Biology 🧬 Unit 7 - The Xylem
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/41
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
1
New cards
What is the function of the xylem
Transport water and mineral ions up the plant (one directional transport)
Provide support to the plant
Provide support to the plant
2
New cards
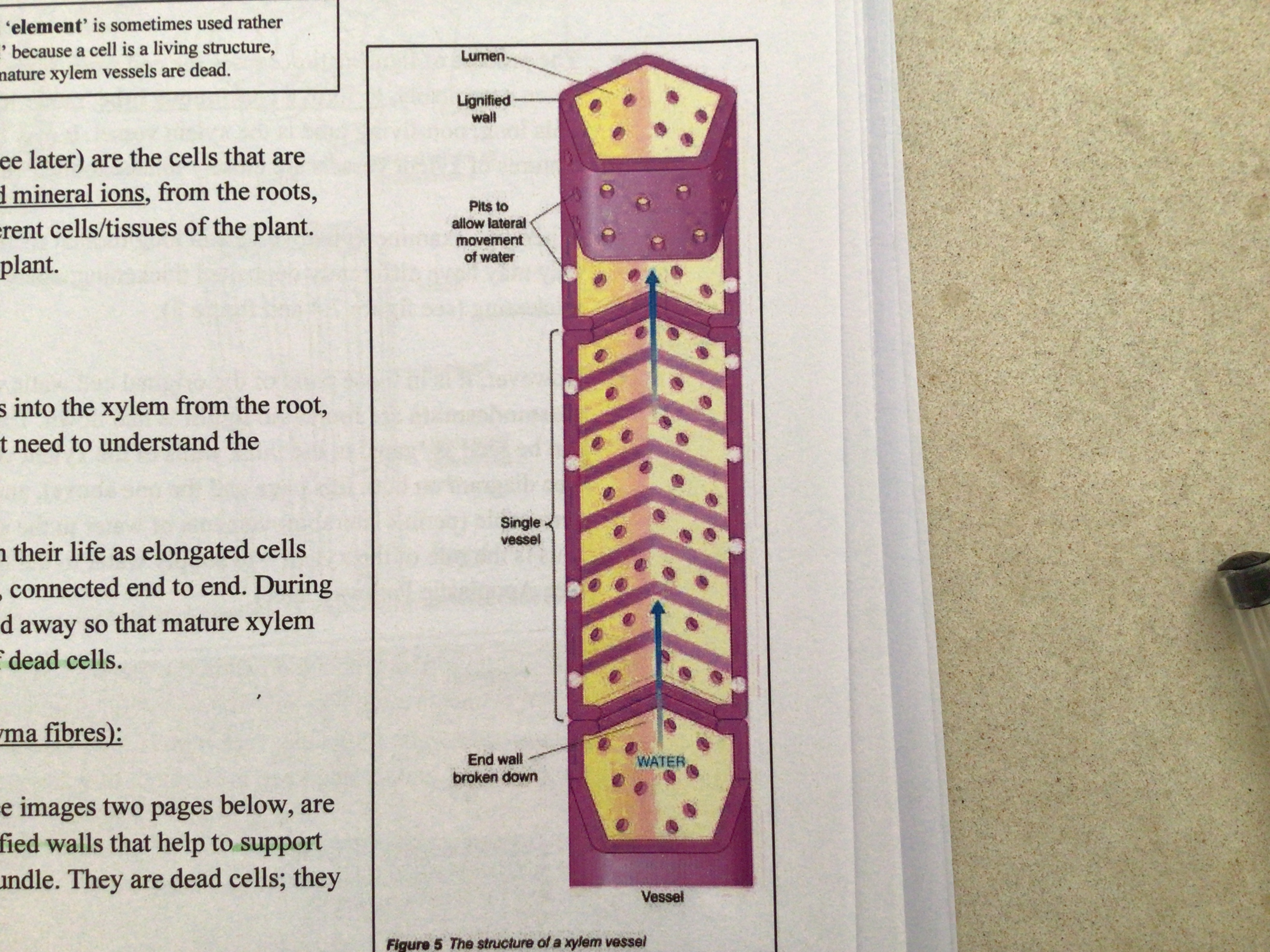
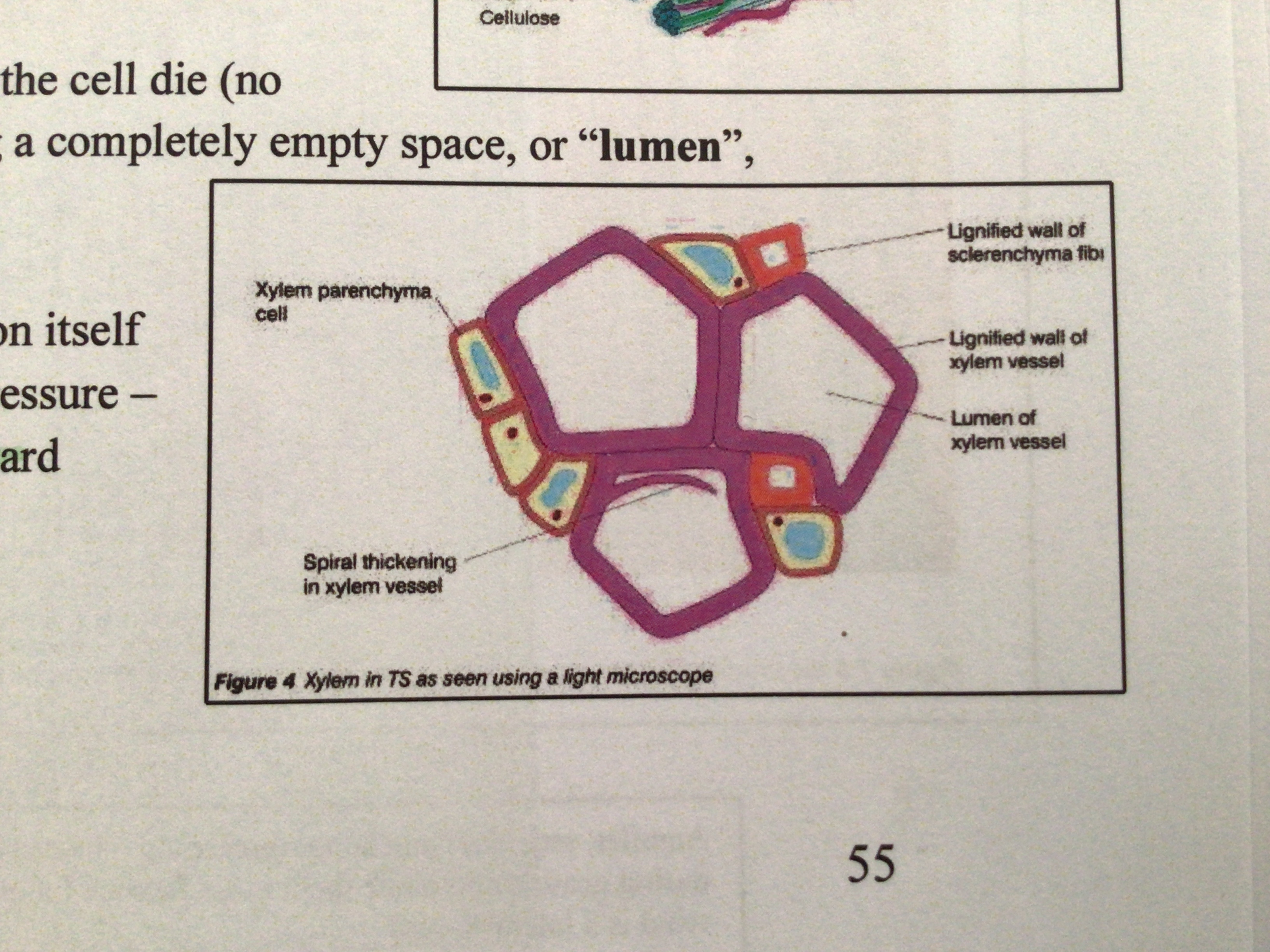
what are sclerenchyma fibres (xylem fibres)
elongated sclerenchyma cells with lignified walls to help support the plant. They strengthen the whole bundle
They are dead cells and have no living contents
They are dead cells and have no living contents
3
New cards
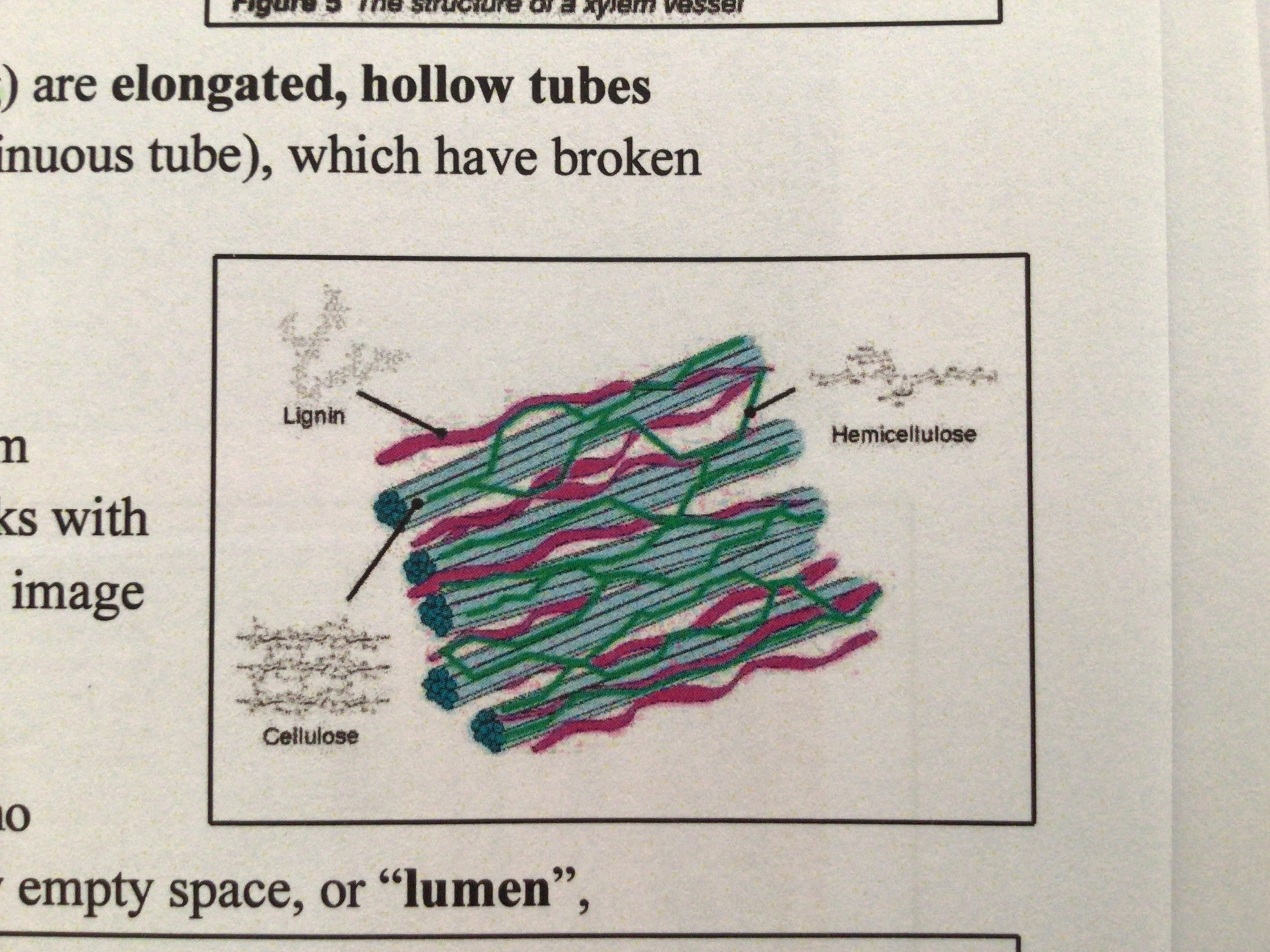
as xylem vessels mature the deposition of lignin hardens the cellulose thickening on the inside of the xylem’s lateral walls making them ………… to water (hydrophobic)
The lignin makes cross links with the ……… that fill the gaps between cellulose fibres
The lignin makes cross links with the ……… that fill the gaps between cellulose fibres
impermeable, hemicelluloses
4
New cards
As lignin builds up the contents of the cell die meaning…
no cytoplasm or nucleus to hinder water flow leaving a completely empty space or ‘lumen’ inside
5
New cards
What does lignin do/prevent
Ensure xylem does not fall in on itself when water moves up through it (resists negative pressure - suction)
Lignin disposition prevents inward collapse due to transpiration pressure
Lignin disposition prevents inward collapse due to transpiration pressure
6
New cards
The process of lignified action causes the end walls of neighbouring vessel elements to break down completely to form a ….
