Understanding Cancer: Causes, Mechanisms, and Treatments
1/92
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
93 Terms
Cancer
A complex group of diseases affecting various cells.
Cell Division
Process by which cells replicate and grow.
Differentiation
Cells develop specialized functions and structures.
Proliferation
Cells divide to produce more cells via mitosis.
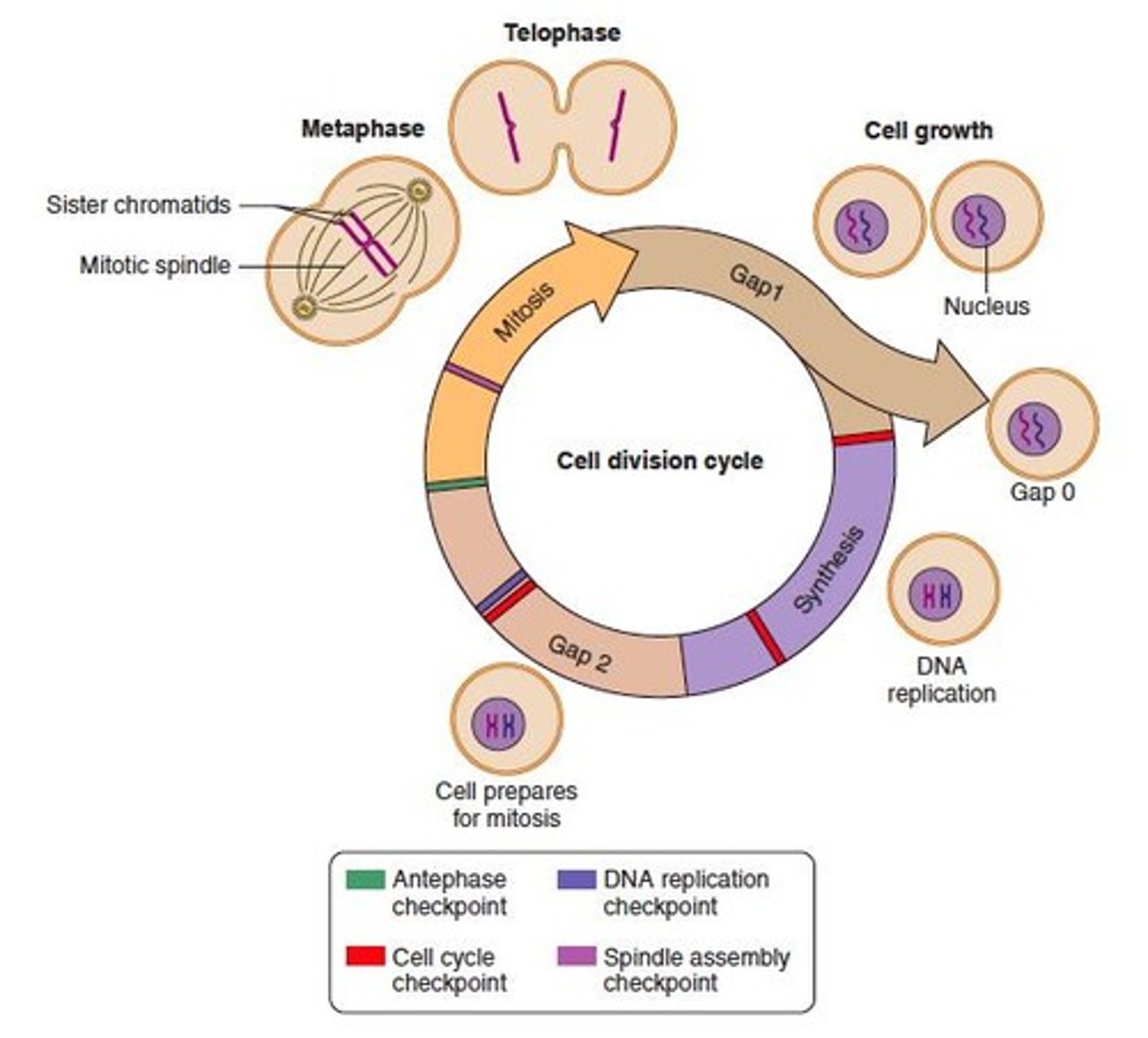
Normal Cell Cycle
Sequence of phases regulating cell growth and division.
