AP Biology units 1 + 2
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
Tyrosine Kinases
Enzymes use ATP; transfer phosphate to proteins; cell cell communication
Capsule is in eukaryotes, prokaryotes, or bacteria"?
Bacteria
Capsules
Slimy outer layer, protects cells, made of polysaccharide (sugar), prevents host from detection
Lysosomes
Digest waste, recycle
Lysosomes in animal or plant
animal cells
Peroxisomes eukaryotic or prokaryotic
eukaryotic
peroxisomes function
organelles that detoxify, breakdown fatty acids for mitochondria
MItochondria function
Produce ATP from glucose; cellular respiration- takes oxygen & produces energy; controls cell apoptosis, growth, division
Contractile vacuoles function
Organelles for osmoregulation; controls water balance; pumps water out to prevent lysing
Turgor
pressure inside central vacuole from water pushing
Cellulose function
Carb; structural support; in cell walls
Chloroplast function
Photosynthesis
parts of chloroplast
grana (thylakoids), stroma, chlorophyll, double membrane, DNA
Desmosomes plant or animal cells
animal cells
desmosomes function
cell structure; connect filaments between cells; form intercellular connections; stability
plasmodesma plant or animal
Plant cell
Bulk Flow
Large transport of liquid/gas;
Plants: phloem, sugars leave to roots
Animals: blood circulation, airflow
Faciliated diffusion
transport proteins, NO ATP, down concentration gradient, uses cells own kinetic energy
Active vs Faciliated diffusion
active goes aagainst concentration gradient and uses pumps
Phagocytosis
type of endocytosis- vesicle w/ macromolecule merges w/ plasma membrane; lets things in
pinocytosis
type of endocytosis- only fluids inside vesicle