continuous tube
7
New cards
What makes the xylem permeable
Pits - permit lateral movements of water to the surrounding tissues
8
New cards
What are pits
Non-lignified areas can be seen as gaps in the thin i walls of the xylem vessel, these pits were where plasmodesmata were found in the original cell walls so no lignin is laid down
9
New cards
What helps increase the adhesion of water molecules
The cellulose in the walls of all xylem elements (pitted and non-pitted areas) this helps to resist the effects of gravity and keep the column of water moving upwards
10
New cards
What are the different types of thickening in xylem vessels
Annular, spiral, reticulate
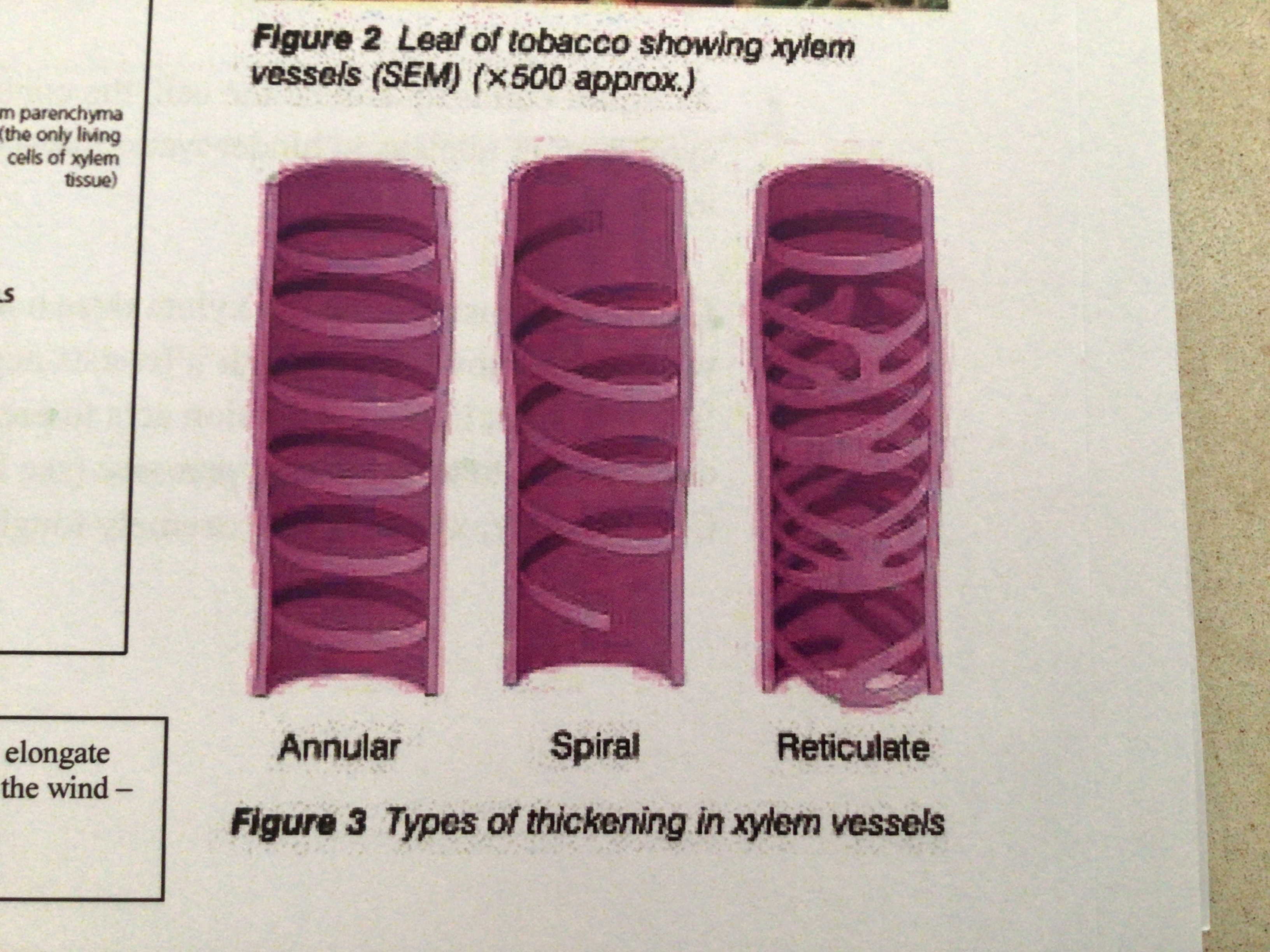
11
New cards
What happens to mineral ions once absorbed by the root
Are transported across the cortex of the root
They converge on the central stele and are actively secreted into the water column flowing up the xylem
The continuing movement of ions across the cortex of the root is partly responsible for the gradient in water potential between soil solution (higher WP) and the cells of the stele (lower WP)
They converge on the central stele and are actively secreted into the water column flowing up the xylem
The continuing movement of ions across the cortex of the root is partly responsible for the gradient in water potential between soil solution (higher WP) and the cells of the stele (lower WP)
12
New cards
What is transpiration
The loss of water vapour from the aerial parts of the plant, mainly the mesophyll cells of the leaves
13
New cards
What 2 things causes water to move up the xylem
1) root pressure
2) the transpiration stream
2) the transpiration stream
14
New cards
What has a strong cooling effect for a plant
Evaporation of water from the cells of the leaf in the light
15
New cards
What is plasmolysis
The loss of water via osmosis and accompanying shrinkage of the cytoplasm away from the cell wall; cell is said to be plasmolysed
‘Can’ be reversed if placed in fresh water however there is a point where it becomes permanent/fatal
