Seasonal Cyclicity and Menstrual Cycle: Reproductive Physiology and Hormonal Regulation
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
Seasonal Anestrus-Cyclicity
Prevents females from conceiving when survival of embryo/neonate would be low.
Hyperthermia
Harms oocytes & early embryos.
Seasonal Breeders
Give birth during spring when nutrition is sufficient for lactation/growth of the neonate.
Short‐Day Breeders (fall)
Examples include sheep, goats, deer, and elk.
Long‐Day Breeders (spring)
Examples include horses and hamsters.
Obligatory Seasonal Breeders
Rely on seasonal cues to predict when conditions are favorable to reproduction and rearing young.
Facultative (Opportunistic) Breeders
React directly to changes in an environmental variable, not linked to seasonal cues.
Anestrus in Obligatory Seasonal Breeders
GnRH pulse frequency and LH secretion are low; follicles may grow but fail to obtain pre-ovulatory status.
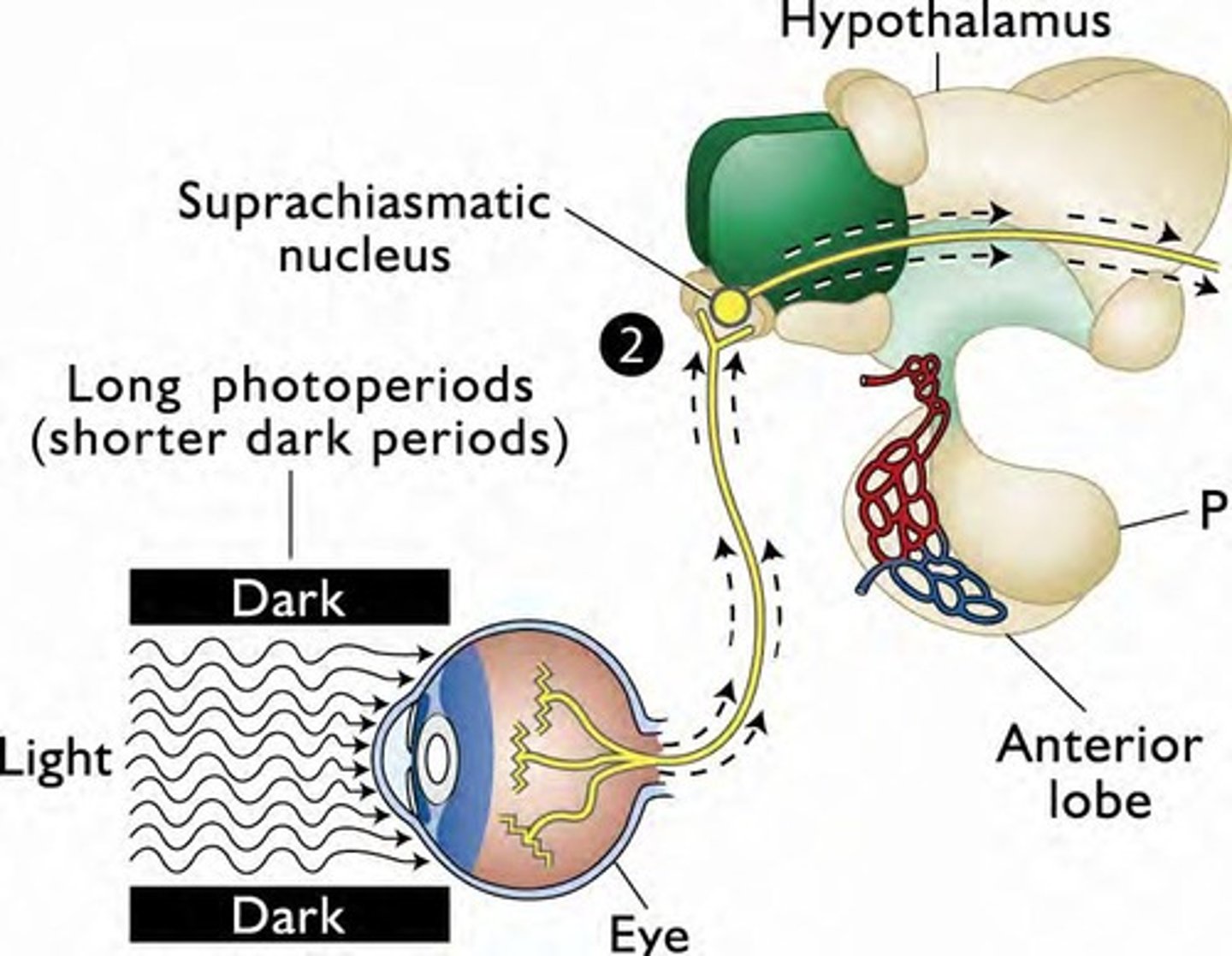
Photoperiod
Regulated by the duration of light exposure, affecting GnRH pulse frequency, detected by retina.
