Proteins and Amino Acids structure
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
What are proteins?
Polymers or long chains of amino acids
Can be described as peptides, polypeptides or proteins depending on length
How are they made?
Synthesised in cells through translation of RNA
Chemical synthesis is also possible
manual- lab
automated- machine
Examples of proteins
Proteins can be natural ligands e.g. met enkephalin
( natural painkillers)
Proteins can be drugs e.g. monoclonal antibodies, insulin ( known as Biologics )
Proteins are the major type of drug target
Why do proteins matter?
They are important in how drugs work
eg .
-receptors, they change shape
-enzymes- require chemical reactions
-nuclear receptors- DNA , protein synthesis, longer hours
- ion channels - really fast , =transport of essential ions
How do we draw and represent molecules?
SKELETAL FORMULA
-molecules aren't flat ,3d
-no need to draw all hydrogens ,only draw functional groups
What is the primary structure of a protein ?
The order/sequence of amino acids
The proteins - have a backbone -which joins the aa
residues- side chains, reponisable for binding =decides the type/strenght of bonding interactions within drug molecules
makes amide bonds =rigidity
Name the functional group of each of the residues
thiol- represents sulfa
alkyl group-methyl groups
phenol- benzene,alcohol
arene-benzene
What is secondary structure?
Hydrogen bonds between peptide backbones
Areas of order within protein structure
Two main types α-Helix and β-sheet
NOTE- ordering = more rigidity ,caused by h-bonds
Describe alpha- helix and its properties?
Coiling of chains
Hydrogen bonds between amides
Residues point outwards- less interaction
less steric interaction between them
stabilise the structure
Describe Beta pleated sheet?
layering of chains
Can run in either direction
parallel or anti parallel
Held together with hydrogen bonds between amides in different layers
Residues point outwards
less steric interaction between them
stabilise the structure
What is tertiary structure?
Overall 3d shape of a protein - THE MOST IMPORTANT FOR DRUG ACTION
Achieved by additional interactions between side chain residues
Folding of peptide chain brings diverse amino acids into close proximity ⇒ binding site
What is the importance of tertiary structure in drug action ?
Folded up decides where the drug attaches /binds because it binds to non- neighbouring amino acids
What is Quaternary structure?
-Proteins that are made up of multiple proteins e.g. haemoglobin
-Individual proteins called subunits
-Structure caused by surface interactions between residues on the subunits
How many amino acids are commonly found in nature?
20 amino acids
-11 made in the body ,9 from our diet ( all are alpha amino acids)
What do Residues and functional groups determine?
-size
-shape
-the type of bonds that can be formed (reactive bonds- covalent ..,Interactive bonds- non permanent bonds hydrogen,ionic bonds)
What is the difference between Alpha amino acid and Beta Amino acids?
Alpha- One carbon between the functional groups
Beta- 2 carbons between them -useful when designing drugs to stabilise the structure into peptides
NOTE- Synthetic amino acids can be incorporated into drugs to increase stability
What are the groups Amino acids can be sorted into ?
