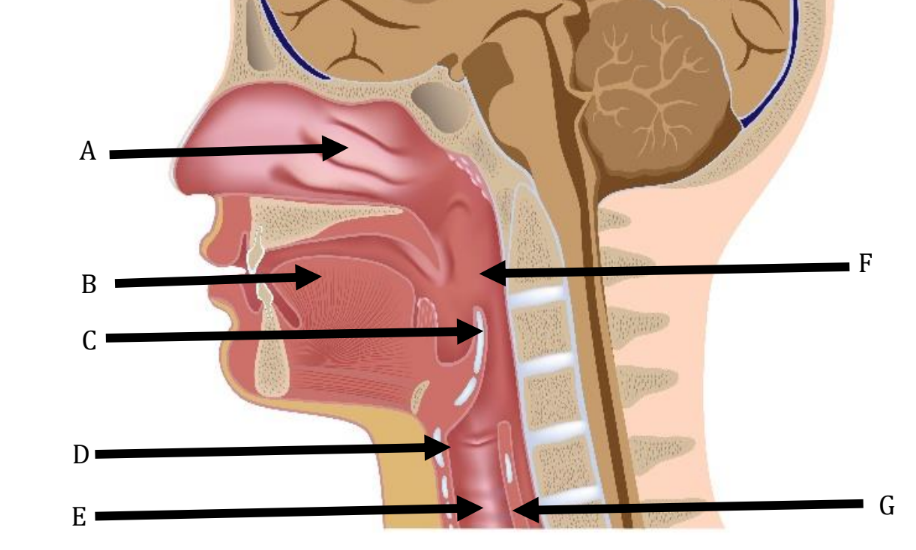
B
Tongue
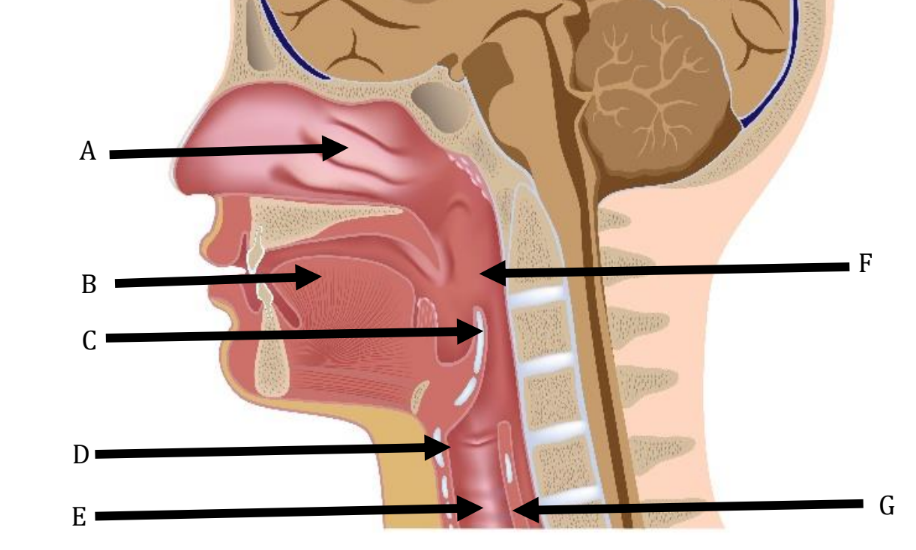
C
Epiglottis
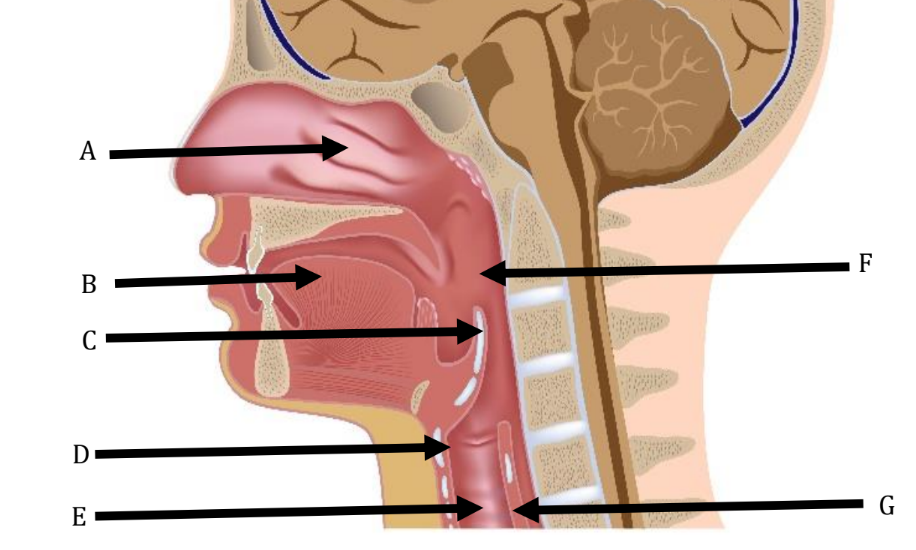
D
Larynx
E
Trachea
F
Pharynx
G
Esophagus
Air enters the body through the __________ and ____________.
