IB Biology HL - Unit B2.2: Organelles + Compartmentalization
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
Organelle
Discrete cell structure performing specific functions.
Solid organelles
Includes ribosomes and cytoskeleton components.
Single membrane-bound organelles
Includes lysosomes and endoplasmic reticulum.
Double membrane-bound organelles
Includes nucleus and mitochondria.
Cell wall
Non-organelle structure providing support to cells.
Cytoskeleton
Non-organelle structure maintaining cell shape.
Cytoplasm
Non-organelle fluid filling the cell.
Compartmentalization
Separation of cellular processes into distinct areas.
Ultracentrifugation
Technique for separating cell components by density.
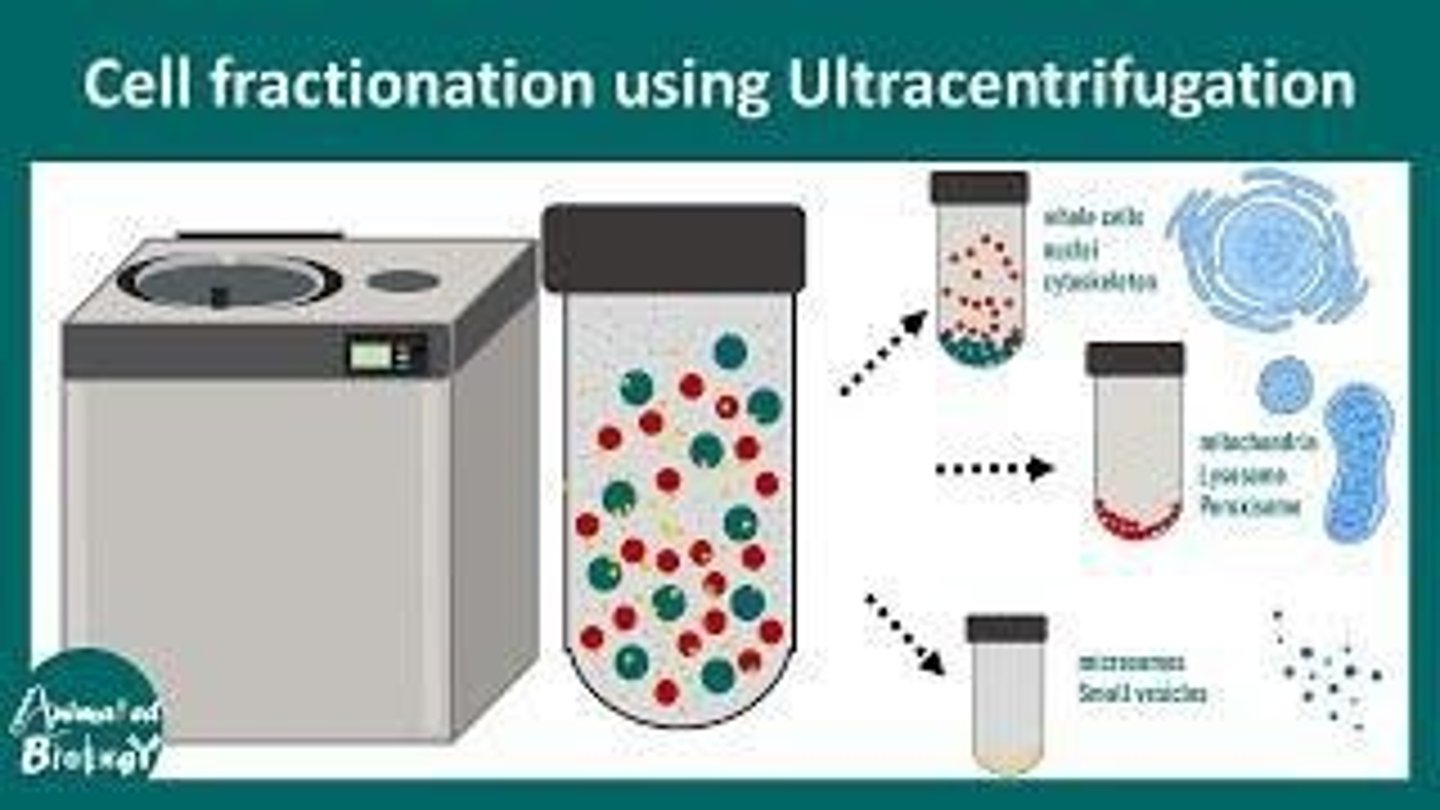
Cell fractionation
Process of isolating organelles from cells.
