Art History World Art Before 1400 BCE Midterm 1
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
76 Terms

Artist, Name, Location, Time
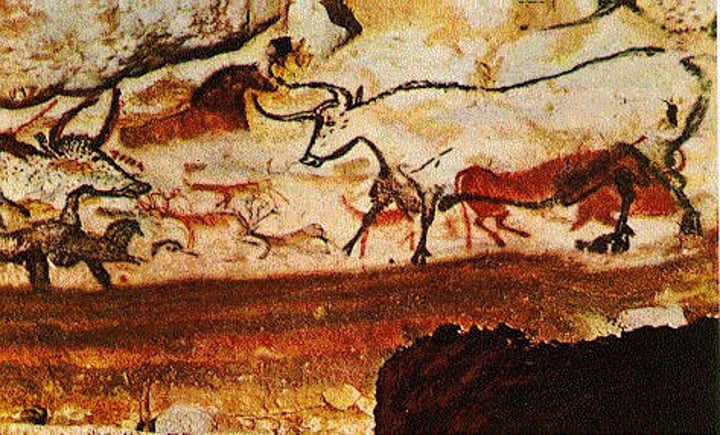
Hall of the Bulls
Lauscaux Caves, France
15000BCE, Paleolithic
Painting on Limestone
Discovered in the 1940's
Created over thousands of years as seen by overlapping paintings

What key characteristics define the Paleolithic period?
42000-6500 BCE
From earliest known things we define as art, to the rise of settled communities
Small handheld figures
Made from local materials
More female than male
More human than animal
Lack of detailed anatomy
Exaggerate female sex characteristics
Less imaginative
Often naked
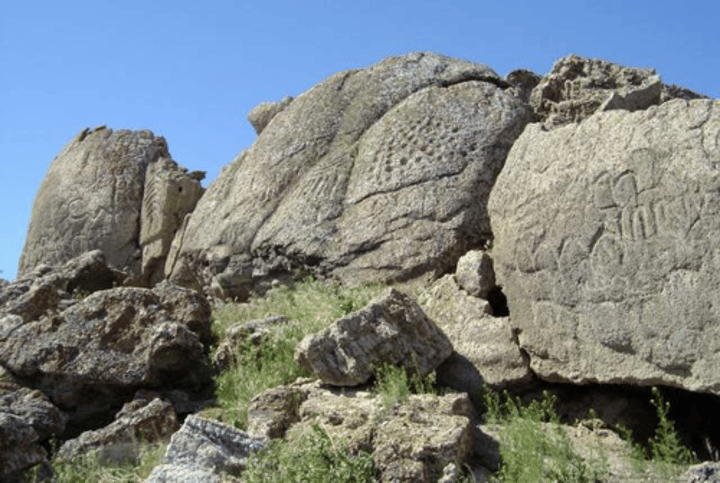

Artist, Name, Location, Time
Petroglyphs at Winnemucca Lake
Nevada, Arizona
14000BCE, Paleolithic
Oldest known petroglyphs
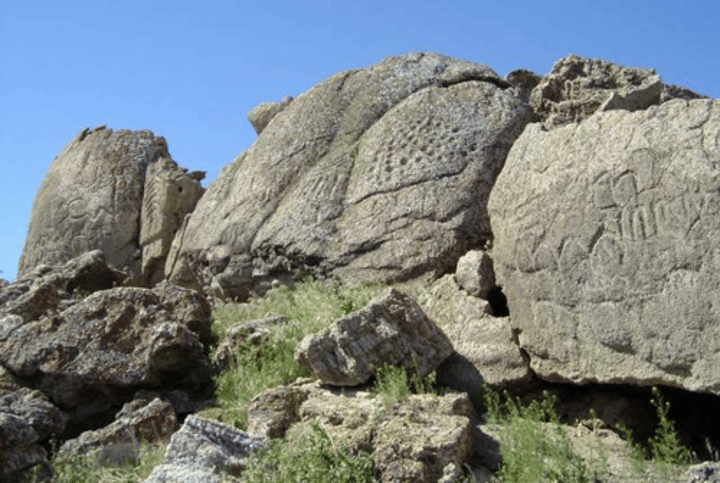

What are petroglyphs?
Incisions or carvings on rock surfaces. They are hard to date due to weathering.