Nose and Mouth
Once air enters the body, it enters the first tube, the _________ which carries both gases, food, and water.
Pharynx
The pharynx splits in two; the __________________ carries food and water down to the stomach.
Esophagus
When we swallow food or water the ___________________ closes off the trachea, which prevents choking.
Epiglottis
Air travels towards the lungs through the second tube, the _____________.
Trachea
The vocal cords can be found in the ___________, passing air over them creates sound.
Larynx
As the trachea enters the thorax, it splits into the left and right ______________.
Primary Bronchi
From here there are several branches known as _____________ that end in air sacs called ___________.
Bronchioles and Alveoli
In the lungs, gas is exchanged between the ___________ and a network of blood vessels known as _____________________.
Alveoli and Capillaries
Gases move from an area of ____________ to an area of ____________.
High Concentration to Low Concentration
That means that _________ moves into the blood and __________ is removed from the blood.
O2 and CO2
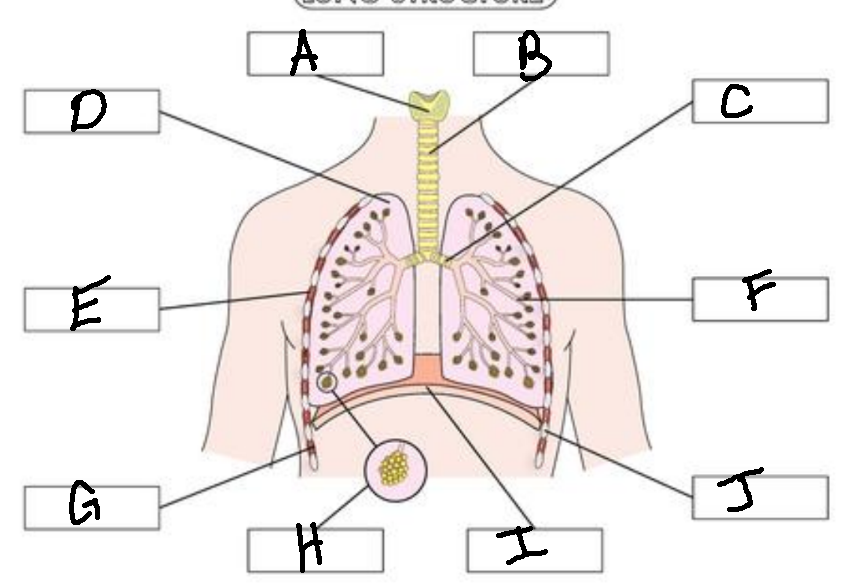
A
Larynx
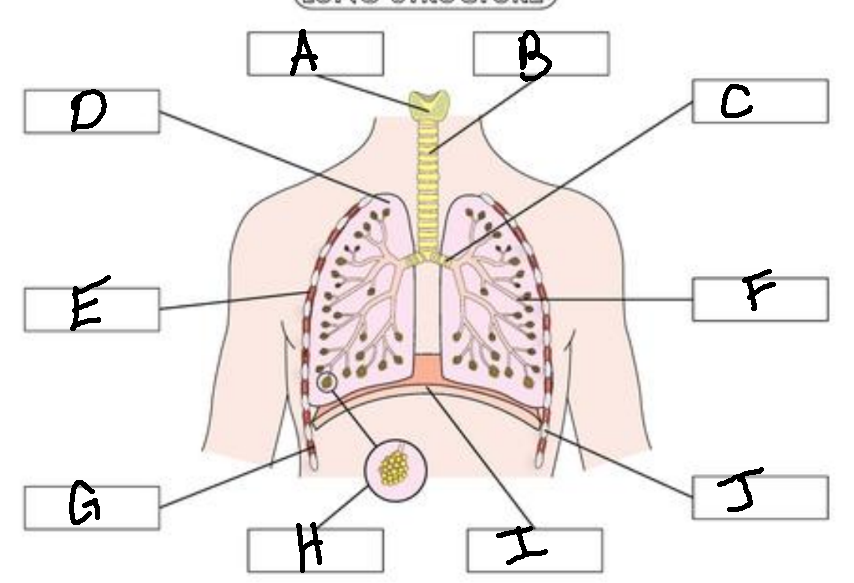
B
Trachea
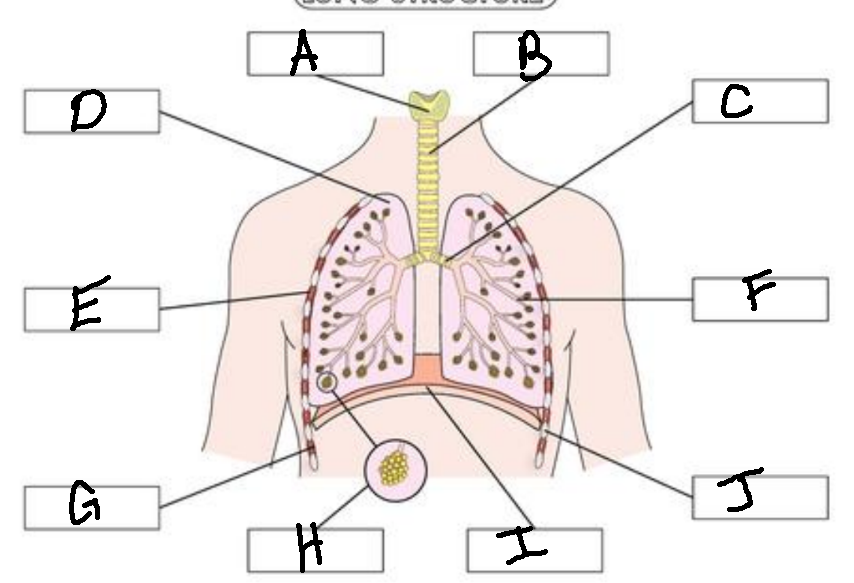
C
Bronchus
