UGBA- Chapter 6, Chapter 7-8
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
A production function defines the output that can be produced:
A) at the lowest cost, given the inputs available.
B) for the average firm.
C) if the firm is technically efficient.
D) in a given period if no additional inputs are hired.
E) as technology changes over time.
C
A function that indicates the maximum output per unit of time that a firm can
produce, for every
combination of inputs with a given technology, is called:
A) an isoquant.
B) a production possibility curve.
C) a production function.
D) a cost function
C
Which of the following inputs are variable in the long run?
A) Labor
B) Capital and equipment
C) Plant size
D) all of these
D
For many firms, capital is the production input that is typically fixed in the short
run. Which of the
Would the following firms face the longest time required to adjust their capital
inputs?
A) A firm that makes DVD players
B) Computer chip fabricator
C) Flat-screen TV manufacturer
D) Nuclear power plant
D
When labor usage is at 12 units, output is 36 units. From this, we may infer that:
A) the marginal product of labor is 3.
B) the total product of labor is 1/3.
C) the average product of labor is 3.
D) none of the above
C
The law of diminishing returns assumes that:
A) there is at least one fixed input.
B) all inputs are changed by the same percentage.
C) additional inputs are added in smaller and smaller increments.
D) all inputs are held constant
A
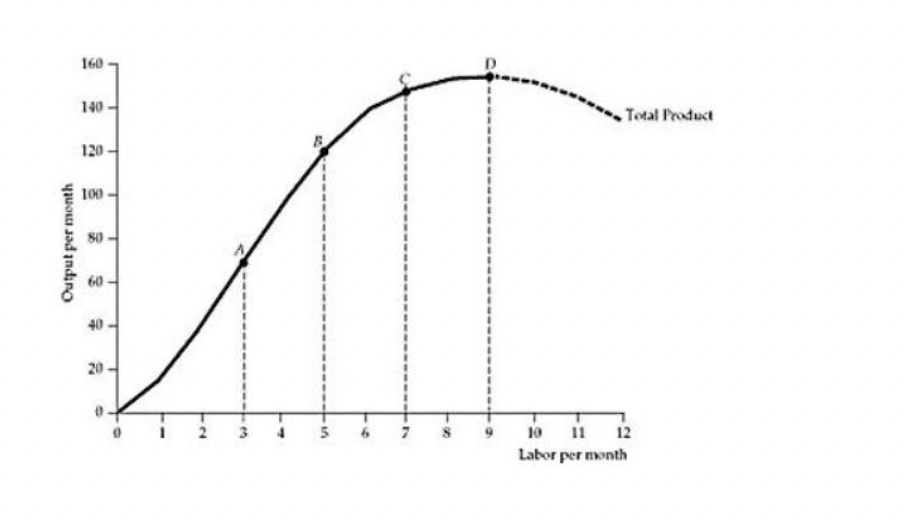
Refer to the Figure above. At point A, the marginal product of labor is:
A) rising.
B) at its minimum.
C) at its maximum.
D) diminishing.
A
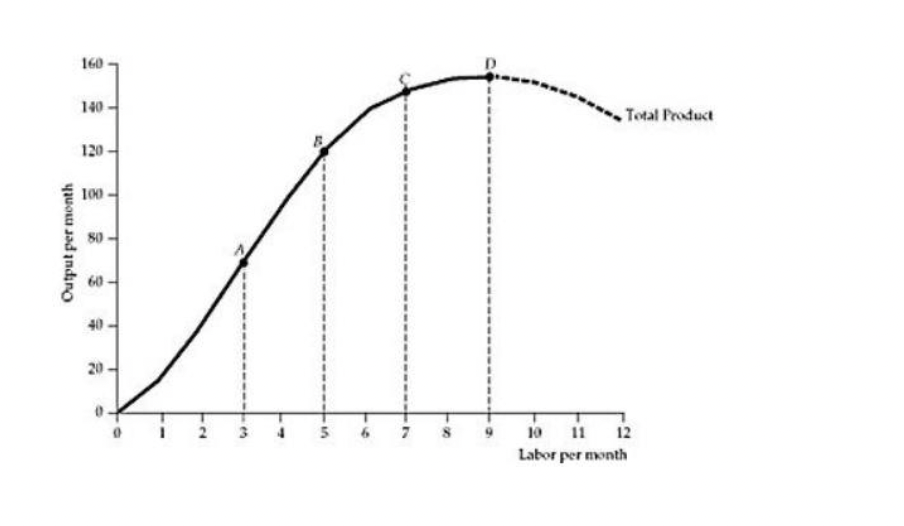
Refer to the Figure above. At which point on the total product curve is the
average product of labor
the highest?
