structure and functions of membranes
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
What are cell membranes used for
Signalling, transporting and sensing
What is the fluid mosaic model
1972
Fluid = phospholipid bilayer which is constantly moving
Mosaic = proteins embedded in bilayer
What is the structure of the bilayer
Hydrophilic phosphate head and a hydrophobic lipid tail
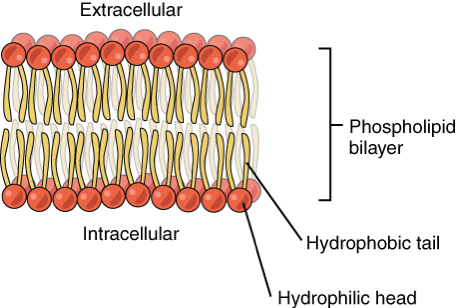
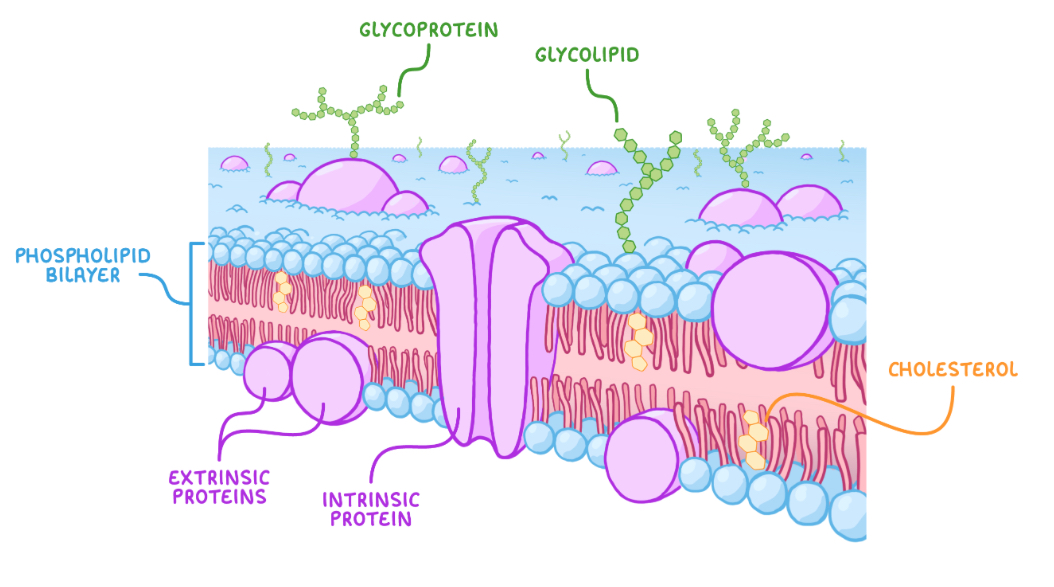
What is the structure of the membrane
Phospholipid bilayer
Cholesterol to add stability
Proteins
Glycoproteins
Glycoliopids
Why is the bilayer structured in the way it is
So that the centre is hydrophobic, which makes sure water solvable substances cannot pass but lipid solvable substances can
What is the need for cholesterol
Provide stability
Has regions of hydrophilic and hydrophobic
Hydrophobic regions bind to phospholipid tails so that they are closer together and reduces fluidity
What are the 2 types of protein in a membrane
Intrinsic and extrinsic
Intrinsic proteins
Embedded through both sides of bilayer
Include channel and carrier proteins to transport large molecules and ions
Extrinsic proteins
On one side of bilayer
Provide support to membrane and involved in cell signalling
Glycoproteins
Intrinsic proteins attached to carbohydrates
Glycolipids
Lipids attached to carbohydrates
What are glycoproteins and glycolipids involved in
Cell adhesion - attachment of cells to each other
Cell recognition - cells recognise each other
Cell signalling - communication between cells
What are the 2 main types of cell membranes
Cell surface membranes and membranes around organelles
What is the purpose of cells surface membranes
Surround cells and act as a barrier between cell and environment, control what enters/exits
What is the purpose of membranes around organelles
Compartmentalisation