4.3 Connective Tissue Protects and Supports
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
What are the four functions of connective tissues?
Support, connecting and binding, protection, and transportation.
Embryonic Connective Tissue
All CT derive from the mesodermal layer of the embryo.
Mesenchyme
The first CT to develop in the embryo, all connective tissues are later derived from this one. Clusters can be found around adult tissue and are used for replacement and repair after a connective tissue injury.
Mucous connective tissue (Wharton’s jelly)
A ECT, forms in the umbilical cord, is no longer present after birth.
Connective tissue proper types
Loose connective tissue: areolar, adipose, and reticular; Dense connective tissue: dense regular, elastic, and dense-irregular.
Supportive connective tissue types
Cartilage: Hyaline, fibrocartilage, and elastic; Bone
Fluid connective tissue types
Blood and lymph
Connective tissue proper
Both tissues have a variety of cell types and proteins fibers suspended in a viscous ground substance.
Loose connective tissue
Loosely organized fibers, leaves large spaces in between.
Dense connective tissue
Reinforced by bundles of fibers that provide tensile strength, elasticity, and protection.
Supportive connective tissue
Provide structure and strength to the body, protect soft tissues.
Fluid connective tissue
Specialized cells circulate in a watery fluid containing salts, nutrients, and dissolved proteins.
Fibroblast
Make protein fibers, ground substance, and collagen fibers.
Fibrocyte
A less active fibroblast.
Adipocyte
Cells that store lipids (fats).
White adipocyte
Store fats as a single large drop, low metabolic activity, appears yellow.
Brown adipocyte (in infants)
Store fats as many droplets, high metabolic activity (is thermogenic and therefore breaks down fats, releases metabolic heat), looks brown due to mitochondria.
Mesenchymal cell
Multipotent adult stem cell. Differentiates into any type of CT cell when needed for repair and healing.
Phagocytes
Immune system cells; can ingest foreign substances, microorganisms, and
dead or damaged cells by phagocytosis.
Macrophage
Engulf infectious agents and cellular debris, can be a resident or migrant cell.
Neutrophils
Phagocytic WBC, migrant cell.
Mast cell
Contain cytoplasmic granules that release histamine and heparin, causing vasodilation at the site.
Collagen fiber
Made of fibrous protein, form a long straight fiber. CFs have great tensile strength, resist stretching, and give ligaments/tendons their resilience and strength.
Elastic fiber
Contains elastin, elastin will return to its original shape after being stretched or compressed.
Reticular fiber
Formed from collagen fiber protein subunits, found in reticular tissue of soft organs (Liver and spleen).
Parenchyma
Functional cells, blood vessels, and nerves of an organ.
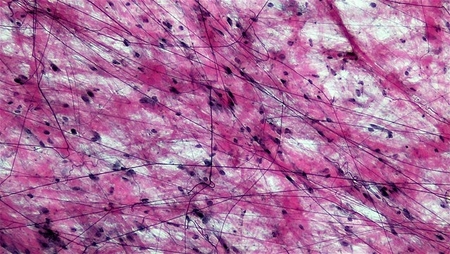
Areolar tissue
Little specialization, it fills the spaces between muscle fibers, surrounds blood and lymph vessels, and supports abdominal cavity organs.