-for drug interaction
-bond forming ability is most useful
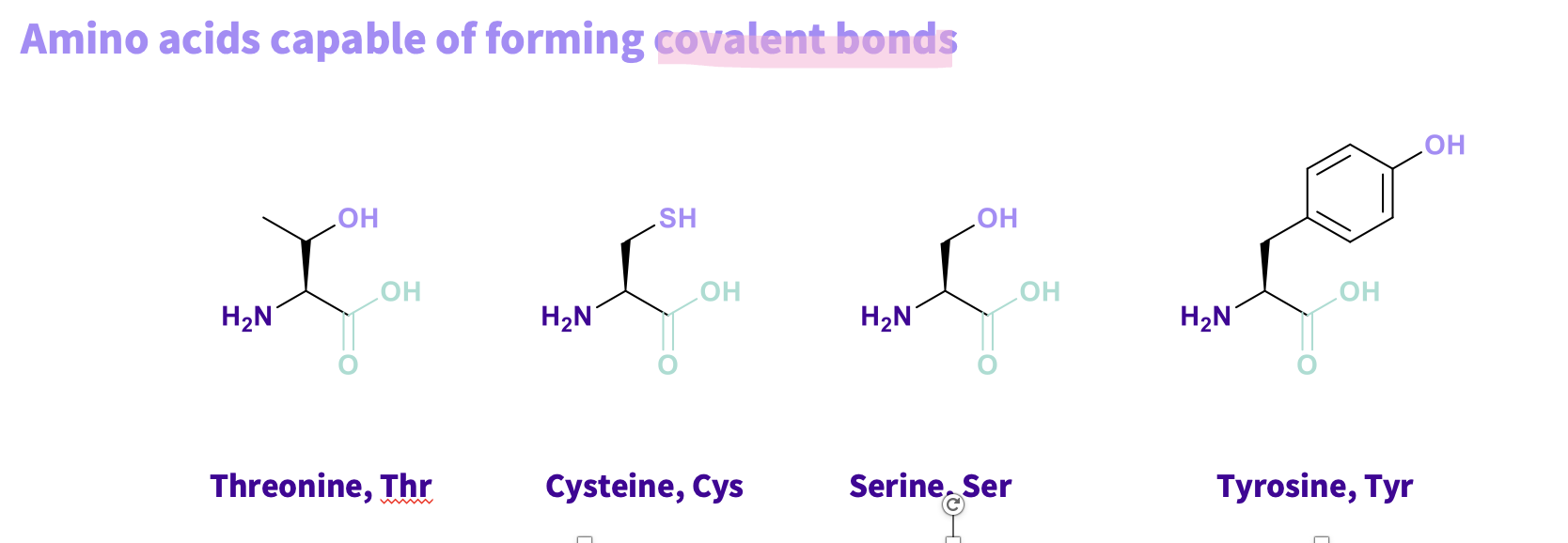
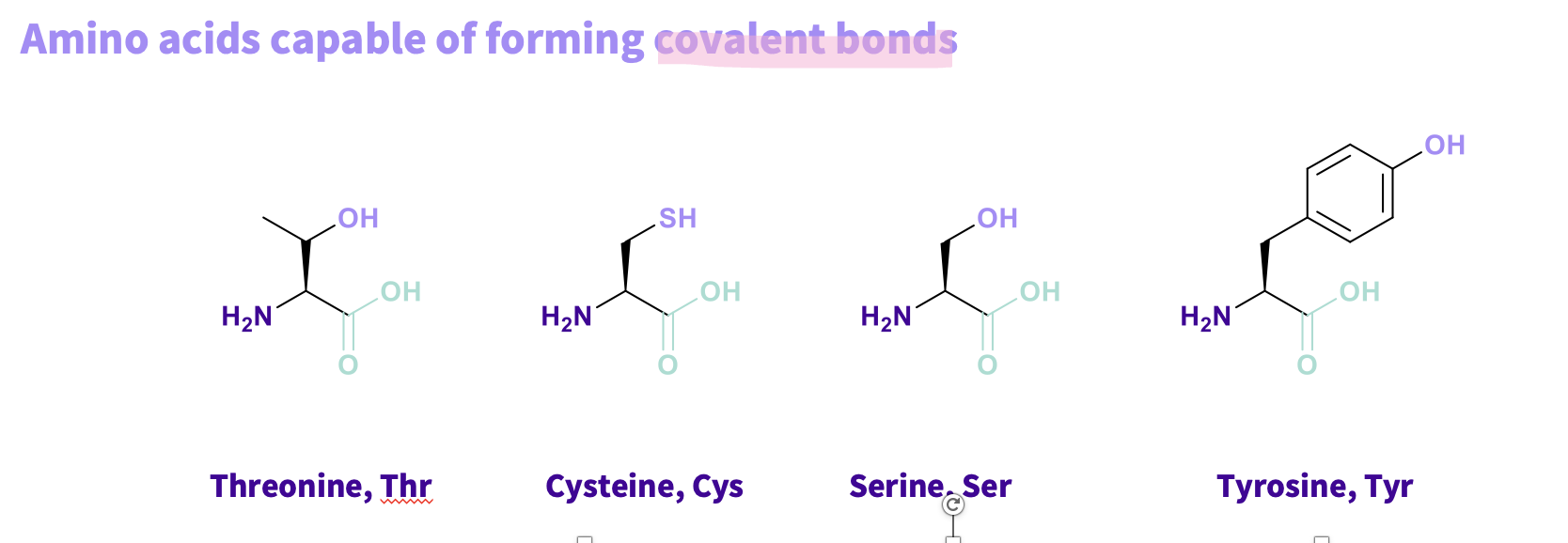
What are the Amino acids that are capable in forming covalent bonds and what do have in common ?
