A level chemistry chapter 23: chemical energetics
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
Define standard enthalpy change of atomisation
The enthalpy change when one mole of gaseous atoms are formed from the elements in its standard state
Define lattice energy
The enthalpy change when that takes place when one mole of a substance is formed from its gaseous ions. If gaseous ions are turned into a solid lattice, the enthalpy is negative.
What are the factors that affect lattice energy and explain why
Ionic charge: increasing the ionic charge increases the attraction between the positive and negative ions meaning a larger, more negative lattice formation enthalpy.
Ionic radius: decreasing the ionic radius means the ions are closer together in the lattice so the attraction between the ions is stronger meaning a larger, more negative lattice formation enthalpy.
Define first electron affinity
It is the energy released when one mole of gaseous atoms each gains an electron to form one mole of -1 ions.
What is trend of electron affinity down the group?
EA decreases down the group because although nuclear charge increases, electron shielding and atomic radius increase so there is less attraction between the nucleus and an incoming attraction. This means less EA energy is released down the group.
What are the exception to the general trend in EA energy down the group?
Fluorine and oxygen are exceptions to this rule as they have lower EA than expected due to their relatively small size so are already crowded with electrons which repel an incoming electron.
Define lattice dissociation enthalpy
It is the enthalpy change that takes place when one mole of an ionic compound is broken down to form its gaseous ions
Define standard enthalpy of hydration
The enthalpy change that takes place when one mole of gaseous ions dissolve in water
Define standard enthalpy of solution
The enthalpy change that occurs when one mole of an ionic solid dissolves in water to form a solution of infinite dilution
Energy cycle with enthalpy change of solution and hydration
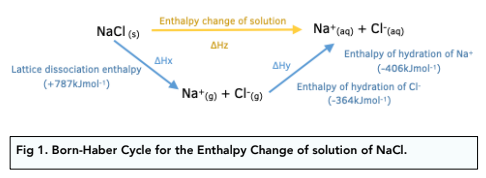
What are the factors that affect enthalpy of hydration and explain why
Ionic radius: enthalpy change of hydration becomes more exothermic with decreasing ionic radii because smaller ions have greater charge density resulting in stronger ion-dipole attractions between the water molecules and the ions in the solution, more energy is released when they become hydrated.
Ionic charge: enthalpy of hydration is more exothermic for ion with larger ionic charges. Higher the ionic charge, higher the charge density, higher attraction.
What is entropy
the number of possible arrangements of the particles and their energy in a given system