Unit V - AP World History Test Study Flashcards
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
What is the main idea of enlightenment principles?
reason and logic to understand the world
have individual rights - natural rights
challenge traditional beliefs - monarchies
the social contract - govt. runs from the consent of the government
people have to sacrifice some of their rights in return for order and protection
Church and state should be separated - drawing a line between political and religious authority
From a test question
legal equality
political equality
popular sovereignty
What are natural laws?
Natural laws are universal principles governing human behavior, based on reason and observable patterns
What are the natural rights that John Locke stated?
life, liberty and estate
What are the foundational principles of the new United States of America after the Declaration of Independence?
liberty, equality and democracy
What was the Haitian Revolution?
Successful slave revolt
led by enslaved africans + Toussaint Louverature
againts french colonial rule
What is the difference between the liberal beliefs and the conservative beliefs?

Common theme that is reflected in the American Declaration of Independence, the French Declaration of the Rights of Man and Citizen, and Bolivar’s Jamaica Letter
the idea of natural rights
equality
popular sovereignty
right to overthrow the government if it is tyrannical
Who was Adam Smith (Wealth of Nations)?
founder of the modern political economy
The main figure in the Scottish Enlightenment
Wealth of nations
Laissez- faire - minimal government intervention in the economy
based on the idea that individuals pursuing their interests will benefit society
Capitalism
Free and open market (determined by supply and demand)
Who was John Stuart Mill?
Found laissez-faire to be inhumane to workers
tried to get social reforms passed
Labor unions, child labor laws, laws ensuring safe working conditions
Utilitarianism - “the greatest good for the greatest number of people”
Did not want to end capitalism but wanted to address growing problems
Who is Karl Marx?
Founded Marxism
Talks about the struggle between the bourgeoisie (the capitalist class) and the proletariat (the working class)
Is driving the world behind human history and class struggles
Says to transition to communism by a worker revolution
have a classless society
Communist Manifesto
outlines the principles of communism
critiques capitalism
calls for the working class to unite against the “B“ to achieve a classless society through revolutionary movements
It is considered the foundational text for socialist movements worldwide
What are the two purposes of a colony?
1) To serve as a market for your goods
2) Provide cheap, raw materials
What are some factors that led to the growth in the European railroad network around 1850?
Industrialization
Improvements in the steam engine tech
Government support (due to the potential for economic development)
Urbanization (growth of cities)
Ability to connect major industrial centers (wider customer bases = More $$)
Technology diffusion
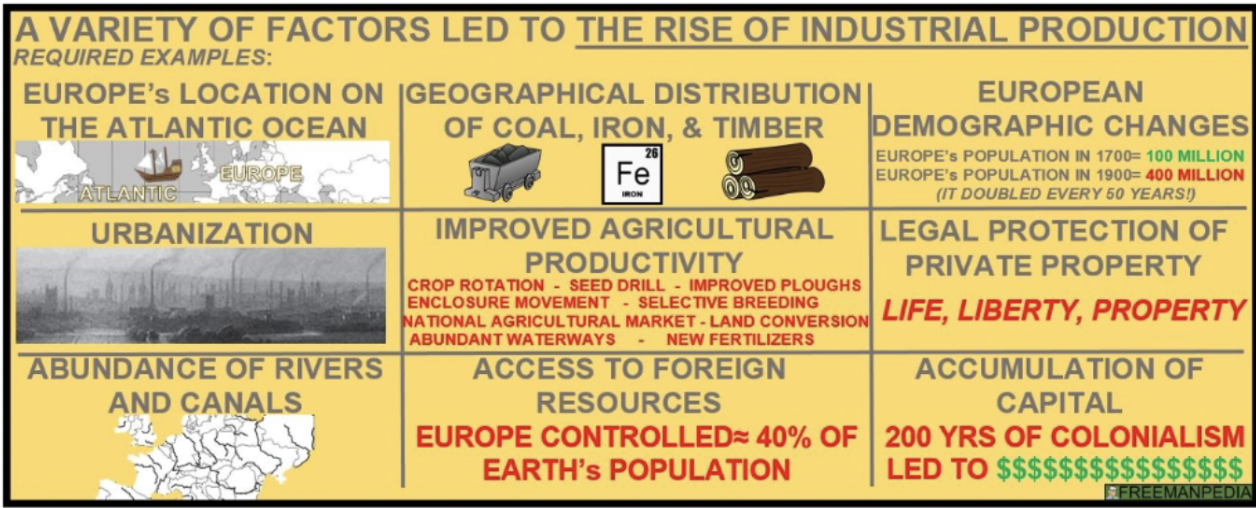
Reasons for the Industrial Revolution starting in Great Britain
proximity to waterways
access to rivers and canals
the geographic distribution
What is the Cottage System?
work at home
the cotton weaving thing
but too slow - and less profits for the owner
What is the Factory System?
work with machines
people became overworked
dangerous conditions
long days
child labor
women serving in 2 roles - domestic and work
repetitive factory life
new classes - working and aristocrats
BUT IN THE END - OWNERS MADE MORE PROFIT
Leaders of Latin American independence movements
creoles
What is Manifest Destiny?
influenced westward expansion
The U.S was destined to expand across the North American Continent
was often invoked to justify U.S annexations
What was the Ghost Dance Movement?
