07 - Auditory, Olfactory, Taste
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
external ear
concentrates sounds
shape filters spectrum of sounds we hear
ridges filter frequencies → enables elevation localization of sound source (above vs below)
blocking pinna (ear shape) → poor elevation detection
middle ear
converts sound waves in air into mechanical vibrations along ossicles
collects and concentrates force from sound onto ossicles
amplifies sound into cochlea
protection from environment
cochlea
transduction of auditory frequency in basilar membrane of cochlea
pitch = frequency
sound creates traveling wave, which peaks at frequency-specific location
high frequency → detected at base
low frequency → detected at apex
organ of Corti
structure in cochlea of inner ear that produces nerve impulses in response to sound vibrations
inner hair cell → sends information to brain along afferent fibers
outer hair cell → amplifies sound; receives signals from brain through efferent fibers
contains prestin motor protein to amplify sensitivity of sound
changes length in response to stimulation
brain can modulate outer hair cells to adjust sensitivity
noise-induced hearing loss
chronic exposure to one frequency
exposure to intense sound at one frequency
damages hair cells only at that location in cochlea
hair cell transduction
traveling waves cause shearing forces on hair cells
stereocilia deflection
ion channel opening
NT release onto auditory nerve
taste
helps animals seek necessary foods and reject harmful foods; dependent on concentration and context
sweet (energy) → sugars, alcohols, glycols, aldehydes
bitter (potential toxins) → long chain organic substances, alkaloids
sour (acidity) → pH
salty (electrolytes) → salts
umami (amino acids) → L-glutamate
taste bud anatomy
taste buds sit in invaginations of papillae
taste receptor cells synapse onto afferent nerves
microvilli contact oral cavity
basal cell located at base for cell regeneration
taste transduction
salty, sour → ionotropic
direct ion entry causes depolarization
leads to Ca2+ influx for NT release
increase in afferent nerve firing
sweet, bitter, umami → metabotropic
G-protein coupled receptor that uses second messengers
causes Ca2+ release in cell for NT release
bypasses depolarization pathway
TRP channels
temperature receptors
capsaicin → activates heat receptors
menthol → activates cold receptors
tongue regions
different amounts of taste sensitivities in different papillae
bitter → back of tongue
salty, sweet → front of tongue
sour → sides of tongue
umami → widespread throughout tongue
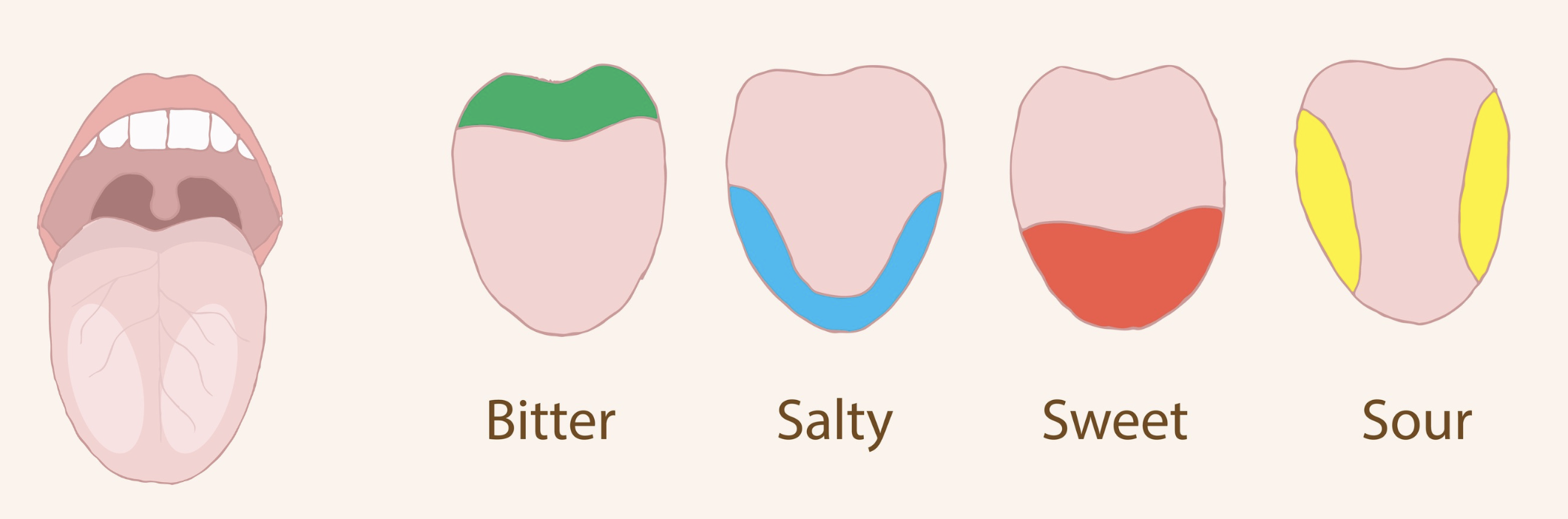
sensory innervation of tongue
bitter → CNIX (glossopharyngeal)
posterior 1/3 of tongue
triggers gag reflex as protective function
other tastes → CNVII (facial)
anterior 2/3 of tongue
gustatory cortex
taste represented at bottom of brain
different parts of brain sensitive to different kinds of tastes
olfactory receptor cells
located in nasal epithelium
cilia interface with nasal cavity
axons pass through cribriform plate
cribriform plate → bony border between nasal cavity and brain
synapse in olfactory bulb at glomeruli
glomeruli integrates information from different olfactory receptor cells
same receptor → same glomerulus
each odor activates pattern of glomeruli
smell = pattern recognition
olfactory transduction
all olfactory receptors are metabotropic (GPCR)
no direct ion channels
use second messengers for Ca2+ influx
odorant receptor protein
receptors located on cilia of olfactory receptor cells
each receptor is structurally similar but has small structural differences that changes what molecules they are sensitive to
conserved vs variable amino acids
mutations further change sensitivities
each olfactory receptor neuron expresses one type of odorant receptor
specific to one class or type of odor, but sensitive to a variety of compounds
central olfactory pathways
olfactory signals do not pass through thalamus
medial olfactory area → projects to limbic system
senses can directly affect emotion
lateral olfactory area → projects widely to other cortical areas and hippocampus
senses can trigger memories
orbitofrontal cortex
region of brain that receives taste and smell
experience of taste influenced by sense of smell
creates flavor