‘Can’ be reversed if placed in fresh water however there is a point where it becomes permanent/fatal
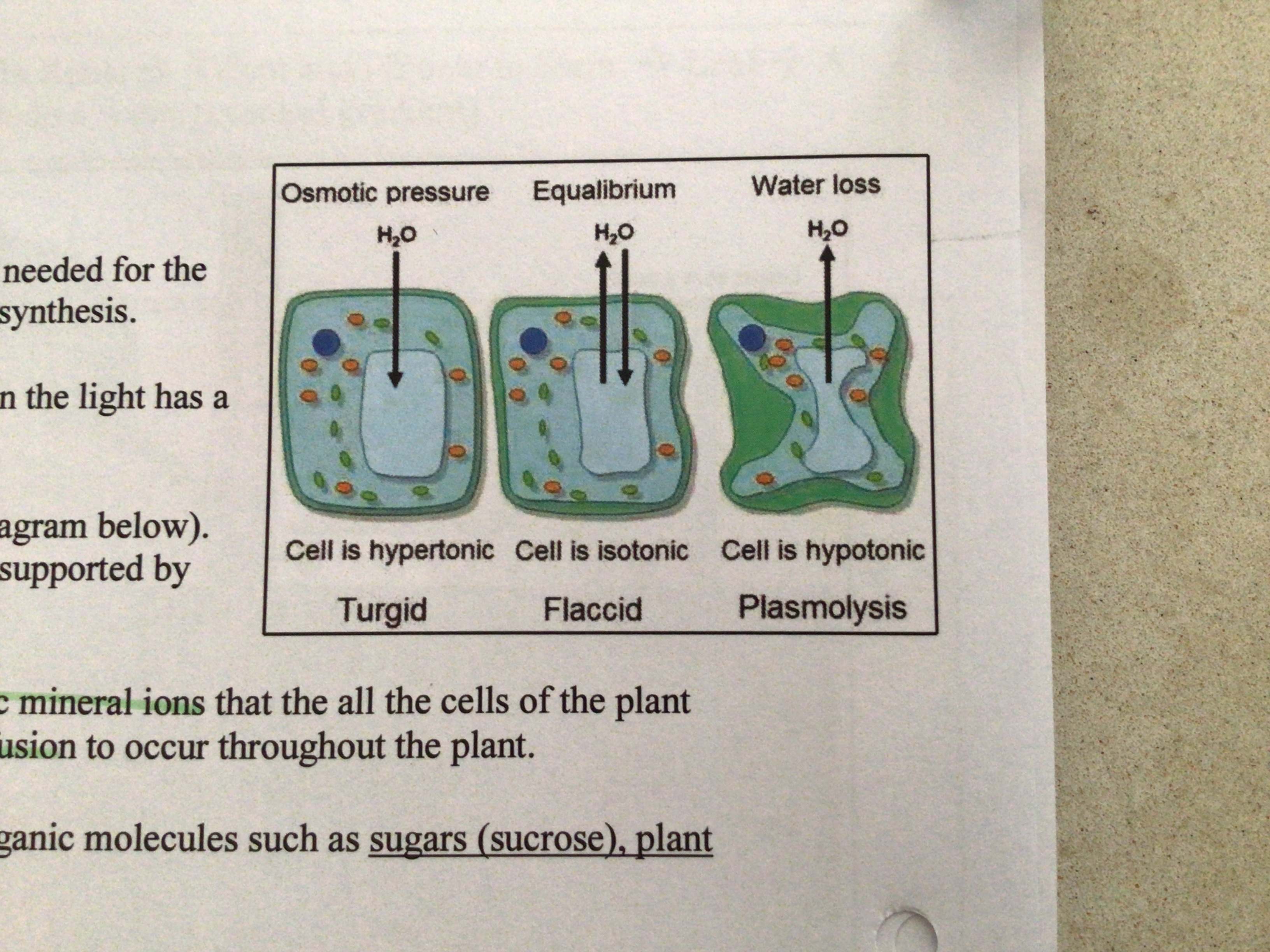
16
New cards
Explain how root pressure causes water to move up the plant
Transpiration reduces the water (hydrostatic) pressure at the top of a xylem vessel compared with the pressure at the base, so causes water to flow up the vessels
Plants may also increase the pressure difference between top and bottom by raising water pressure at base of vessels
Epidermal/endodermal cells actively transport mineral ions into the xylem vessels; reducing water potential inside the xylem vessels and causes water to move into the xylem vessels through the symplast down the water potential gradient via osmosis
The entry of water into the xylem vessels of the roots causes a ‘root pressure’ the continual movement of water into the xylem vessels serves to push the water molecules already in the xylem vessel further upwards
The pushing/upwards force of root pressure is sufficient to push water up the xylem vessel of the stem to a height of 2-3 metres
Plants may also increase the pressure difference between top and bottom by raising water pressure at base of vessels
Epidermal/endodermal cells actively transport mineral ions into the xylem vessels; reducing water potential inside the xylem vessels and causes water to move into the xylem vessels through the symplast down the water potential gradient via osmosis
The entry of water into the xylem vessels of the roots causes a ‘root pressure’ the continual movement of water into the xylem vessels serves to push the water molecules already in the xylem vessel further upwards
The pushing/upwards force of root pressure is sufficient to push water up the xylem vessel of the stem to a height of 2-3 metres
17
New cards
When is root pressure particularly important
In spring before the growing season when the leaves have not formed and are therefore not transpiring
18
New cards
how does hydrostatic pressure cause water to move up the xylem
