Chemistry - Electrolysis
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
Why do covalent compounds not conduct electricity?
There are no freely moving charged particles
When do ionic compounds conduct electricity?
When molten or in an aqueous solution
Why do ionic compounds only conduct electricity when molten or in an aqueous solution?
The ionic bonds are broken, allowing ions to move freely.
Anion
Negatively charged ion
Cation
Positively charged ion
Electrolysis
Binary ionic compound are compounds consisting of just two elements joined together by ionic bonding
E.g. lead(II) bromide
These compounds undergo electrolysis and always produce their corresponding element
The positive ion will migrate towards the cathode and the negative ion will migrate towards the anode
Therefore the cathode product will always be the metal and the product formed at the anode will always be the non-metal
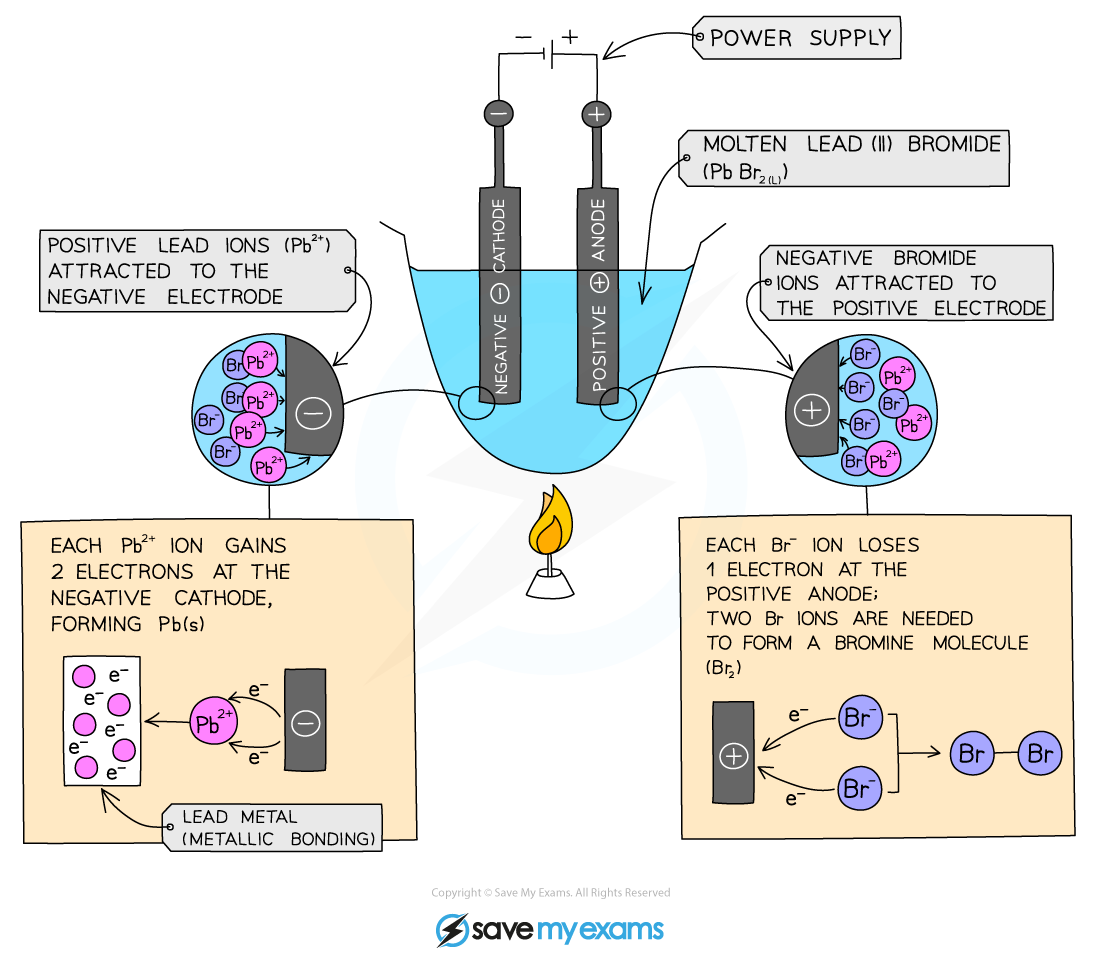
Electrolysis Method
Add lead(II) bromide into a crucible and heat so it will turn molten, allowing ions to be free to move and conduct an electric charge