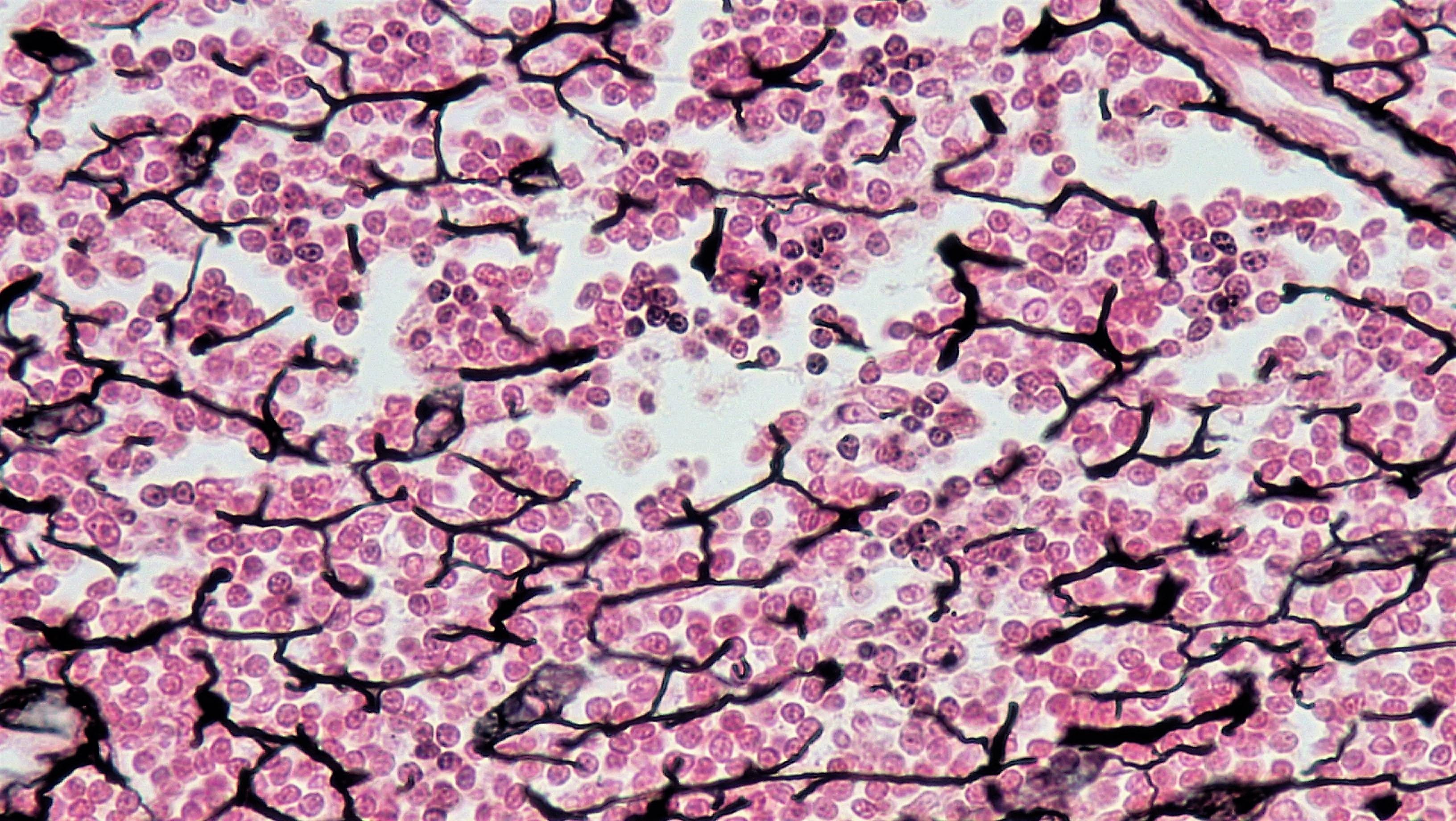
Reticular tissue
Mesh-like web, supportive framework for soft organs such as lymphatic tissue, the spleen, and the liver.
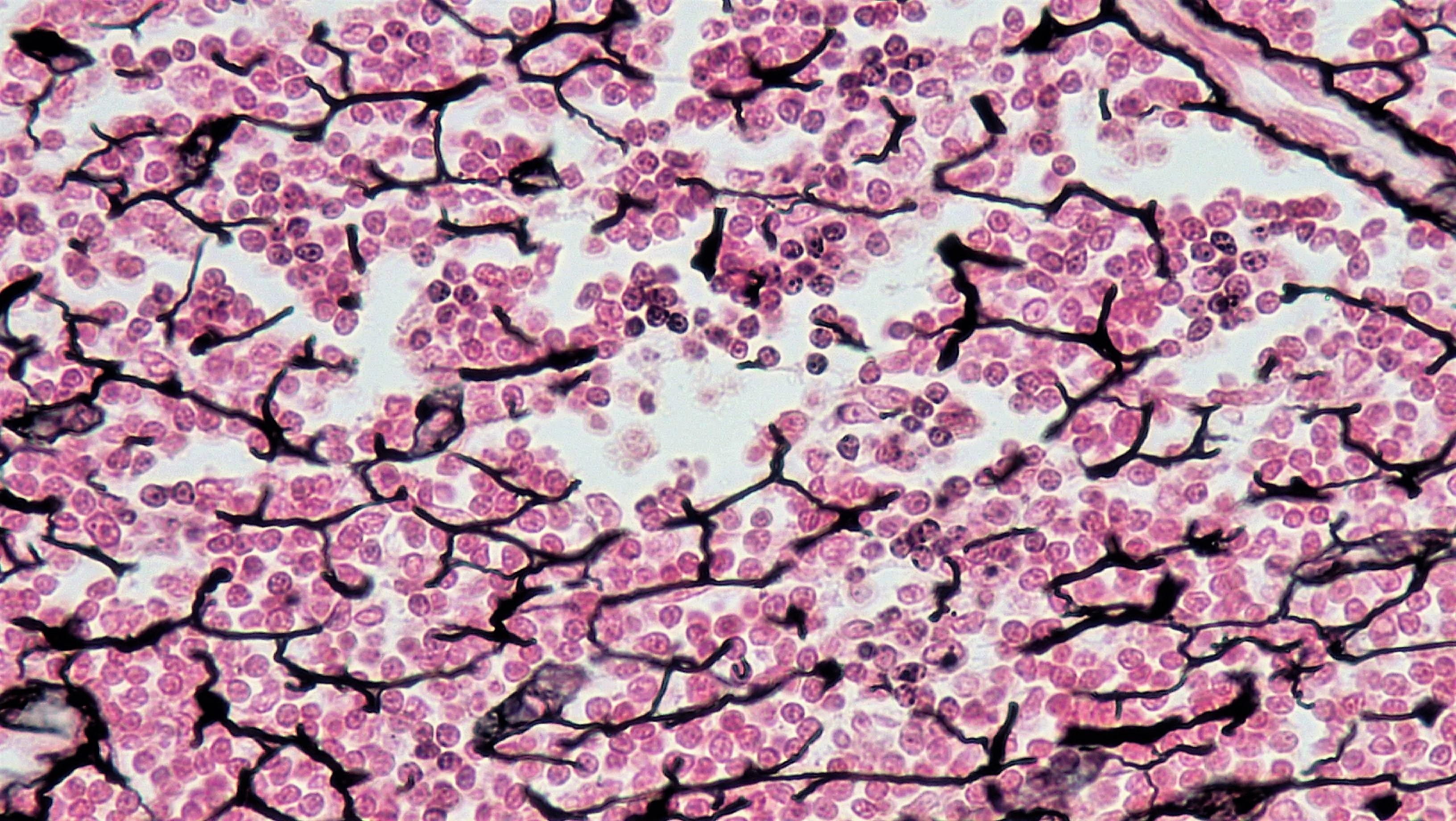