G1 Phase
Initial growth phase before DNA synthesis.
S Phase
Phase where DNA is replicated.
G2 Phase
Preparation phase for mitosis after DNA synthesis.
Mitosis
Process of cell division producing two daughter cells.
Checkpoints
Regulatory points ensuring proper cell cycle progression.
Apoptosis
Programmed cell death to eliminate damaged cells.
Undifferentiated Cells
Cells that regress to less specialized forms.
Cancer Cell Characteristics
Distinct features differentiating cancer from normal cells.
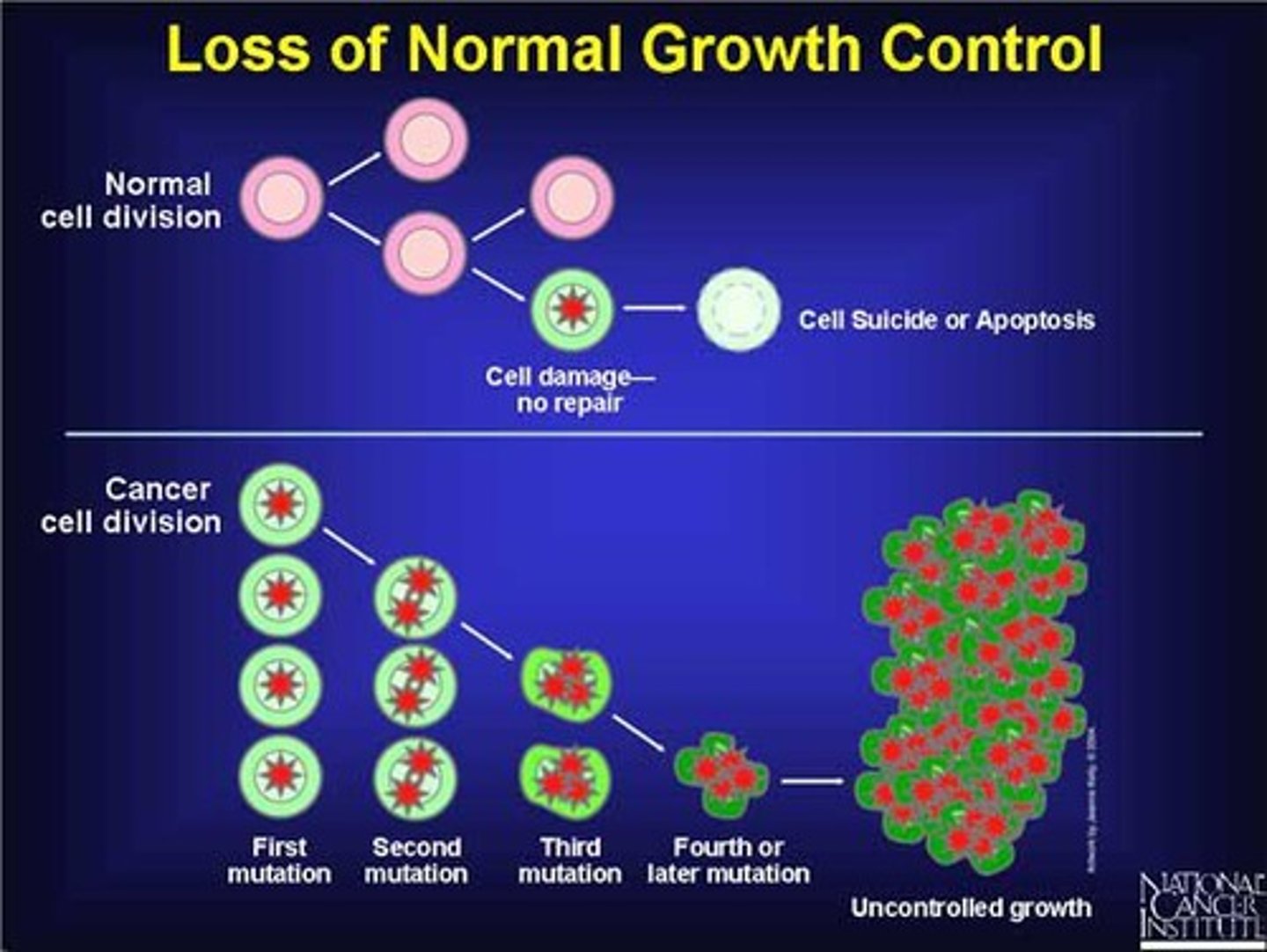
Abnormal Nuclei
Enlarged nuclei with irregular chromosome numbers.
