BIOL111 invertebrates + vertebrates
1/158
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
159 Terms
metazoa
multicellular organisms → animals
animal proportion
89% of eukaryotic species
biomass percentage
plants= 82%
animals only 1%
all other life = 17%
difference of biomass in plant vs animal
animals get around
not as tall as trees
no need for supporting structures
animal sister group
choanoflagellate - from molecular phylogenetics
what is an animal?
member of sister group of choanoflagellates
eukaryotic
heterotrophic
multicellular
mobile at some stage of life
diplontic life cycle
no cell walls
diploid somatic cells
heterotrophic
use-preformed organic materials as energy and carbon source
modes of feeding
predators
detritivores
omnivores
filter feeders
herbivores
parasites
other heterotrophic groups
prokaryotes
protists
plants
fungi
tissues
groups of similar cells organized into a single units
can function together as organs to complete complex tasks
protozoa
used to be called unicellular animal
not a monophyletic group
have no close phylogenetic relationship with animals
metazoa
animal taxa
protozoa examples
ciliates
chaos/amoeba
plasmodium, causes malaria
type of structural support
hydrostatic skeleton
exoskeleton
endoskelleton
hydrostatic skeleton
organism perform simple but efficient movement
limited possibility for the attachment of limb
dependence of a humid environment
exoskeleton
firm, rigid structure
non living covering
in arthropods, doesn’t grow with animal
motling
ecdysozoans
endoskeleton
rigid structure inside the body
vertebrates = living tissue
some invertebrate= non living
movement
reduces competition, enhances genetic diversity, expands distribution range
exceptions of diploid somatic cells
male honeybee
rotifers → female dominant
characters unique to animals
neurons & nervous system
muscle cells
germ layers - blastula& gastrula stage
evoluted early in the animal phylogenetic tree but not at its very root
prorifera
clade name of sponges
earliest animals to appear in the fossil record
9000 species mostly marine
sessile as adults, motile as larvae
primitive features - specialized cells but no tissues or organs
endoskeleton
clade
a monophyletic group or taxon
includes the most recent common ancestor of a group of organisms and all its descendents
are barnacle animals?
semi parasitic
crustaceans
exoskeleton
nauplius larva
barnacle larvae
allows them to spread → motile
common stage of many crustaceans
diplontic
majority of life cycle spent on diploid stage
cleavage
multiple rounds of rapid cell divisions - mitotic
→ formation of many cells from one cell (morula,blastula)
gastrulation
in folding,invagination
formation of embryonic tissue layers
formation of head-tail axis
morula
hollow sphere- filled with fluid
before gastrulation
32-64 cells
endoderm
“inner skin”
→ digestive tract and repiratory
ectoderm
epidermis
nervous system
mesoderm
not in eveyr animal
mosrt internal organs
muscle cells
skeletal systems
gonads
endoskeleton of sponges
spicules and a network of elastic fibers for support
sponge eating
create strong water current for filter feeding
choanocytes = collar cells, choanoflagellate like cells
heterotrophic filter feeders
spicules
rigidity in extracellular matrix
non organic matter
SiO2
CaCO3
spongin
proteins in extracellular matrix
flexible support
sponge extracellular matrix
non. cellular space
collagen and glycoproteins
some support provided
bath sponge
high spongin content
glass sponges
high SiO2 content
sponge asexual reproduction
fragmentation - not self induced , brought by a wave of predatord
internal budding - clone of parent
nO MEIOSIS
sexual reprodction of sponge
no gonads
cells and eggs are produced in chanocytes or amoebocytes
broadcast sperm
sperm is trapped by choanocytes of a female sponge
fertilized eggs develop in extracellular matrix
motile larvae
cnidaria species
jellyfish
sea anemones
corals
hydrozoans
cindaria
11 k species
mostly marine
microscopic to many meters long
simple nervous system and muscular tissue
mesoglea
act as hydroskeleton of cindarians
provides structural support
xtracellular matrix
made of collagen and proteoglycans
cnidarian orientation
polyp - sessile
medusa - motile
medusa
motile
usually sexual stage
has mouth and tentacles
polyp organization
endoderm cells = taking up food
external “ectoderm like layer”
have sensory neurons - for light / temp
nematocytes → shootout poison
radial symmetry of polyp
oral to aberal
cindarians nervous system
simple nerve net - diffuse
no integration of signal
sensory information can come in from any direction
how do cnidarians gain energy?
