Biocatalytic Reduction (Final)
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
Biocatalyst
Any living or dead cells, cell extracts, pure enzymes
Advantages of using a Biocatalyst
Inactivated C-H functionalized, stereoselective, conversion at preferred temp and pH, catalyst reused
Nobel Prize winner 2018 for Directed Evolution
Frances Arnold, Gregory Winter, and George Smith
Goal of the lab
Reduce ketone using carrot peelings as reagent. Compare results to reduction with NaBH4
Enzymes can ___ ___ reduction of prochiral ketone giving __ enantiomer.
Selectively catalyze, one enantiomer
What reagent was used in the reduction?
Carrot peelings, a biocatalyst
Enantiomers are ___ that are __ -__ mirror images.
Stereoisomers, non-superimposable
ALL physical properties of ___ are the ___.
Enantiomers, the same
What is different between enantiomers?
Interaction with another chiral material or with plane-polarized light (opposite signs)
In an achiral environment reactions with achiral or racemic material gives __ or __ product (no __).
Gives achiral or racemic product (no enantioselectivity)
How to get a pure enantiomer?
Asymmetric synthesis— chiral reagents/catalysts with chiral environment
Addition of metal hydride reagents to __ yields __ __.
Aldehydes yields primary alcohols.
Reaction with metal hydrides
Nucleophilic hydride “H-” reagent adds to polarized C=O
What was the solvent and proton source for the NaBH4 reaction?
Ethanol
What enzyme do the carrots contain?
Keto-reductase enzyme
Enzymes are proteins, or polymers of __ amino acids.
Chiral amino acids.