Artist, Name, Location, Time
Woman of Willendorf
Austria
Paleolithic, 24000 BCE
Carved Limestone & Ochre
Thought to be symbol of fertility


Artist, Name, Location, Time
Lion Headed Figure
Found in Germany
38000 BCE
Paleolithic
Carved from mammoth tusk
Earliest example of something we know is thought rather than seen - imagination

What is Mesopotamia?
An umbrella term for many different city states in the region of Iraq.

Artist, Name, Location, Time
Ruins of Anu Urka
Warka, Iraq
3300-3000 BCE, Mesopotamian (Sumerian)
Ziggurat temple
What is a ziggurat? What is it used for?
A ziggurat is a temple of Mesopotamian culture. They resemble pyramids in the tall, steeped structure, but had different usages. Ziggurats are a place of worship and prayer. They are built upwards to be closer to the gods. They were viewed as a connection between ground and gods.

Artist, Name, Location, Time
Inanna Vase
Warka, Iraq
3300-3000 BCE, Mesopotamiaan
36 inches tall

Artist, Name, Location, Time
Enheduanna Disc
2200 BCE, Mesopotamian (Akkadian)
What are key figures of Mesopotamian Art?
Less exaggerated, more realistic anatomy
Lots of clay work, but not necessarily pottery (engravings, carvings, imprints)
Clear stories
Clear Religious figures
Characters shown on flat ground, split into registers
Ziggurats
feet off ground lines- motion

Artist, Name, Location, Time
Queen Puabi's Funeral Ensemble
2500 BCE, Mesopotamian
Made of gold, lapis lazuli, carnelian

Artist, Name, Location, Time
Lyre with Bull's Head
2500 BCE, Mesopotamian
Depicts the epic of Gilgamesh (written by Enhedunna)
What is an epic?
A long form poem.
What are megalithic structures?
Large stone structures that are one of the markings of the Neolithic period.

Artist, Name, Location, Time
Stonehenge
England
3100-1600 BCE
Neolithic
One of the best known megalithic structures
Burial site

Artist, Name, Location, Time
Iniskim Umaapi (Majorville Medicine Wheel)
Neolithic
Alberta - Bassano
4500-3200 BCE-still in use
What key characteristics define the Indus River Valley Civilizations period?
2600-1900 BCE
Metal work, clay pots, systems of writing
Less religious, more interested in play
Lots of jewellery
Small figures
Seals
Carving
Bronze casting
Seems to worship females more

Artist, Name, Location, Time
Seated Mother Goddess
Mergarh (Pakistan)
3000-2500 BCE, Indus Valley

Artist, Name, Location, Time
Harappan Terracotta Fragments
Pakistan
3200-2500 BCE, Indus Valley
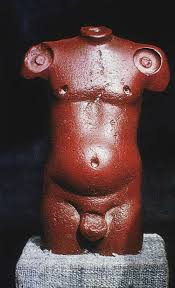
Artist, Name, Location, Time
Harappa Torso
Pakistan
2000 BCE, Indus Valley


Artist, Name, Location, Time
Indus Girl Dancing
2500 BCE, Indus Valley
Bronze casting
What is high relief?
a carved panel where the figures project with a great deal of depth from the background, appearing 3D.

How can you tell later Mesopotamian art from earlier art?
Later art maintains the same ideas as earlier art (ground lines, bulgy eyes, beards, side profiles, hieratic scales) but show better motion and time, look more complicated, and contain more layers. The feet off the ground lines how movement, motion and sense of time

Artist, Name, Location, Time
Queen of the Night Relief Statue
1800-1750BCE, Mesopotamian (old Babylonian)
Ishtar (Inanna) in her hybrid form
What are votive figures?
Votive Figures
2700BCE, Mesopotamian
Offering figures that represent eternal prayers when people are outside the temple

What are cylinder seals?
Small cylinders that imprint a story.