NA spiritual movement
was made based on the belief that European settlers would be driven away
Goal = Revive traditional ways of life, including the return of the buffalo, and the spirits of deceased ancestors
Consequences - The Bureau of Indian Affairs considered these dancers a threat and ordered the arrest of the Sitting Bull
What was the goal of the Seneca Falls Convention
demanded equal political and economic rights for women in the U.S
Outcome of the Opium War
Treaty of Nanjing
Unequal trade
Britain gets considerable trading rights with the Chinese
1843 - Britain gets Hong Kong
1833 - Christian missionaries return to China
huge embarrassment for the Chinese
led to the Taiping rebellion
showed that China was crumbling from within
Tried the SELF -STRENGTHING MOVEMENT
Chinese govt. tried to institute reforms to regain control (failed)
ended up losing Taiwan, Korea, and Vietnam
Issues facing the Russian, Ottoman, and Qing Empires and Tokugawa Japan
struggled to keep up with the modern world
Russia was falling behind in industrialization, had a weak economy, and kept losing wars because its army was outdated.
The Ottoman Empire was losing land to revolts and wars, had bad leaders, and its economy and military were no match for Europe.
The Qing Empire was beaten by foreign powers in the Opium Wars, and huge problems, such as the Taiping Rebellion and weak rulers, made it worse.
Tokugawa Japan stayed isolated for too long, so their army and economy were outdated, and they had to open up to foreign powers, which caused big changes at home.
They all had trouble modernizing and staying strong.
Opium Wars
The conflict between China and Western powers
they fought over the opium trade which resulted in China being forced to open its ports to Western merchants
Results of the Crimean War
the defeat of the Russian empire
Tanzimat Reforms
made to modernize the empire and make it more competitive with other nations
also made to preserve the empire
to reorganize the Ottoman Empire on enlightenment and constitutional forms
Count Sergei Witte’s economic modernization program
focused on making Russia stronger and more industrialized
expanded railways, especially the Trans-Siberian Railway, to connect the country and boost trade
pushed for growth in industries like coal, steel, and oil to modernize Russia’s economy
Since the country didn’t have enough money, he brought in foreign loans and investments to fund these changes
In 1897, he introduced the gold standard to stabilize Russia’s currency and improve its trade with other nations. His plan aimed to drag Russia into the modern industrial world.
Tokugawa Japan before Matthew Perry
isolated due to the policy of seclusion from the Tokugawa shogunate
military government
economic focus (through agriculture)
Factors that led to the Taiping Rebellion
A lot of hardship
corruption within the Qing Dynasty
Anti-Manchu settlement
influence of Christian ideologies - Hong Xiquan = younger brother of Jesus
unequal treaties and the opium war - led to discontent
Similarities between the Japanese and Russian Industrial process
did industrialization rapidly due to Western pressure
adopted Western tech to modernize economies
focused on military development
labor exploitation during the initial stages
What is the Boxer Rebellion?
Society of Righteous and Harmonious Fists (Boxers)
Chinese peasant uprising against the Chinese government
Anti-Qing, anti-European, and anti-Christian
Goal: To drive out the Europeans and Japanese
The rebellion was successful at first but was eventually crushed by Europeans
Humiliating defeat again for the Chinese government
Chinese culture started to crumble
1901 - foot binding was abolished
1905 - The Chinese Examination System was eliminated
By 1911, the government was toppled and imperial rule came to an end
The Republic of China was born
Egypt Under the Ottoman Empire
The Ottomans controlled it from the 1500s, but local leaders, especially the Mamluks, ran the show. Later, in the 1800s, Muhammad Ali came in, kicked the Mamluks out, and turned Egypt into his own mini-empire while still acting like he was loyal to the Ottomans. He modernized Egypt by building up the army, improving farming, and starting new industries. Even though Egypt was part of the Ottoman Empire, it was basically doing its own thing by the 19th century.
Chinese Self Strengthening Movement
Chinese govt. tried to institute reforms to regain control (failed)
ended up losing Taiwan, Korea, and Vietnam
The White Man’s Burden by Rudyard Kipling
talks about colonization of the world by European and North American powers
says it is a humanitarian mission
says imperialism is good and it is a way to civilize the natives
also warns about the loss of life and native resistance though
What is Social Darwanism?
some people are just better
“survival of the fittest”
relates his theory of evolution to human societies
those who are stronger or more advanced are naturally destined to dominate others
used to justify racism and social inequalities
Technologies that allowed colonial expansion into the interior of Africa and Asia
maxim guns, steamships, railroads, canals, telegraph
What is the “Civilizing Mission”?
Western is more advanced than local
going to civilize these people
Ex. Berlin Conference
What is the Sepoy Rebellion?
Indian soldiers who fight as the army of the British East India Company
Causes
Overseas travel
Remarriage
Rifles
Mistrust of British
Sepoys killed British troops, women, and children
Cawnpore (400 British troops and several hundred civilians surrender)
British Response (Cawnpore)
Results
Neither side trusted the other
1858 - British Crown takes control of India (Viceroy)
Massive troop occupation
Indians were heavily taxed (American colonists)
New educational system (English)
Built roads, canals, universities, medical centers, postal service, and railroads
Policies hurt Indian local industry (cotton textiles)
Massive famine
Racism
What is the Carlisle Indian School
example from the civilizing mission
Settler Colony
The number of European settlers outnumber the indigenous pop.
New Zealand
North America
Australia
Non- settler colony
The Indigenous population outnumbers the European settler
Middle East
Pacific Islands
India
Africa