Enzymes act as __ and in the chiral environment __ __ occur.
Catalysts, enantioselective reactions occur.
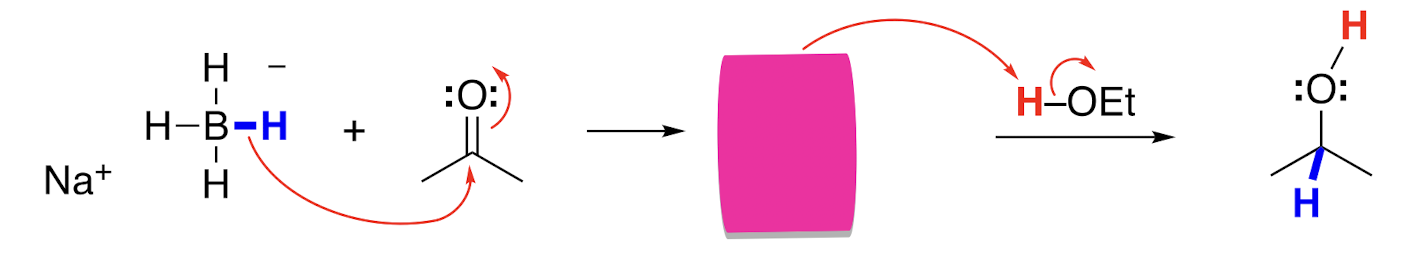
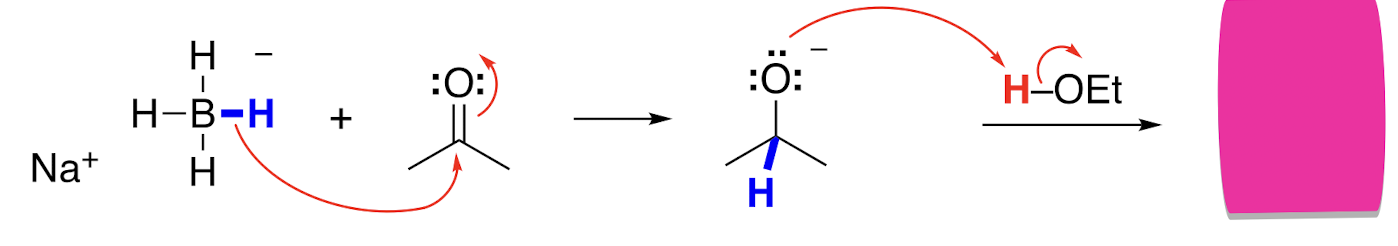
Reduction with NaBH4 intermediate
Csp2 to a Csp3 with a negative oxygen
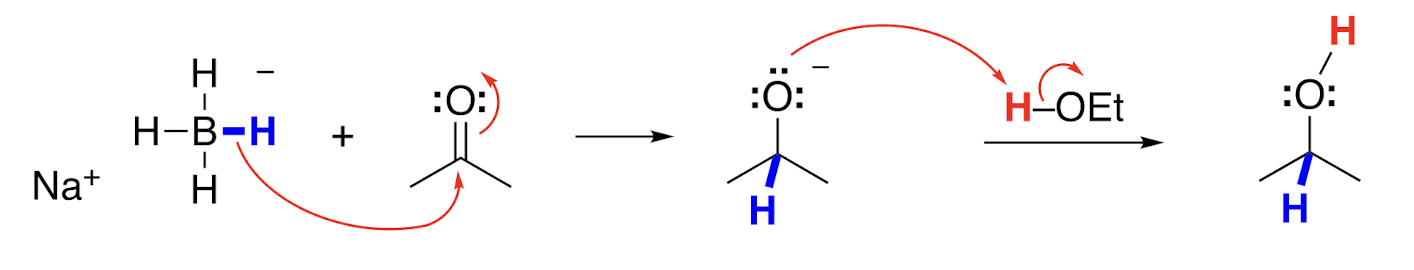
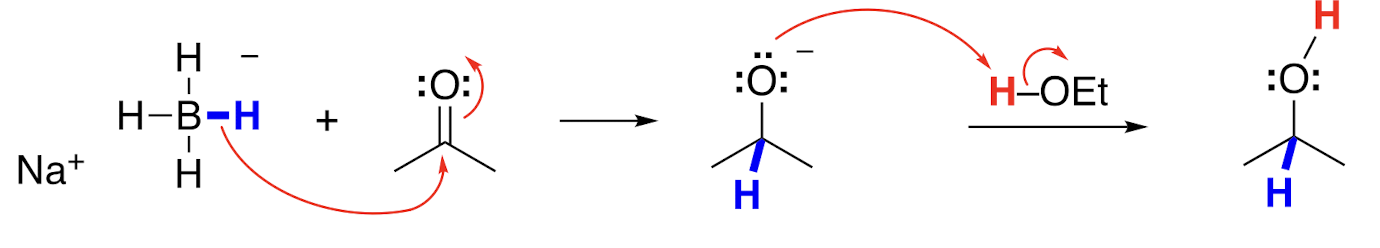
Product of NaBH4 reduction, with ethanol
Ketone to alcohol
What is Rf?
Retention factor for TLC
How to calculate Rf values
Distance of A / Distance solvent travelled
(measured from where the spots are)
TLC mobile phase
Nonpolar organic solvent, travels UP the plate
TLC stationary phase
Thin silica gel layer, polar solid
TLC versus column chromatography
TLC is small scale and Column Chromatography is larger scale
Column mobile phase
Nonpolar organic solvent, travels DOWN the column
Column stationary phase
Silica gel layer in tube, polar solid
Principles of separation (TLC and Column)
Polar substances associate with silica gel and move slower
Nonpolar compounds travel __ and polar compounds travel __.
Nonpolar travel further/faster, Polar travel less/slower.
Equilibrium constant for stationary and mobile phase
K = A(stationary)/ A(mobile)
What does the polarimeter measure?
Rotation of the angle of plane-polarized light by chiral, non-racemic compounds
What is resolution?
Separation of two enantiomers, but is wasteful because half the mass is undesired
What is a prochiral ketone?
A ketone with two different R groups that can become chiral when reduced
TLC is used to determine the __ of a compound, the satus of an ongoing reaction, or as a preliminary means of __.