Differential centrifugation
Method separating particles based on size and density.
Transcription
Process of synthesizing RNA from DNA.
Translation
Process of synthesizing proteins from mRNA.
Eukaryotic cells
Cells with compartmentalized organelles and nucleus.
Prokaryotic cells
Cells without a defined nucleus or organelles.
Gene expression regulation
Control of how genes are expressed in cells.
Post-transcriptional modification
Editing mRNA before translation occurs.
Ribosomes
Sites of protein synthesis in cells.
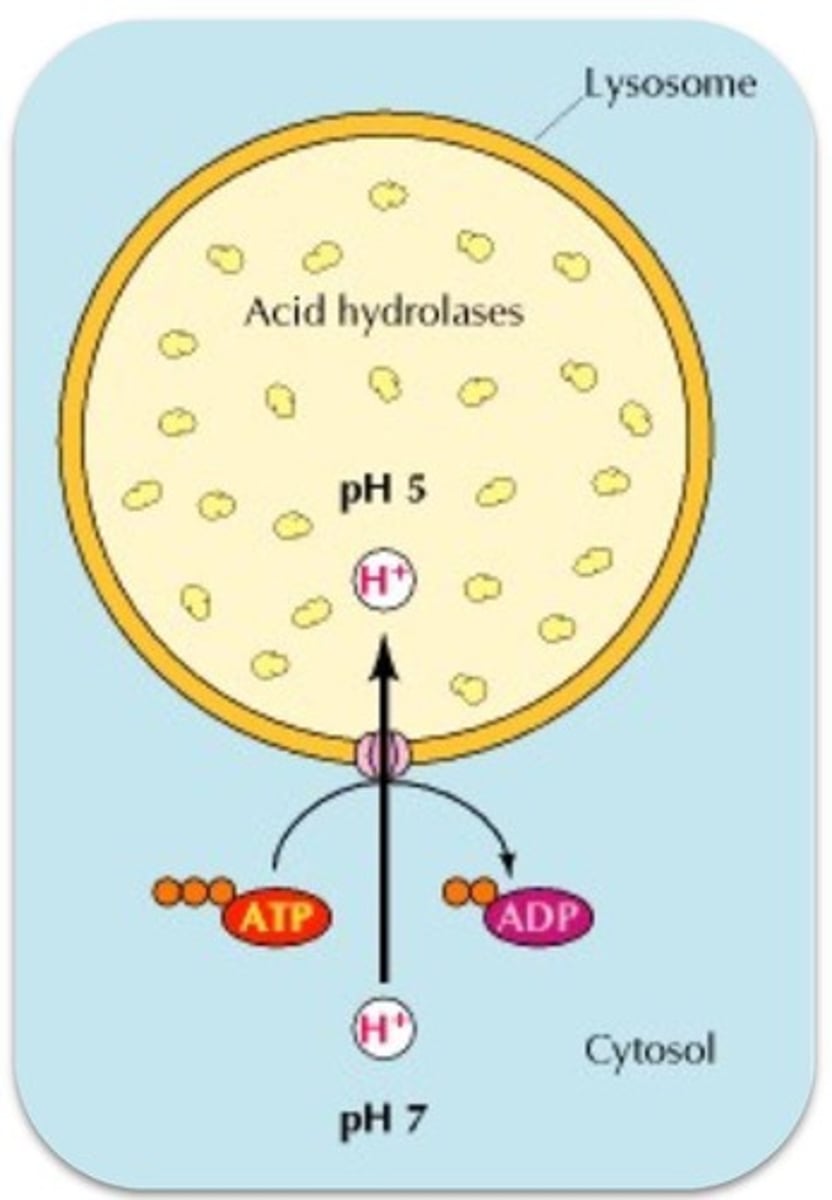
Lysosomes
Organelles containing digestive enzymes.
Mitochondrial function
Involves energy production through cellular respiration.
Chloroplasts
Organelles responsible for photosynthesis in plants.
Nobel Prize for Cell Organelle Research
Awarded in 1974 for significant discoveries in cell biology.
Post-transcriptional modification
mRNA alterations before leaving the nucleus.
Gene expression regulation
Controls cellular response and specialization.
Compartmentalization
Formation of membrane-bound organelles in cells.
