week 1- Biochem
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
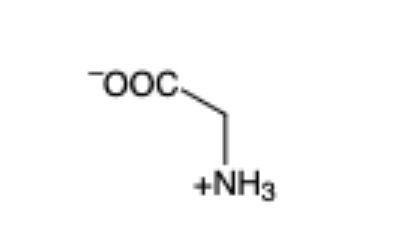
Glycine
(Gly, G) —- not chiral
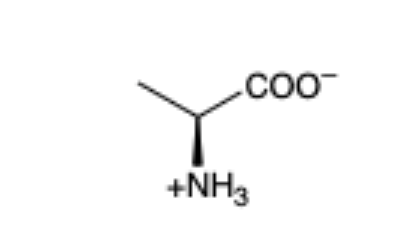
Alanine
(Ala, A)
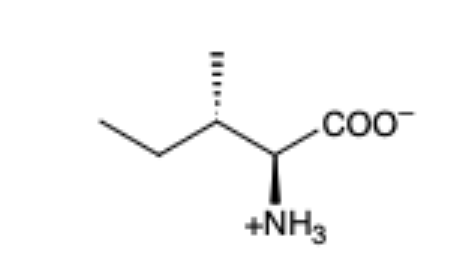
Isoleucine
(lle, l)
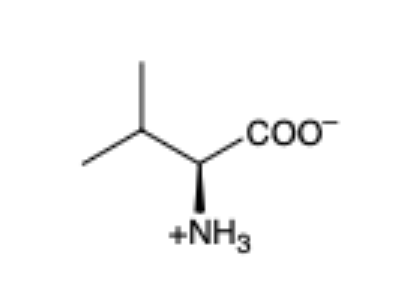
Valine
(Val, V) hydrophobic and aliphatic
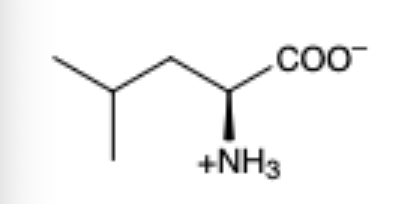
Leucine
(Leu, L)
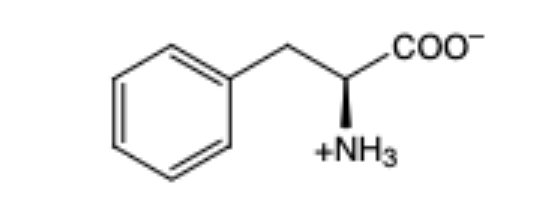
Phenylalanine
(Phe, F) Aromatic, hydrophobic
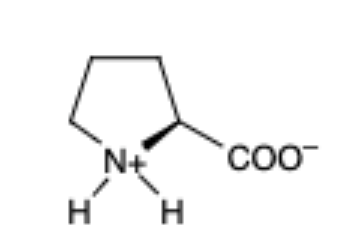
Proline
(Pro, P)
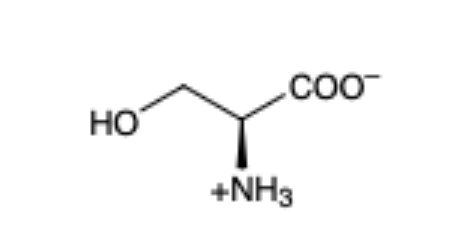
Serine
(Ser, S)
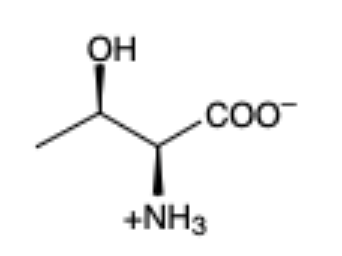
Threonine
(Thr, T)
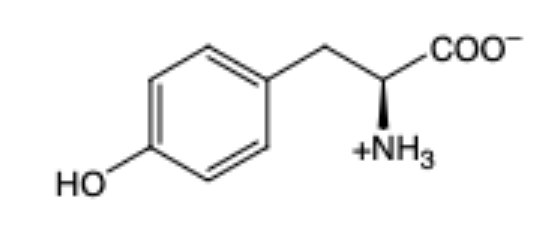
Tyrosine
(Tyr, Y) hydrophilic (polar) and aromatic
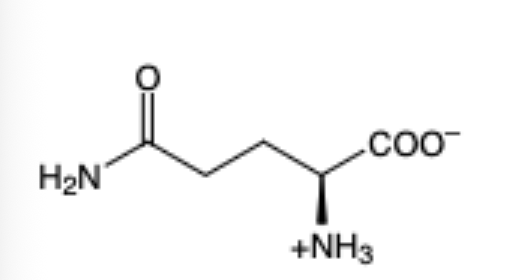
Glutamine
(Gln, Q)
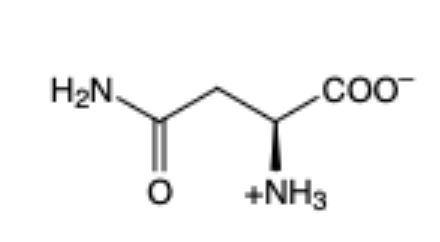
Asparagine
(Asn, N)
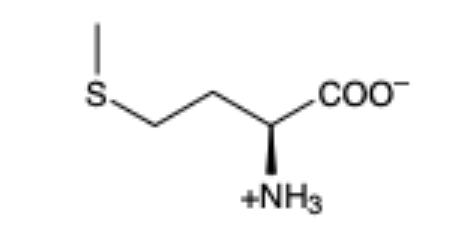