Removal of water from xylem vessels in the leaf reduces the hydrostatic pressure in the xylem vessels
The hydrostatic pressure at the top of the xylem vessel becomes lower than the pressure at the bottom
This pressure difference causes water to move up the xylem vessels - like sucking on a straw causing a pressure difference
The hydrostatic pressure at the top of the xylem vessel becomes lower than the pressure at the bottom
This pressure difference causes water to move up the xylem vessels - like sucking on a straw causing a pressure difference
19
New cards
The lower the hydrostatic pressure the ……. The water potential
lower
20
New cards
What is the main mechanism by which water moves up the xylem
cohesion-tension hypothesis (the transportation stream)
21
New cards
What is cohesion
the force by which individual molecules stick together. Inside xylem vessels water molecules are bonded together by hydrogen bonds (force of cohesion) forming a continuous unbroken column of water
22
New cards
What does cohesion of water molecules ensure and what does it create
How does adhesion help with this
How does adhesion help with this
Ensures that water is lost at the leaf by evaporation, it pulls the column of water further up the stem to replace the water molecules being lost. This creates a tension inside the xylem vessels
This process is helped by adhesion:
Many short-lived hydrogen bonds from between the water molecules and the lignin and cellulose molecules of the xylem vessels
This process is helped by adhesion:
Many short-lived hydrogen bonds from between the water molecules and the lignin and cellulose molecules of the xylem vessels
23
New cards
What is adhesion
The force by which individual molecules (in this case water) cling to surrounding material and surfaces
24
New cards
What do cohesion and adhesion of water help with
Help to keep the water in a xylem vessel moving as a continuous column of water
Water is drawn up the stem so water flow in the xylem is always upwards