Purity of a compound, means of identification
How does teh mobile phase travel through the stationary phase?
Capillary action
The more __ the compound, the lower its Rf value.
Polar
A pure compound should produce a __ spot in TLC. More than that in the same vertical line indicates impurity.
A single spot
Column chromatography works well when the compounds and its impurities have __ __ __ in TLC.
Different Rf values
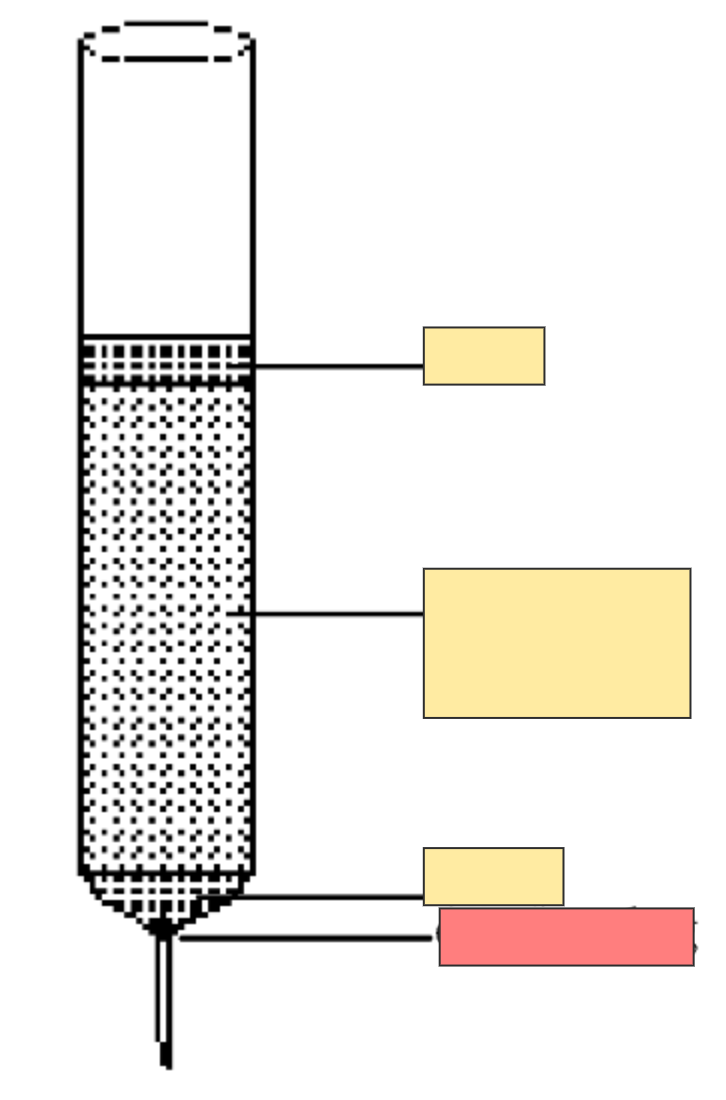
Column chromatography set up
Cotton plug
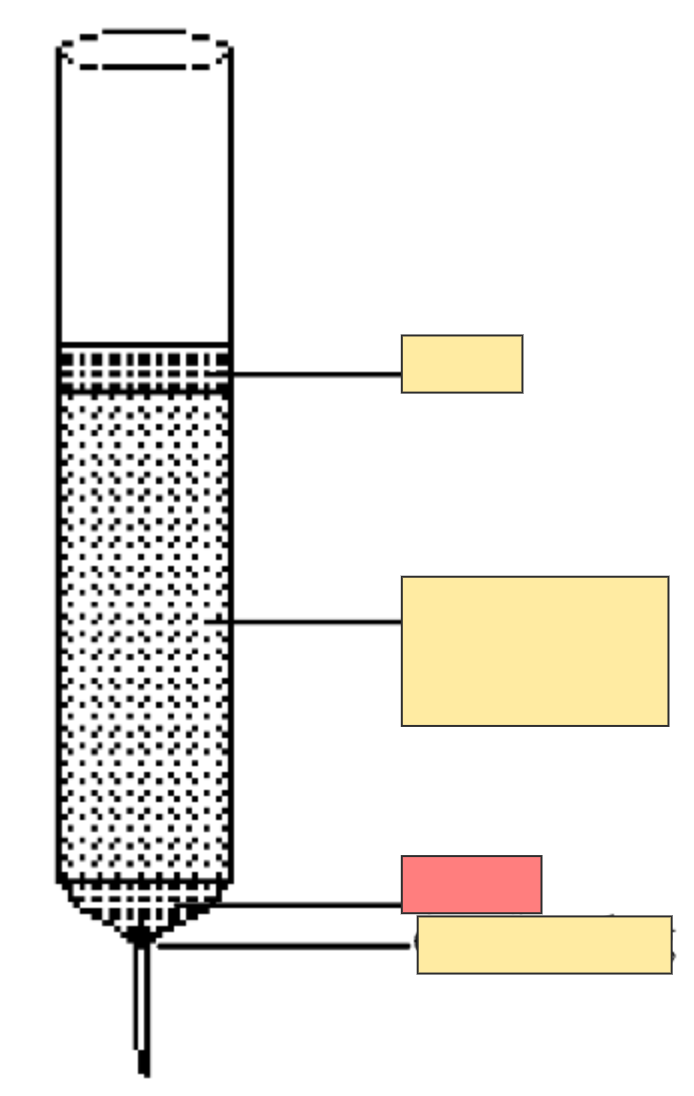
Column chromatography set up
Sand
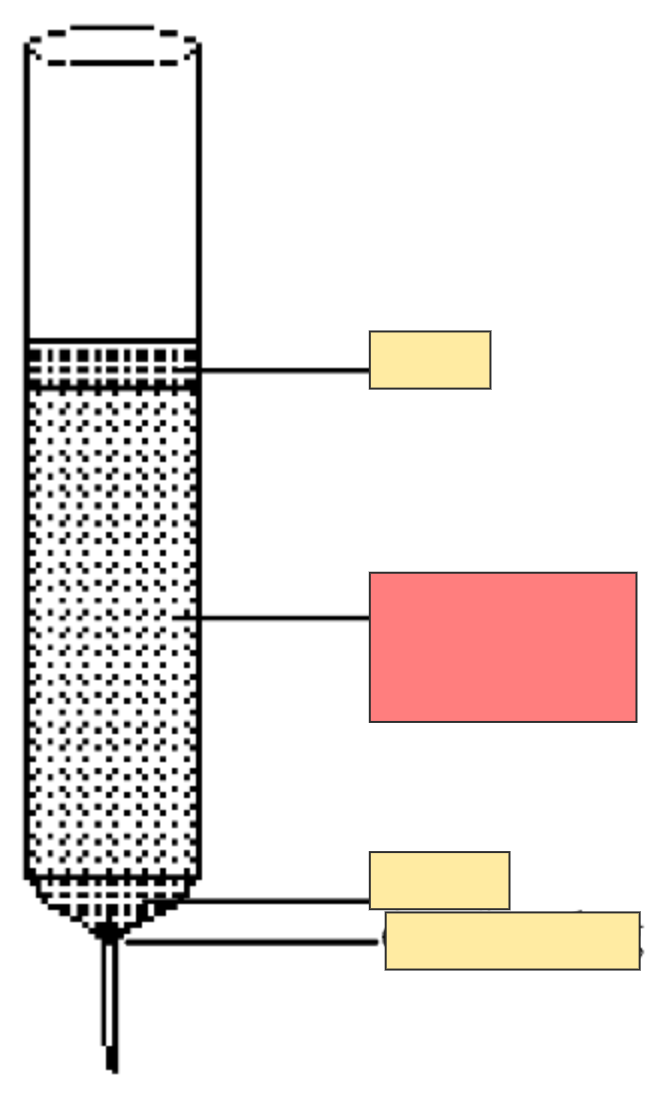
Column chromatography set up
Absorbent silica gel
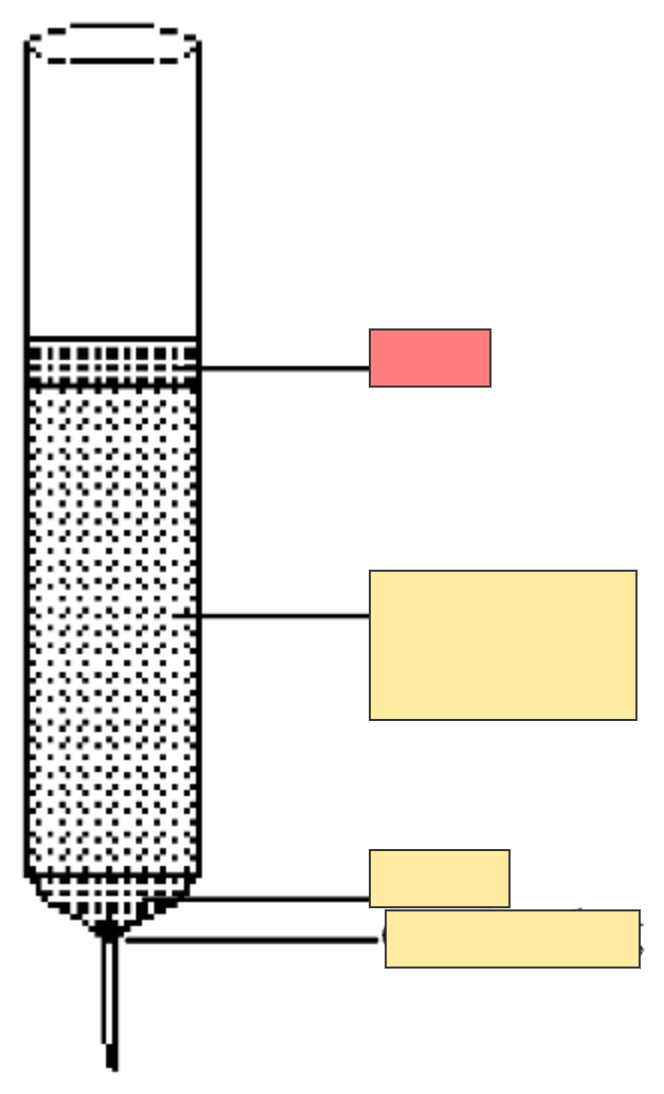
Column chromatography set up
Sand to hold sample
Rf depends greatly on nature of compounds and solvent: no __ values.
No standard values
In aqueous or ethanol solution, NaBH4 behaves as a source of a __ __, adding H- to aldehydes and ketones.
Hydride nucleophile
An addition of a hydride to an aldehyde or ketone makes an __ __ that can accept a proton from water or ethanol to make the product.