Lysosomes
Organelles containing enzymes for macromolecule breakdown.
Acid hydrolases
Enzymes in lysosomes active at pH 5.
pH difference
Cytoplasm pH is 7; lysosomes pH is 5.
H+ ion pumping
Maintains acidic environment in lysosomes.
Phagocytic vacuoles
Isolate engulfed particles for digestion.
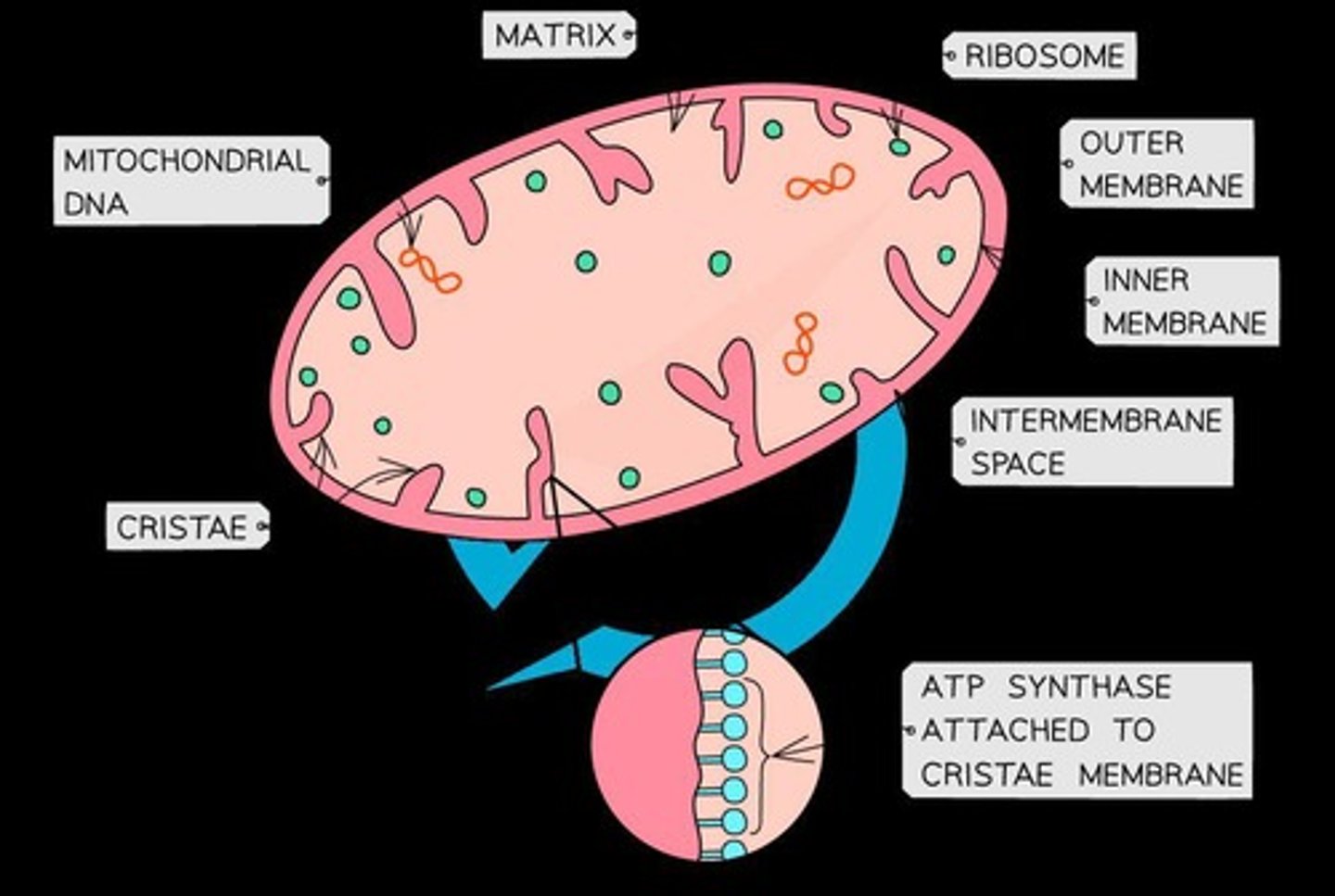
Mitochondrion
Organelle for ATP production via aerobic respiration.
Outer membrane (mitochondrion)
Separates mitochondrion from cytoplasm.
