Power Up - Year 9 Science
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
ecosystem
Involves the interaction of biotic and abiotic things in a given area, contains habitats where organisms live e.g. forests, deserts, coral reefs
community
Is made of different populations interacting with eachother e.g. forest (trees, bears, funghi)
population
a group of the same species of organisms
e.g. a herd of zebras, a school of fish
biotic factors
living factors
abiotic factors
non living factors
Leaf diagram
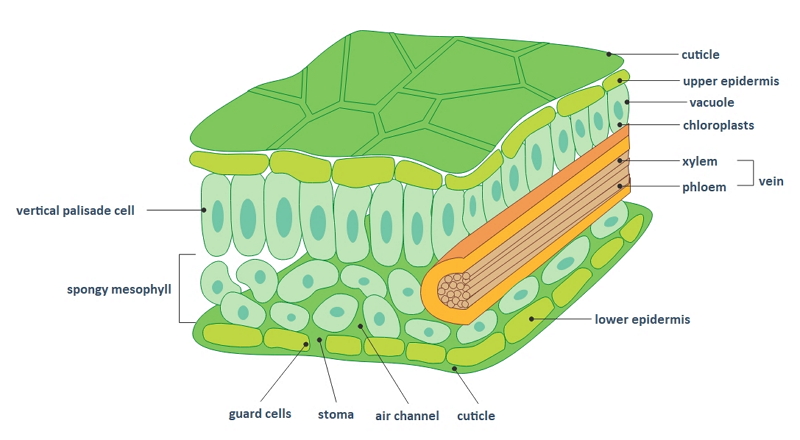
Leaf structure and functions
Palisade mesophyll - contain chloroplast
Stomata - allow carbon dioxide to enter and oxygen to be released
Spongy mesophyll - gaseous exchange
Phloem - transports food from the leaves to the rest of the plant
Xylem - transports water from the roots to the leaves
Guard cells - open and close the stomata
Process of photosynthesis
photosynthesis occurs in the chloroplasts of the mesophyll. Chloroplast absorbs light energy from the sun, when combined with carbon dioxide and water, it traps this energy in the chemical bonds of glucose.
Chemical equation
CO2+H2O = C6H12O6O2
Carbon dioxide + water with the sunlight make glucose + oxygen
Cellular respiration
The process of converting stored energy into usable energy. It occurs in the mitochondria.
Process of cellular respiration
The energy stored in plants (as glucose) is released as a molecule called ATP
Chemical equation
Oxygen + glucose = carbon dioxide + water + ATP
aerobic respiration
Produces more ATP
Occurs in mitochondria
Produces carbon dioxide and water as a waste product
Requires oxygen
Used when heart rate and breathing rate rise
anaerobic respiration
Doesn’t require oxygen
Occurs in cytoplasm
Used in the first 1 - 2 minutes of exercise
Produces less ATP
Produces lactic acid as a waste product (animals)
aerobic equation
Glucose + oxygen = Carbon dioxide + water + ATP
anaerobic equation
Glucose = lactic acid + ATP
(lactic acid broken down by liver)
Anaerobic respiration (funghi, yeast and bacteria)
Glucose = ethanol + carbon dioxide + ATP
food chain
feeding relationship
food web
Shows all the connections between the food chains, it has multiple paths
Energy loss and transferal
Only ten percent is passed from each level
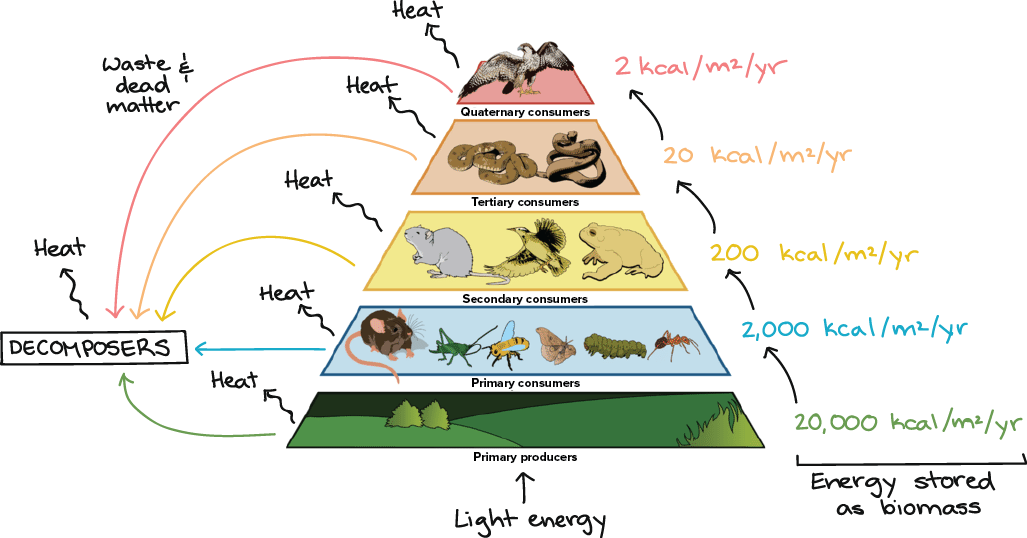
producers vs consumers
Producer - organisms that can photosynthesise
Consumer - Primary consumers eat producers
Secondary consumers eat primary consumers
role of decomposers
Break down dead organic matter into simpler inorganic substances.
Factors that disrupt ecosystems
Natural disasters and human activities
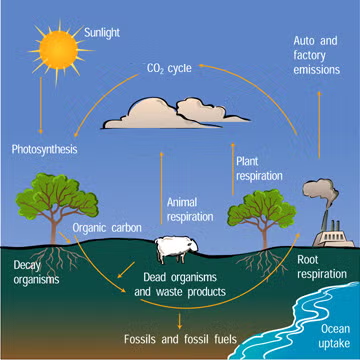
The Carbon Cycle
Carbon cycle examples
CO2+H2O = C6H12O2
C6H12O6+O2 = H2O+CO2+ATP