Business Flash Cards (MVIS 2025)
1/73
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|

74 Terms
What is Gross Profit?
It's the money a company makes from selling its products or services, after paying for the direct costs to make them.
What is Revenue?
It's the total money a company makes from selling its products or services before any costs are taken out.
What is Profit Margin?
It's how much profit a company makes compared to its sales, often shown as a percentage.
What is Markup?
The extra money added to the cost of a product to decide its selling price.
What does ROCE stand for?
Return on Capital Employed
What is ROCE?
Return on Capital Employed shows how well a company uses the total money invested in it to make profits.
What is Current Ratio?
Current Assets divided by Current Liabilities.

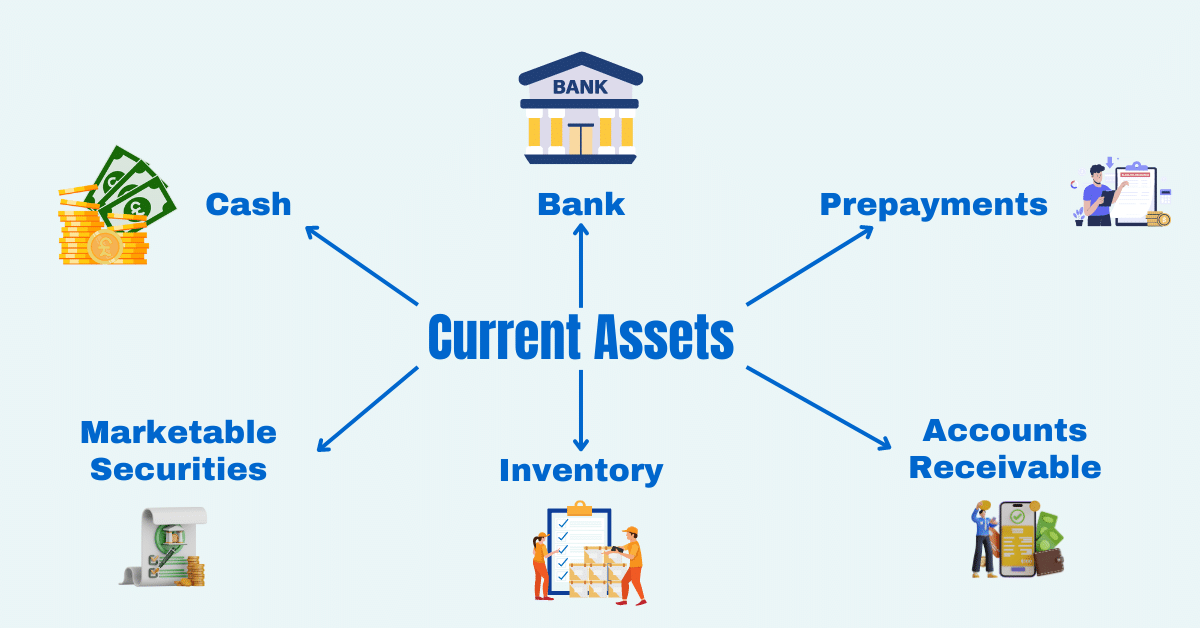
What are Current Assets?
Current Assets are assets that are expected to be converted into cash or used within one year, including cash, accounts receivable, and inventory.

