Test 1
1/146
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
147 Terms
Elements in Organic Compounds
HCONSP
(Please See Her New Orange Cat - PSHNOC)
Orbitals
Represents location of electron in an atom
Probability maps which show a statistical distribution of where the electron is likely to be found
Atomic orbitals are denoted by __Orgo focuses on __
s, p, d, f
s, p
s orbitals are _
s orbitals are spherically symmetric
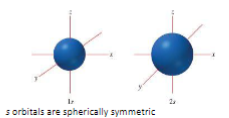
The 2s orbital has a _
The 2s orbital has a nodal surface
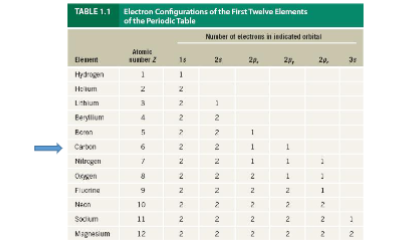
Electron configurations
Be familiar
Polarity is based on _
Polarity is based on differences in electronegativity between the 2 atoms in the bond

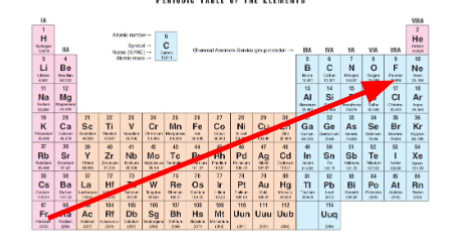
Trend of electronegativity on periodic table
Electronegativity greatest in the North East
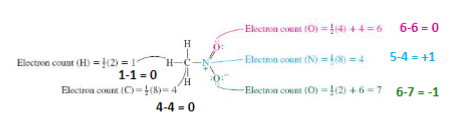
Formal charge
who owns the electrons
analysis shows us how to place charges
very strong indicator of a structure’s behavior
How to calculate formal charge
(Electrons owned by the atom) = (one electron per bond) + (all lone pair electrons)
(Formal charge) = (valance electrons) - (electrons owned by the atoms)
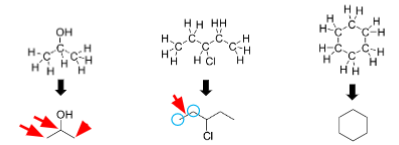
Carbon stability
C - anions very unstable
C - cations very unstable
C only likes having 4 bonds
Line drawings
a simplification of expression of the carbon skeleton
Each end and every bend in between indicate carbon atoms
Hydrogens on carbons are inferred
Only heteroatoms and their Hs are explicitly drawn
Formal charges, when present, ae ALWAYS shown explicitly
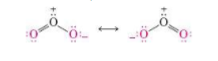
Resonance
Electron delocalization
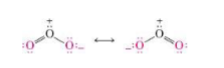
Resonance Rules
Connectivity is remains the same (no moving single bonds)
Number of electrons and net charge is the same
Number of unpaired electrons is the same
Any structure that exceeds octet rule for 2nd row elements is invalid
Predicting the major contributor
The structure with the greater number of covalent bonds contributes more
When octet rule satisfied, the major structure has least charge separation
When octet rule satisfied, the major contributor has the negative charge on most electronegative element
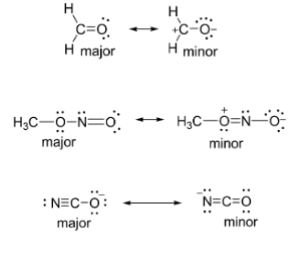
Rank in order of major to minor contributors
Left most, right most, middle
Left most is the superior major contributor because of the octet rule
