10 - Biology unit 1 Anatomy and Physiology
5.0(2)Studied by 20 people
Card Sorting
1/54
Last updated 8:42 PM on 2/1/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
55 Terms
1
New cards
Squamous
flat cell
2
New cards
Epithelium
occurs as sheets of tightly packed cells that cover body surfaces and line internal organs and cavities (same as epithelial tissue)
3
New cards
Simple
one cell layer thick
4
New cards
Gross anatomy
anatomy that can be seen with the naked eye (e.g. femur, heart)
5
New cards
Histology
the study of microscopic anatomy (the fancy name)
6
New cards
Tissue (2)
* a group of many similar cells that perform a specific function
* there are four types of tissue
* there are four types of tissue
7
New cards
Cells (4)
* cell is the basic unit of life
* all living things on earth are made of cells
* nothing smaller than a cell is alive
* e.g. red blood cell, neuron
* all living things on earth are made of cells
* nothing smaller than a cell is alive
* e.g. red blood cell, neuron
8
New cards
Epithelial Tissue
occurs as sheets of tightly packed cells that cover body surfaces and line internal organs and cavities (same as epithelium)
9
New cards
Cuboidal
cube-shaped cell
10
New cards
Columnar
column-shaped cell
11
New cards
Stratified
many cell layers thick
12
New cards
Physiology
the study of how the parts of the body work
13
New cards
Microscopic Anatomy
anatomy that requires a microscope to be seen (e.g. capillaries)
14
New cards
Anatomy
the study of the parts of an organism and how they are linked to one another
15
New cards
5 structural levels of the body
cell, tissue, organ, organ system & organism
16
New cards
4 types of Epithelial tissue
Simple Squamous Epithelium, Simple Cuboidal Epithelium, Simple Columnar Epithelium & Stratified Squamous Epithelium
17
New cards
4 types of Connective Tissue
Loose Connective tissue, Adipose tissue (fat tissue), Blood & Bone
18
New cards
Connective Tissue
a type of tissue in which cells are **not** tightly packed together
19
New cards
3 types of Muscle Tissue
Skeletal Muscle, Cardiac Muscle & Smooth Muscle
20
New cards
bones (1)
* give structure to the body
21
New cards
blood (2)
* carries substances around the body
* e.g. oxygen and nutrients
* e.g. oxygen and nutrients
22
New cards
Adipose tissue (3)
* fat tissue
* stores energy
* provides insulation
* stores energy
* provides insulation
23
New cards
loose connective tissue (1)
* connects skin to underlying tissue (muscle or bone)
24
New cards
skeletal muscle (5)
* fatigues
* striated(has microscopic light and dark bands)
* it is attached to our bones
* when it contracts it produces all of our gross (big) movements
* e.g. biceps, abdominal muscle
* striated(has microscopic light and dark bands)
* it is attached to our bones
* when it contracts it produces all of our gross (big) movements
* e.g. biceps, abdominal muscle
25
New cards
cardiac muscle (3)
* striated(has microscopic light and dark bands)
* most of the heart is made up of cardiac muscle
* doesnt fatigue
* most of the heart is made up of cardiac muscle
* doesnt fatigue
26
New cards
muscle tissue (2)
* consists of muscles that are able to contract (shorten) to produce all types of movement
* muscle tissue consist of muscle fibers (muscle cells), long cells that are found in bundles
* muscle tissue consist of muscle fibers (muscle cells), long cells that are found in bundles
27
New cards
4 types of tissue
epithelial tissue, connective tissue, muscle tissue & nervous tissue
28
New cards
where is each type of epithelium found?