A) Point A
B) Point B
C) Point C
D) Point D
E) None of the above
B
Refer to Figure above. Which of the following statements is false?
A) At point E the marginal product of labor is decreasing.
B) At point E the marginal product of labor is negative.
C) At point E the average product of labor is decreasing.
D) At point E the average product of labor is negative.
E) At point E the marginal product of labor is less than the average product of
labor
D
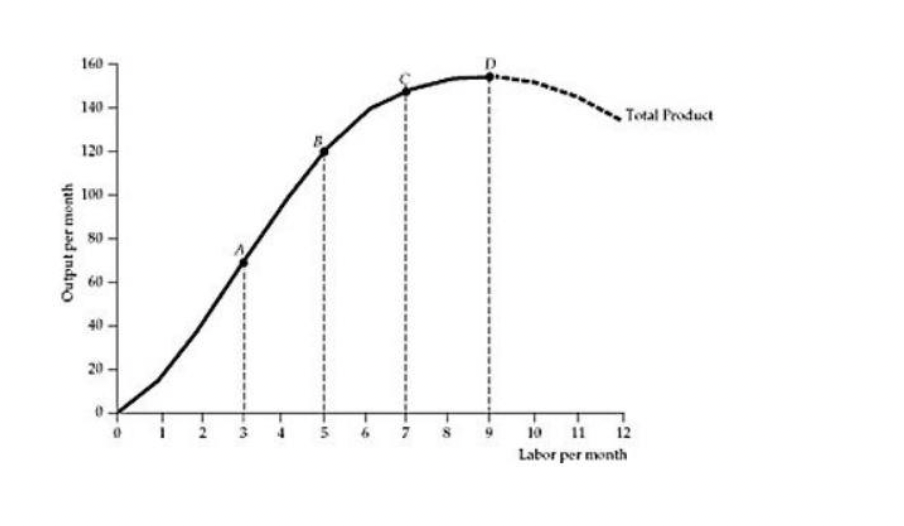
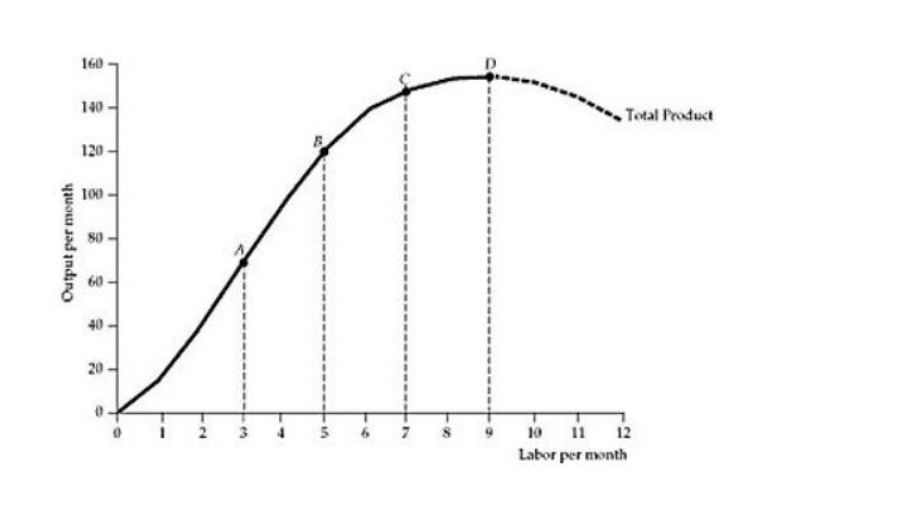
Refer to Figure 6.2.1 above. At point C:
A) the marginal product of labor is greater than the average product of labor.
B) the average product of labor is greater than the marginal product of labor.
C) the marginal product of labor and the average product of labor are equal.
D) the marginal product of labor and the average product of labor are both
increasing.
