Kidneys: Countercurrent Multiplication
1/10
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
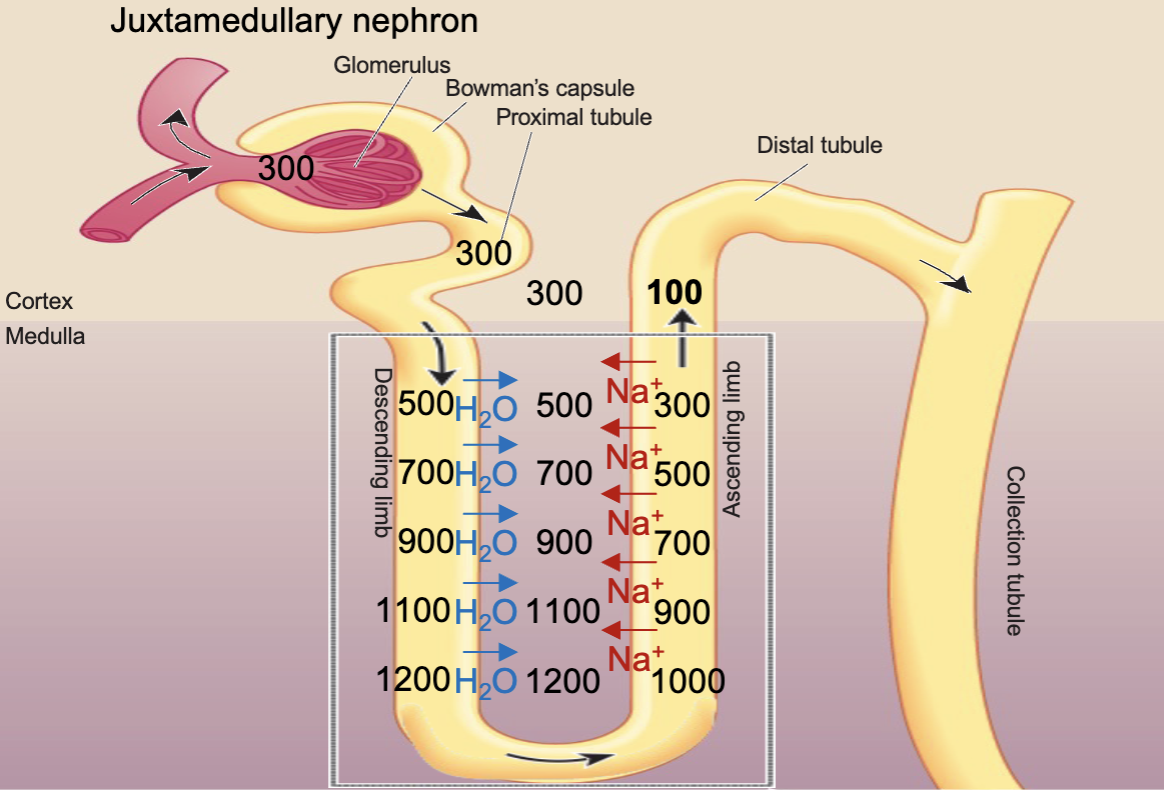
Long Loop of Henle (juxtamedullary nephrons)
Filtrate is isotonic as it enters the loop of Henle, the same Na+ concentration as the ECF/ plasma
Establish the vertical osmotic gradient in the medulla of the kidneys by countercurrent multiplication
An osmolarity gradient is
maintained in the renal medulla
from isotonic to severely
hypertonic (1200 mOsm/liter)
Isotonic
At normal fluid balance and solute concentration
ECF osmolarity is 300 mOsm/ liter
Hypotonic
Excess H2O relative to solute
ECF osmolarity is <300 mOsm/liter
Dilute urine
Hypertonic
Too litle H2O relative to solute
ECF osmolarity >300 mOsm/liter
Concentrated urine
Descending Limb of the loop of Henle
Does not extrude/ impermeable to Na+ (no na+ leak channels)
Highly permeable to H2O (has AQP1)
Ascending Limb of the loop of Henle
Actively transports Na+ out of the tubule into interstitial fluid
Impermeable to H2O
What are the steps in countercurrent multiplication?
Na+ is reabsorbed from the lowest point int he ascending limb of the loop of Henle, creating a hypertonic ECF at that level (200 mOsm/liter difference)
Water from the same level in the descending limb is reabsorbed as it follows the path of Na+, the osmolarity will rise
The water in the medulla is carried away by peritubular capillaries
The hypertonic solution from the descending limb moves to the ascending limb and the Na+ reabsorbed at that vertical level will continue to reabsorb until there is a 200 mOsm/liter difference
These steps repeat until the entire length has a vertical osmotic gradient
The strength of the vertical osmotic gradient depends on…
The length of loop of Henle
The concentration difference between the filtrate and ECF
What is the purpose of countercurrent multiplication?
Produce a hypotonic urine that can be excreted if the ECF within the body has too much water
Establishes a vertical osmotic gradient that can be used by the collecting ducts to concentrate urine if the ECF within the body doesn’t have enough H2O
How does vasopressin control H2O reabsorption in the collecting tubules?
In the face of a water deficit, vasopressin leads to the insertion of AQP2 in the luminal membrane causing H2O to be reabsorbed into the ECF and the urine to have a high Na+ concentration
Vasa Recta (capillaries)
The hairpin loop of the vasa recta by passive countercurrent exchange preserves the vertical osmotic gradient while supplying blood ot the medulla