Water is drawn up the stem so water flow in the xylem is always upwards
25
New cards
Water mostly evaporates from the surface of …….. ……. Cells, a process known as ……… and water vapour leaves through the stomata
Spongy mesophyll, transpiration
26
New cards
As water leaves the xylem vessels in the leaf and then evaporates a …… is set up on the entire water column in the xylem tissue (the tension acts upwards as water is being removed from the top of the plant
\
This loss of water …… the water potential of the spongy mesophyll cells, causing water to move out of the xylem vessel into the surrounding cells down a water potential gradient by ……..
\
This loss of water …… the water potential of the spongy mesophyll cells, causing water to move out of the xylem vessel into the surrounding cells down a water potential gradient by ……..
tension
\
Lowers, osmosis
\
Lowers, osmosis
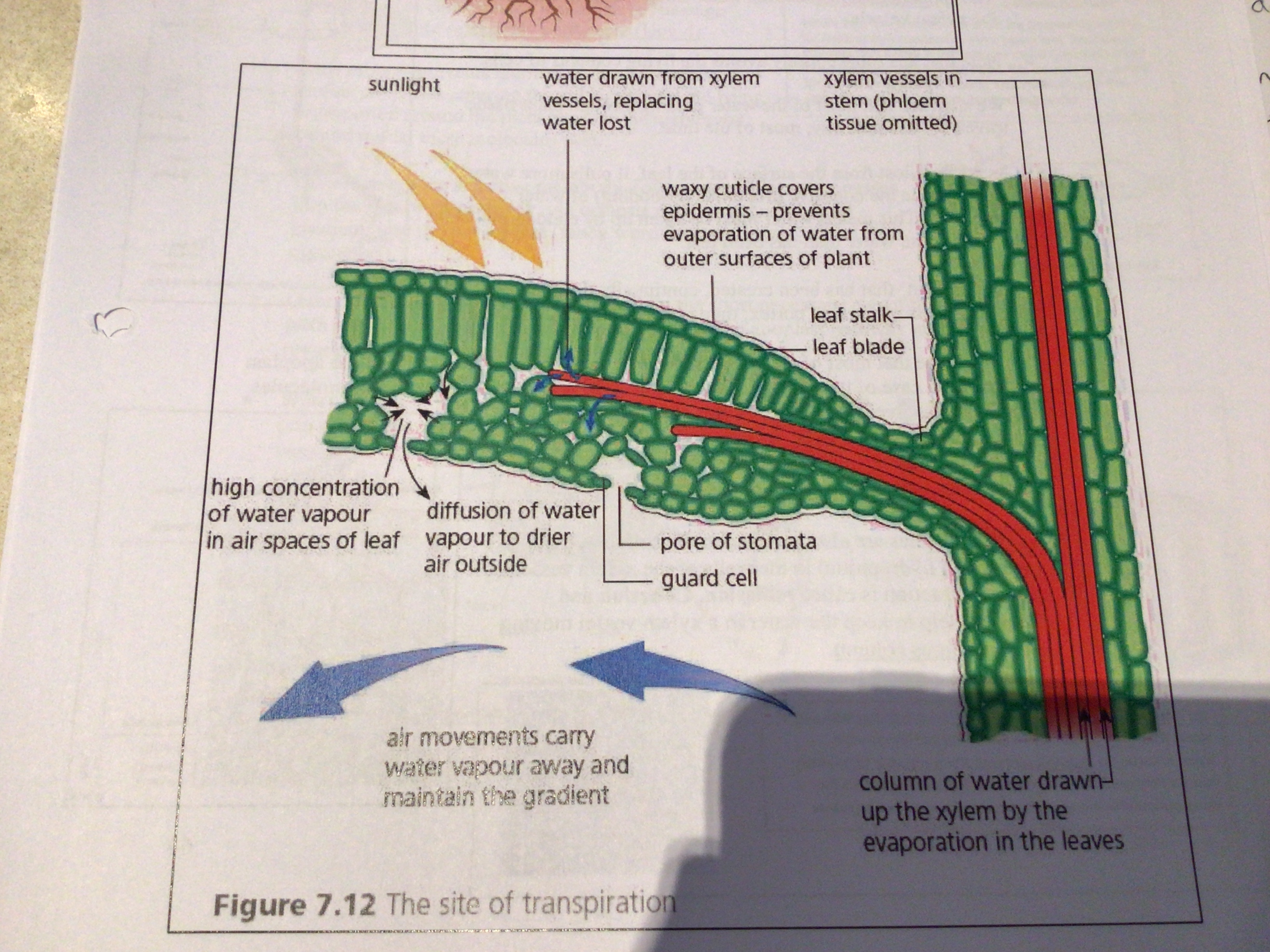
27
New cards
During the transpiration pull there is a …… pressure within the xylem
The more tension, the ….. the diameter of the xylem becomes
The more tension, the ….. the diameter of the xylem becomes
Negative
Smaller
Smaller
28
New cards
Is the apoplast pathway living or non living
Non living as water does not enter the cytoplasm
29
New cards
Describe the apoplast pathway
occurs between the mesh-like cellulose fibres in the plant cell walls (the gaps between each side of the cell wall) these gaps are water-filled so offer little resistance to the flow of water
Water travels from cell wall to cell wall without ever entering the cytoplasm of the cortical cells (cells of the cortex)
The apoplast also includes the water-filled spaces of dead cells of the xylem vessels
Water travels from cell wall to cell wall without ever entering the cytoplasm of the cortical cells (cells of the cortex)
The apoplast also includes the water-filled spaces of dead cells of the xylem vessels
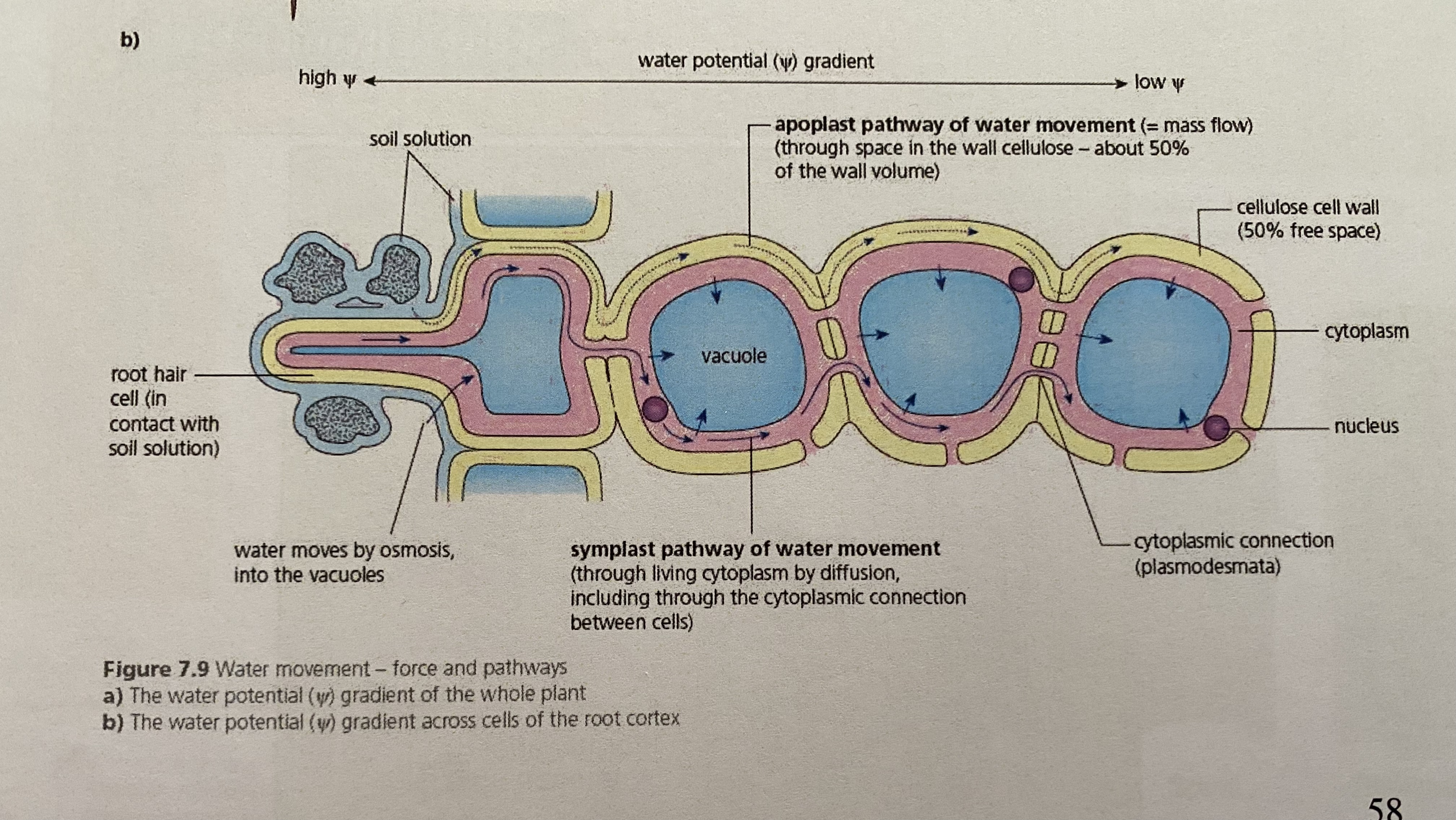
30
New cards
Most water passes through the …….. pathway most of the time, a case of transport by ‘…….. …….’