Inner membrane (mitochondrion)
Contains enzymes for oxidative phosphorylation.
Intermembrane space
Holds protons for chemiosmosis in mitochondria.
Cristae
Folds in mitochondria increasing surface area.
Matrix (mitochondrion)
Contains enzymes for the Krebs cycle.
70S Ribosomes
Enable mitochondria to synthesize some proteins.
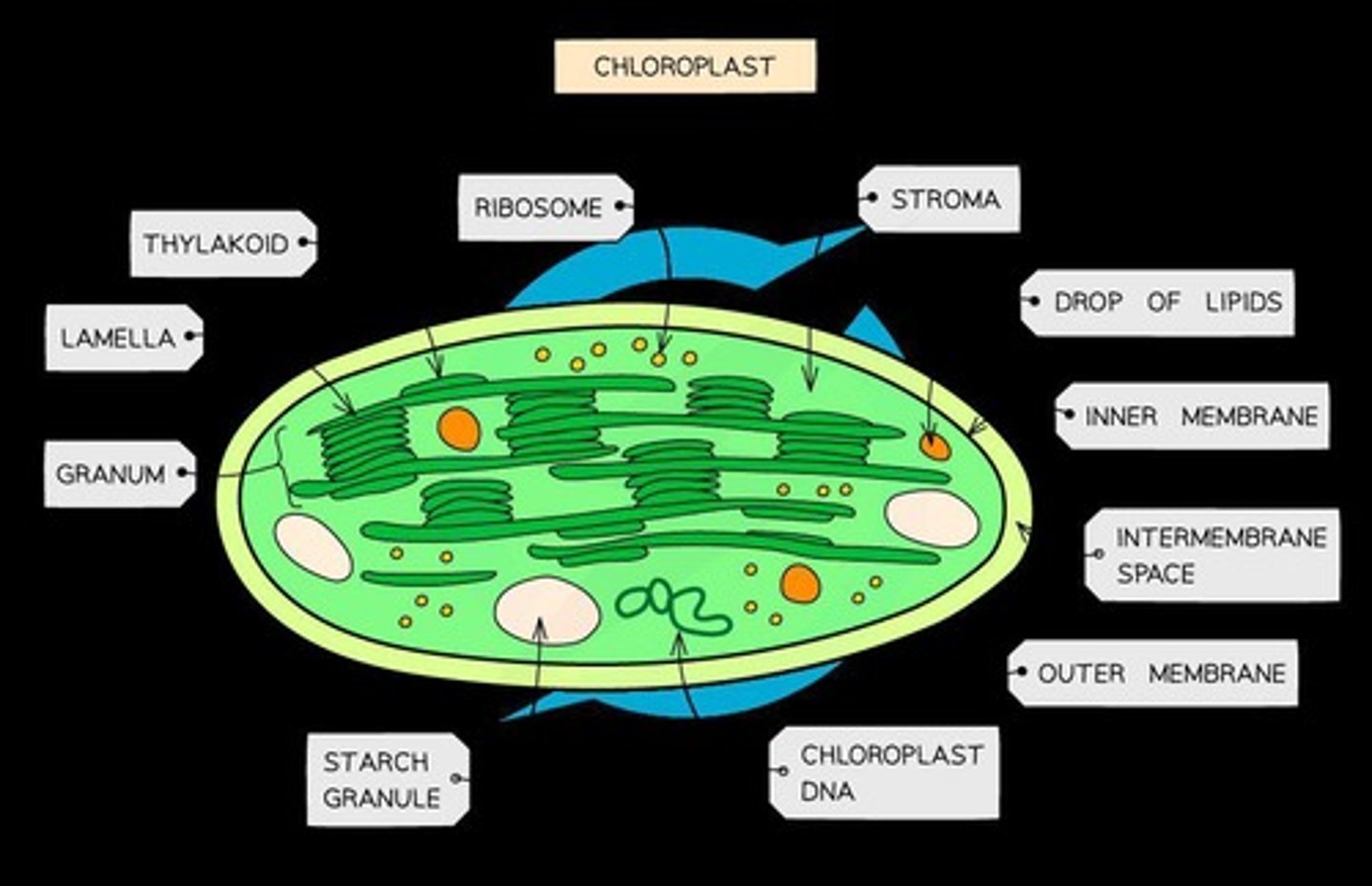
Chloroplast
Organelle for photosynthesis in plant cells.