Right most is a close 2nd but has ion in the middle
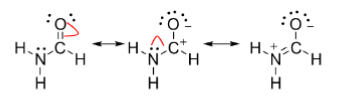
Resonance structures
Depict the ‘limit’ of delocalization
Resonance hybrids
Reflect the average overall delocalization
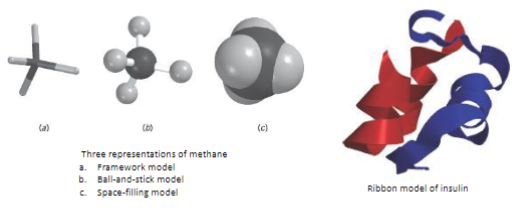
Types of molecular models
a. Framework model
b. ball-and-stick model
c. Space-filling model
d. Ribbon model
Molecular dipoles
Mutual cancelation of dipoles result in no net dipole moment
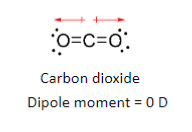
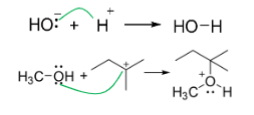
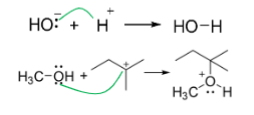
Curved arrows
Represent movement of electrons (Resonance)
Reaction mechanisms
Dissociation (heterolysis)
Bond formation (coordination)
Substitution (e.g: Substitution)
Acid-Base reactions (proton-transfer reaction)
Rules of arrows
correct arrows show movement of electrons only, Not atoms
start arrows at electron source (either a lone pair or a bond, never an atom)
point arrows to electron target (either an atom or a bond, never a lone pair)
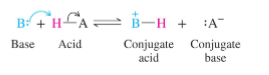
Strong acids form:
a stable anion (weak conjugate base)
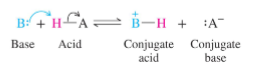
Weak acids form:
an unstable anion (strong conjugate base)
Arrangement of 2 electron pairs
linear (180 degrees)

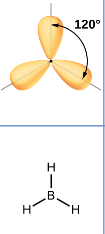
Arrangement of 3 electron pairs
trigonal planar (120 degrees)
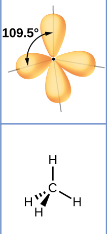
Arrangement of 4 electron pairs
tetrahedral (109.5 degrees)
Molecular Geometry of an atom with 2 bonding pairs and 0 lone pairs
linear
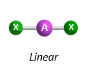
Molecular Geometry of an atom with 3 bonding pairs and 0 lone pairs
trigonal planar
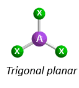
Molecular Geometry of an atom with 2 bonding pairs and 1 lone pair
bent or angular
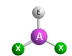
Molecular Geometry of an atom with 4 bonding pairs and 0 lone pairs
tetrahedral
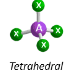
Molecular Geometry of an atom with 3 bonding pairs and 1 lone pair
trigonal pyramidal
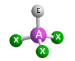
Molecular Geometry of an atom with 2 bonding pairs and 2 lone pairs
bent or angular
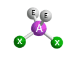
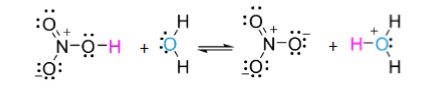
Bronsted Acid
Proton donor (species with an H)
Bronsted Base
Proton Acceptor (species with a pair of electrons)
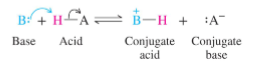
