Anatomy and Physiology Exam 2 full content: Histology and Bones
1/80
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
81 Terms
fibroblast (immature), Fibrocyte (mature)
What are the immature and mature cell names for connective tissue proper?
chondroblast (immature, chondrocyte (mature)
What are the immature and mature cell names for cartilage?
osteoblast (immature), osteocyte (mature)
What are the immature and mature cell names for bone?
hematopoietic stem cell (immature), Macrophage (mature)
What are the immature and mature cell names for blood?
Loose
areolar
adipose
reticular
Dense
regular
irregular
elastic
What are the subcategories of connective tissue proper?
provides reserved fuel, insulates against heat lost and supports and protects organs. found in kidneys, eyeballs, breasts and primarily under the skin in subcutaneous tissue
what is the function of adipose tissue?
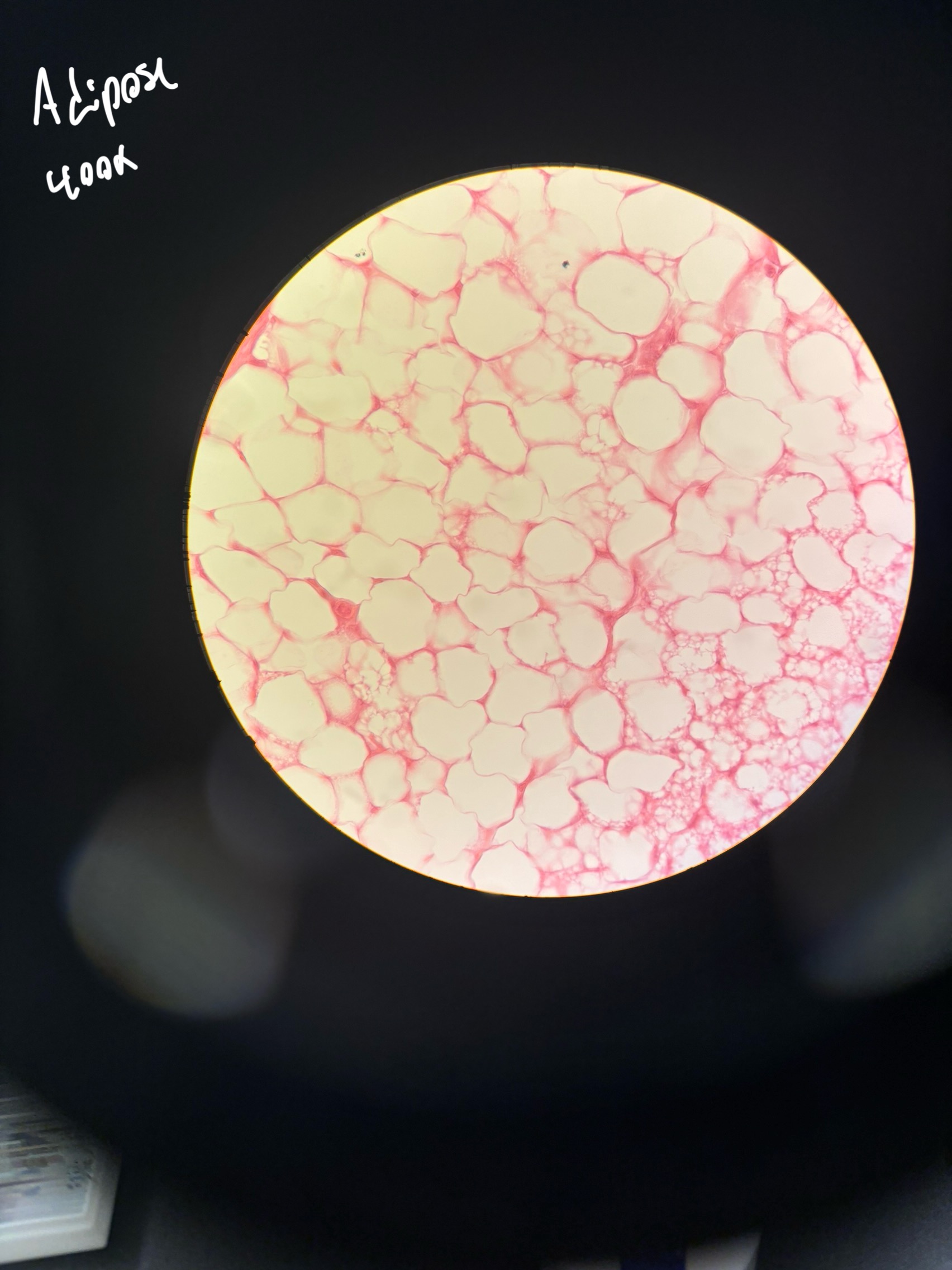
supports other cell types like lymphocytes, mast cells, and macrophages. found in lymph nodes, spleen and bone marrow
What is the function of reticular tissue?