Thylakoid membrane
Contains chlorophyll for light-dependent reactions.
Photosystems
Capture light energy during photosynthesis.
Stroma
Fluid containing enzymes for the Calvin cycle.
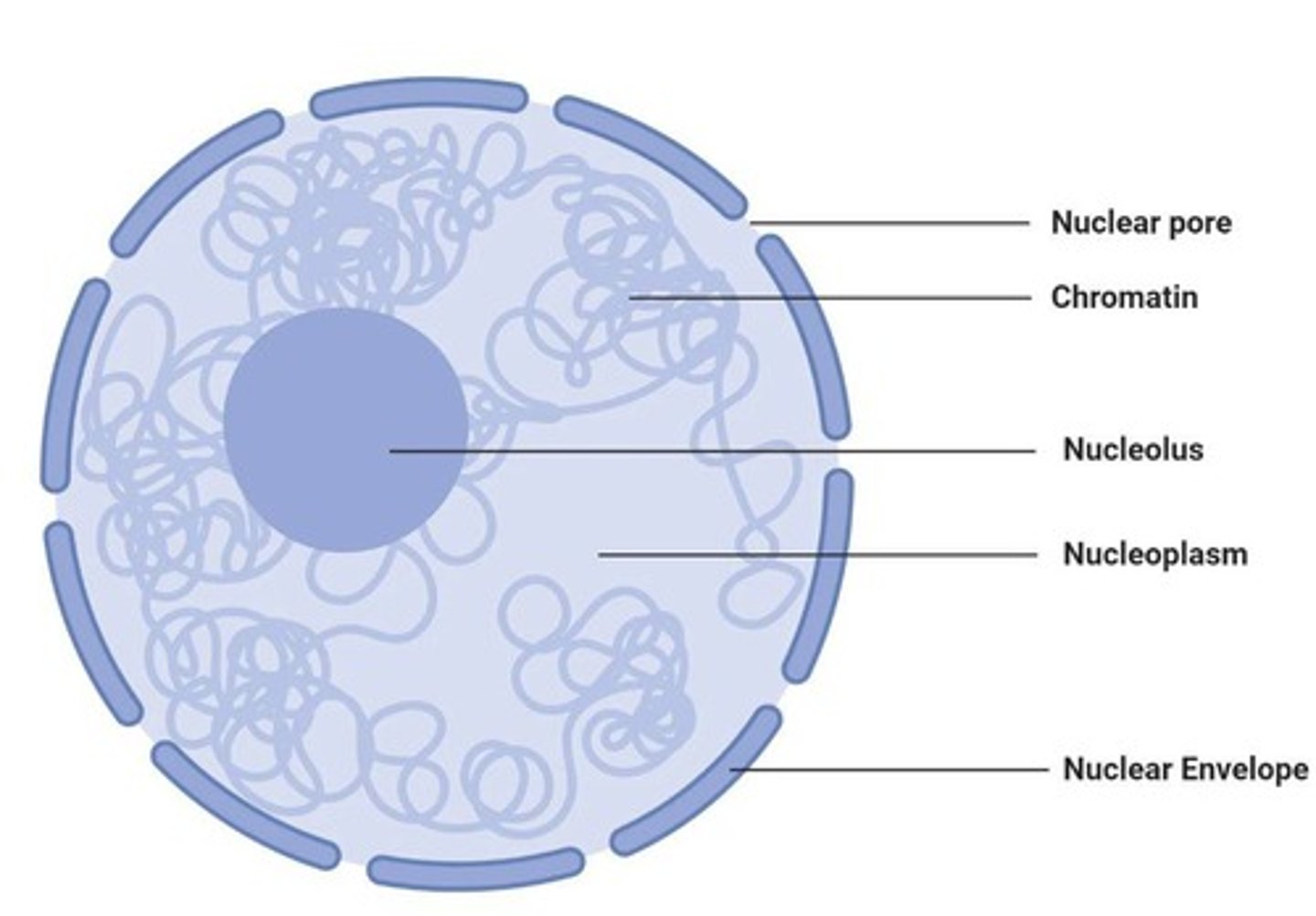
Double membrane (nucleus)
Nuclear envelope with nuclear pores for transport.
Nuclear pore complexes
Selective passageway for molecules in nucleus.