carnivorous, inject prey with toxins and capture the prey
extracellular digestion in gastrovascular cavities
corals and anemones can obtain a large proportion of energy from symbiotic algae - dinoflagellates
hydrozoa /hydra
freshwater animal
no medusa stage - polyp
moves by gliding, floating
2-5mm
portugese man of war
tropical, subtropical oceans
colonial polyps specialized for different function
gonozoiids , gastrozooids, dactylozooids
gaz filled float
tentacles contain cnidoctes
up 50 m long tentacles
pneumatophore
gas float at the top of portigese man of war
freshwater jellyfish
hydrozoa
from asia
invading gatineau river
scyphozoa
true jellyfish
large amount of mesoglea
some nematocyst strong enough to be felt by humans
prey on fish larvae and zooplankton
important for leatherback turtles
cubozoa
box jellyfish
dangerous, lead to paralysis / death
anthozoa
heterotrophic animals
agregation of polyps
sea anemones
retract tentacles in defense
tentacles have cnidocytes
predatory animal
mutualistic relationships with particular species of fish and shrimps
corals
form colonies of myriad of genetically identical polyps
secrete calcium carbonate to form hard skeleton that becomes the framework of coral reefs
mutualistic relationship with dinoflagellates
coral bleaching
serious recent ecological problem
zooxanthellae expelled → coral dies
brought by pollution, temp rising, bacteria causing disease
ctenophores
marine predators
“comb jellies”
shared characteristic of cnidaria and ctenophora
diploblastic
radial symetry
gelatinous body
tentacles
nerve and muscle cells
unique features of ctenophora
bioluminescence
8 rows of ctenes , comb-like ciliated plates for locomotion
colloblasts- adhesive cells
bilateria
all animalia excluding first two branches
platyhelminthes/flatworms
25k species
aquatic/terrestrial
“free living” or parasites
1mm/10m
cephalization
concentration of neurons and sensory structures at anterior end of animal
sense organs probe environment
enables directed locomotion
cephalization is linked to directed movement
flatworm sensory structures
mechanoreceptors
chemoreceptors
photoreceptors
flatworm nervous system
neurons at anterior end
primitive brain - two cerebral ganglia
longitudinal nerves
turbellaria/ planarians
free living platyhelminths - the only one
very few in freshwater/soil
msot in sea water
parasitic platyhelminthes
monogenea
trematodoa
cestoda
monogeneans
ectoparasites : mostly on frogs, reptiles, cepalotods
trematoda
flukes, endoparasites
schistosomiasis
caused by parasitic trematodes
common in asia, africa and south america
disease rarely causes death but damages organs and slows development
cestoda
tapeworms, endoparasites
host-specific
no mouth , no digestive system
protective cuticle forms around embryos and terminal proglottids break off, passed via feces
scolex
suckers/hooks of tapeworms
proglottids
reproductive segments of tapeworms
major evolutionary developments within bilateria
mesoderms forms secondary body cavity
fate of the blastopore
spiral vs radial cleavage
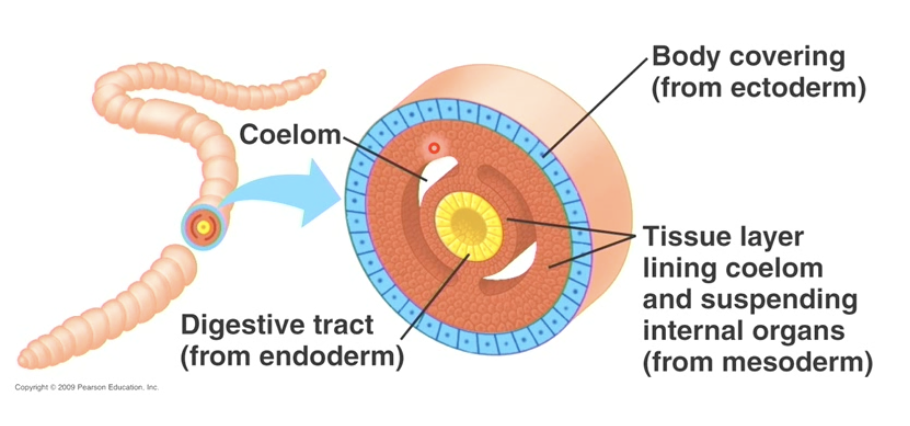
the coelom fromation
secondary body cavity
blastocoel is primary body cavity
cells of mesoderm occupy primarily body cavity, then split in a way to themselves form a secondary body cavity.