simple squamous - lines alveoli
simple cuboidal - tube in the kidney
simple columnar - intestines
stratified squamous - skin, esophagus
simple cuboidal - tube in the kidney
simple columnar - intestines
stratified squamous - skin, esophagus
29
New cards
2 types of anatomy
gross anatomy and microscopic anatomy
30
New cards
smooth muscle (2)
* doesn't have bands
* found in the wall of the digestive system and in the wall of our arteries and veins
* found in the wall of the digestive system and in the wall of our arteries and veins
31
New cards
Nervous tissue
* forms the brain, spinal cord and nerves
* used as a communication system within the body
* signals are transmitted very rapidly within nerve cells (neurons)
* used as a communication system within the body
* signals are transmitted very rapidly within nerve cells (neurons)
32
New cards
Neuron (4)
* made of 5 parts
* aka nerve cells
* look very different from other cells
* they have long extensions that allow the to send messages over long distances
* aka nerve cells
* look very different from other cells
* they have long extensions that allow the to send messages over long distances
33
New cards
organ
a group of tissues that work together to perform a function
34
New cards
Organ system
* a group of organs that work together to perform a specific function (or functions)
* 8 systems
* 8 systems
35
New cards
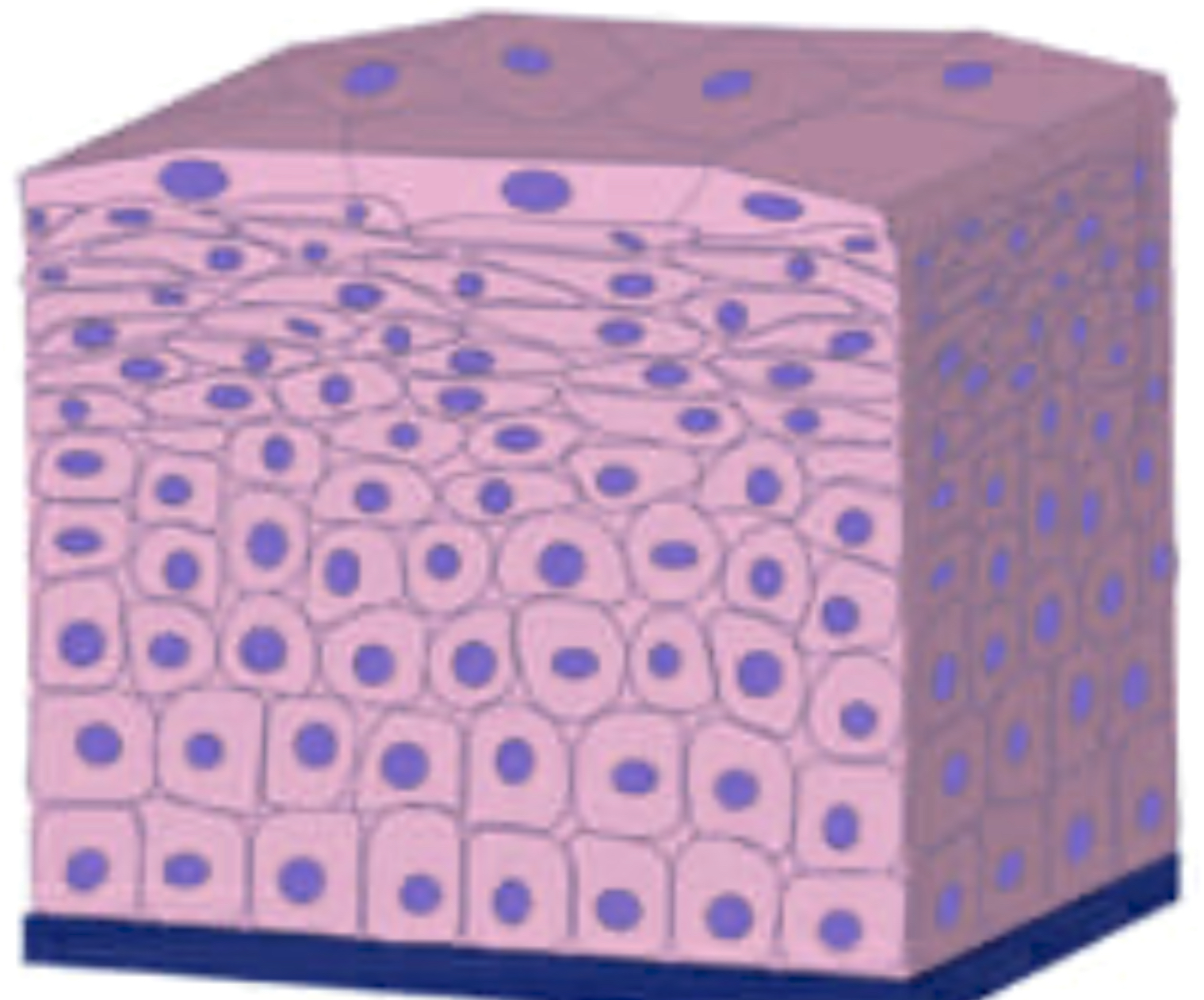
name the tissue
stratified squamous epithelial tissue (pic)
36
New cards
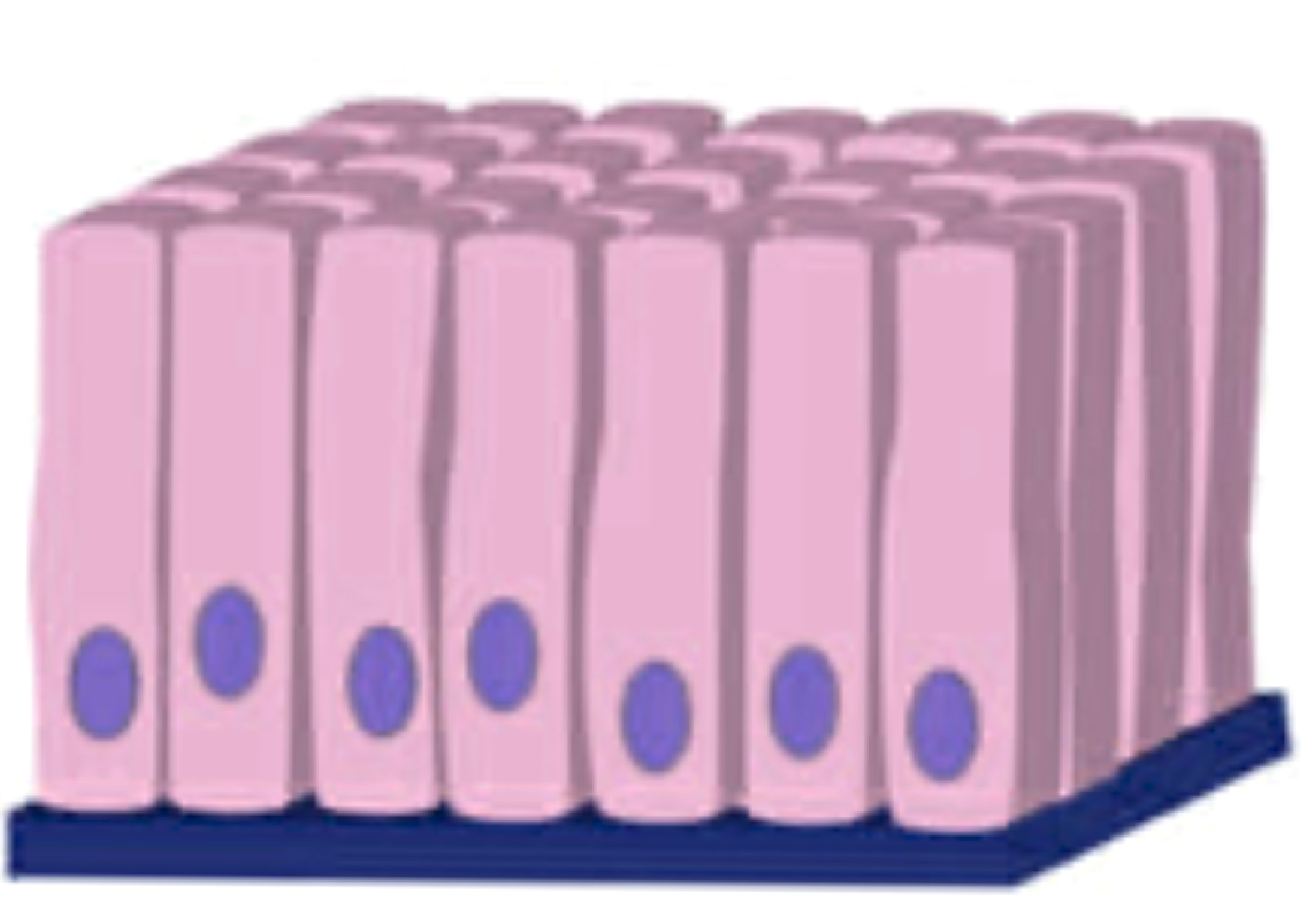
name the tissue
simple columnar epithelial tissue (pic)
37
New cards
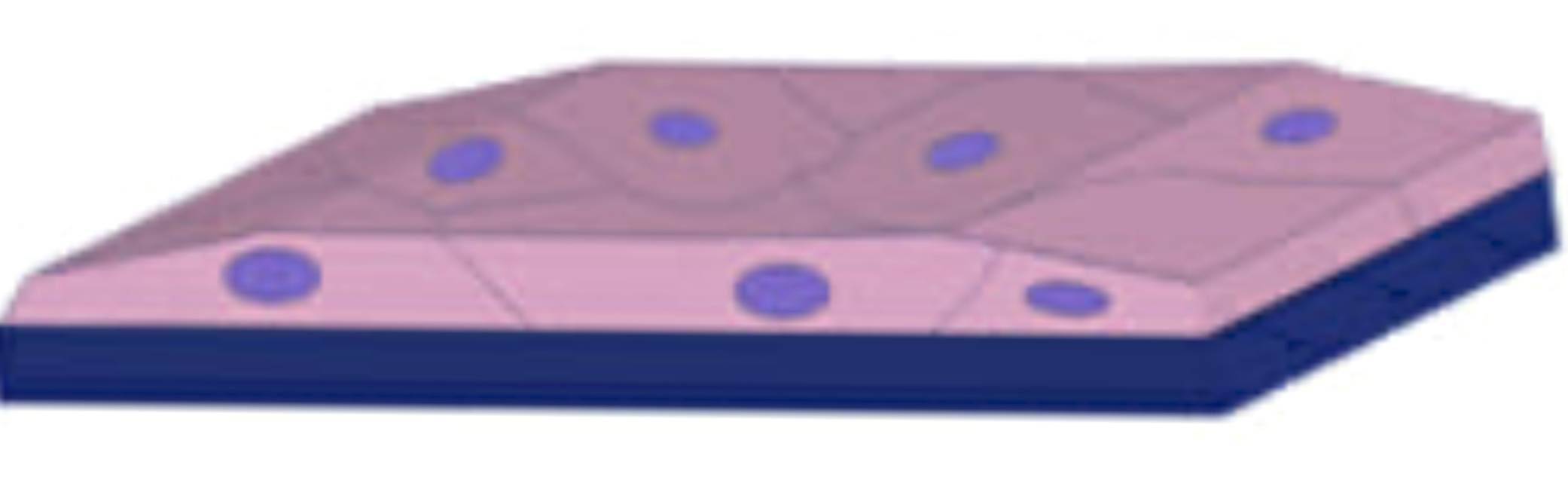