Cell Cycle Checkpoints
Mechanisms to prevent errors during cell division.
Unlimited Replication
Cancer cells can replicate indefinitely without control.
Proto-oncogenes
Genes that promote normal cell growth and division.
Tumor Suppressor Genes
Genes that inhibit cell division and prevent tumors.
Genetic Mechanisms
DNA alterations leading to cancer development.
Radiation Therapy
Cancer treatment using high-energy radiation.
Chemotherapy
Use of drugs to kill or slow cancer cell growth.
Immunotherapy
Treatment that boosts the body's immune response against cancer.
p53 Gene Therapy
Targeted therapy involving the p53 tumor suppressor gene.
Apoptosis
Programmed cell death occurring after division limit.
Telomeres
Chromosome ends that shorten with each cell division.
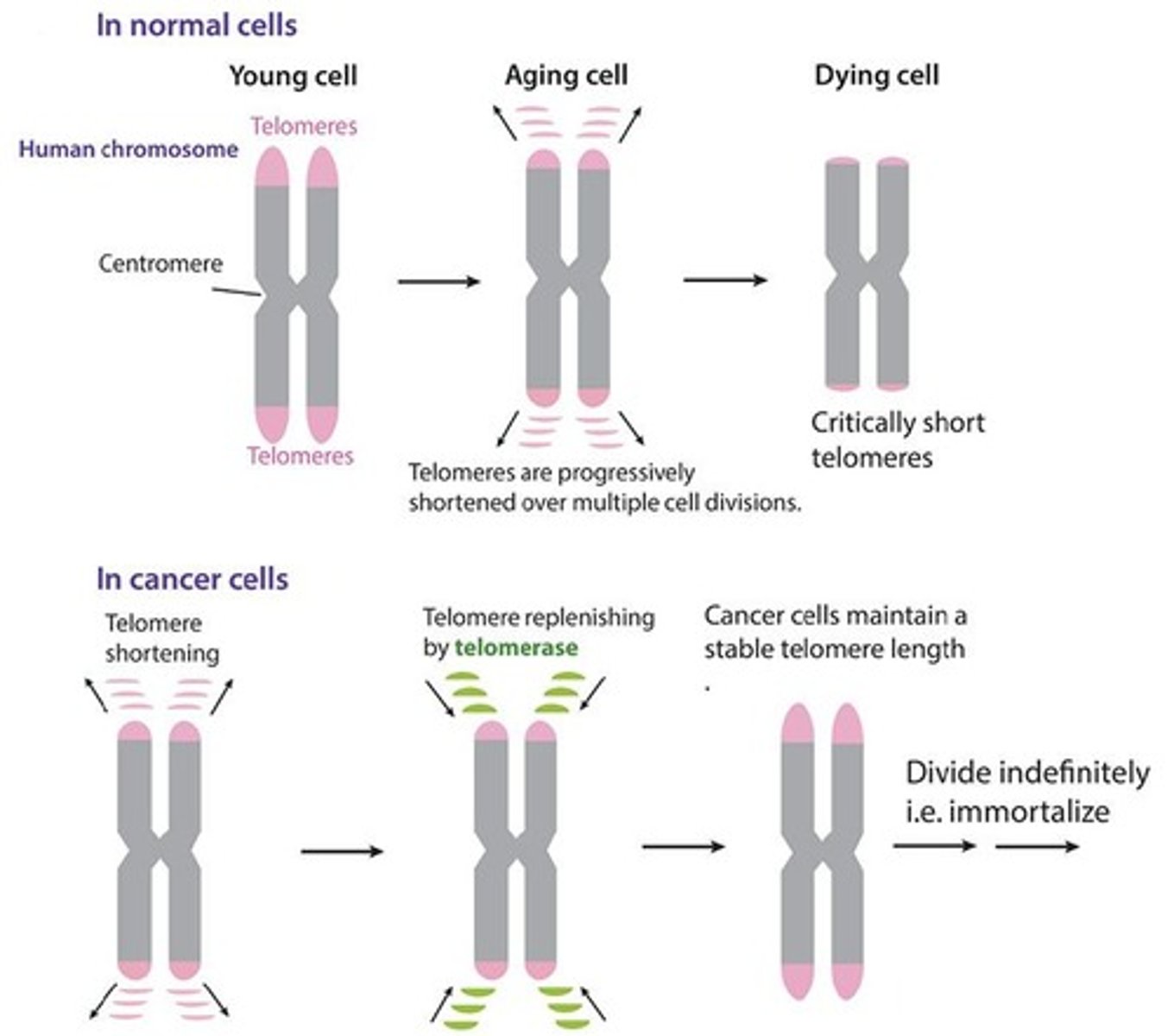
Telomerase
Enzyme that extends telomeres, promoting cell immortality.
Malignant Tumor
Cancerous tumor that invades surrounding tissues.
Benign Tumor
Non-cancerous tumor that does not invade tissues.
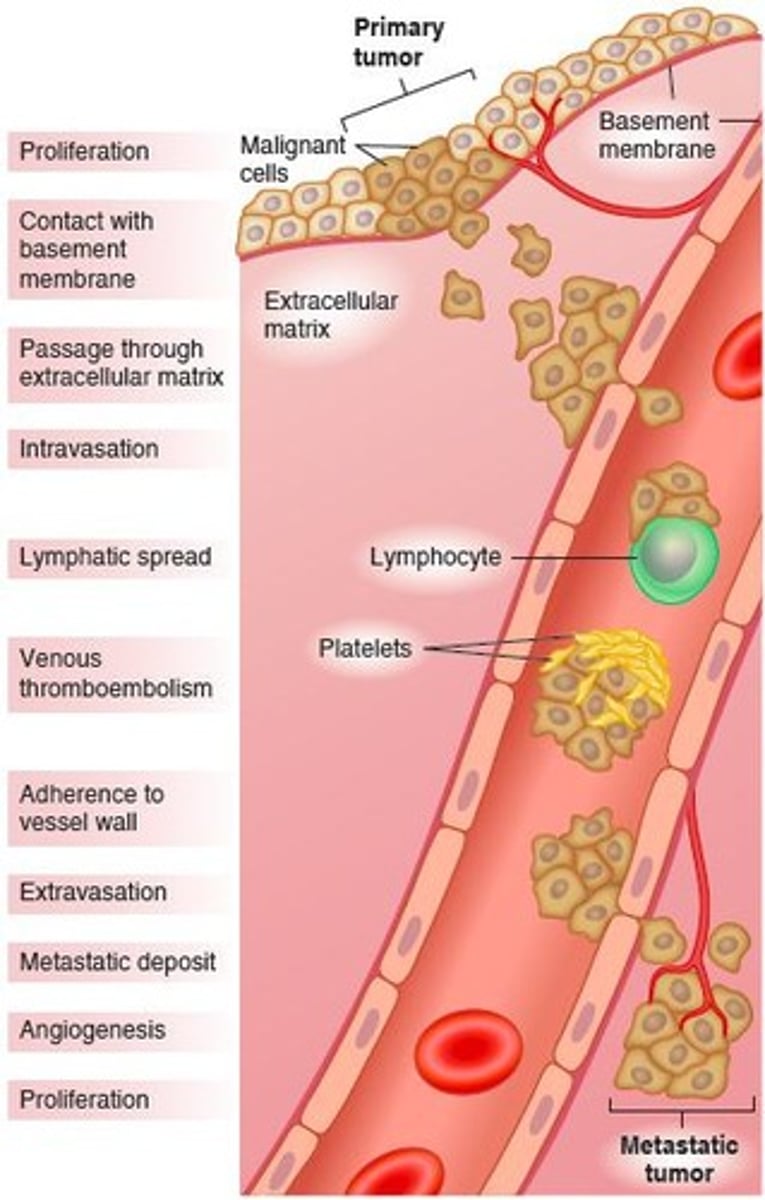
Metastases
Spread of cancer cells to distant body sites.
