3.1.6 Chemical equilibria
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
Dynamic equilibrium
When the concentrations of the reactants and products are constant, and the forward and backward reactions are going at the same rate
Can only occur in a closed system (nothing get can get in or out) which is at a constant temperature
Le Chatelier’s principle
A theory that states that if there’s a change in concentration, pressure or temperature, the equilibrium position will move to help counteract the change
The effect of changing concentration
If the concentration of a reactant increases, the system counteracts the change by shifting the equilibrium to the right, forming more products
If the concentration of a product increases the system counteracts the change by shifting the equilibrium to the left, forming more reactants
If concentration of either decreases the opposite happens

The effect of changing pressure
Changing the pressure only affects equilibria involving gases
If the pressure increases, the equilibrium shifts to the side with the fewer gas molecules, reducing the pressure, hence counteracting the change
If the pressure decreases, the equilibrium shifts to the side with the more gas molecules, increasing the pressure, hence counteracting the change

The effect of changing temperature
If the temperature increases, the equilibrium shifts in the endothermic direction (positive direction)
If the temperature decreases, the equilibrium shifts in the exothermic direction (negative direction)

Le Chatelier’s principle with industrial processes
Equilibrium constant
A ratio worked out from the concentration of the products and reactants once a reversible reaction has reached equilibrium
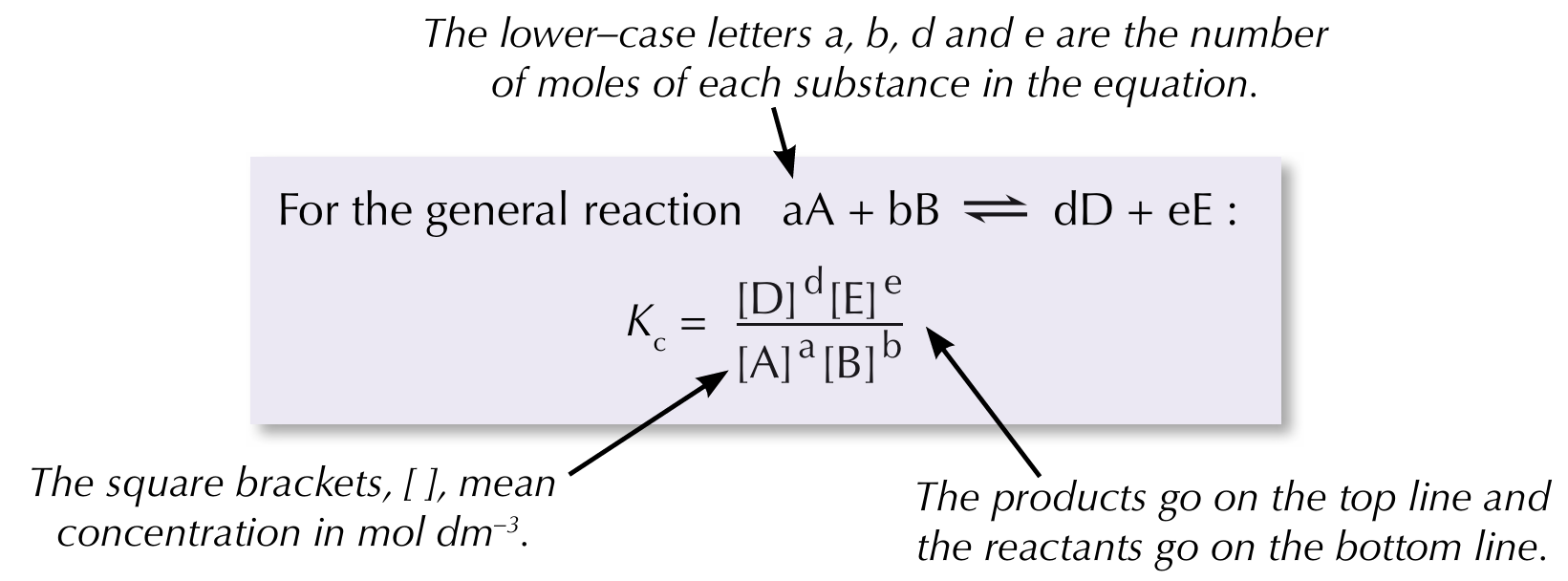
Calculating equilibrium constant
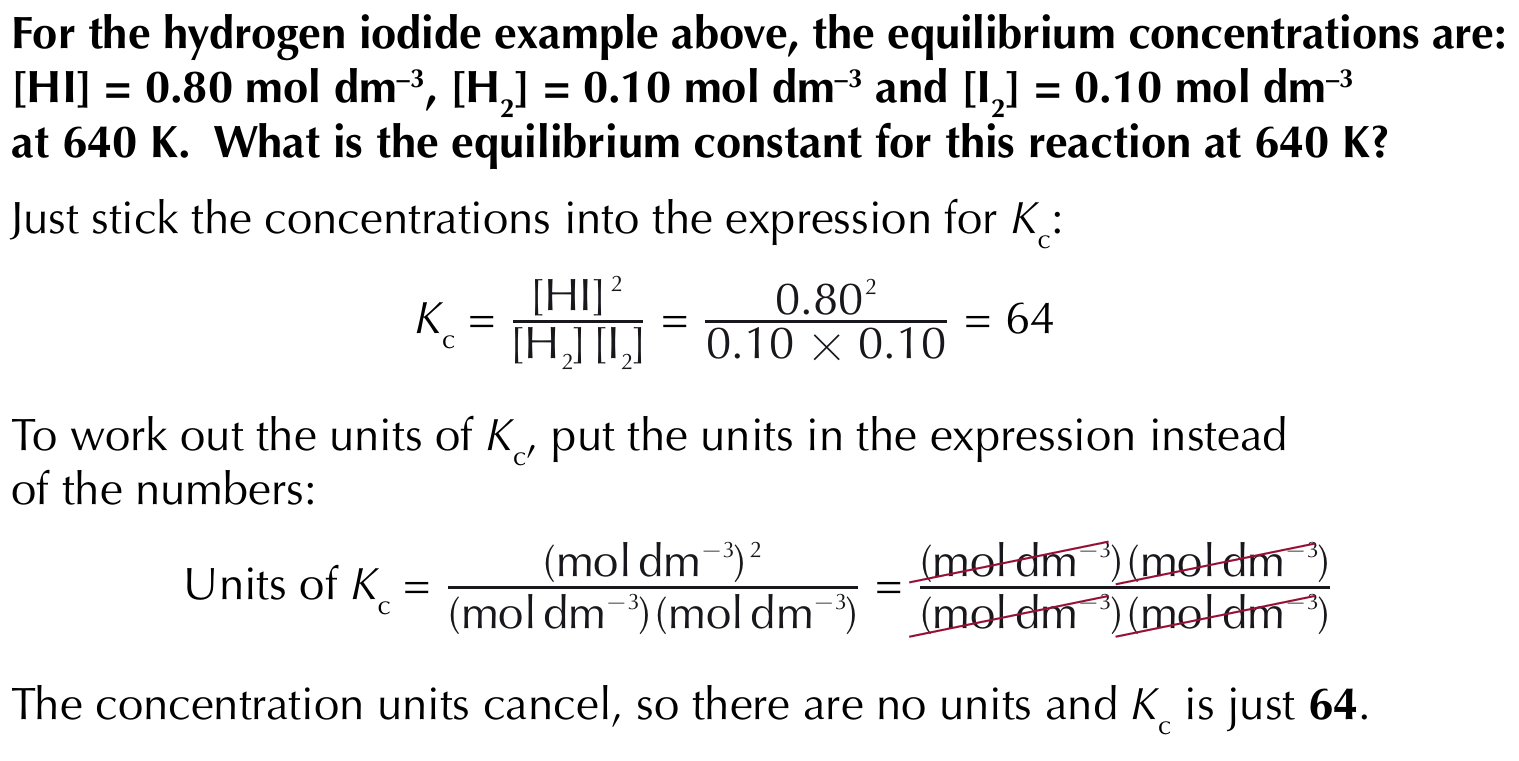
If you know the equilibrium concentrations, you can use the expression to work out equilibrium constant
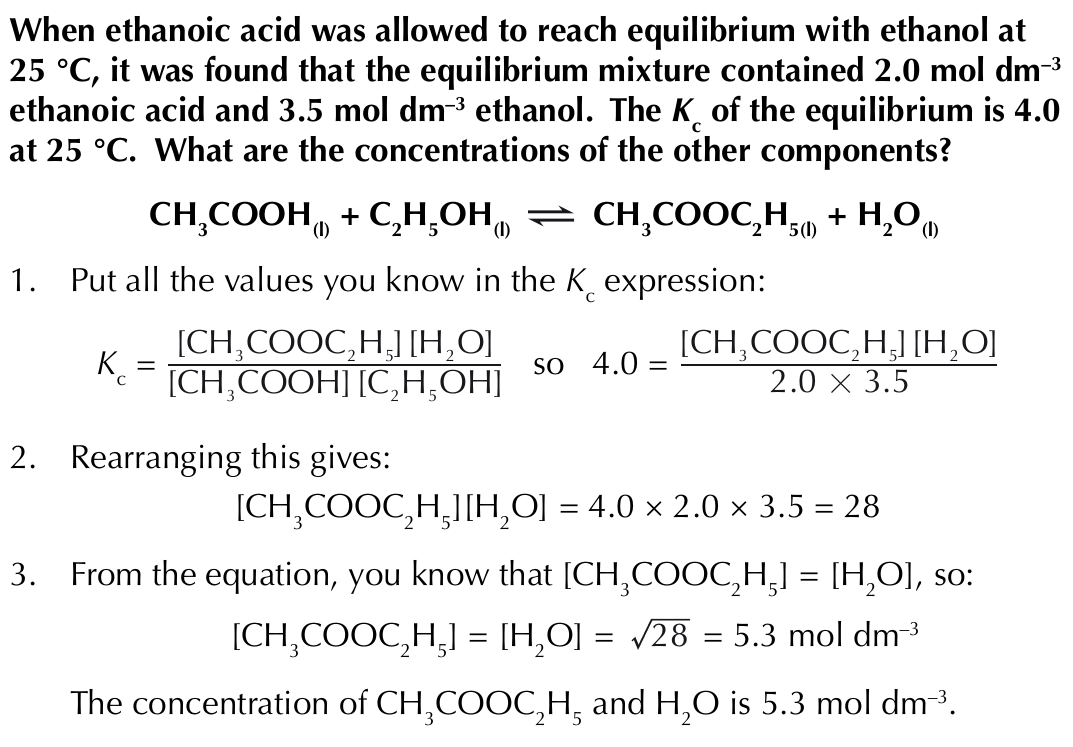
Calculating unknown equilibrium concentrations
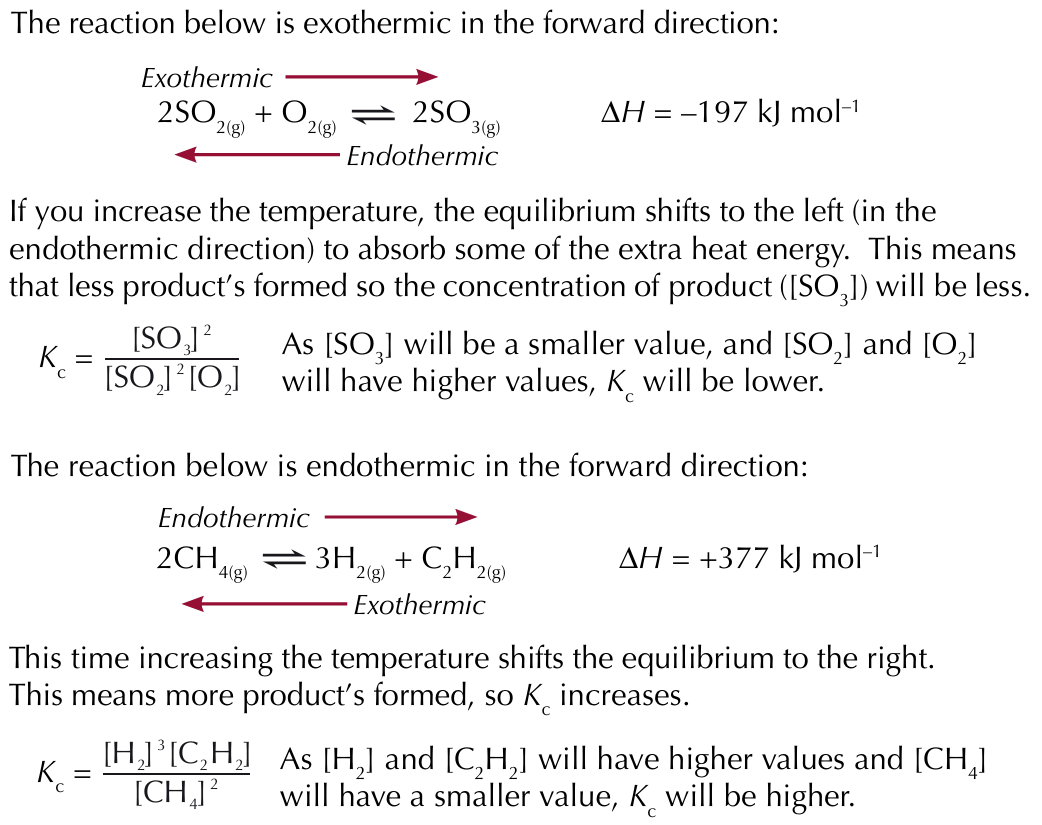
Factors affecting the equilibrium constant - changing temperature