name the tissue
simple squamous epithelial tissue (pic)
38
New cards
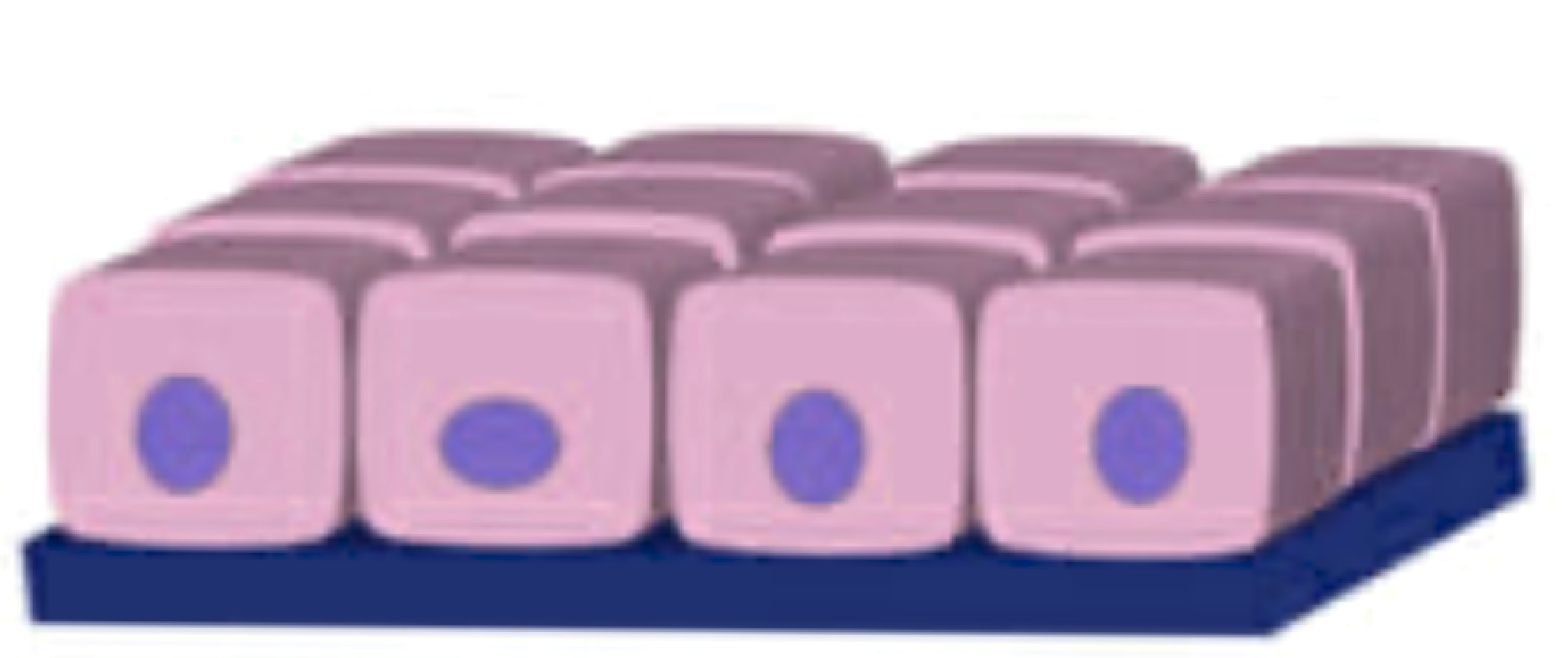
name the tissue
simple columnar epithelial tissue (pic)
39
New cards
draw and label a neuron
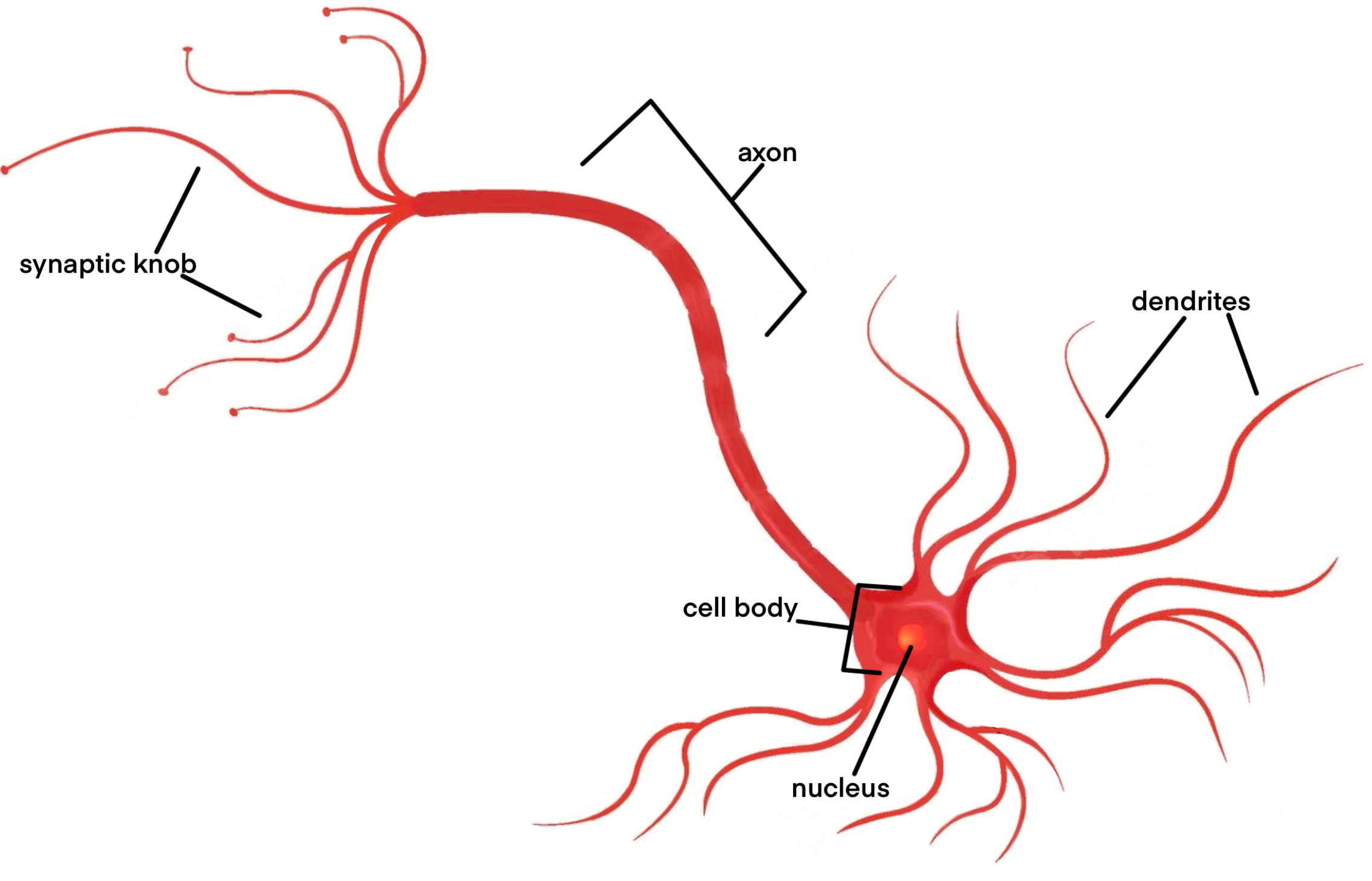
40
New cards
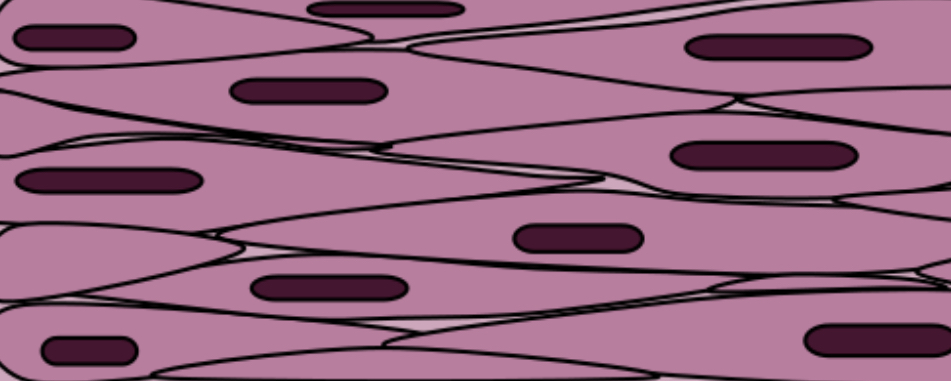
name the tissue
smooth muscle (pic)
41
New cards
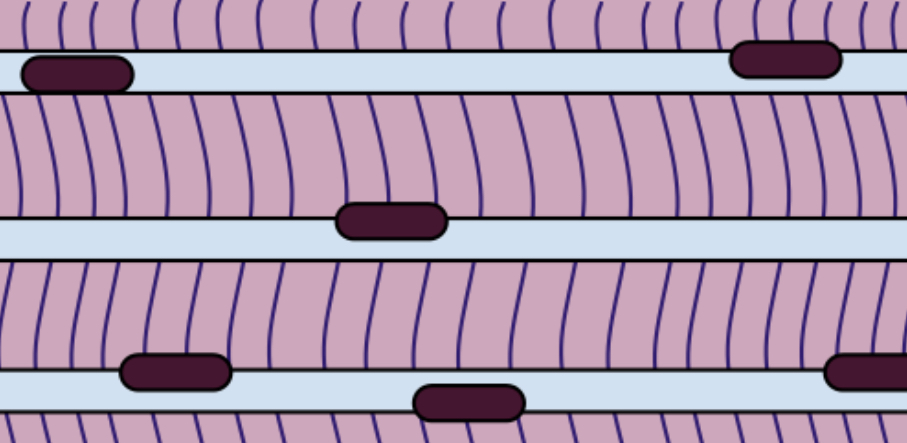
name the tissue
skeletal muscle (pic)
42
New cards
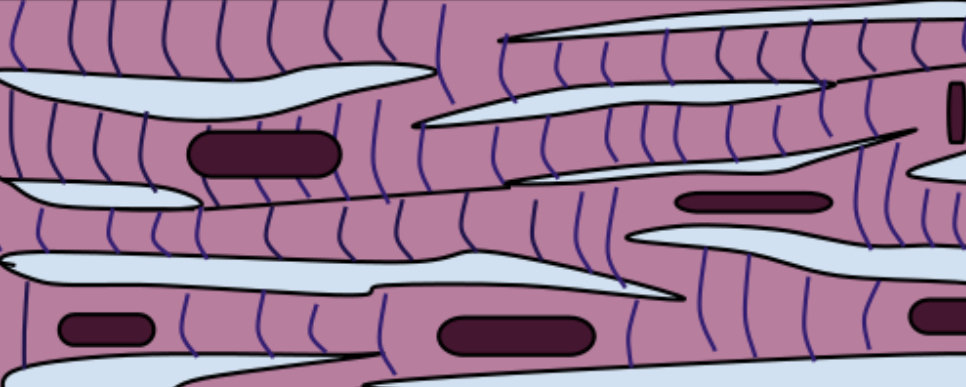
name the tissue
cardiac muscle (pic)
43
New cards