Apoplast, mass flow
31
New cards
Are cellulose and lignin hydrophobic or hydrophilic
both hydrophilic
32
New cards
The casparian strip is a waterproof strip found in the ……… it blocks the ……… pathway so that water and ions have to be transported by the …….. pathway. It’s responsible for selective mineral uptake and controls the water …….. - it lowers the water potential in the xylem so that water moves up the xylem
endodermis, apoplast, symplast, potential
33
New cards
The only way for water to cross the endodermis is through the ….. of the endodermal cells not through the cell walls
As endodermal cells get older the Suberin deposits become more extensive except in certain cells called …….. cells, through which water can continue to pass freely, this is the route water must take
This gives plants control over what mineral ions pass into the xylem as everything has to cross the cell surface membrane here (preventing harmful toxins/viruses entering xylem)
As endodermal cells get older the Suberin deposits become more extensive except in certain cells called …….. cells, through which water can continue to pass freely, this is the route water must take
This gives plants control over what mineral ions pass into the xylem as everything has to cross the cell surface membrane here (preventing harmful toxins/viruses entering xylem)
Cytoplasm (symplast pathway)
Passage
Passage
34
New cards
once through the selective membrane of passage cells water passes into the ……. Pathway via osmosis and into the cytoplasm
Symplast
35
New cards
What happens to water once through the casparian strip and the short distance of the symplastic pathway
Most water returns to the apoplast pathway and travels the remaining short distance to reach the xylem vessels
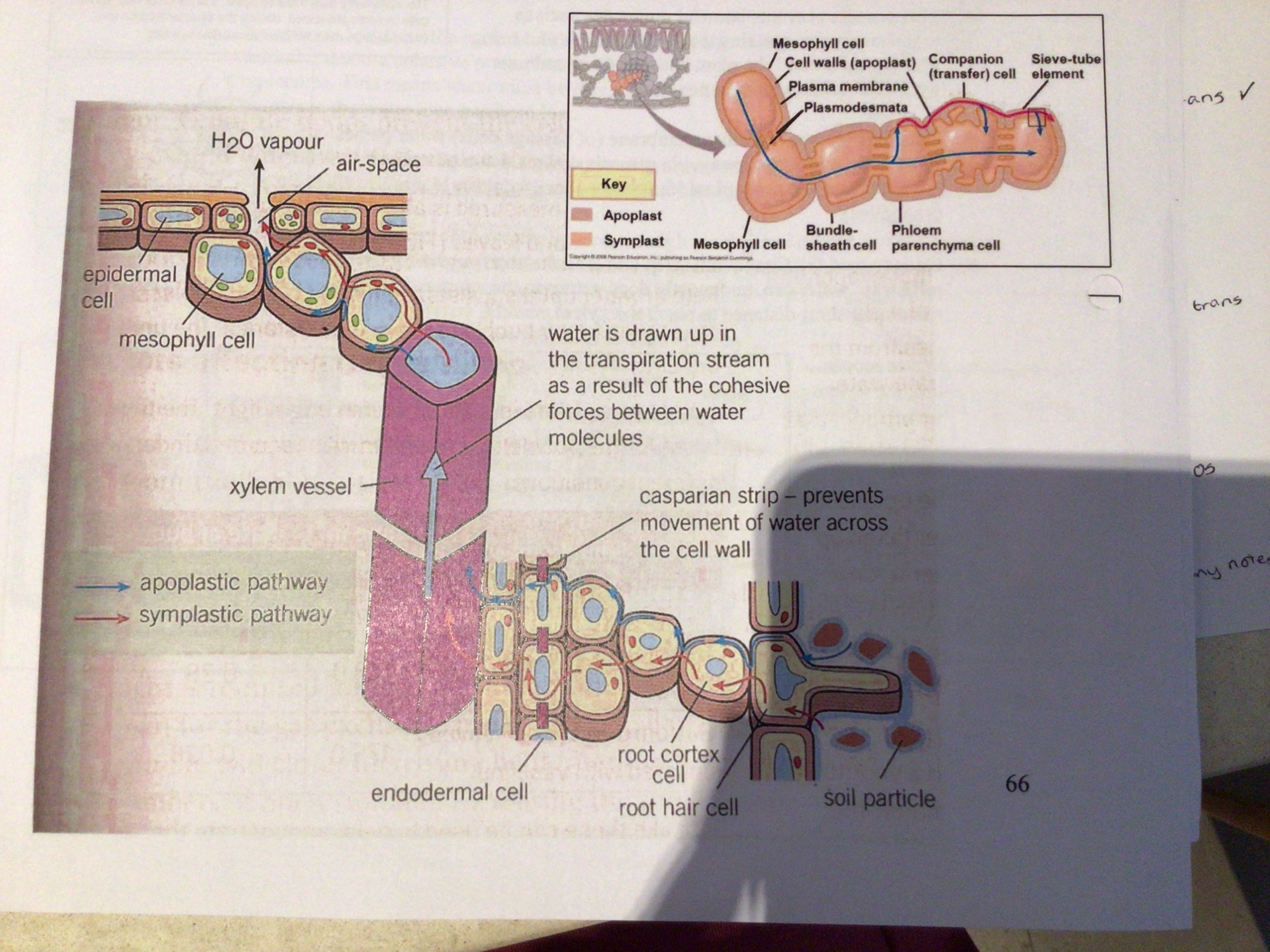
36
New cards
How does water move into the xylem vessels
through the pits in their walls
37
New cards
Where are the apoplastic and symplastic pathways found