If the temperature change results in more products being formed, K꜀ will increase
If the temperature change results in less products being formed, K꜀ will decreases
Factors affecting the equilibrium constant - changing concentration
If the concentration of one thing in the equilibrium mixture changes, then the concentrations of the others must change to keep the value of K꜀ the same
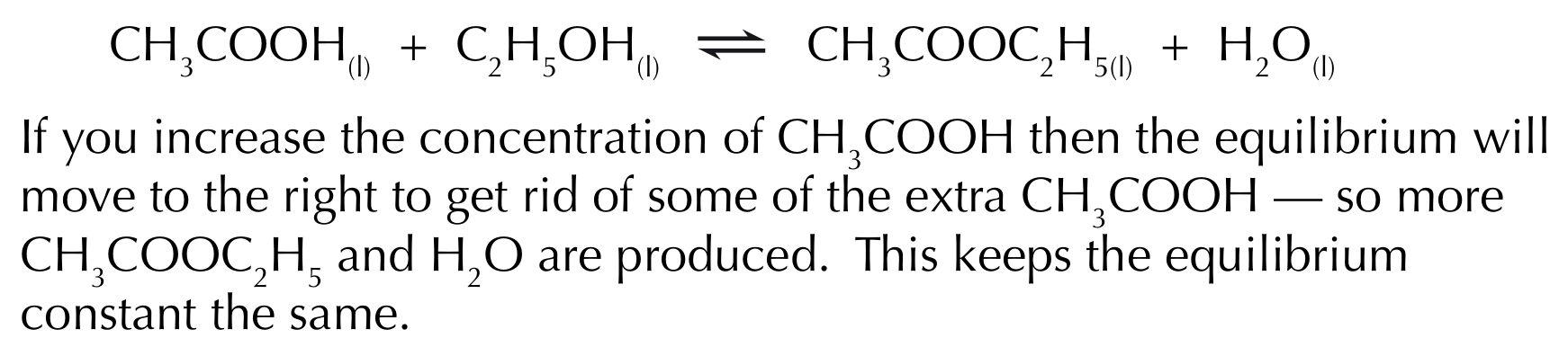
Factors affecting the equilibrium constant - adding a catalyst
When a catalyst is added there is no change to the position of the equilibrium or to the value of K꜀ as the catalyst will increase the rate of reaction of both the forward and backward reaction by the same amount