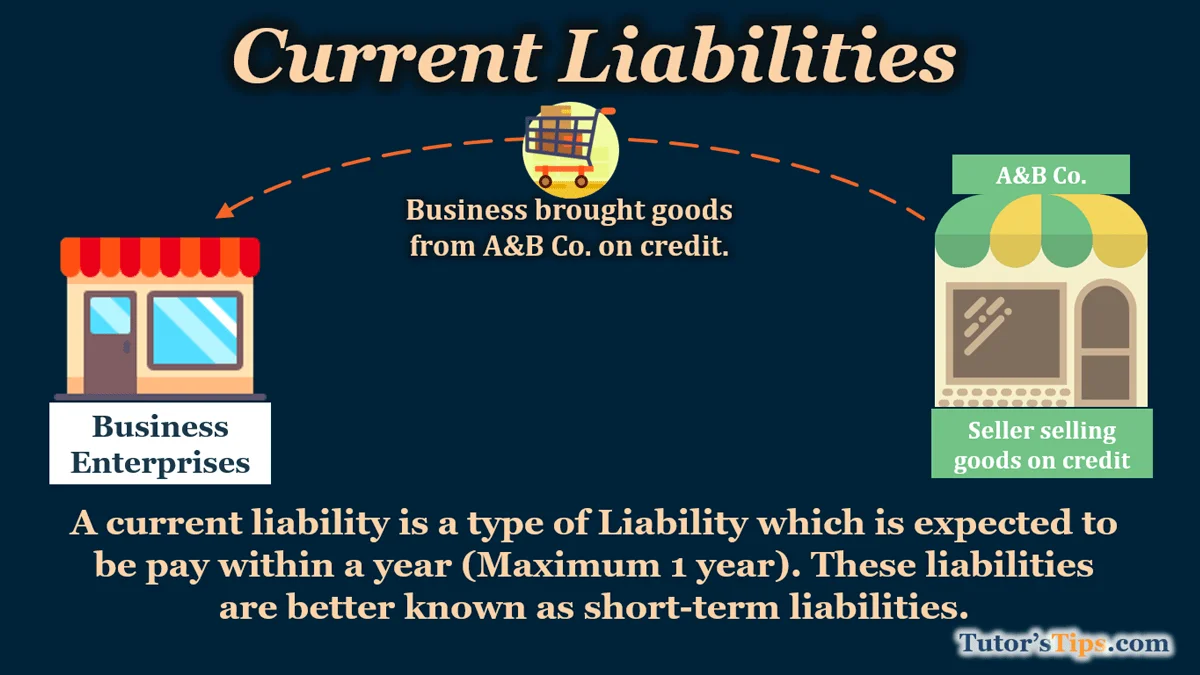
What are Current Liabilities?
Current Liabilities are obligations a company must pay within one year, including accounts payable, short-term debt, and other short-term obligations.
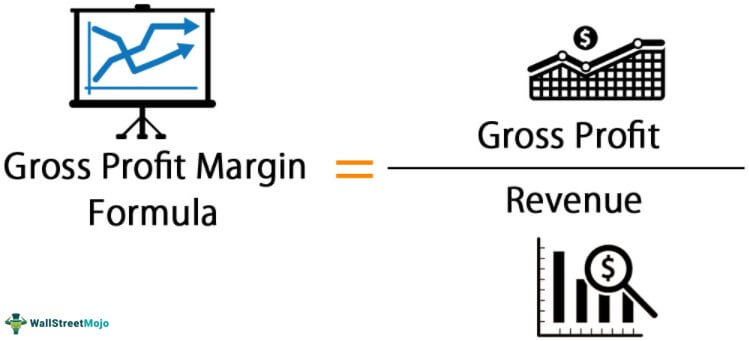
What is Gross Profit Margin?
Gross Profit Margin is calculated by taking Gross Profit and dividing it by Revenue, expressed as a percentage. It indicates the percentage of revenue that exceeds the cost of goods sold.
What is Below-The-Line (BTL) promotion
Marketing activities aimed at specific individuals or groups rather than the general public.
6 examples of Below-The-Line promotions
Loyalty programmes
Email marketing to existing customers
Personalised discounts or offers
Direct mail
Sponsorship of small community events
Free samples or in-store demonstrations
What is Sole Trader?
A person who is the exclusive owner of a business.
What is a discount?
A reduction in the price of a product or service.
What is Venture Capital?
Money that investors give to new businesses to help them grow, in exchange for owning part of the company.

What is a Franchise?
A business model where a company allows another to operate using its brand and model in exchange for payment.
What is Cost of Sales?
The cost involved in producing the goods or services that you sell.
What is Profit?
A financial gain.
What is Marketing Mix?
The key elements businesses use to market their products or services - Product, Price, Place, Promotion
What is an Overdraft?
When you spend more money than your bank account actually has and the bank covers the shortfall.
What is Retained Profit?
The money a company earns that it keeps (reinvests, saves, or uses to pay debt)
What is Crowdfunding?
Raising small amounts of money from many people (the crowd)
What does Capital intensive production mean?
It is the production process that relies heavily on machinery, equipment and technology rather than labour.
What is a fixed cost?
Expenses that remain the same no matter how much a company produces, such as rent, property tax, insurance, and depreciation.
What is the span of control?
The number of employees that each manager is responsible for managing.
What is the Total Revenue?
The total amount of money that you made from your sale of goods and services.
What is the break-even point?
The point when the total cost and the total revenue are equal.
Define non-financial business
Define Financial business
Define demography.
What are government grants?
What is meant by business rates?
What are trade blocs?
What is protectionism?
Define Market Pull.
Define End Product.
Define Industrial Tradition.
Define Constraints.
Define World Trade Organisation (WTO).
Shared costs and liability.
Shared profits and losses.
Shares cannot be publicly advertised for sale.
Shareholders have limited liability.
Must follow strict legal and financial regulations.
(wrt to Boston Matrix)
(wrt to Boston Matrix)
(wrt to Boston Matrix)
(wrt to Boston Matrix)