Working memory
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
What is Baddeley (2010) definition of working memory
“Working memory refers to the system/s that are assumed nescaserry in order to keep things in mind while performing complex tasks such as reasoning, comprehension and learning” (Baddeley, 2010)
What is the modal model of memory
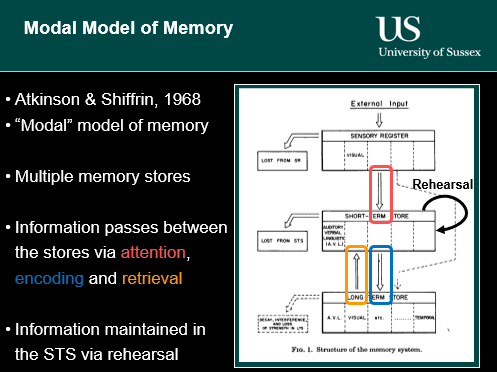
What are the problems with the modal model of memory
There is only one short-term store (STS)
How can you only two things at the same time
patients were found that have selective damage to the STS but no major difficulties with comprehension, problem solving. general intelligence ect
the amount of time items spend in the STS dictates how well they are stores in long-term memory
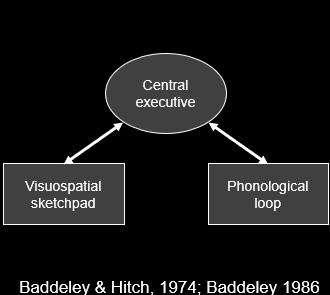
Baddeleys working memory model
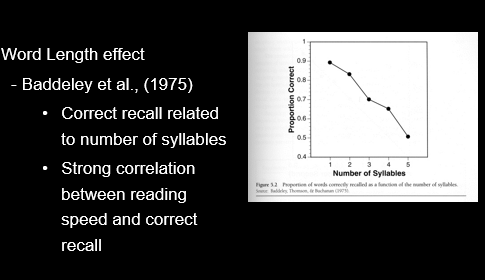
What is the capacity of the phonological loop and why
•If tested using unrelated words, digits, letters, etc., around 7 items
•Word Length effect
-Baddeley et al., (1975)
Presented lists of 5 words to write down in order
List A: some, harm, bond, yield, hate
List B: …
List C: …
List D: …
List E: association, considerable, representative, individual, immediately
•Word Length effect
-People only remember what they can say in around 1.5 secs
-To remember words or numbers people will generally repeat them to themselves (under their breath – “sub-vocally”)
-This is done via an “articulatory loop”
What are the functions of the visuospacial sketchpad
Sequences of visually guided actions
seeing things “in the minds eye”
What is the capacity of the visospaical sketchpad
6-7 items (similarly to the phonological loop)
•Some have argued the visuospatial sketchpad can contain a fixed number of items (e.g. 4 or 7)
•Others have argued working memory is a limited resource which is shared between all items
Baddeleys working memory model interim summary
•We have dedicated working memory “buffers” for some specialised types of information
•These buffers are independent
-Information held in one buffer does not interfere with another
-This is how we can do two things at the same time (e.g. listen to a lecture while doodling)
•The buffers are thought to be controlled by a “Central executive”
•
What are the problems with Baddeleys working memeory model
•People are able to repeat back meaningful sentences and paragraphs far better than unrelated words
•Baddeley and Wilson (2002)
•Tested 23 “amnesic patients”
•Found many examples where immediate prose recall was normal
•Recall after a delay was highly impaired
While this pattern might not surprise an experienced clinician, it does present a problem for the version of the working memory model proposed by Baddeley”
What are features of an episodic buffer
-a limited-capacity system that integrates information from a different sources
-
-“episodic“: it holds information about episodes or events as the unfold over time
-
-Interfaces between what is happening now and long-term memory
Evidence for reactivation of epsiodic information

What is a newer perspective of this
•Hierarchical process view (Hasson et al., 2015)
-Most working memory models separate ongoing information processing (attending to what’s around us) from information that we are holding in mind
-
-But ongoing information processing requires us to accumulate information over time
-
-This happens over different timescales in different brain circuits
Integrating information over different timescasles

Integrating information over different timescales
•Lerner et al., scanned people listening to the different conditions
•
•Looked for brain regions that showed coherent activity across individuals
•
•Supports the hierarchical process view
What is an episodic buffer
n working memory, a "buffer" refers to the episodic buffer, a temporary storage system that integrates information from different sources (like the phonological loop and visuospatial sketchpad) and long-term memory to create a unified, coherent experience or "episode," allowing for a sense of time and sequence.
conclduint comments
•Working memory is such a big concept it’s unlikely that there can be a single “model” of it
•
•Specific buffers have specific purposes, but understanding one may not help us understand other aspects of working memory
•
•The hierarchical process view addresses how working memory supports ongoing information processing
-But what about when reasoning or problem solving?