how does the photoperiod regulate the duration of melatonin release that affects GnRH?
info is sent to superachiasmatic nucleus (SCN) IN the hypothalamus VIA the optic nerve
after the info is recieved at the SCN, where does it go to?
the superior cervical ganglion (SCG)
what happens after info is sent to the SCG?
sympathetic neurons from the SCG project into the pineal gland to regulate melatonin release, ultimately regulating GnRH and gonadotropin secretion
Melatonin
Secreted by the pineal gland in a circadian fashion; minimal during light and maximal during darkness.
Hormone of darkness (melatonin)
Provides accurate information about the light-dark cycle.
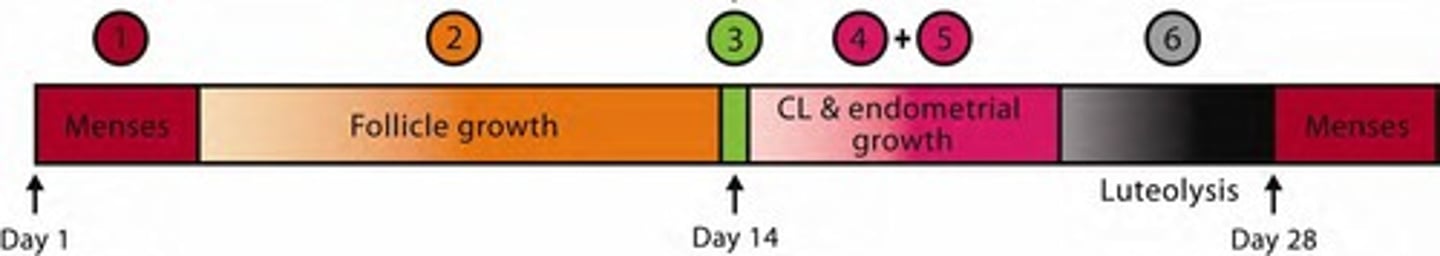
Menstrual Cycle
Events that occur in a female's reproductive system between two successive menstrual periods
Amenorrhea
Lack of bleeding.
Dysmenorrhea
Painful menstruation
GnRH
Gonadotropin-releasing hormone that regulates reproductive functions.
Kisspeptin
A neuropeptide that plays a role in the regulation of GnRH secretion.
GnIH
Gonadotropin-inhibitory hormone that impacts reproductive hormone secretion.
Suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN)
Part of the hypothalamus that receives information about light exposure.
Superior cervical ganglion (SCG)
Sends signals to regulate melatonin release from the pineal gland.
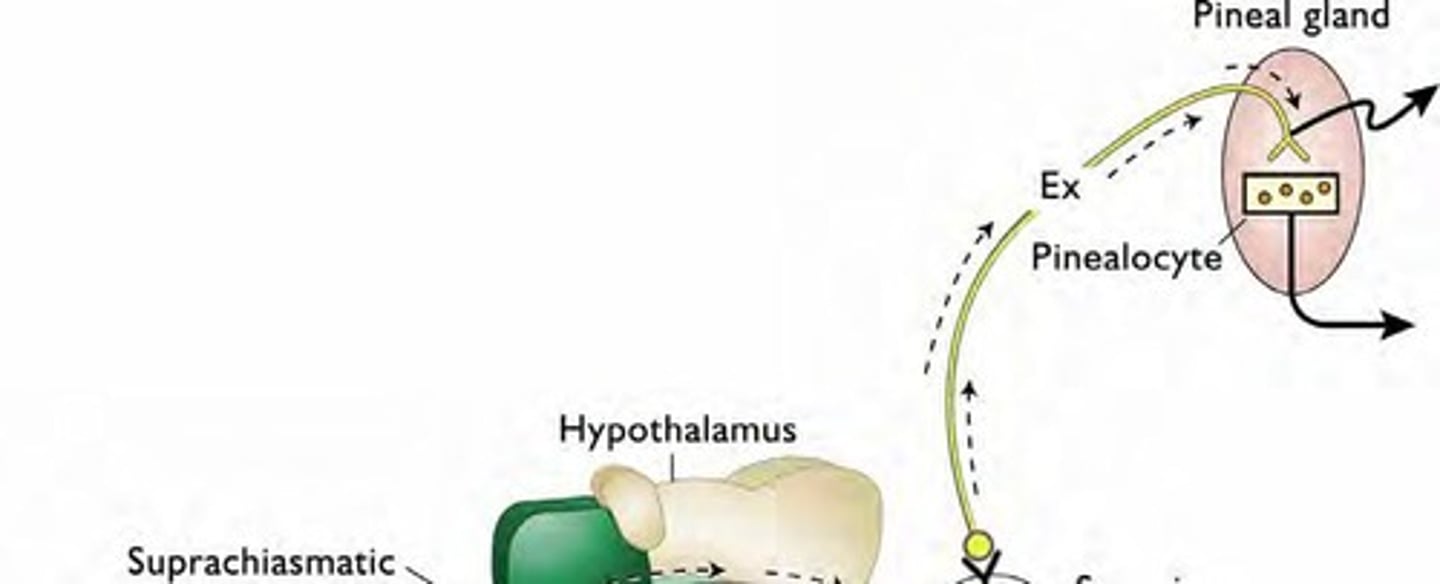
Pineal gland
Gland that secretes melatonin.