Dense regular
Fibers run parallel, forms ligaments and tendons.
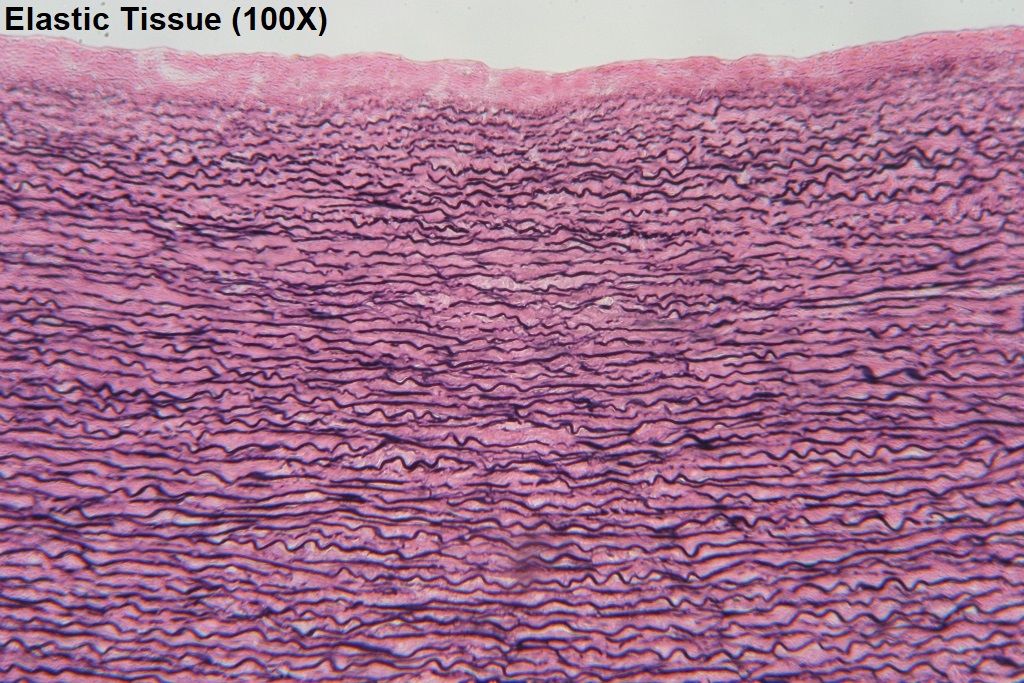
Elastic tissue
Elastin and collagen fibers, allows ligament to return to its original shape after stretching.