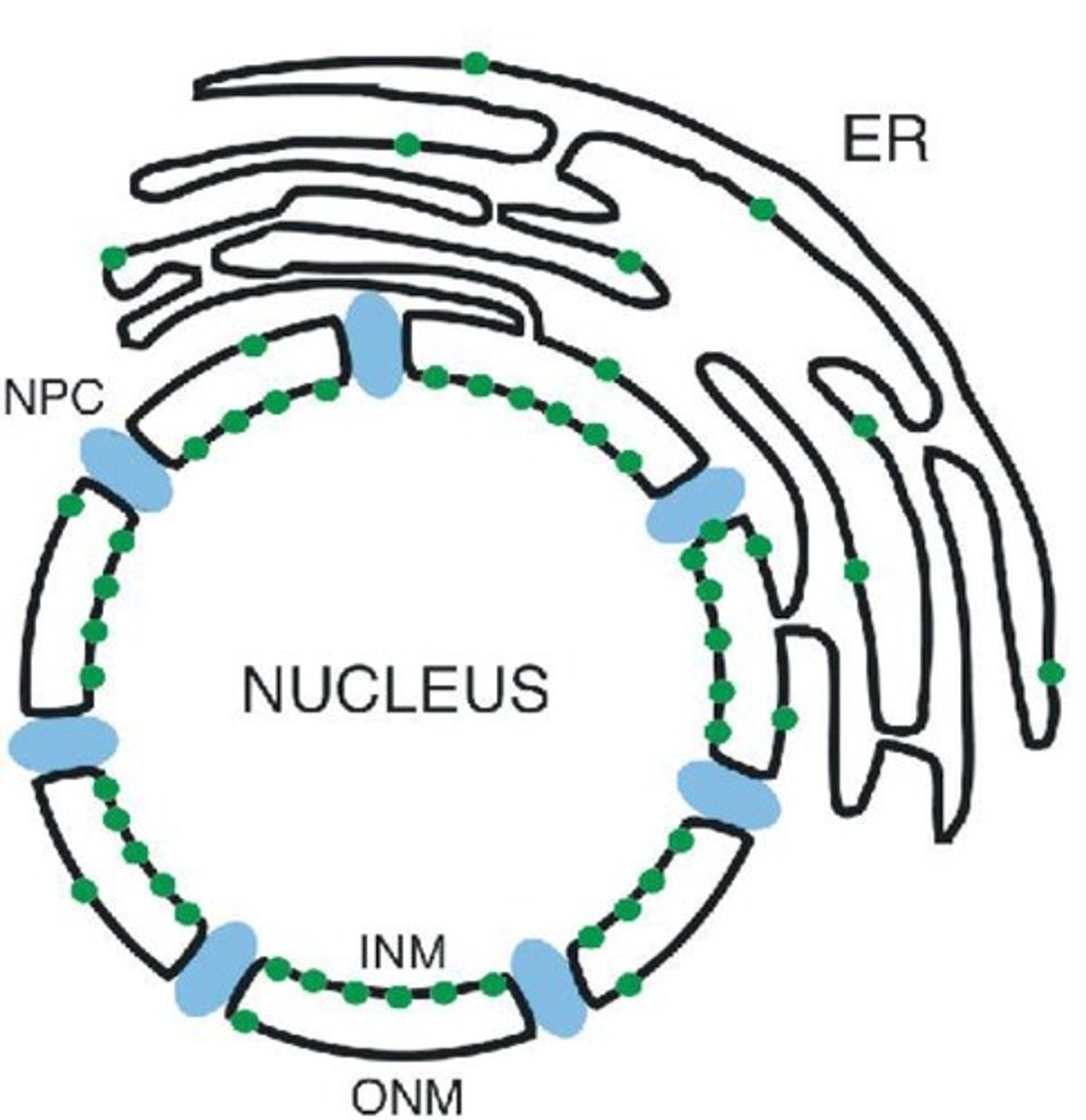
Nuclear membrane dynamics
Breaks down and reforms during cell division.