Methionine
(Met, M)
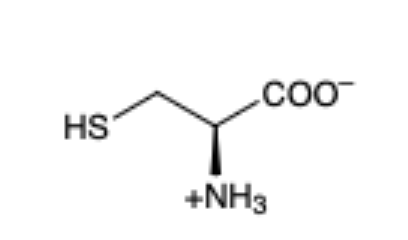
Cysteine
(Cys, C)
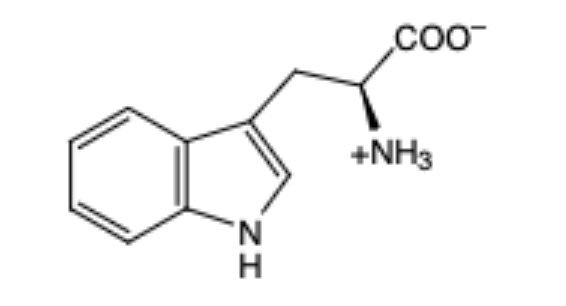
Tryptophan
(Trp, W) aromatic and hydrophobic
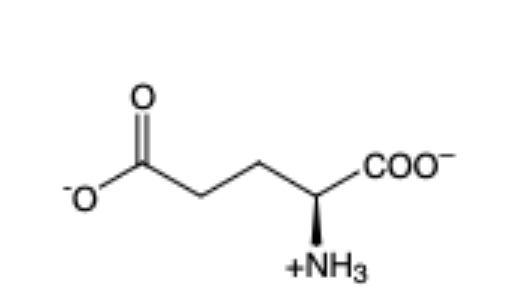
Glutamic Acid
(Glu, E) — acidic (- charge)
Histidine
(His, H) aromatic and basic (because of nitrogen that has extra lone pairs—- + charged)—- pka = 6-6.5
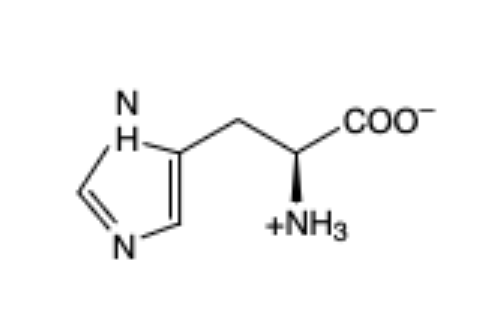
Arginine
(Arg, R)— aliphatic and basic because of nitrogen so has a + charge (pka - 12.5)
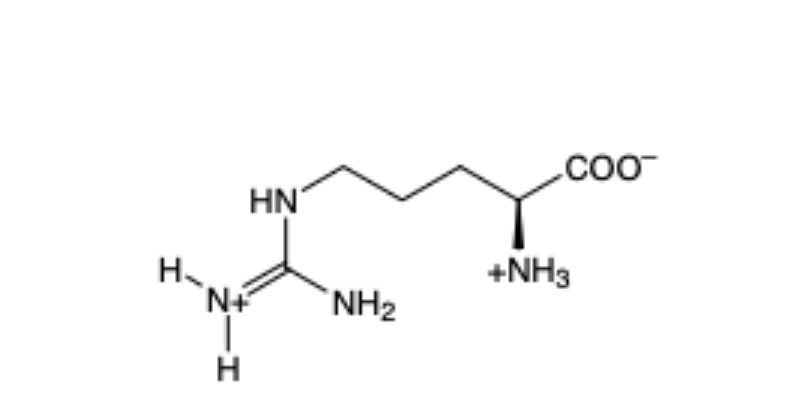
Aspartic Acid
(Asp, D) — acidic (- charge)
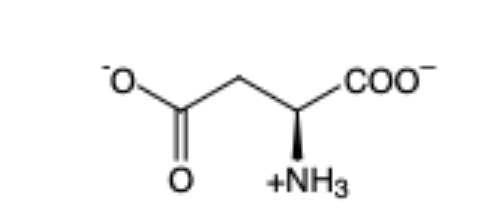
Lysine
(Lys, K) - aliphatic and basic because of nitrogen so has a + charge (pka = 10.5)
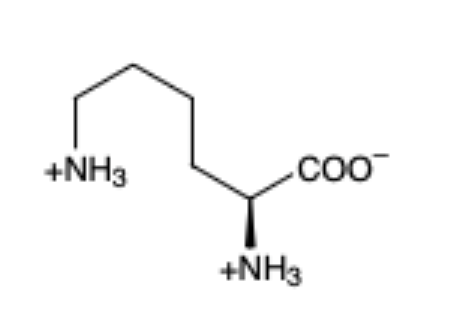
Principle elements
CHNOPS
What is glycolysis
breaking down carbohydrates
Basic solvent of biology
Water
What can form hydrogen bonds
FON
What is a hydrogen bond?