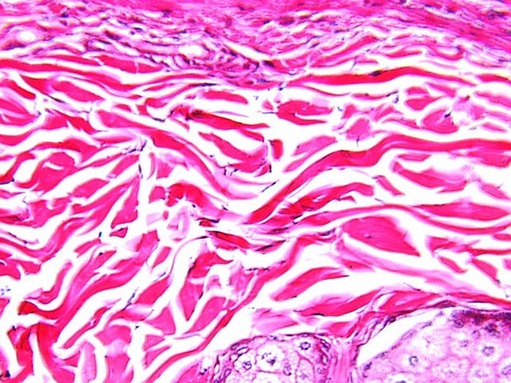
Dense-irregular
Random direction fibers, has greater strength in all directions and less strength in a particular direction. (Dermis of the skin, and arterial walls can regain their original shape after stretching).
Chondrocytes
Cartilage cells, embedded in the cartilage matrix, occupy lacunae. Cartilaginous tissue is avascular, thus it heals very slowly.
Lacuna (Lacunae)
House of cartilage cells.
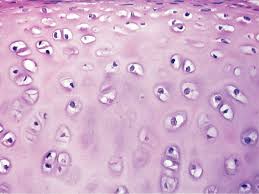
Hyaline cartilage
Short and dispersed collagen fibers. Surface is smooth, HC is strong and flexible. Found in the rib cage, nose, and covers bones where they meet to form moveable joints.
Articular cartilage
Links to the sternum, ribs, frames sections of respiratory tract, and in nose
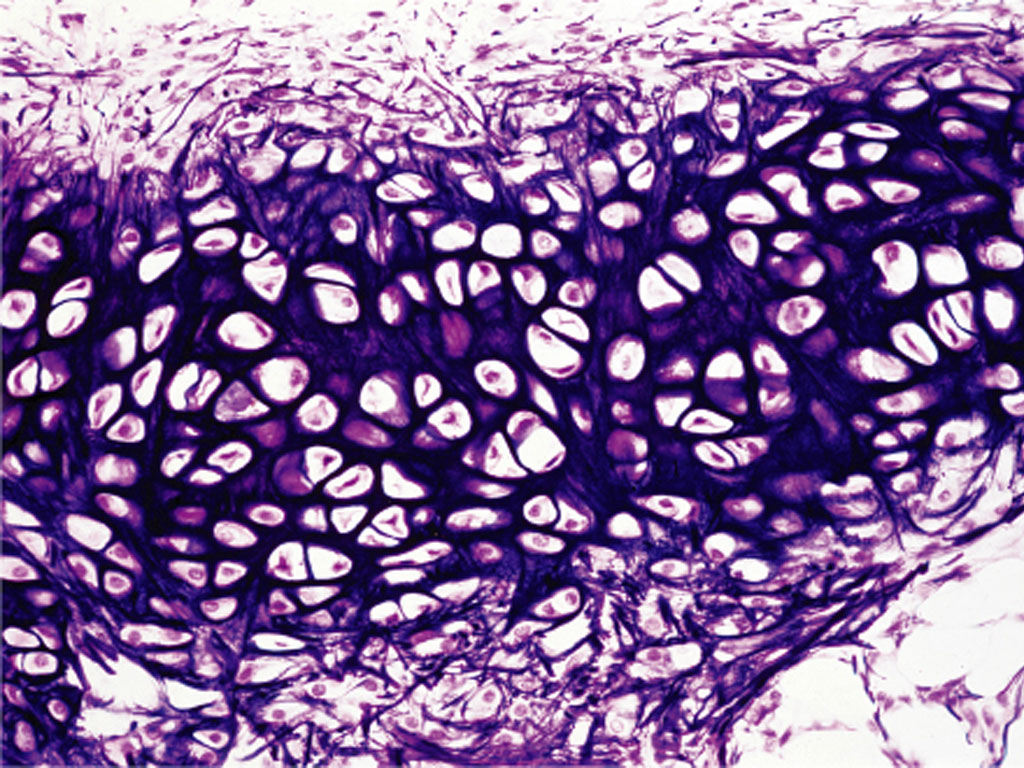
Fibrocartilage
Thick collagen fibers, is therefore tough. Is found in the menisci in the knee joint and the intervertebral discs.