Artist, Name, Location, Time
Ishtar Gate
675BCE, Mesopotamian (Babylonian)
Controlled city access and decorated with depictions of major deities.
Who is Inanna?
Inanna is a goddess of sex, fertility, war, and harvest, who was worshipped in different cultures with different names.
What are Sumerians accredited with?
Wagon wheel, pottery wheel, metal casting, time in increments of 60, crops
Wrote in clay slates with pictographs (cuneiform writing)
What is low relief?
When an artwork appears to be popping out a little but still looks like a 2D image. Used to decorate walls often by flat rock sculptures that would often have also been painted.

What are steles?
Upright stone slabs that tell stories, often commemorating death, using hierarchical scales. The use of these scales was outside Mesopotamian norms.

Artist, Name, Location, Time
Victory Stele of Naram-sin
2225 BCE, Mesopotamian (Akkadian)
6 feet 6 inches tall
What key characteristics define the Neolithic period?
Roughly 6500 - 2000 BCE
Megalithic structures
Marked by people moving together
Evidence of larger groups coming together and working on larger structures that require cooperation
Who was Enheduanna?
She was the oldest known literary figure. She was a poet, princess and priestess dedicated to the Moon Goddess Nanna (variation of Inanna). The first found epic was written by her. She is accredited with the connection of variant gods across similar Mesopotamian cultures.
What is Ochre?
A naturally occurring reddish stone. The pigment can be applied to stone to make "art".

Artist, Name, Location, Time
Vessel With Goddess (Inanna?)
2400 BCE, Mesopotamian
What are some important things to know about Ancient Egypt?
3000 - 330 BCE
Polytheistic (belief in multiple deities)
Strong beliefs towards the continuation of life through the afterlife
Pharoah/King's protection in the afterlife was vital for the community's wellbeing.
What is a register?
System of organizing space; in vases, specifically horizontal bands used to divide patterns.
What is iconography?
The traditional images or means of representing a subject; also the study of meaning of images.

Artist, Name, Location, Time
Inanna Vase
Warka
3200-3000 BCE, Mesopotamian
Divided into registers, which allows it to have a narrative
What are Ka statues?
Statues that are intended to provide a resting place for the ka of the person after death.
What is Ka?
The soul, spirit or life force of a person

Artist, Name, Location, Time
Great Pyramids of Giza
2500 BCE, Ancient Egypt
Pyramids of three rulers: Khufu, Khafre and Menkaure

Artist, Name, Location, Time
Khafre Ka Statue
2500 BCE, Ancient Egypt

Artist, Name, Location, Time
Menkaure and Queen
2475 BCE, Ancient Egypt

Artist, Name, Location, Time
Seated Scribe
2400 BCE, Ancient Agypt

Artist, Name, Location, Time
Judgement of Hunefer Before Osiris
1285 BCE, Ancient Egypt
What are some key aspects of the Persian Empire?
550 BCE- 330 BCE
Cyrus the Great asserts control over Mesopotamia and eventually parts of Pakistan, Egypt, India and Greece
Creates a massive centralized state, at its height estimated to rule 40% of the world's population and be the wealthiest state in the world at that time.
Has distinct start and end date

Artist, Name, Location, Time
Persepolis- Ruins of Ceremonial Complex
518 - destroyed 300 BCE, Persian Empire
Marvdash

Artist, Name, Location, Time
Low Reliefs from Apadana (Audience Hall) of Darius and Xerxes
500 BCE, Persian
Low relief

Artist, Name, Location, Time
Relief sculpture from Palace at Susa
500 BCE, Ancient Persian
Glazed brick

Artist, Name, Location, Time
Architects: Kallikrates and Iktinos.
The Parthenon
Athens
447-432 BCE, Classical Greece
Dedicated to Athena
What three periods do we divide Ancient Greece's Cultural ID into?
Archaic: 600-480 BCE
Classical: 480-323 BCE (which can sometimes be divided even further into Early, High and Late classical
Hellenistic: 323-31 BCE

Artist, Name, Location, Time
Metropolitan Kouros (young male)
600 BCE, Archaic Greek
Terracotta

Artist, Name, Location, Time
Berlin Kore
570-560 BCE, Archaic Greek
Female version of Kouros
How do Kores differ from Kouros?
Kouros were the idea of masculine almost sex symbols during this time when it was seen as normal for an older man to "claim" and "educate" a younger male. Kores are the female equivalent of Kouros. Since women were not depicted as sex symbols, Kores are always clothed. They are often found in temples, making offers to or even representing goddess.