A weak attraction between molecules where one molecule give a hydrogen and the other accepts it.
Hydrogen bond donor
has a hydrogen attached to a FON and gives the hydrogen (ex: OH,NH)
Hydrogen bond acceptor
Receives the hydrogen and is either a FON with enough lone pairs to grab they hydrogen (ex: C=O, OH)
Amino Acid R groups
acids, anime, amides, thiol
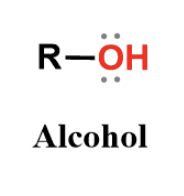
alcohol
hydroxyl group, polar (so water soluble) and forms hydrogen bonds
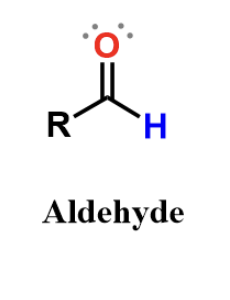
aldehyde
carbonyl, polar and found in some sugars
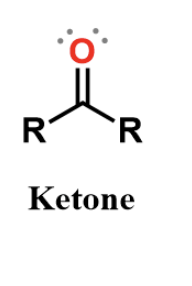
ketone
carbonyl, polar and found in some sugars
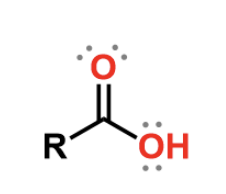
acids
carbonyl, weak acid (bears a negative charge when it donates a proton
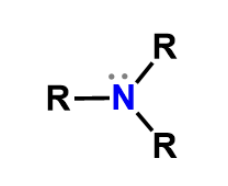
Amine
Amino, weak base that bears a positive charge when it accepts a proton
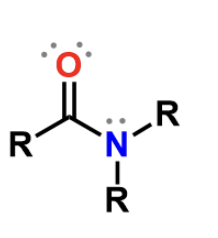
Amide
Amido, polar but doesn’t bear a charge
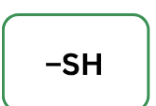
Thiol
easily oxidized and can form disulfide bonds readily.
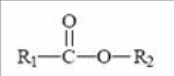
Ester
found in certain lipid molecules
Alkene
Important structural component in many biomolecules.
