4. Industry and Commerce
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
Industrialisation
start when and why at that time
18th century, earlier than in other Europ. countries due to:
• moderate climate & topography
• political stability
• accessible deposits of coal & iron
• availability of labourers
• availability of capital
• potential markets
Industrialisation: “Workshop of the World”
UK as most powerful economy worldwide over majority of 19th ct
around 1850:
-UK coal & raw iron production abt as much as rest of europe combined
-cotton processing uk: 267000t, rest of europe: 162000t
-UK responsible for c. 28% of all industrial goodds and c, 25% of all trade worldwide
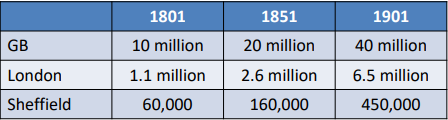
Industrialisation: Social & Cultural implications
• Population growth, particularly in cities
→ overcrowding
→ bad sanitation
• Standardisation of daily life & products
• Availability of mass-produced products
Transport revolution
before: transport by foot or if rich, by horse
-building of canals btw. industrial centres in 1800: move heavy goods
-invention of steam engine: development of railway: first railway between liverpool and manchester 1830 → private companies, not centralised
-1845 many new railways → excitement, overwhelm
-railway makes people who would have never met be able to communicate
transport revolution
shipbuilding and merchant navy
19th century: shipbuilding as important part of UK economy
→ biggest merchant navy in the world
decline during 20th century
The Rise (and Fall?) of Trade Unions
• around 1800: ‘combination’ of workers prohibited
• from 1825: trade unions allowed (restrictions)
• Trade Union Act (1871): greatly expands rights of TUs, including the right to strike
• in the 19th cent., many small unions for skilled workers (→ special interests)
• 20th cent., growing importance of nation-wide unions, e.g., National Union of Mineworkers (NUM), and the supra-structure Trade Union Congress (TUC)
• political influence through Labour Party
The 1970s & 1980s – Oil Crisis
-stop selling oil to certain countries → high inflation:
Unions demand higher wages
Miners strikes in 1972 & 1974
he 1970s & 1980s – Winter of Discontent (1978/79)
• Background: ‘social contract’ with unions to limit wage increase to bring down inflation (1975-77)
• No new agreement reached • Series of strikes
• Cold winter isolates part of the country
• PM James Callaghan (Labour) denied there was a serious situation
• Elections in May 1979 bring Tory victory → Margaret Thatcher becomes PM
he 1970s & 1980s – Miner’s Strike 1984/85
National Coal Board announces closure of 20 mines, loss of 20,000 jobs
• Strikes against the closure of coal mines
→ not backed by nation-wide vote
→ not backed by TUC
→ labelled ‘illegal’ strike
→ only affected some coal fields
→ led to divisions within NUM
• Pitted PM Thatcher against NUM president Scargill
• Thatcher on unions: “the enemy within”
• Strike ended after almost a year, without any NCB concessions
→ more closures of mines followed
20th Century: Decline of UK Industry
1950: 30% iof UK wealth came from manufacturing
2016: only 12%
Rise (and Fall) of the Department Store
Shopping becomes leisure activity (for the rich) during the later 18th century
• Employment opportunity
• Turn 19th/20th cent.: cultural institutions
→ e.g., Harrods
• From 1950s, national chains
→ e.g., Debenhams
• 21st cent.: online shopping leads to decline/demise
→ e.g., Debenhams liquidated 2021
Financial Market – Banks
• Bank of England founded 1694
• Bank of Scotland founded 1695
• 18th century: numerous banks established
• late 18th century: “merchant banks”
→ Rothschild & Baring prominent
• 1930s banking services offered to less wealthy
• 1980s increased deregulation
→ massive expansion of banking sector
UK Currency (before 1971)
Pound / Shilling / Pence (£/S/d)
12 Pence to the Shilling, 20 Shillings to the Pound
Legal System(s)
‘Civil Law’ – historically derived from Roman law, based on legal principles, codified e.g. “Code Napoleon” or “Bürgerliches Gesetzbuch”
→ legal system in most of continental Europe
‘Common Law’ – customary law, based upon judicial decisions in previous cases (precedent)
→ legal system in England, the USA and many countries of the former British Empire
‘Statute Law’ – system of law set down by a legislature (i.e., parliament) in written statutes (also: statutory law)