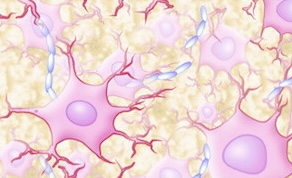
name the tissue
nervous tissue (pic)
44
New cards
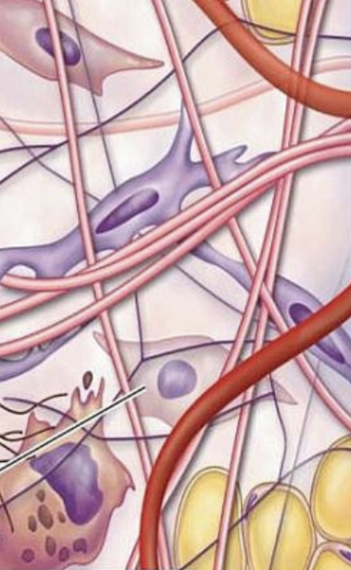
name the tissue
loose connective tissue (pic)
45
New cards
Digestive System (2)
* stomach and intestines
* breaks down food and absorbs it into the blood
* breaks down food and absorbs it into the blood
46
New cards
Circulatory System (2)
* heart, arteries, veins
* transports substances throughout the body
* transports substances throughout the body
47
New cards
Respiratory System (2)
* trachea, lungs