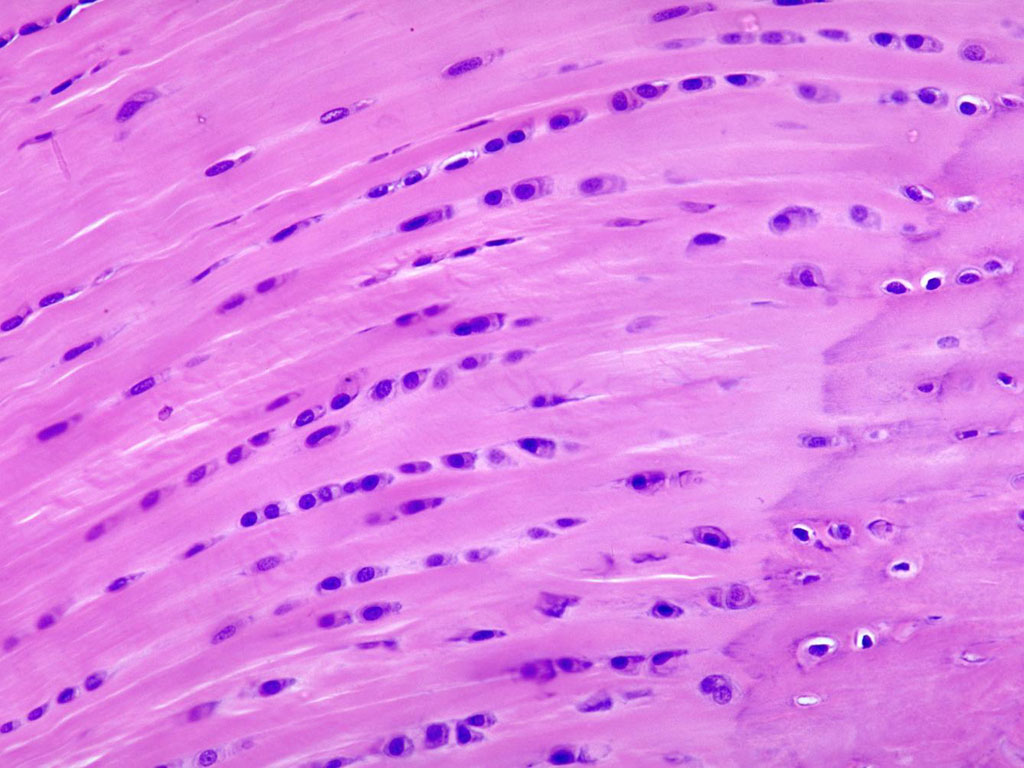
Elastic cartilage
Elastic fibers and collagen, provides rigid support and elasticity. Found in the ear lobes.
Bone
Hardest connective tissue, protects internal organs and supports the body.
What makes up the ECM of bone?
Collage fibers embedded in a mineralized ground substance containing hydroxyapatite (a form of calcium phosphate).
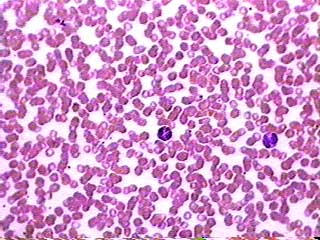
Erythrocyte
RBCs, transport oxygen and some CO2.
Leukocyte
WBCs, defend against harmful microorganisms or molecules. Can sometimes enter adjacent tissues.
Platelets
Cell fragments involved in blood clotting.
Lymph
Contains a liquid matrix and WBCs. L capillaries are very permeable and allow larger molecules and extra fluid to enter the lymphatic vessels.