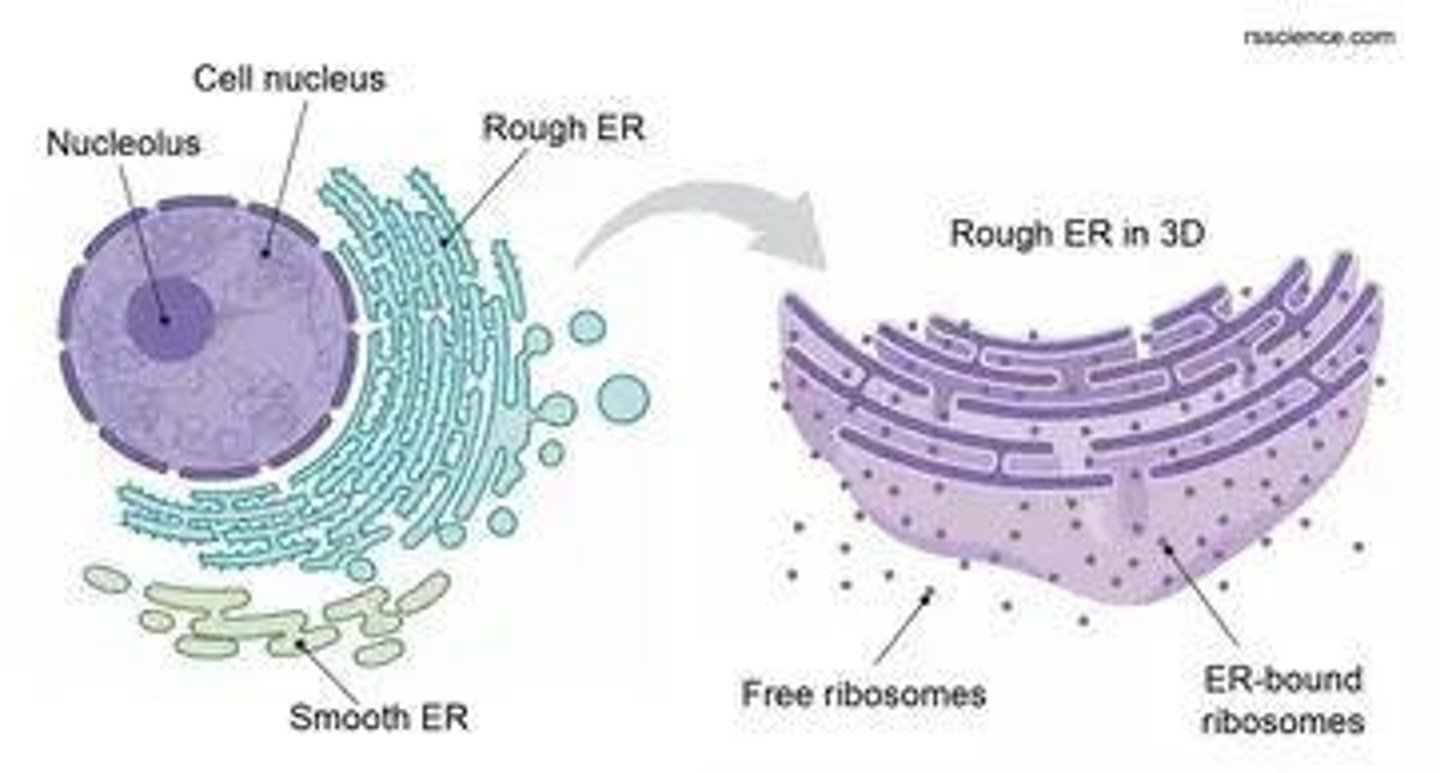
Ribosomes
Cellular structures that synthesize polypeptides.
Free Ribosomes
Ribosomes that float in cytoplasm, synthesize internal proteins.
Bound Ribosomes
Ribosomes attached to rough ER, synthesize export proteins.