In a column on the periodic table, the _ the conjugate base anion the _ the acid
In a column on the periodic table, the LARGER the conjugate base anion the STONGER the acid
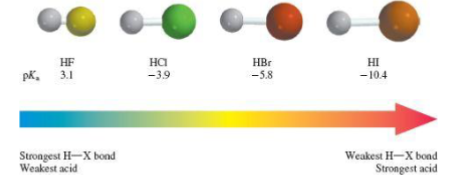
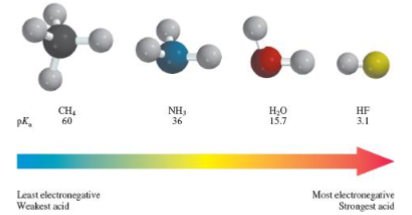
Across a row in the periodic table, _ is the most accurate predictor of acid strength
Across a row in the periodic table, ELECTRONEGATIVITY is the most accurate predictor of acid strengthThe more electronegative the stronger the acid
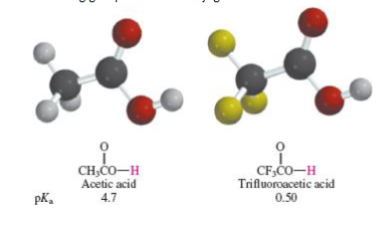
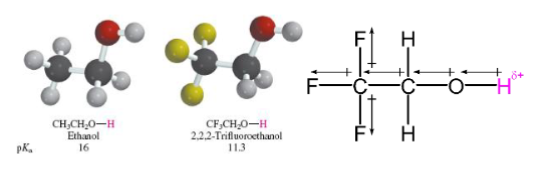
Inductive withdrawing groups near the conjugate base anion atom _ the acidity
Inductive withdrawing groups near the conjugate base anion atom INCREASE the acidity
If the CB anion can delocalize electrons then CB is _ and the parent acid is _
If the CB anion can delocalize electrons then CB is WEAK and the parent acid is STRONG
Acid Base Reaction proceeds to form _
Acid Base Reaction proceeds to form weaker acid or base
Lewis Acid
Electron acceptor
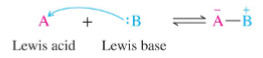
Lewis Base
Electron donor
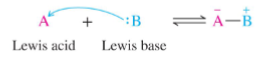
What are the classes of hydrocarbons?
Alkanes
Alkenes
Alkynes
Arenes
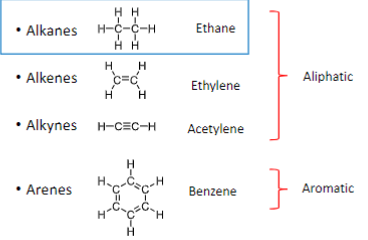
Which classes of hydrocarbons are Aliphatic?
Ethane, Ethylene, and Acetylene
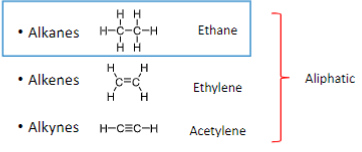
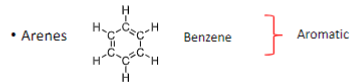
Which classes of hydrocarbons are Aromatic?
Arenes
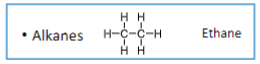
The general chemical formula for alkanes
CnH2n+2
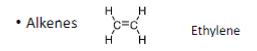
The general chemical formula for alkenes
CnH2n
The general chemical formula for alkynes
CnH2n-2
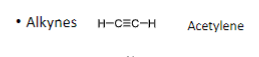
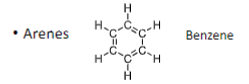
The general chemical formula for arenes
CnH2n-6mm is number of rings
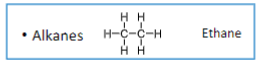
Alkanes have _ bonds
Single
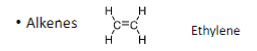
Alkenes have _ bonds
double
Alkynes have _ bonds
triple
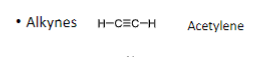
Arenes have _ bonds
Alternating double and single
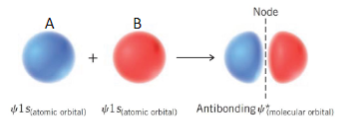
Antibonding
A-B out of phase
Energy Cost
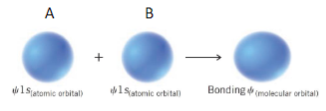
Bonding
A+B in phase
Energy saved
sp3 hybridization
Are the average of the 4 contributing orbitals and are equal in energy
Tetrahedral
sp2 hybridization
Are the average of the 3 contributing orbitals: 2s orbital and 2 of the 2 px and the 2py orbitals