Circadian fashion
Refers to biological processes that follow a roughly 24-hour cycle.
Menstruation
Sloughing of endometrium.
Menorrhagia
Excessive menstrual bleeding (> 8-10 days, > 80 mL).
Oligomenorrhea
Little menstrual bleeding.
Menarche
First menstrual bleeding (median = 12.77 years).
Menstrual Cycle Length for 15-19 year olds
35 days.
Menstrual Cycle Length for 30 year olds
30 days.
Menstrual Cycle Length for 35 year olds
28 days.
Menstrual Cycle Hormonal Changes
Includes proliferative and secretory phases.
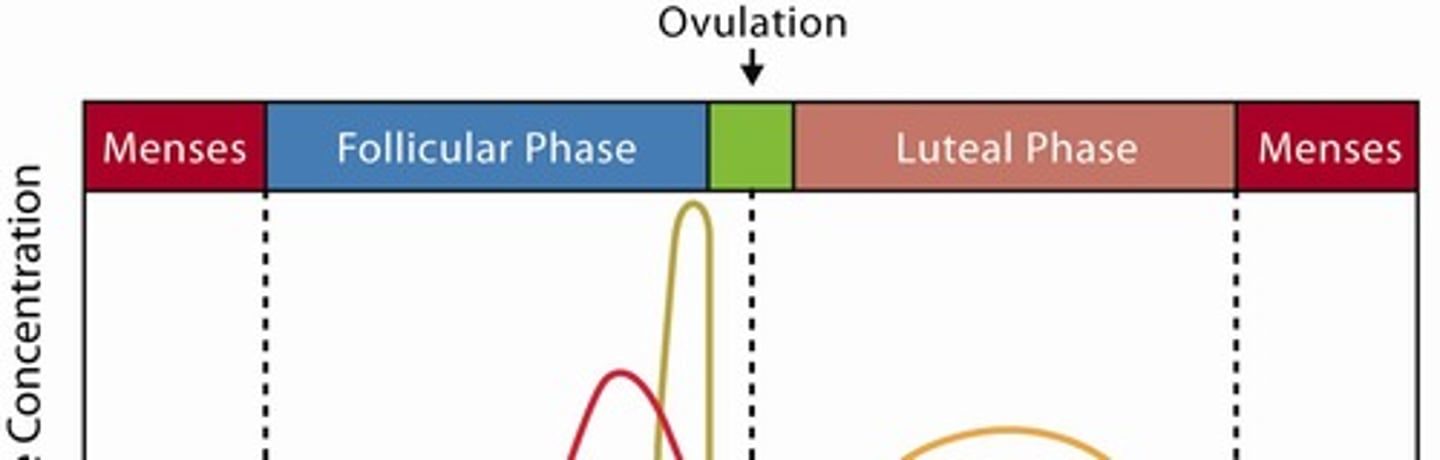
CL lifespan in human
12-14 days unless pregnancy occurs.
Menstruation Process
Drop in P4 and E2, endometrial PGF2α, vasoconstriction, necrosis.
Lactational Amenorrhea
Method of family planning effective for first 6 months if criteria strictly followed.
