General Ecology Exam 3- UWSP
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
67 Terms
Ecological community
an assembly of a population of two or more species occupying the same geographical area at a particular point in time
Competition fitness effects
-/-
Exploitation (predation, herbivory, parasitism) fitness effects
+/-
Mutualism fitness effects
+/+
Commensalism fitness effects
+/0
Amensalism fitness effects
-/0
Neutralism fitness effects
0/0
Why did the equation dN/dt = rN((K-N)/K) not work?
That was for intraspecific competition, not interspecific
α
competition coefficients
α12 is
the effect of an individual of species 2 on the population growth of species 1
α21 is
the effect of an individual of species 1 on the population growth of species 2
What did the logistic growth equation add to include interspecific?
-α12N2
why do we use isoclines of zero population growth to make predictions about the long-term outcome
coexistence is more likely when the magnitude of interspecific competition is relatively low
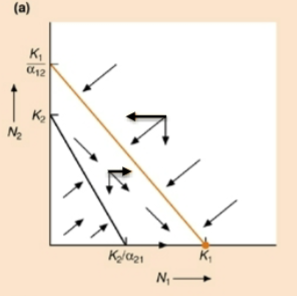
Which species wins?
Species 1 wins
Stable equilibrium at K1
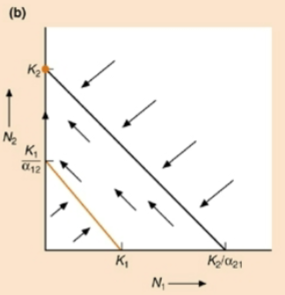
Which species wins?
Species 2 wins
Stable equilibrium at K2
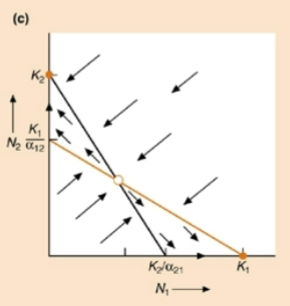
Which species wins?
Winner varies
Stable equilibrium at either K1 or K2 depending on starting conditions
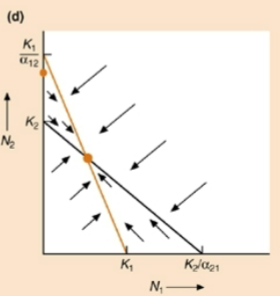
Which species wins?
both, stable equilibrium
Predation
broadly refers to the consumption of one organism (prey) by another organism (predator)
Lotka-Volterra predator-prey equations mimic
the predator-prey patterns we see in nature and can be used to explore predator-prey cycles
Lotka-Volterra predator-prey equations refer to the prey as
Hosts
Lotka-Volterra predator-prey equations refer to the predators as
Parasites
Why are predators described as parasites and prey as hosts?
the equation was initially developed in the context of parasite-host interactions
prey population is limited by
predation
predator population is limited by
prey abundance
consumption rate of prey
pNhNp
Lotka-Volterra prey equation
dNh/dt = rhNh - pNhNp
in Lotka-Volterra prey equation what is rh
host per capita rate of increase
in Lotka-Volterra prey equation what is Nh
Number of hosts
in Lotka-Volterra prey equation what is pNh
predation rate
in Lotka-Volterra prey equation what is Np
number of predators
predator birth rate equation
cpNhNp
what is c in predator equation
host to predator conversion rate
what is dp in predator equation
the mortality rate of predators
Lotka-Volterra predator equation
dNp/dt = cpNhNp - dpNp
Mutualism
any interaction from which all participants gain a
fitness benefit
facultative mutualisms
species that can live without their mutualistic partners
obligate mutualisms
mutualistic relationships that are obligatory (one or both can’t live without the other)
Symbiosis
some interactions are super tight knit
Swollen thorn acacia
Native to new world
What are swollen thorn acacia traits
enlarged thorns with a soft, easily-excavated pith, enlarged foliar nectaries, and Beltian bodies
what are Beltian bodies
leaflet tips that are modified into concentrated food sources (lipid proteins and carbs)
Whistling thorn acacia
Africa
What are elaisomes
small structures attached to a seed
why are elaisomes important to whistling thron acacia
the ants will take the elaisome and drag it into their grave yard and eat the elaisome, then the seed will grow in nutrient dense area
Myrmecochory
seed dispersal by ants
Why do ants in swollen thorn acacia avoid the flowers
the flowers produce a chemical repellent, which repels the ants from the inflorescences but is apparently not noticed by pollinating bees
Why would David Moeller (2004) argue that facilitation can reduce the effects of competition among sympatric Clarkia spp
Facilitation can ameliorate the effects of things like competition (heterospecific Clarkia spp. compete for similar resources but also help each other indirectly by attracting pollinators to the region in which they occur)
pollen limitation
many angiosperm do not use the amount it should use
What does commensalism mean
interspecific interactions where one species benefit and the other species is not effected
examples of commensalism
Large ungulates (such as cattle) and birds (such as cattle egrets), where the movement of ungulates stirs up insects, upon which the birds feed
What does amensalism mean
interspecific interactions where one species is harmed and the other species is not affected
examples of amensalisms
Ungulates trampling grass
What does neutralism mean
What is species diversity and how do we quantify it?
diversity index
Most diversity indices are functions of both
species richness and species evenness
Robert Whittaker on abundance
few plant species have low coverage, most plant species have moderate coverage, few plant species have very high coverage
Frank Preston on abundance
Few bird species are rare, most bird species are moderately abundant, few bird species are abundant
what did Deborah Rabinowitz mean when she discussed what she called the seven forms of rarity
organisms only have Small geographic ranges, Narrow habitat/resource
specificity, or small populations
primary productivity
the synthesis of organic compounds from atmospheric or aqueous carbon dioxide via photosynthesis
primary productivity is quantified by
measuring changes in biomass
Robert MacArthor found that
plant communities with greater foliage height diversity supported more diverse bird communities
Equilibrium theory of island biography
theoretical construct first published in the 1960’s by Robert MacArthur and E.O. Wilson, that seeks to explain and/or predict levels of diversity on islands
large and near islands will support ___ amount of species
most
latitudinal gradient in species diversity
observation that species diversity is highest near the equator and declines with increasing latitude
Red Queen Hypothesis (Leigh Van Valen)
Proposes that species must constantly evolve in order to survive while pitted against ever-evolving and opposing organisms in a constantly changing environment
how did J.H. Brown argue that red queen hypothesis might be related to higher species diversity in the tropics
the species needed to sprint to just keep up with the changes and were never getting ahead
What are the six processes JH brown describes
Time since perturbation
Productivity
Environmental heterogeneity
Favorableness
Niche breadth and interspecific interactions
Differences in speciation and extinction rates