E) Both B and D are correct
B
Which of the following statements does not explain why US healthcare
expenditures are higher than in other countries?
A) Government policies have shifted the healthcare production function downward
over time.
B) Consumer incomes have increased, which allows consumers to purchase more
health care.
C) The US health care system is relatively inefficient compared to other countries
D) Demand for health care in the US has increased, so health care production occurs at a higher point on the total product curve than in other countries.
A
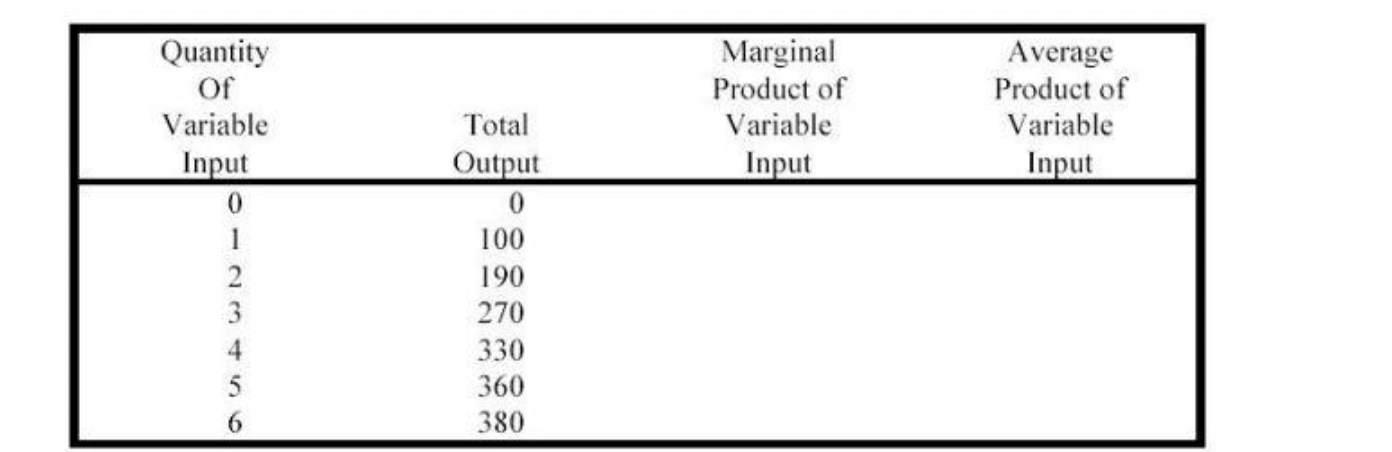
Complete the table
The marginal rate of technical substitution is equal to:
A) the absolute value of the slope of an isoquant.
B) the ratio of the marginal products of the inputs.
C) the ratio of the prices of the inputs.
D) all of the above
E) A and B only
E
An L-shaped isoquant:
A) is impossible.
B) would indicate that the firm could switch from one output to another costlessly.
C) would indicate that the firm could not switch from one output to another.
D) would indicate that capital and labor cannot be substituted for each other in
production.
E) would indicate that capital and labor are perfect substitutes in production
D
In a production process, all inputs are increased by 10%; but output increases
by less than 10%. This
means that the firm experiences:
A) decreasing returns to scale.
B) constant returns to scale.
C) increasing returns to scale.
D) negative returns to scale
A
Farmer Jones bought his farm for $75,000 in 1975. Today the farm is worth
$500,000, and the interest rate is 10 percent. ABC Corporation has offered to buy
the farm today for $500,000 and XYZ Corporation has offered to buy the farm for
$530,000 one year from now. Farmer Jones could earn net profit of $15,000 (over
and above all of his expenses) if he farms the land this year. What should he do?
A) Sell to ABC Corporation.
B) Farm the land for another year and sell it to XYZ Corporation.
C) Accept either offer as they are equivalent.
D) Reject both offers
A
Prospective sunk costs:
A) are relevant to economic decision-making.
B) are considered as investment decisions.
C) rise as output rises.
D) do not occur when output equals zero
A
The total cost (TC) of producing computer software diskettes (Q) is given as: .
What is the variable cost?
A) 200
B) 5Q
C) 5
D) 5 + (200/Q)
E) none of the above
B
Carolyn knows the average total cost and average variable cost for a given level
of output. Which of the following costs can she not determine given this
information?