Artist, Name, Location, Time
Anavysos Kouros
530 BCE Archaic Greek

Artist, Name, Location, Time
Kritios Boy Kouros
480 BCE Classical Greece
This was significant in showing the development of contrapposto
What is contrapposto?
Italian for counterpose. The idea of a weight bearing leg. The figure is show with a bent knee (bearing leg) and appears ready for movement.
What are some key points of change from Archaic to Classical Greek?
The development of contrapposto. Significant differences in realism and naturalism, and a shift in the idea of masculinity (young, thin, almost feminine to beefy, bearded warriors). Some key events that may have contributed to this change is the union of the Greeks, which lead to the defeat of Persia in the Battle of Marathon (480 BCE), as well as the development of democracy.

Artist, Name, Location, Time
Dying Warrior (1)
500 BCE Archaic Greek
in West Pediment of the Temple of Aphaia
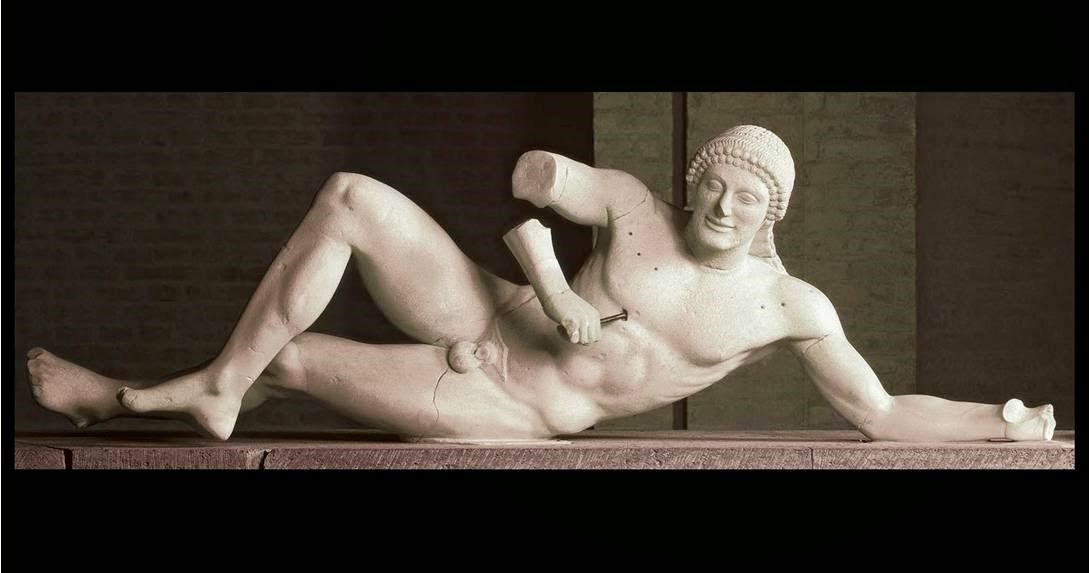

Artist, Name, Location, Time
Dying Warrior (2)
490-480 BCE Classical Greek
in East Pediment of the Temple of Aphaia
shows differences between Archaic and Classical through realism

Artist, Name, Location, Time
Archer (Paris)
500-490 BCE Archaic Greek
This work was reconstructed in the theorized polychrome in 2004 by Brinkmann and Brinkmann