Add two graphite rods as the electrodes and connect this to a power pack or battery
Turn on the power pack or battery and allow electrolysis to take place
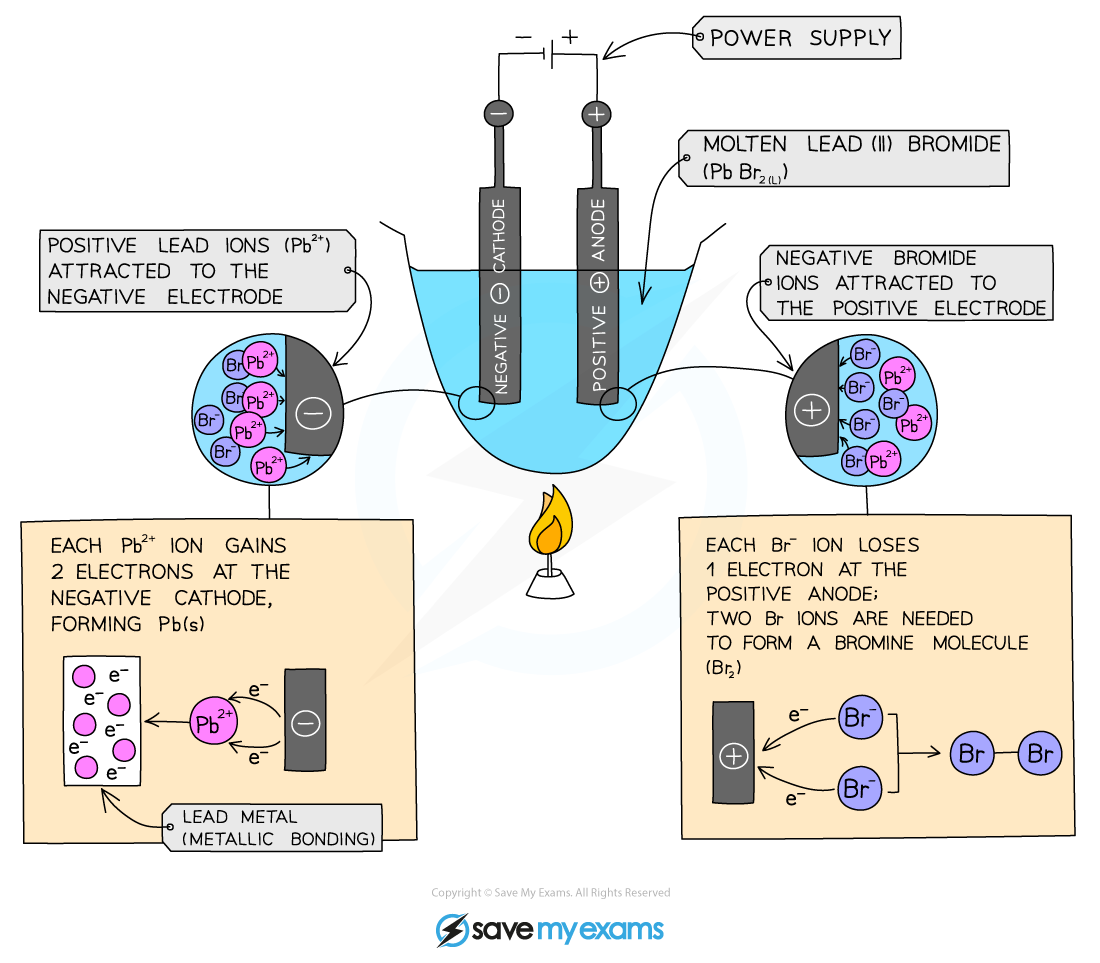
What happens at the anode?
Negative bromide ions move to the positive electrode (anode)
At the anode, they lose two electrons to form bromine molecules
There is bubbling at the anode as brown bromine gas is given off
The negatively charged ions lose electrons and are thus oxidised
What happens at the cathode?
Positive lead ions move to the negative electrode (cathode)
At the cathode they gain electrons to form grey lead metal
The lead deposits on the bottom of the electrode
The positively charged ions gain electrons and are thus reduced
Oxidation (electrons)
When a substance loses electrons (OILRIG)
Reduction (electrons)
When a substance gains electrons (OILRIG)
In the electrolysis of molten lead(II) bromide the half equation at the negative electrode (cathode) is:
Pb2+ + 2e– ⟶ Pb Reduction
At the positive electrode (anode) bromine gas is produced by the discharge of bromide ions:
2Br– – 2e– ⟶ Br2 Oxidation
OR
2Br– ⟶ Br2 + 2e–