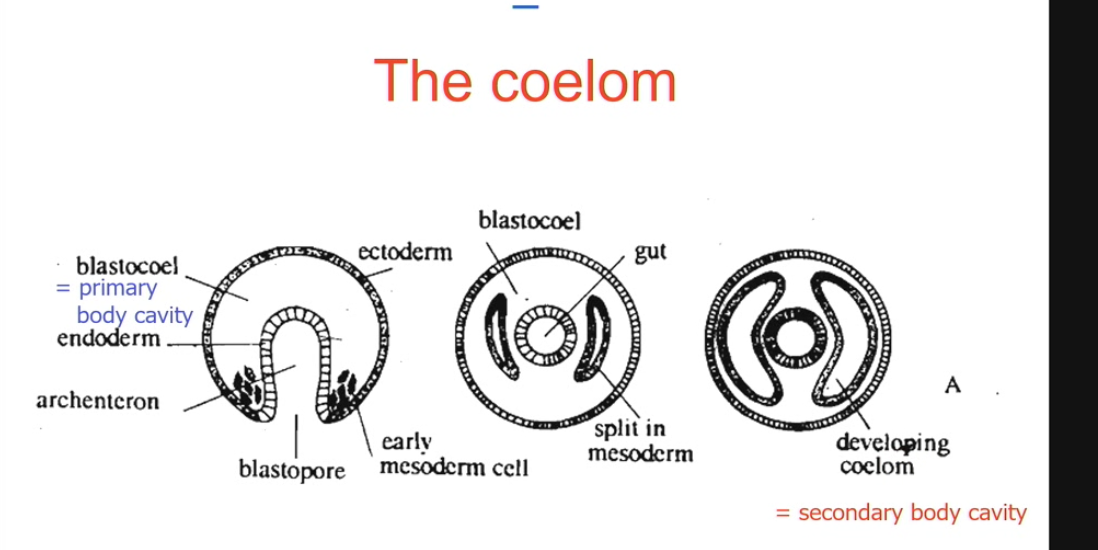
annelida coelum
secondary layer can be filled with liquid
useful if you want to build external skeleton
protostomia
blastopore develops into mouth, anus forms later
deuterostomia
blastopore develops into anus, mouth develops later
radial cleavage
new cells that are formed are smaller than old cells
new cells lay exactly on top of old cells
animals that do spiral cleavage
mollusca
annelida
platyhelminths
trocophore larva
a planktonic larval dispersal life stage common in both marine annelida and mollusca
annelida
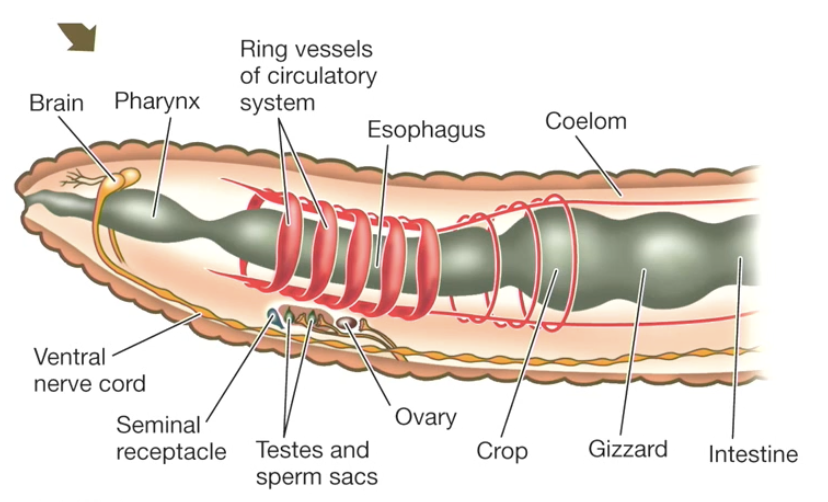
segmented worms or ringed worms
body divided into metameres
17 species
aquatic and terrestrial
0.5-3m
coelom, used as a hydrostatic skeleton
metamerism of an annelid worm
linear repetition of similar body segments
→ observed externally and internally → nerves, blood vessels, excretory organs
regional differentiation
segments are similar but each can be modified
brain, pharynx, specialization of gut organs
advantages of metamerism
multiple copies of organs
efficient nervous control - ganglion in each segment and faster control
increases body size by unit repition
regeneration
annelid NS
anterior brain
ventral nerve cord
segmental ganglia
polychaeta / bristle worms
mainly marine
detritivores, filter feeders
many have ees, palps, tentacles
parapodia- muscular flaps with setae , locomotion and respiration
fan worms
hydrothermal vents - symbiosis with chemosynthetic bacteria
oligochaeta
terrestrial and few aquatic
10 k species
no parapodia, few setae
light sensitive cells
hermaphroditic
clitellium
organ from oligochaeta reproduction
secretes a cocoon for embryo development - no specialized larvae stage
hirudinea /leech
mainly freshwater
ectoparasitic and carnivorous
no setae
anterior and posterior sucker
hermaphroditic - no larval stage, clitellium
mollusca
85 k species
2nd largest animal group after arthropods
both terrestrial and aquatic
mollusca characteristics
bilateral symmetry , triploblastic , protostomes with reduced coleom
trochophore larvae
major groups include polyplacophora, gastropoda, cephalopoda
unique molluscan traits
mantle
radula
foot
radula
rasping mouth organ for food uptake
mantle
dorsal sheet of tissue
secretes shell or spicules
forms mantle cavity with gills - continuous with the sea for gas exchange
foot of mollusca
ventral muscular organ for creeping movement