Midterms
1/50
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Data types, Variable, operators, and expression
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
Primitive Data Types
built into the java language.
these are data that are not objects and have no methods.
Integer Types
Includes Byte, Short, int, and long.
are signed, positive, and negative values since java does not support unsigned values.
High-order bit
defines the sign of an integer value, and java manages it differently by adding a special “unsigned right shift“ operation
Byte
smallest integer type that represent a small number
-128 and 127
Short
-32768 and 32787
Int
default option usually for java because when you use int or short it gets promoted to ___
-2,147,483,648 to 2,147,484
Long
hold a higher number compared to a regular integer.
A capital letter “L“ is placed right after the value
ex. 20987L;
Floating Point Types
are also called “real numbers“
used when evaluating an expression that need fractional accuracy such as the computation of square root or a transcendental.
Flaot
single precision floating point.
takes half the space of a double precision so it may be faster on some processors.
f is placed to the right of the value
Double
Double processors
can be faster than single precision on a modern processors that have been optimized for high-speed mathematical calculation.
Character Types
can be divided into two a.) bye for a character (ASCII) and b.) a type in itself (Unicode)
ASCII
American Standard Code for Information Interchange
a code that assigns numbers to letters, digits, etc
Unicode character
made to support characters that are not traditionally used in (US) English and do not work with compilers.
Char data type
was created to support the unicode characters
Boolean
used for logical values and can hold true or false value.
Abstract Data types
based on primitive data types but with more functionality.
ex. string
Constant
value cannot be changed
final keyword
Variable
values can be changed in a program
defined by the combination of an identifier, a type, and a optional initialization depending on the task to be performed
Variable Naming Convention
variable names are nouns must begin with a lowercase letter
If a variable name contains two letter the first word must start with a lowercase and the following words must start with an Uppercase
variable names must start with a letter, dollar sign, or an underscore.
keywords cannot be used as variable name
Literals
values that may be assigned to primitive- or string-type variables and constant.
Boolean literals
are true and false cannot use numbers
Integer literals
numeric data that can be represented as octal, hexadecimal, and binary literals
Octal
starts with a zero prefixed
ex. int sex = 6;
Hexadecimal
number prefixed with 0x
ex. int x = 0xffff;
Binary literal
number starts with 0B or 0b
Floating-point literals
numbers that have a decimal fraction.
suffix letter F or f is added to the number otherwise will be flagged as loss of precision.
Character literals
must be enclosed in single quotes ‘‘
String literals
enclosed in ““
Operators
used to compute and compare values and test multiple conditions.
Arithmetic Operators
mathematical operators
Operand = value to be computed
Addition, subtraction, Multiplication, Division, and modulus.
Assignment Operators
assigns the specific value, variable, and/or functions to another variable.
Assignment, add, subtract, multiple, division assignment
Unary Operators
only requires one operand
Increment +1
Decrement -1
Logical Complement - inverts the value of boolen
Prefix or Pre-increment
ex. x = 7, then the value will be 8 because ++x = 8
suffix or post-increment
ex. x = 12, then the value of x- - will be 11.
Comparison
All mathematical operation involving comparison between two values
Shift Operators
work on bits of data
involves moving the bit pattern to the left or right.
Bitwise Operators
perform operations bit-by-bit.
AND
results in a 1 if both bits are 1, but if any other combinations results in a 0
OR
results in a 0 when both the bits are 0. Any other combination results in 1.
XOR
Results to 0 if bits are same values, if not results in 1.
Logical Operators
used to combine the results of boolean expressions.
share similarities to bitwise but is limited to boolean expressions.
Logical AND
if both operands are non-zero, expression returns true, otherwise it returns false.
Logical OR
If one or both the operands are non-zero, the expression returns true; otherwise, it returns FALSE.
Conditional Operators
used to control the flow of the program.
mainly used in loop statement
Order of Precedence of Operators
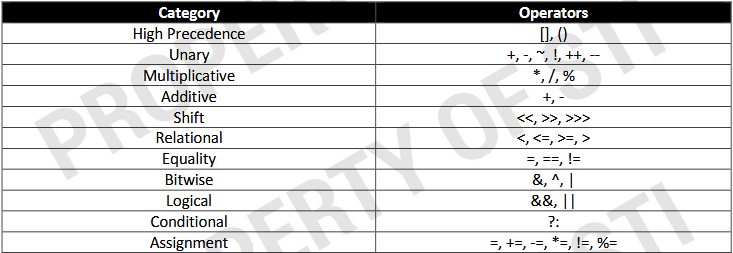
Expression
combination of variables, constant, literals, and operators to produce a single value.
Arithmetic Expression
expression that returns a numeric value based on the operators and operands used
Assignment Expression
expression that involves assigning a value to a variable.
Relational Expression
expression that compares values using relational operators
Logical Expression
expression involving logical operators.
Conditional Expression
expression involving the use of the ternary operator (?:) to assign a value based on a condition.