A) Total cost
B) Average fixed cost
C) Fixed cost
D) Variable cost
E) Carolyn can determine all the above costs given the information provided.
E
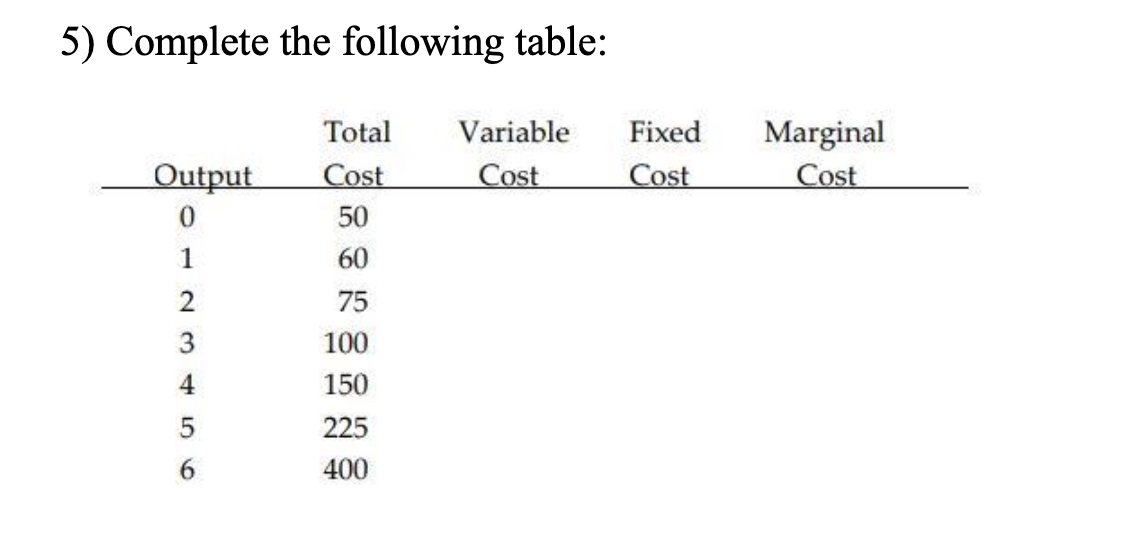
^
^
Use the following two statements to answer this question:
I. The average cost curve and the average variable cost curve reach their minima at
the same level of output.
II. The average cost curve and the marginal cost curve reach their minima at the
same level of output.
A) Both I and II are true.
B) I is true, and II is false.
C) I is false, and II is true.
D) Both I and II are false
D
Consider the following statements when answering this question:
I. If the marginal product of labor falls whenever more labor is used, and labor is
the only factor of production used by the firm, then at every output level the firm's
short-run average variable cost exceeds marginal cost.
II. If labor obeys the law of diminishing returns and is the only factor of production
used by the firm, then at all output level short-run average variable costs exceed
marginal costs.
A) I is true, and II is false.
B) I is false, and II is true.
C) I and II are both true.
D) I and II are both false.
A
In our analysis, it is best to treat capital as if it was:
A) rented, even if it was purchased.
B) purchased, even if it is just rented.
C) purchased and rented.
D) rented first, then purchased
A
An effluent fee is imposed on a steel firm to reduce the amount of waste
materials that it dumps in a
river. Use the following two statements to answer this question:
I. The more easily factors of production can be substituted for one another (for
example, capital can be used to reduce wastewater), the more effective the fee will
be in reducing effluent.
II. The greater the degree of substitution of capital for wastewater, the less the firm
will have to pay in effluent fees.
A) Both I and II are true.
B) I is true, and II is false.
C) I is false, and II is true.