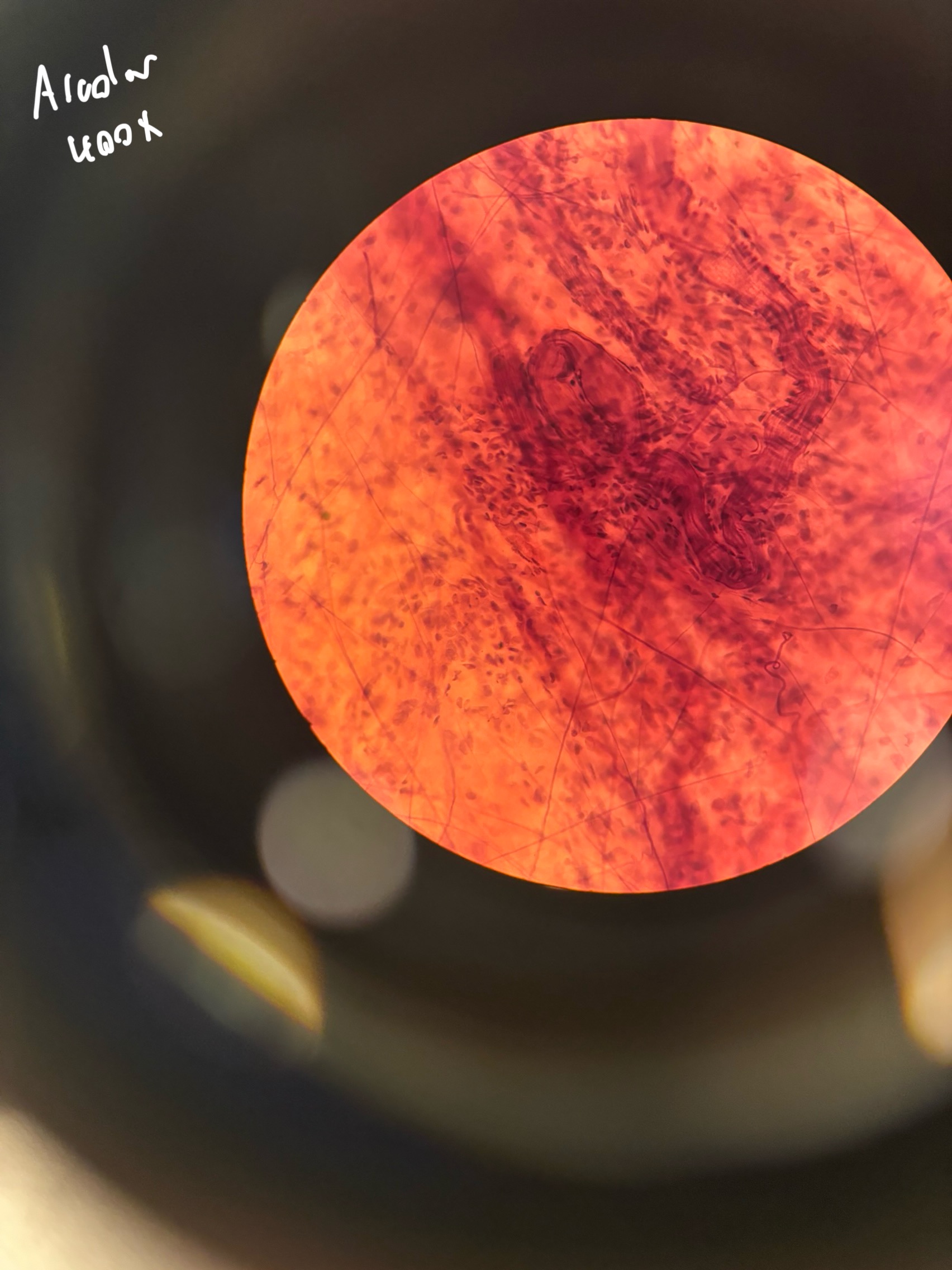
attaches muscle to bones and other muscles, withstands tensile strength. found in tendons, ligaments etc.