They occur in the root, stem and leaf
38
New cards
Describe how water moves in the symplastic pathway
1. Water enters the cytoplasm by osmosis through the partially permeable membrane
2. Water moves into the sap in the vacuole through the too plastic by osmosis
3. Water may move from cell to cell through the plasmodesmata
4. Water may move from cell to cell through adjacent cell surface membranes and cell walls
39
New cards
Describe how water moves in the apoplastic pathway
1. Water enters the cell wall
2. Water moves through the cell wall
3. Water may move from cell wall to cell wall through the intercellular spaces
4. Water may move directly from cell wall to cell wall
40
New cards
What are plasmodesmata
Strands of cytoplasm that directly connect one cell to the adjacent cell so that water can take a cytoplasmic route across the cortex, towards the endodermis, essentially creates a continuous cytoplasm extending from the root hair to the xylem at the centre of the root
41
New cards
When transpiration rates are especially high, more water travels by the ……. Pathway
Apoplastic
42
New cards
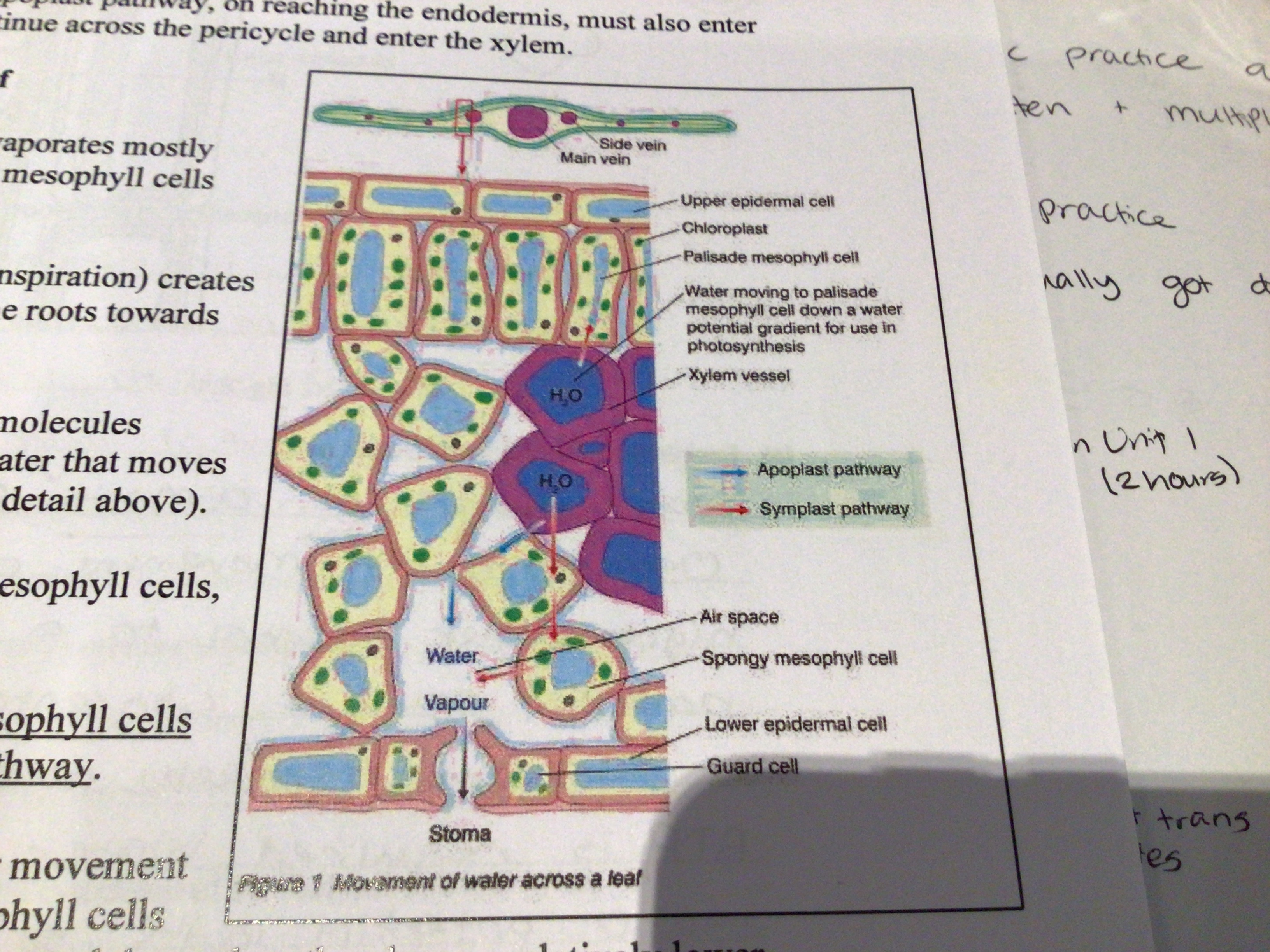
How does water move from the xylem across the leaf
Once water is lost from the spongy mesophyll cells and into the air spaces around them, they have a relatively lower water potential as they have lost water from their cytoplasm.
So water enters from neighbouring cells
These adjacent cells have also lost water so they also need more water from neighbouring cells
In this way a water potential gradient is established that pulls water from the xylem across the leaf mesophyll and finally into the atmosphere
So water enters from neighbouring cells
These adjacent cells have also lost water so they also need more water from neighbouring cells
In this way a water potential gradient is established that pulls water from the xylem across the leaf mesophyll and finally into the atmosphere