Contact Inhibition
Normal cells stop dividing upon cell contact.
Growth Factors
Chemical signals regulating cell growth and division.
Angiogenesis
Formation of new blood vessels by tumor cells.
Proto-oncogenes
Normal genes promoting cell growth and division.
Oncogenes
Mutated proto-oncogenes causing uncontrolled cell division.
Tumor Suppressor Genes
Genes that inhibit cell growth and division.
p53 Gene
Tumor suppressor gene linked to various cancers.
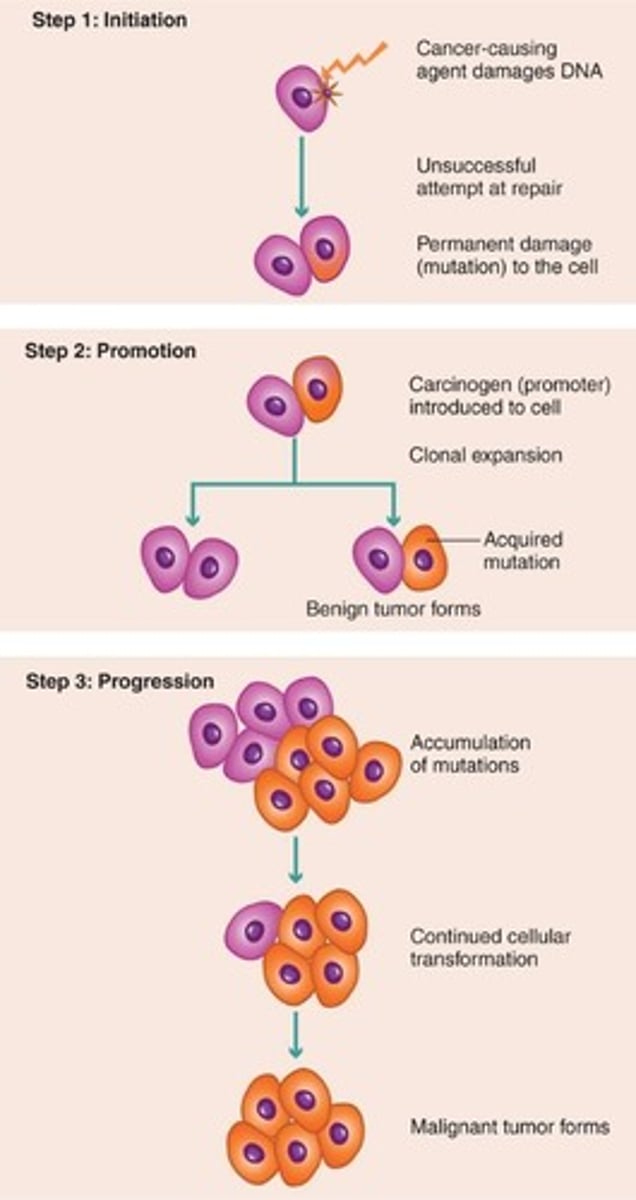
Carcinogenesis
Process of cancer development through mutations.