What is the function of dense regular connective tissue?
withstands tension exerted in many directions and provides structural strength. found in fibrous capsules in joints.
what is the function of dense irregular connective tissue?
allows tissue to recoil after stretching. found in large arteries, ligaments in the vertebral column and in the lungs.
What is the function of dense elastic tissue?
hyaline
elastic
fibrocartilage
What are the three types of cartilage?
supports and reinforces, resilient cushion against constant stress. found in embryonic skeletons, end of long bones and joint cavities
what is the function of hyaline cartilage?
maintains shape of a structure while allowing flexibility. found in the ears, and epiglottis
What is the function of Elastic cartilage
tensile strength absorbs compressive shock. found intervertebral discs, pubic bone, meniscus
what is the function of fibrocartilage?
supports and protects, provides levers for muscles, stores calcium and other minerals. located in bones.
What is the function of Osseous tissue?
mucus
serous
cutaneous
synovial
What are the 4 types of membranes?
secretes mucus to lubricate. found in hollow opening exposed to the outer world
What is the function and locations of mucus membranes?
lines the internal subdivisions of the ventral body cavity.
What is the function and locations of serous membranes?
covers the surface of the body. Thick and waterproof.
what is the function and location of cutaneous membranes?
found in synovial joints to provide cushioning between bones and aid the menisci.
what is the function and location of the synovial membranes?
highly vascular
highly cellular
responsible for most types of body movement
possess myofilaments which cause movement
What are the 4 features of muscle tissue?
neurons and neuroglia
what are the two major cell types of nervous tissue?
inflammation and regeneration
what are the two types of tissue repair?
inflammation has components of both negative and positive feedback loops
what type of feedback mechanism is inflammation?
supports
protection
assistant in moving
mineral homeostasis
blood cell production
triglyceride storage
What are the 6 main functions of the skeletal system
bones
cartilage
tendons
ligaments
what are the 4 components of the skeletal system
Diaphysis
What is the shaft t of a long bone called?
epiphysis
What are the proximal and distal ends of the bone called?
metaphysis
What is the region between the epiphysis and the diaphysis called?
periosteum
what is the 2 outermost layers of the long bone called?
endosteum
what is the internal lining of a long bone called?
medullary cavity
what is the tube in the diaphysis called that reduces the weight of the long bone?
osteoprogenitor cells
osteoblasts
osteocytes
osteoclasts
What are the 4 cells present in bone tissue
interstitial lamellae
the area between neighboring osteons
lacunae
the space where osteons are found
canaliculi
nutrient channels filled with extracellular fluid
appositional growth and interstitial growth
What are the two ways in which cartilage grows?
appositional growht
cartilage forming cells in the surrounding perichondrium secrete new matrix against the existing matrix
interstitial growth
chondrocytes divide and secrete new matrix, expanding the cartilage from within (mitosis)
initial formation of bone (from hyaline cartilage)
growth of bone during development (occuring at growth plates during puberty)
remodeling of bone
bone repair
what are the four stages of ossification
intramembranous ossification
endochondral ossification
what are the two methods in which osteogenesis occurs
intramembranous ossification
development of bone beginning in the ~8th week of fetal development
development of an ossification centre through the fibrous connective tissue membrane
osteoid is secreted and calcified
immature spongy bone and periosteum form
compact bone replaces superficial spongy bone, red bone marrow develops
what are the steps of intramembranous ossification?