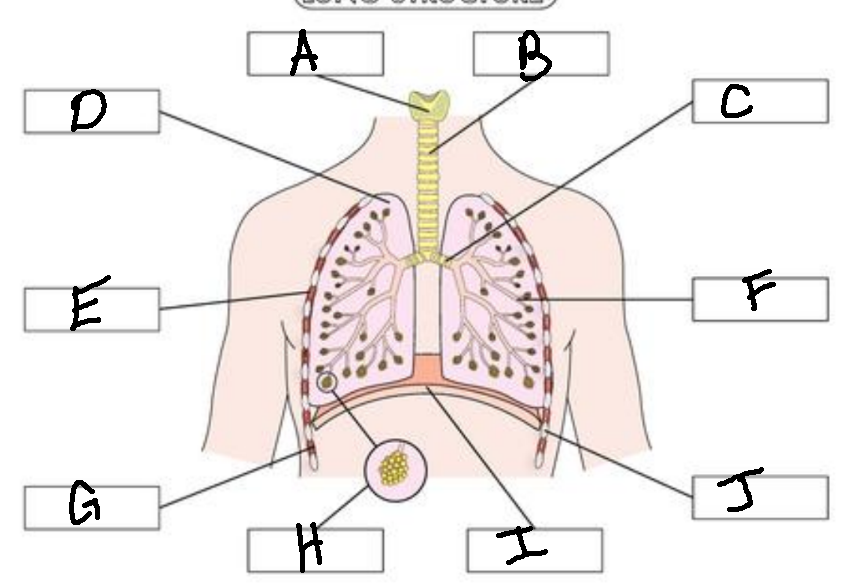
D
Lung
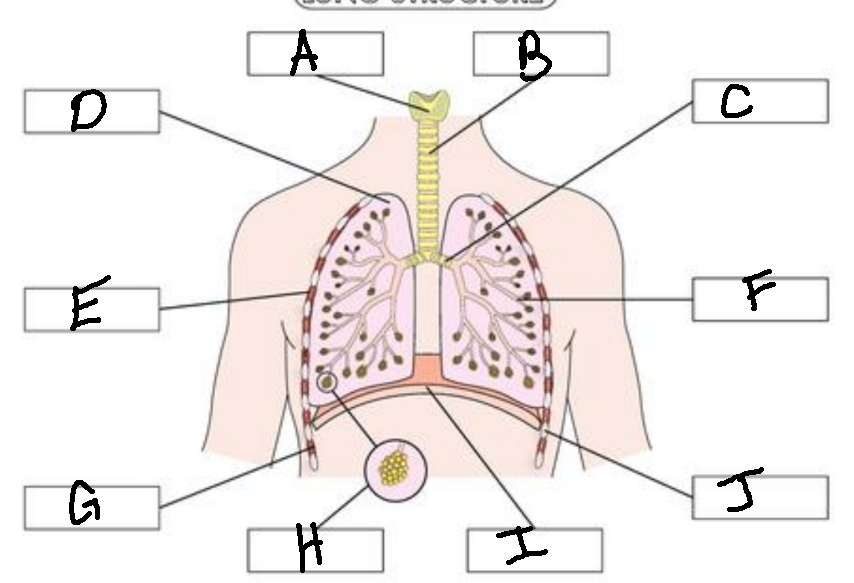
E
External Intercostal Muscle
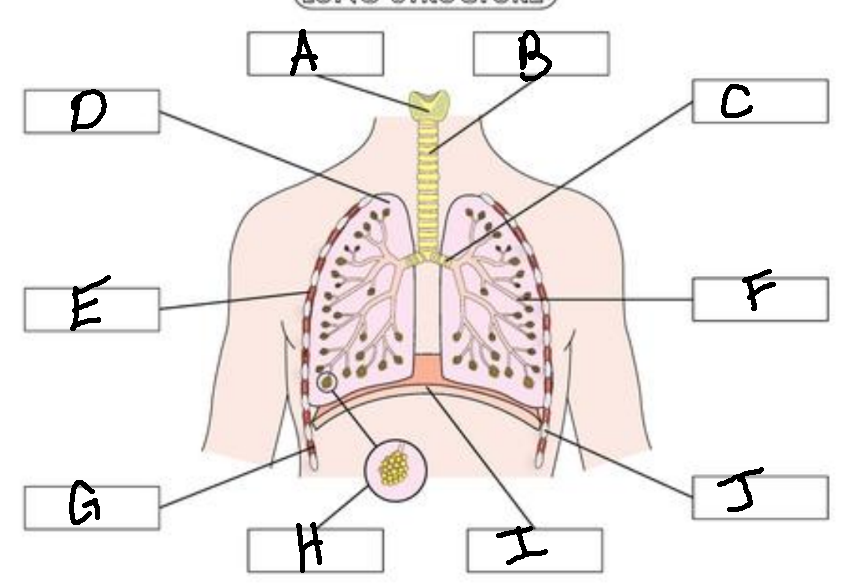
F
Bronchiole
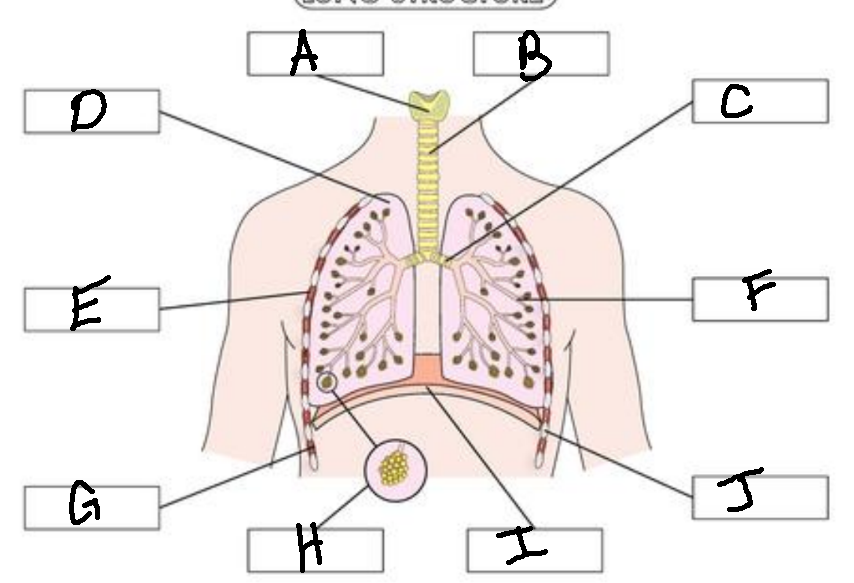
G
Internal Intercostal Muscle
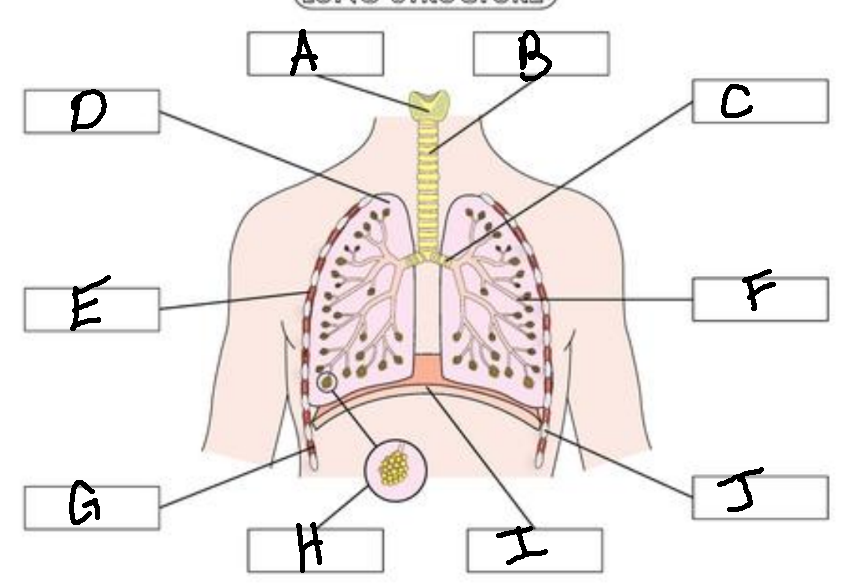
H
Alveoli
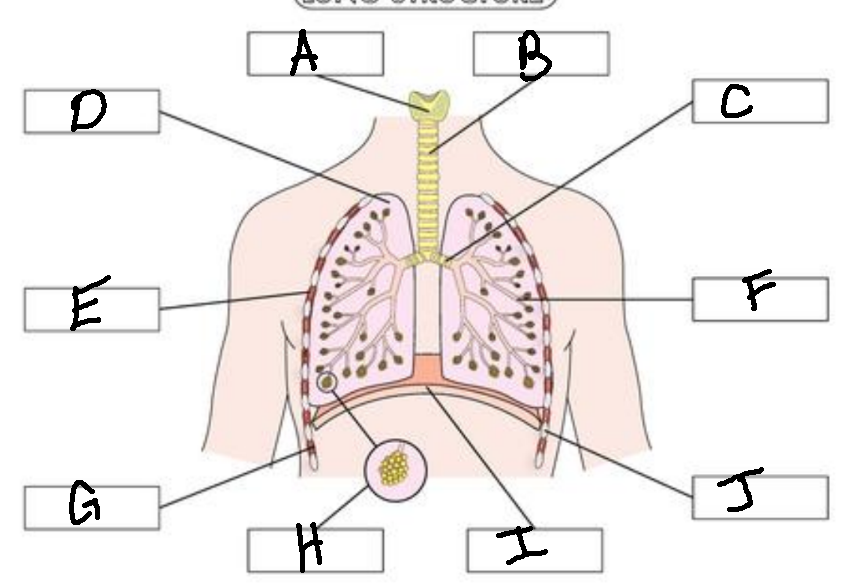
I
Diaphram
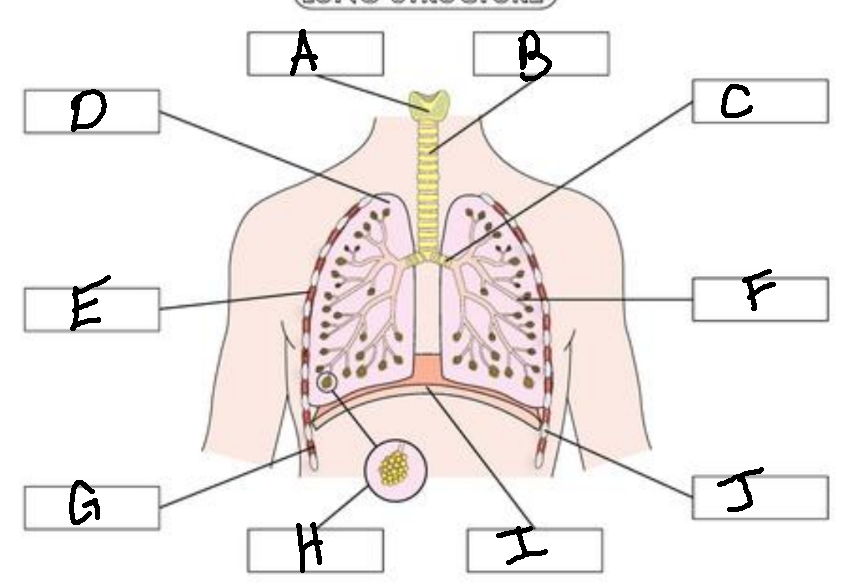
J
Ribs
The passageway for food, water, and air.