Shape at centers is planar
Constitutional isomers
Same molecular formula
Different connectivity
Different physical properties
n-alkanes
condensed structural formulae of the higher n-alkanes
CnH2n+2
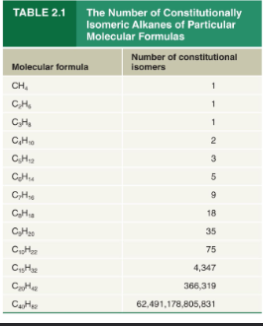
Number of constitutional isomers compared to molecular formula
The number of constitutional isomers possible quickly increases with each added carbon
IUPAC name of unbranched alkanes with 7 carbons
Heptane
Steps to IUPAC Nomenclature
Find the longest continuous chain of C atoms, assign a parent name to the compound corresponding to the IUPAC names of the unbranched alkane having the same number of carbons
List the substituents attached to the longest continuous chain in alphabetical order
Use the prefixes di-, tri-, tetra, and so on when the same substituent appears more than onceIgnore these prefixes when alphabetizing
Number from the end of the chain in the direction that gives the lower locant to a substituent at the first point of difference
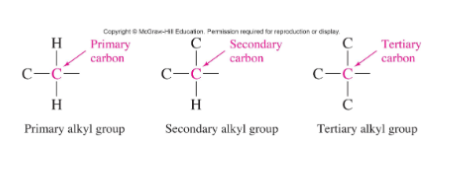
Alkyl groups (Primary vs Secondary vs Tertiary)
Correlates to the number of carbon attached to the carbon in question
3 common complex branch alkyl groups
Isopropyl
Tert-butyl
Sec-butyl
Another name for the complex branch alkyl group: 1-methylethyl
Isopropyl
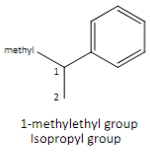
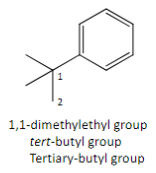
Another name for the complex branch alkyl group: 1.1-dimethylethyl
Tert-butyl group
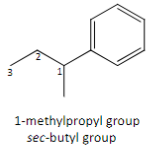
Another name for the complex branch alkyl group: 1-methylpropl
Sec-butyl group
Nomenclature for cycloalkanes
Same as with linear alkanes just add cycloalkane in front of parent names
Keep locant numbers low (the sum should be as low as possible)
Physical Properties of alkanes (there’s 4)
Low melting point
Poor solubility in water
Boiling point lower than analogous amines or alcohols
Boiling points change among isomers
What affects boiling point of alkanes
Stronger intermolecular attractive forces increase the boiling points
Dipole-dipole (including hydrogen bonding)
Dipole/induced-dipole
Induced-dipole/induced dipole
Combustion of alkanes
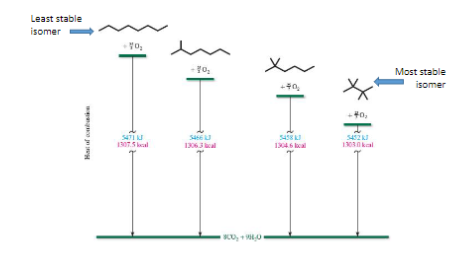
Based on stability of isomers
The less stable the greater the heat of combustion
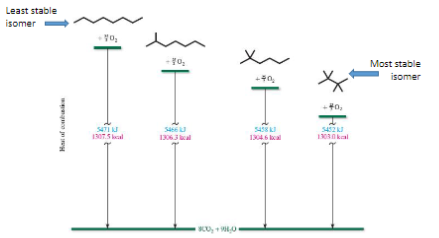
Stability of isomers
The more branching means more stable means less energy released