Alkoxide ion
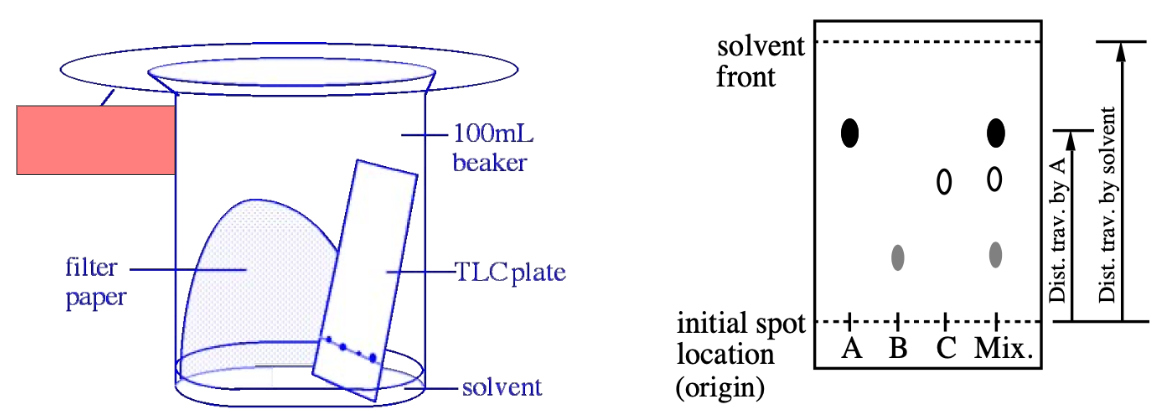
TLC
Watch glass, prevents solvent evaporation
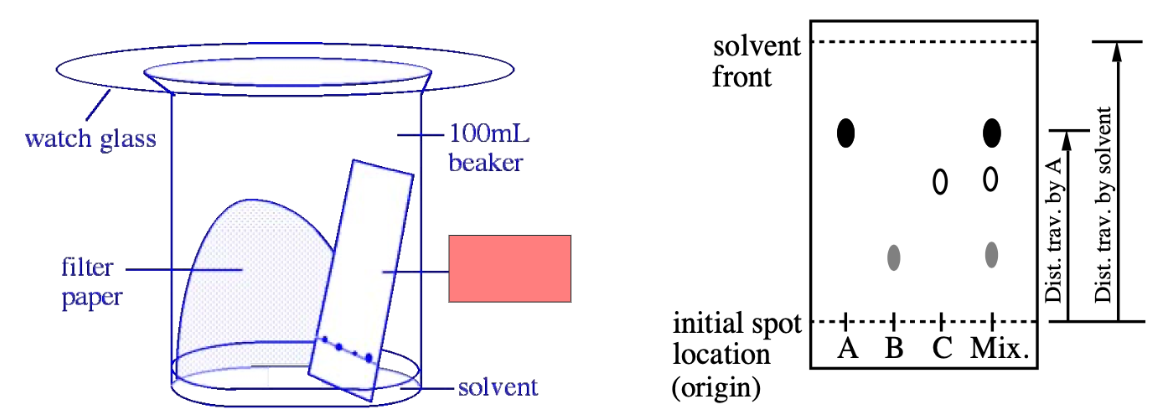
TLC
TLC plate
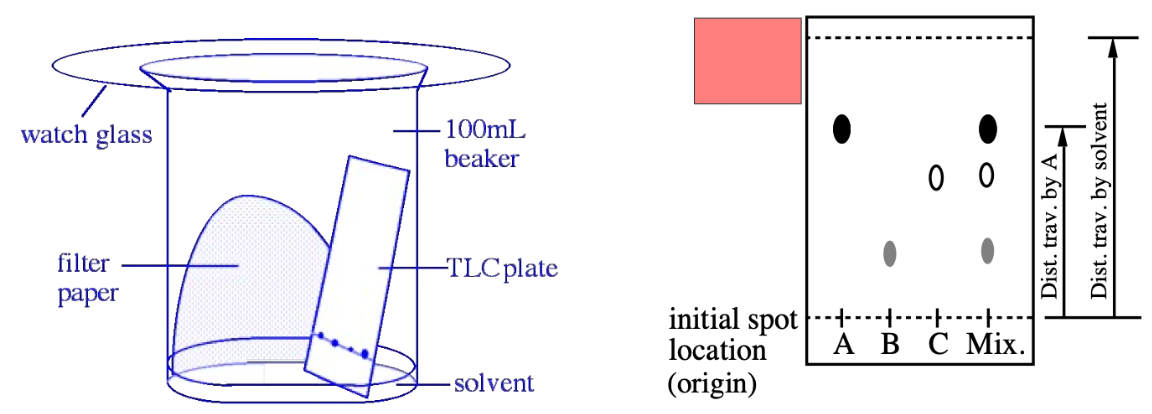
TLC
Solvent front