What determines amino acid properties
r chains
What kind of amino acids do all proteins contain
L- animo acids
Non covalent interactions Ranked
ionic interactions
hydrogen bonds
hydrophobic interaction
van der Waals
n-terminus
nh3 or nh2 not attached to amino acid sequence (start of chain)
c-terminus
COOH bond
pH < pka
amino acid will protonate so makes acid positive
pH > pka
amino acid will deprotonate so negative
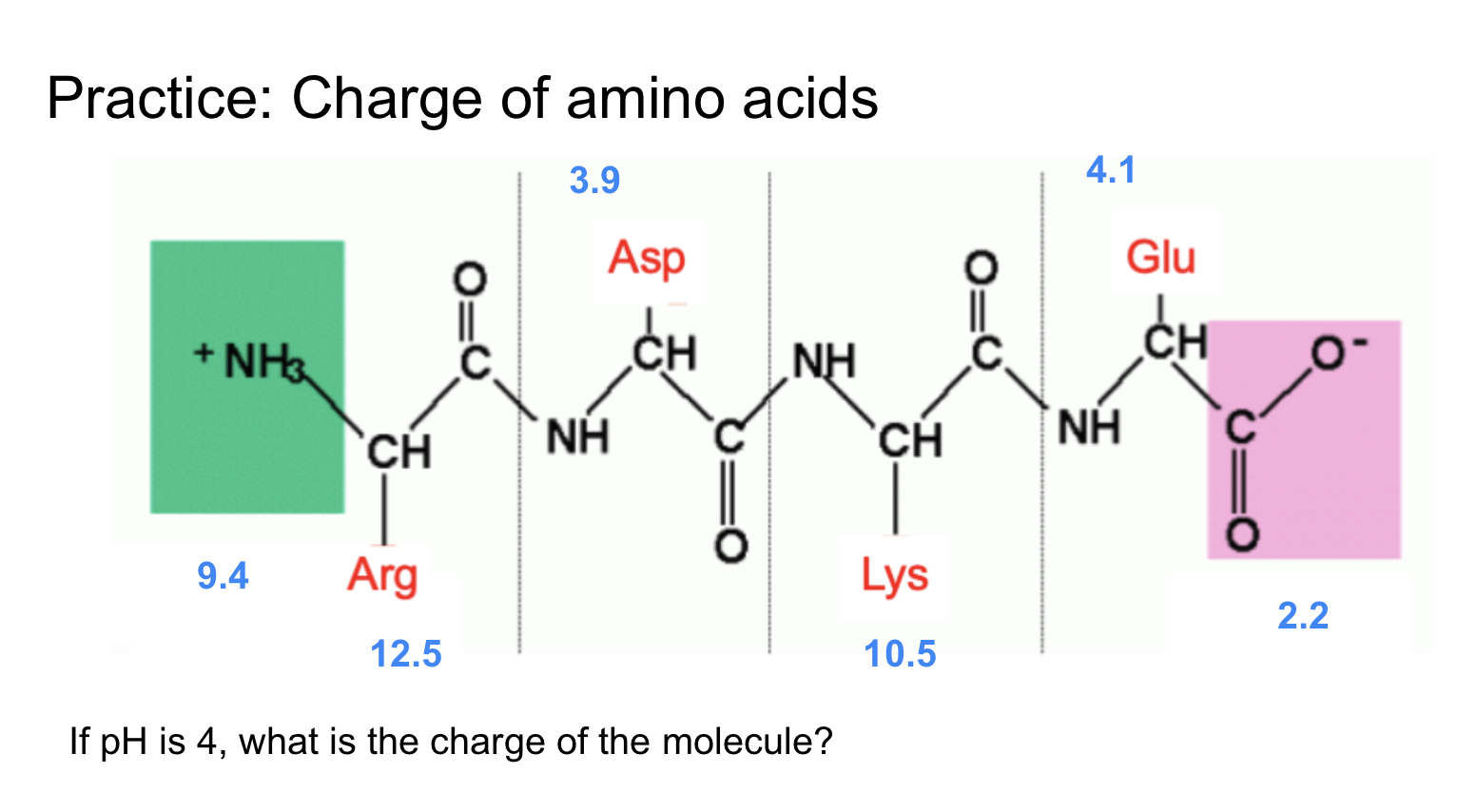
NH3—- ph<pka = +1
Arg—- ph<pka = +1
Asp—- ph>pka = -0.5 (because pka and ph are similar)
Lys—- ph<pka = +1
Glu—- ph<pka = +0.5
COOH —-ph>pka = -1
Total: 2
delta G < 0
forward rnx spontaneous
delta G > 0
reverse rxn spontaneous or forward rxn non spontaneous
Catalyst (enzymes)
DO NOT change delta G values, they only change the activation energy by lowering it so the reaction can happen more readily in the forward and reverse. It doesn’t change the ratio of products and reactants.
6 types of enzymes
Oxidoreductases
transferase
hydrolases
lyases
isomerases
ligases
IMF
Intramolecular (in the same molecule)
ionic bonds (crystal)
single, double, triple covalent bonds
Intermolecular bonds (between molecules)
ionic interactions
hydrogen bond
dipole dipole interactions
London dispersion forces
A good substrate
doesn’t need to bind tightly to the enzyme but binds tightly when activated to the transition state
Enzyme complementary to substrate
“lock and key” and more energy is needed to bind
larger activation energy
Enzyme complementary to transition state
promotes the traditions state (lowers it) by causing hydrogen bonding between substrate and enzyme so the substrate can bind and break.
conformation change
shorter activation energy