D) Both I and II are false
A
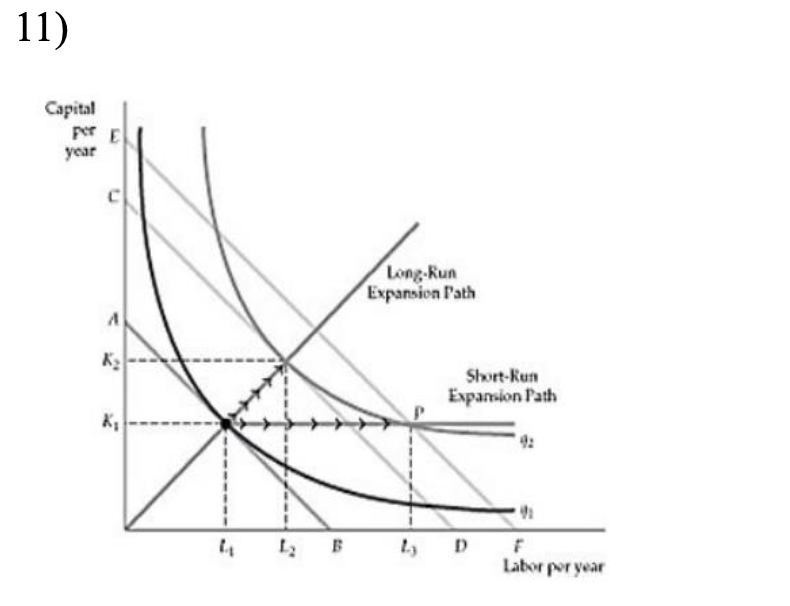
Refer to Figure above. An increase in production, from q1 to q2:
A) is more costly in the short run than in the long run.
B) uses more capital in the short run.
C) uses less inputs in the long run.
D) costs the same in the short run or in the long run.
A
Assume that a firm's production process is subject to increasing returns to scale
over a broad range of outputs. Long-run average costs over this output will tend to:
A) increase.
B) decline.
C) remain constant.
D) fall to a minimum and then rise
B
A price taker is:
A) a firm that accepts different prices from different customers.
B) a consumer who accepts different prices from different firms.
C) a perfectly competitive firm.
D) a firm that cannot influence the market price.
E) both C and D
E
Which of the following is an example of a homogeneous product?
A) Gasoline
B) Copper
C) Personal computers
D) Winter parkas
E) both A and B
E
Which of the following is a key assumption of a perfectly competitive
market?
A) Firms can influence market price.
B) Commodities have few sellers
C) It is difficult for new sellers to enter the market.
D) Each seller has a very small share of the market.
E) none of the above
D
Several years ago, Alcoa was effectively the sole seller of aluminum
because the firm owned nearly all of the aluminum ore reserves in the
world. This market was not perfectly competitive because this situation
violated the:
A) price-taking assumption.
B) homogeneous product assumption.
C) free entry assumption.
D) A and B are correct.
E) A and C are correct.
E
Revenue is equal to:
A) price times quantity.
B) price times quantity minus total cost.
C) price times quantity minus average cost.
D) price times quantity minus marginal cost.
E) expenditure on production of output
A
Suppose your firm operates in a perfectly competitive market and
decides to double its output. How does this affect the firm's marginal
profit?
A) Marginal revenue and marginal cost increase
B) Marginal revenue increases but marginal cost remains the same
C) Marginal cost may change but marginal revenue remains the same
D) Marginal revenue and marginal cost decrease
B
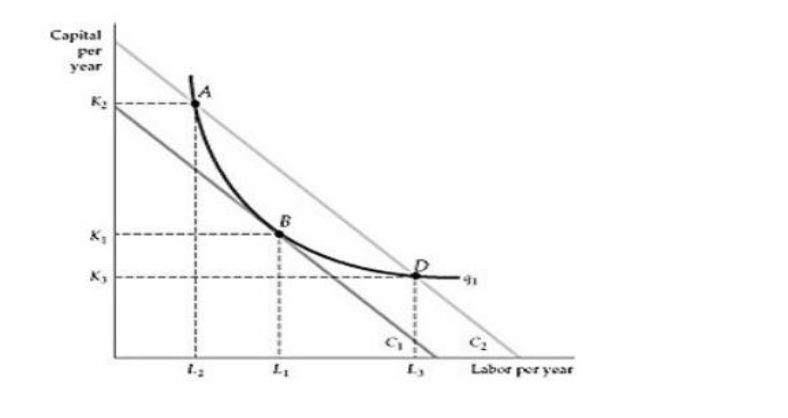
Refer to Figure above. Which point on the graph shows the optimal combination
of inputs?
A) Point A when the production process is capital intensive
B) Point B
C) Point D when the production process is capital intensive
D) All three points, A, B and D are optima
B