Pharynx
The tube that carries food to the stomach.
Esophagus
The tube that carries oxygen to the lungs.
Trachea
Where the vocal cords are found.
Larynx
Covers the trachea when you swallow food.
Epiglottis
The membrane that covers the lungs and thorax.
Pleural
The first two branches of the trachea in the thorax.
Primary Bronchi
The many branches of the trachea that end in air sacs.
Bronchioles
Air sacs in the lungs where gas exchange occurs.
Alveoli
The muscle that separates the thorax and abdomen, assists with inhalation and exhalation.
Diaphragm
What is the function of the respiratory system?
To supply the body with oxygen for cellular respiration and release carbon dioxide from the body
Is the respiratory system under voluntary or involuntary control? Explain.
It is under involuntary control because it is regulated by the medulla oblongota (regulates rate and depth) and pons (regulates tempo) and by sensors in the aorta and carotid arteries (regulates CO2 levels). It is also voluntary because we can control our breathing.
What gas diffuses into the blood from the alveoli during respiration?
Oxygen
What gas diffuses from the blood into the alveoli during respiration?
Carbon Dioxide
What are three features that make alveoli the ideal site for gas exchange?
Large Surface Area: Lungs contain millions of tiny alveoli
Thin Walls: Once cell thick
Large Capillary Network: Maintain continuous gas exchange
The lungs and thorax are covered in a membrane, separated by a pleural cavity that is filled with fluid. How is this important for respiration?
It keeps the lungs lubricated which reduces friction and allows the lungs to expand without damage.
Name 5 structures or tissues that air passes through on the way to the lungs, in order from the atmosphere to the lungs.
Nasal Cavity → Pharynx → Larynx → Trachea → Primary Bronchi
Describe how the diaphragm and intercostal muscles coordinate to increase the volume of the thorax. Is this inhalation or exhalation?
The diaphragm contracts and pulls downward and the muscles between the ribs contract and pull upward. This increases the size of the thoracic cavity and decreases the pressure inside. This is inhalation.
Describe how the diaphragm and intercostal muscles coordinate to decrease the volume of the thorax. Is this inhalation or exhalation?
The diaphragm relaxes, and the volume of the thoracic cavity decreases, while the pressure within it increases. The lungs contract and air is forced out. This is exhalation.
How does changing the volume of the thoracic cavity affect the pressure felt by the lungs compared to atmospheric pressure?
Increasing the volume lowers the internal pressure below atmospheric levels, drawing air into the body. Decreasing the volume raises the internal pressure above atmospheric levels, forcing air out of the body.
How many lobes are the right and left lobes divided into?
The right lung is divided into three lobes: the superior, middle, and inferior lobes. The left lung is divided into two lobes: the superior and inferior lobes. This asymmetry exists because the left lung must make room for the heart.
Gas Exchange
Gas diffuse from a region of higher partial pressure to lower partial pressure. Blood from the right side of the body going to the lungs has a higher partial pressure of CO2 and a lower partial pressure of O2. In the alveoli there is a lower partial pressure of CO2 and a higher partial pressure of O2. When the blood passes the capillaries in the alveoli, CO2 will diffuse into the alveoli and O2 will diffuse into the blood. The blood going to the tissue has a higher partial pressure in O2 and a lower partial pressure in CO2. In the tissues there is a low partial pressure of O2 and high partial pressure of CO2. When the blood passes the capillaries in the tissues, CO2 will diffuse from the tissue to the blood and O2 will diffuse from the blood to the tissue. The blood going to the heart has a higher partial pressure in CO2 and a lower partial in O2.