Initiation
First step of carcinogenesis involving DNA damage.
Promotion
Second step of carcinogenesis with additional mutations.
Progression
Final step of carcinogenesis leading to tumor formation.
Cell Division Rate
Cancer cells divide more rapidly than normal cells.
Invasion
Cancer cells invade surrounding tissues and blood vessels.
Cellular Abnormality
Cancer cells become structurally and functionally abnormal.
Tumor Protein 53
Key tumor suppressor gene, guardian of the genome.
Cell Checkpoint Proteins
Proteins regulating cell cycle progression and division.
Proto-oncogene
Gene promoting cell growth; acts as gas pedal.
Tumor suppressor genes
Genes inhibiting cell growth; act as brakes.
Neoplasia
New tissue growth; can be benign or malignant.
Mutation
Genetic change affecting cell function or behavior.
Germ line mutations
Mutations in gametes passed to offspring.
Somatic mutations
Mutations in body cells; may cause cancer.
Invasion
Tumor infiltrates and destroys adjacent tissues.
Metastasis
Cancer spread to distant sites via blood or lymph.
Seeding
Cancer cells spread in body fluids or membranes.
Biopsy
Tissue sample taken for cancer diagnosis.
Carcinogens
Environmental agents increasing cancer risk.
Genetic predisposition
Inherited mutations raising cancer risk.
BRCA-1 and BRCA-2
Genes increasing breast and ovarian cancer risk.
Age
Older age increases cancer risk exposure.
Hormones
Sex steroids can trigger reproductive cancers.
Obesity
Increased inflammation linked to higher cancer risk.
Reduced immunity
Lowered immune function increases cancer susceptibility.
Chemical carcinogens
Substances like tobacco causing specific cancers.
Radiation
DNA damage from ionizing and UV radiation.
Viruses
Pathogens causing cancer by disrupting cell signaling.
Angiogenesis
Formation of new blood vessels to supply tumors.
Apoptosis
Programmed cell death; prevents cancer cell survival.
Pathophysiology
Study of cancer's biological mechanisms and effects.
Screening
Early detection methods to identify cancer presence.
American Cancer Society (ACS)
Organization promoting cancer awareness and early detection.
Change in bowel habits
Alterations in normal bowel function indicating potential cancer.
Sore that does not heal
Persistent wound suggesting possible malignancy.
Unusual bleeding
Abnormal discharge indicating potential cancerous conditions.
Thickening or lump
Physical changes in tissue that may signal cancer.
Indigestion
Digestive difficulties that could indicate gastrointestinal cancer.
Change in wart or mole
Alterations in skin lesions that may suggest skin cancer.
Nagging cough
Persistent cough that may indicate lung cancer.
Ovarian cancer incidence
Lower than breast cancer but higher mortality rate.
Mortality-Incidence Ratio (MIR)
Ratio of cancer deaths to new cases diagnosed.
Liquid biopsy
Non-invasive test using body fluids for cancer detection.
Histopathology
Microscopic examination of tissue for cancer diagnosis.
Imaging techniques
Methods like PET, CT, and MRI to visualize tumors.
Tumor imaging
Visual assessment of tumors using various imaging methods.
Enzyme tests
Tests for cancer markers in large populations.
Tumor grade
Classification based on cellular differentiation and prognosis.
Staging
Classification of cancer based on tumor size and spread.
Renal Cell Carcinoma
Kidney cancer often diagnosed at advanced stages.
Lung cancer statistics
Causes one-third of all cancer deaths, primarily from smoking.
Colorectal cancer diagnosis
Identified via colonoscopy and biopsy of polyps.
Conventional cancer treatment
Includes surgery, radiation, and chemotherapy methods.
Immunotherapy
Uses immune system to target and destroy cancer cells.
p53 gene therapy
Targets cancer cells lacking p53 gene for destruction.
Cancer prevention measures
Lifestyle choices to reduce cancer risk.