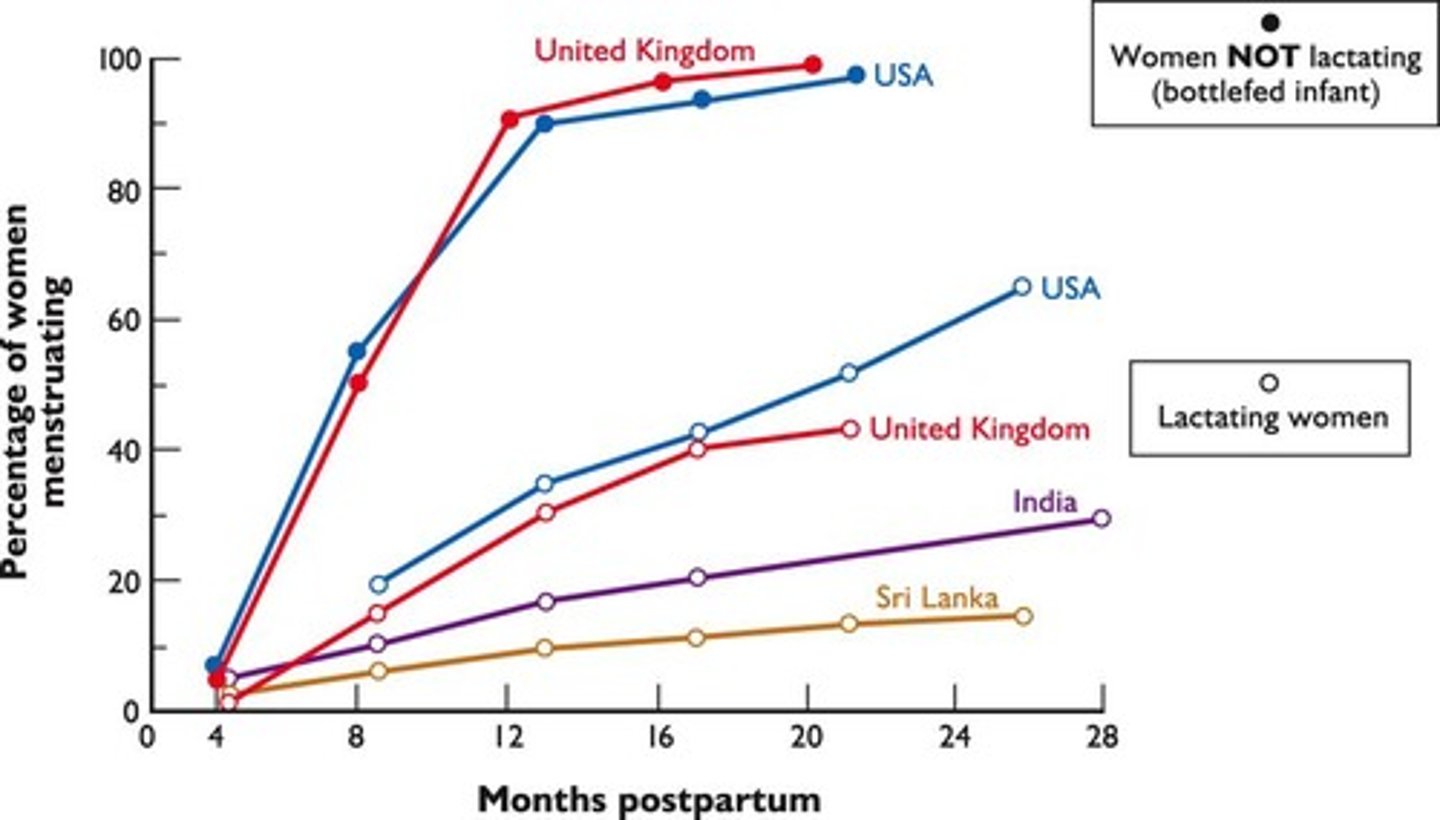
Criteria for Lactational Amenorrhea Success
Dependent on frequency of feeding (>6x d/n), contact with infant, mother's nutritional status.
Historical Discovery of Ovum
First discovered in 1827, menstruation connected to ovum in 1863.
Cultural Beliefs about Menstruation
Some tribes believed menstruation was due to demon attacks on the reproductive tract.
what does the estrus cycle begin/end with?
estrus
what does the menstrual cycle begin/end with?
menses
how long is the follicular phase in the estrous cycle?
very short (less than 20% of the cycle)
how long is the follicular phase in the menstrual cycle?
long (50% of cycle length)
when does ovulation occur in the estrous cycle?
the beginning and end of cycle
when does ovulation occur in the menstrual cycle?
in the middle
how long is the luteal phase in the estrous cycle?
very long (80% of the cycle)
how long is the luteal phase in the menstrual cycle?
shorter (50% of cycle)
does the estrous cycle have endometrial sloughing?
NO
why does the menstrual cycle have endometrial sloughing?
there is no pregnancy/embryo present, needs a clean slate so P4 decreases and luteolysis occurs
when is the well-defined period of sexual receptivity in the estrous cycle?
during estrus
when is the well-defined period of sexual receptivity in the menstrual cycle?
THERE IS NONE
where does luteolysis result from in the estrous cycle?
in the uterus
where does luteolysis result from in the menstrual cycle?
in the ovaries (CL self-destructs)
what is the CL lifespan dependent upon?
length of follicular phase