* exchanges oxygen and carbon dioxide between the air outside the body and cells
* exchanges oxygen and carbon dioxide between the air outside the body and cells
48
New cards
Excretory System (2)
* kidneys, bladder
* filters wastes out of the blood
* filters wastes out of the blood
49
New cards
Reproductive System (2)
* ovaries, fallopian tube, testes
* reproduction
* reproduction
50
New cards
Excretory System (2)
* kidneys, bladder
* filters waste out of the blood
* filters waste out of the blood
51
New cards
Musculoskeletal System (2)
* muscles, bones
* movement of the body
* movement of the body
52
New cards
Nervous System (2)
* brain, spinal cord, nerves
* rapid communication within the body, storage of memories
* rapid communication within the body, storage of memories
53
New cards
Endocrine System (2)
* Pancreas, Testes
* produce hormones which act as chemical messengers in the body
* produce hormones which act as chemical messengers in the body
54
New cards
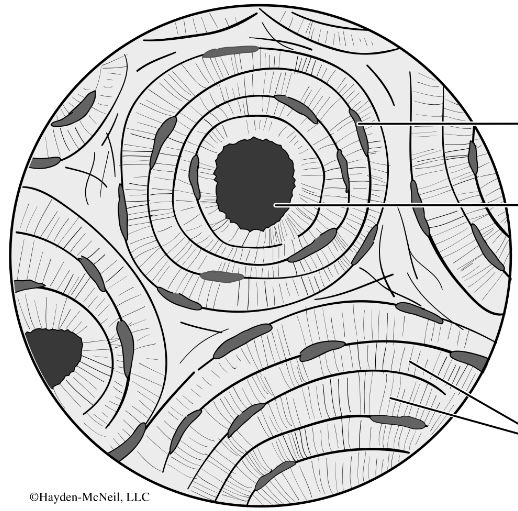
name this tissue
bone (pic)
55
New cards
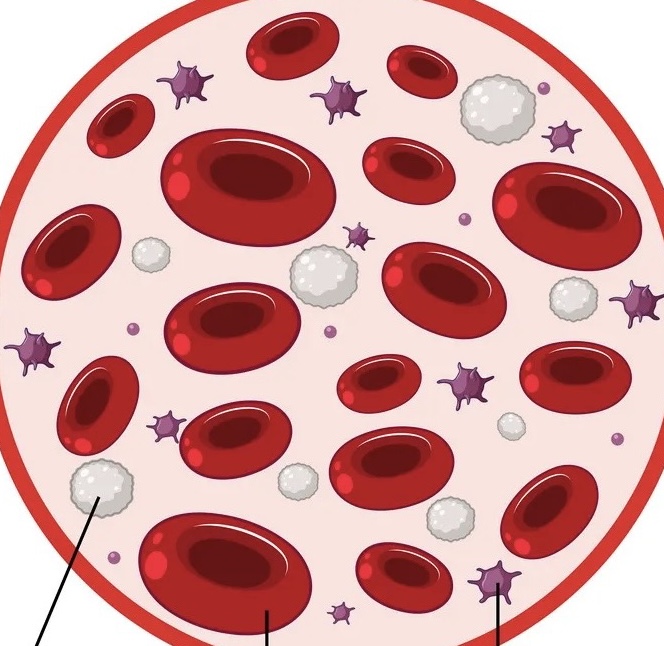
name the tissue
blood (pic)