endochondral ossification
development of bone occuring after the 9th week of fetal development and continuing throughout puberty
bone collar forms around the diaphysis of the hyaline cartilage
cartilage calcifies in the centre of the diaphysis creating cavities
the periosteal bud invades the central cavity creating spongy bone
elongation of the diaphysis, medullary cavity develops and secondary ossification of the epiphyses occurs (occurs at or around the time of birth)
ossification is complete at the epiphyses and hyaline cartilage only remains at the epiphysial plates
What are the steps of endochondral ossification
interstitial growth of cartilage on the epiphyseal side of the epiphyseal plate
replacement of cartilage on the diaphyseal side through endochondral ossification
What two events happen to create bone growth throughout adolescence
cartilage on the epiphyseal side undergoes mitosis whereas cartilage on the diaphyseal side dies and is replaced with bone
What is the difference between ossification at the epiphyseal side and the diaphyseal side
osteoblasts beneath the periosteum secrete collagen fibres creating the bone matrix and forms ridges that follow the blood vessels in the periosteum
bony ridges enlarge and the groove containing blood vessels becomes a tunnel
the periosteum lining the tunnel is transformed into the endosteum and osteoblasts secrete bone matrix to narrow the canal
osteoblasts deep in the endosteum form lamellae and this process is repeated to enlarge bone diameter
what are the stages of appositional growth?
bone resorption- removal of minerals and collagen fibres by osteoclasts (increases blood calcium)
bone deposition- the addition of materials and collagen fibres by osteoblasts
What are the two processes of bone remodeling?
minerals
calcium, phosphorus, magnesium, flouride, manganese
vitamins
A,C,D and K
hormones
IGF’s, HgH, T3 and T4, PTH
mechanical stress
wolf’s law
what are some factors that influence bone development?
Interstitial growth
What type of growth elongates the bone?
Appositional growth
what type of growth widens the bone?
hematoma develops
fibrocartilaginous callus forms
bony callus forms from fibrocartilage
bone remodeling occurs
What are the steps of fracture repair?
osteomalacia and rickets
osteoporosis
Paget’s disease
What are the three major bone disorders?
excessive bone resorption
inadequate bone remodeling
What are the two main mechanisms in which osteoporosis develops
lack of estrogen
calcium metabolism
What are the two main factors of osteoporosis risk?
lumbar spinal fractures
hip fracture
wrist fractures
What are the most common effects of osteoporosis?
the anterior fontanel
What is the largest fontanel that takes the most time to close?
the male pelvis is more dense and thicker with sharper ridges on the ilium. The female pelvis has a greater angle between to pubis to allow for childbirth
What are some of the differences between the male and female pelvis?
arthrology
What is the study of joints called?
fibrous
cartilaginous
synovial
What are the three structural classifications of joints?
Fibrous joint
What is the strongest type of joint?
Synovial joints
What type of joint has a cavity between the two articulating bones?
synarthrosis (no movement)
amphiarthrosis
Diarthrosis (synovial joints)
what are the three functional classifications?
a joint held together by a ligament
What is a syndesmosis fibrous joint?
in between the bones of the skull
where is the only place in the body that suture joints are present?
bones joined by hyaline cartilage such as in the epiphyseal plate
what is a synchondroses cartilaginous joint?
bones joined by fibrocartilage such as in the vertebral column and the pubic symphysis (found at the midline of the body)
What is a symphyses cartilaginous joint?
preventing twisting and torsion at the joint, lowering risk of dislocation
What role does the fibrous layer serve in a synovial joint?
releases synovial fluid into the joint cavity
what role does the synovial membrane serve in a synovial joint?
reduces friction through lubrication
shock absorbent
supplies oxygen and nutrients
removes carbon dioxide and waste
contains phagocytes to remove debris
What are the 5 functions of synovial fluid?
the ACL and PCL
What are two examples of intracapsular accessory ligaments in the knee joint?
Bursae act as cushioning sacs between bones and soft tissues, reducing friction during movement.
What role does bursae play in a joint?
tendon sheaths are long tube like sacs that are filled with fluid and wrapped around the head of the bone, providing a cushion between bones.
how does a tendon sheath reduce friction between bones?
plane (gliding)
found in between the carpals
hinge
knee
pivot
in between the ulna and radius to allow supination
condylar
in between phalanges and metacarpals
saddle
found in thumb
ball and socket
hip and shoulder joint
What are the types of synovial joints and an example in the body?
type of articulating bones
Strength of the ligaments
Arrangement of muscles
Contact of soft parts
Hormones
Disuse
What are some factors that influence range of motion of in a joint?
any disorder that affects the joints
What is arthritis?
a type of arthritis caused by the break down of smooth cartilage causing pain at the joints
What is osteoarthritis?
autoimmune disease which attacks the synovial joint cavity
what is rheumatoid arthritis?
inflammatory arthritis caused by high levels of uric acid in the blood causing crystalization at the joint
What is gouty arthritis