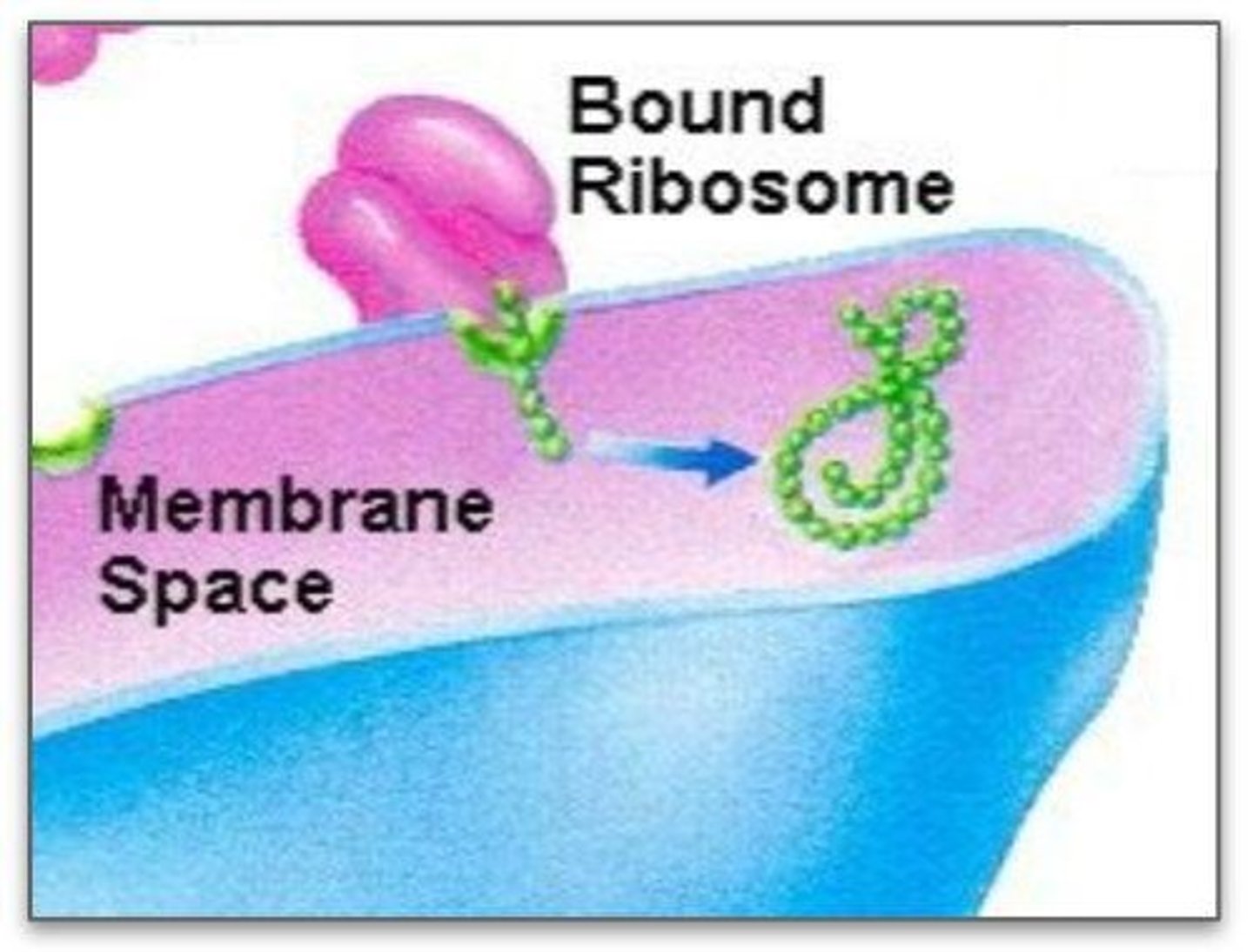
Polypeptide Chains
A sequence of amino acids forming proteins.
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
Membrane system involved in protein and lipid synthesis.
Rough ER
ER with ribosomes, synthesizes proteins for export.
Golgi Apparatus
Stacked sacs modifying and packaging proteins and lipids.
Cisternae
Flattened membrane-bound sacs in the Golgi apparatus.
Glycoproteins
Proteins with carbohydrate groups added for cell functions.
Transport Vesicles
Vesicles that carry molecules to the Golgi apparatus.
Exocytosis
Process of exporting materials from the cell.
Endocytosis
Process of importing materials into the cell.
Vesicles
Membrane-bound sacs transporting substances within cells.
Clathrin
Protein that coats vesicles during their formation.
Lysosomes
Vesicles containing enzymes for macromolecule digestion.
Secretory Vesicles
Vesicles that transport materials to the plasma membrane.
Endomembrane System
Network of membranes producing and transporting molecules.
Phospholipid Bilayer
Double layer of phospholipids forming cell membranes.
Quaternary Structure
Complex protein structure formed by polypeptide chains.
Integral Membrane Proteins
Proteins embedded in the plasma membrane.
Vesicle Formation
Process of vesicles budding from organelles.
Fluidity of Membranes
Ability of phospholipid bilayers to change shape.
Cell Membrane
Barrier controlling entry and exit of substances.