Artist, Name, Location, Time
Riace Warrior
460-450 BCE Early Classical Greek
Bronze sculpture
What are some key points of the Acropolis/High Classical Period?
More confidence in architecture and art due to the win in Battle of Marathon
Badly defeated by Persians in 480BCE
Win again in 479BCE under the leader Perikles
Athenians rebuild the destroyed Athens, including the Parthenon, marking the High Classical Period (450-400BCE)
Limited democracy
Relatively peaceful
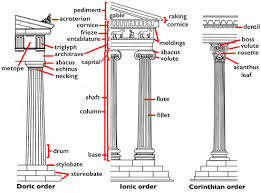
What are the 3 main orders of Greek Architecture?
Doric- no bases, simple capital, entablature only has a sculpture in the metope (Parthenon)
Ionic- fluting bases, columns have fillets, capitals have volutes, there is a sculpture on continuous frieze of entablature
Corinthian- most notable is the more elaborate capitals with leaves, columns have slight curve and visually are taller
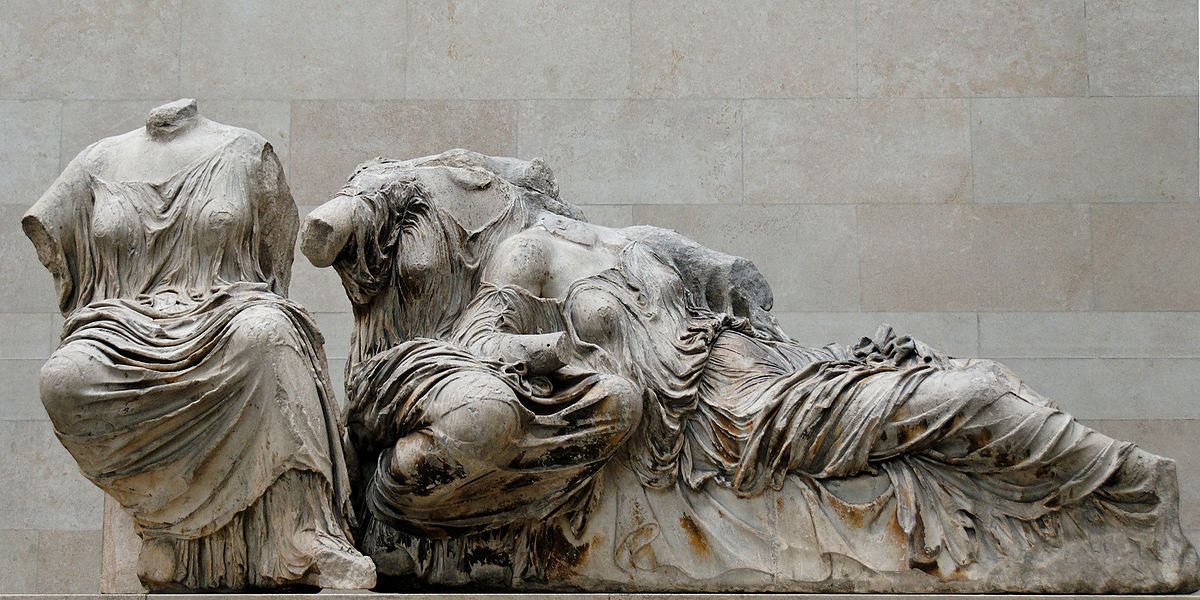

Artist, Name, Location, Time
Pedimental Sculpture from the Parthenon
435 BCE, Classical Greek
Depicts titanesses and goddesses, Hestia, Dione, and Aphrodite

Artist, Name, Location, Time
Detail of a metope from the Parthenon
Centaur and Lapith
435BCE Classical Greek
Artistic direction by Phidias

Artist, Name, Location, Time
Polykleitos
Spear Bearer (Doryphoros)
450-440 BCE Classical Greek
What are the canon of proportions?
A set of rules that describes the "best" proportions- gives ratios that determine the relation of parts to the whole

Artist, Name, Location, Time
Ancient Greek Water Jug
430 BCE Classical Greek
Depicts the "perfect" Greek family; warrior man, mother woman

Artist, Name, Location, Time
Praxieteles
Aphrodite of Knidos
360 BCE Late Classical Greece
first records nude goddess sculpture
What are the key points of the Hellenistic Era?
323-30BCE
More contact with other surrounding cultures due to the overwhelming expansion under the power of the Greats
Marks the end of the Persian Empire

Artist, Name, Location, Time
Haglsandros, Polydorus, and the Athendoros of Rhodes
Lacoon and his sons
First Century BCE Hellenistic Greek