endosymbiosis
cells inside each other in symbiotic relationship.
says eukaryotes formed when a larger prokaryote engulfed smaller prokaryotes that had specific functions
Plant & animal cells similarities
mitochondria, nucleus, ribosomes, cytoplasm, E.R, golgi, double membrane
Plant only components
Chloroplast, central vacuole, cell wall
Animal cells only component
Lysosomes
Chloroplast func
photosynthesis; light dependent reactions inside thylakoids where chlorophyll takes sunlight and converts to ATP;
Calvin Cycle- inside stroma, uses ATP to convert carbon dioxide into glucose (sugar, food)
Synthesize amino acids & fatty acids
gas exchange thru stomata
MItochondria func
Apoptosis and oxygen production
Convert glucose into ATP
Apoptosis
why is hydrogen bonding important for waters properties?
Cohesion - hydrogen bonds allow water to stick to itself, also surface tensioin
Adhesion - water sticks to other things bc of hydrogen bonds, also capillary action
High heat capcity- hydrogen bonds must be broken to gain temp.
Density - when water freezes, hydrogen bonds arrange molecules to crystal
Name functionl groups
Hydroxyl (-OH), Carbonyl (C=O), Carboxyl (-COOH), Amino group (-NH2), Sulfhydryl (-SH), PHosphate group, Methyl (-CH3)
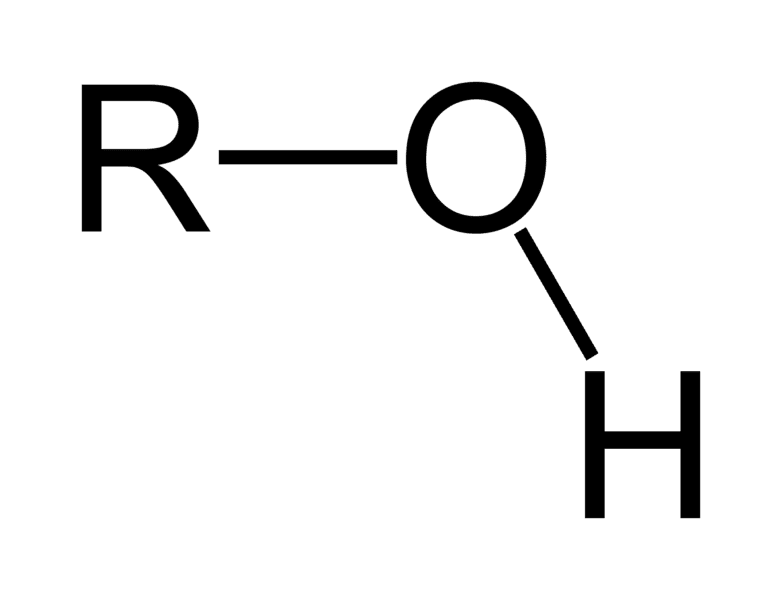
name the functional group
Hydroxyl
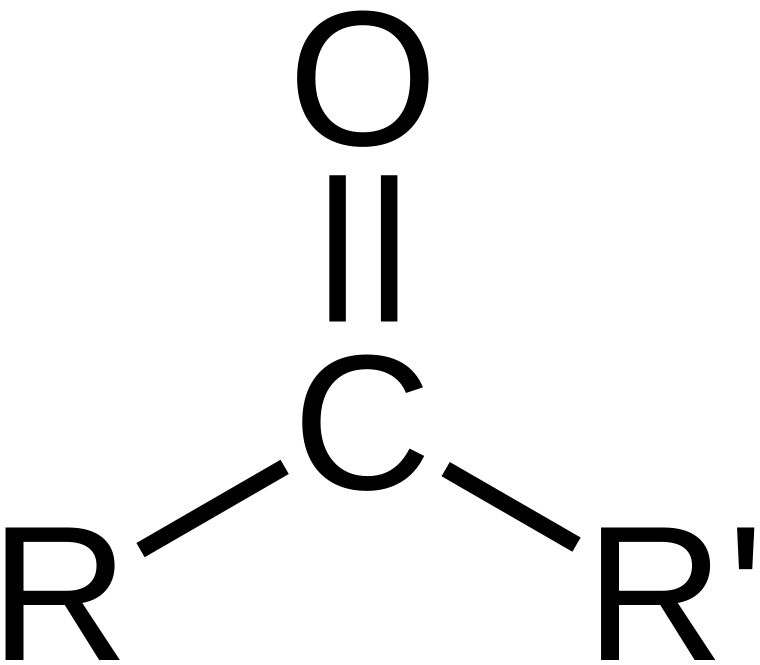
Name the func group
Carbonyl
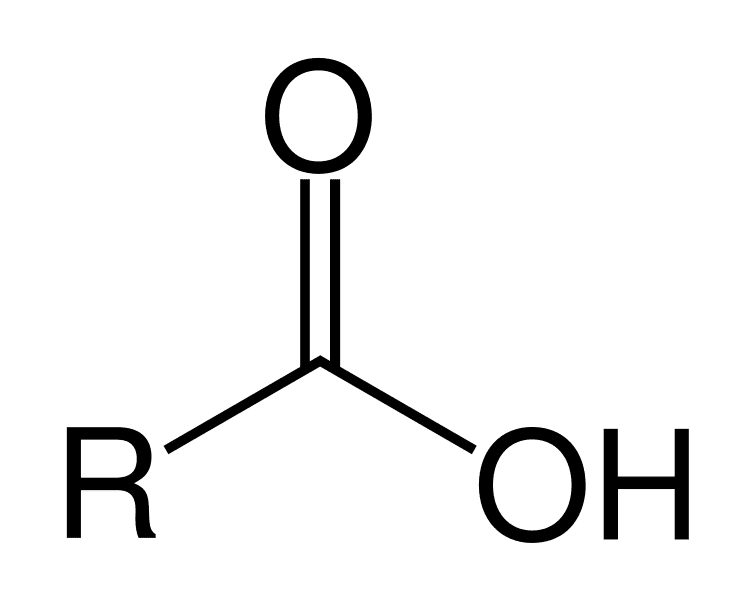
Carboxyl

Amine
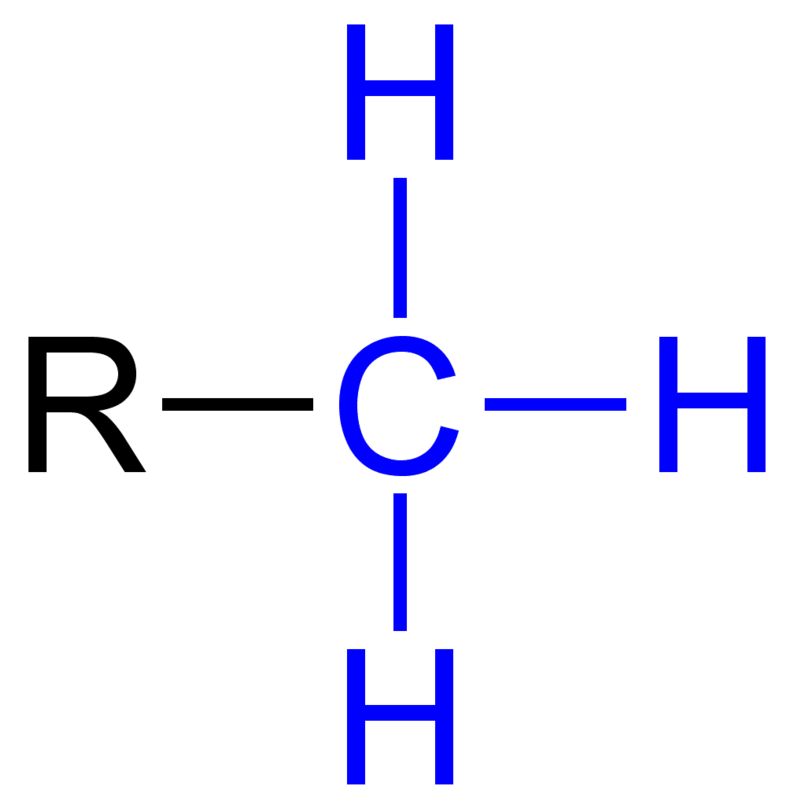
Methyl
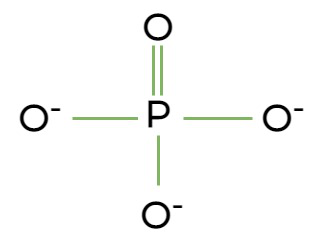
phosphate
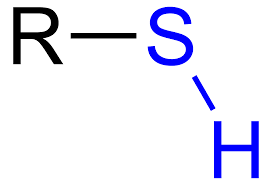
sulfhydryl
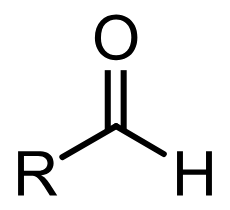
aldehyde
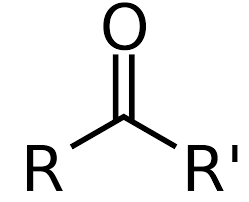
ketone