Threonine, Thr
Cysteine, Cys
Serine, Ser
Tyrosine, Tyr
all have alcohol and thiols they can lose hydrogens ,turned into a nucleophile , to form a covalent bond (STRONGEST BONDS)
Note - Directional – between two molecules
Why are the amino acids formed by covalent bonds important?
Most important in enzyme interactions/inhibitors with drugs
In receptors cause receptor block- permanently changed can’t be reversed – don’t want covalent bonds
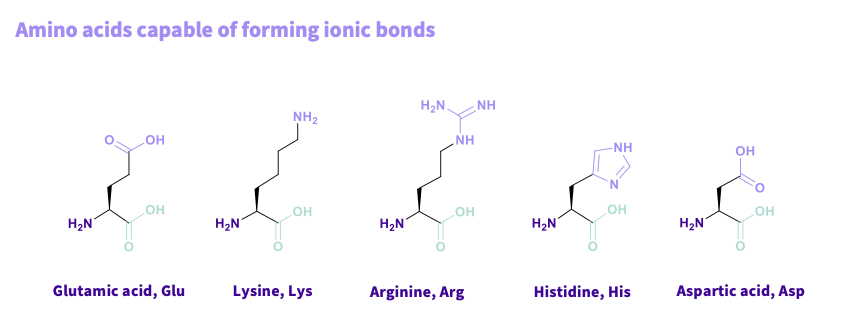
What are the amino acids that are capable in forming ionic bonds and what do they have in common?
Glutamic acid, Glu,
Lysine, Lys
Arginine, Arg
Histidine, His
Aspartic acid, Asp
common - have carboxyl acid groups, amine group ( base) ,can lose or gain a hydrogen involved in ionic interaction
NOTE- acid = - ve lysine= + ve
Why are amino acids that form ionic bonds important ?
Really important in all drug receptor and drug enzyme interactions
Allow strong binding but also dissociation
STRONG BUT CAN BE REVERSED
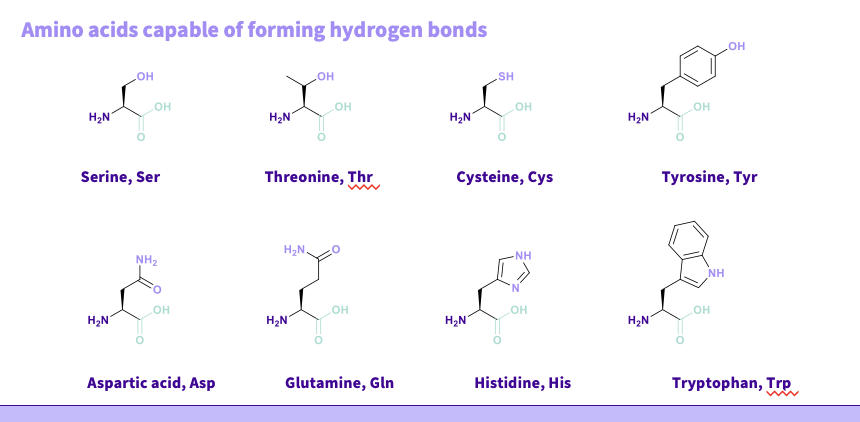
What are the amino acids that can form Hydrogen bonds?
Serine, Ser
Threonine, Thr
Cysteine, Cys
Tyrosine, Tyr
Aspartic acid, Asp
Glutamine, Gln
Histidine, His.
Tryptophan, Trp.
NOTE - Hydrogen bonds are weaker and usually require lots for strength
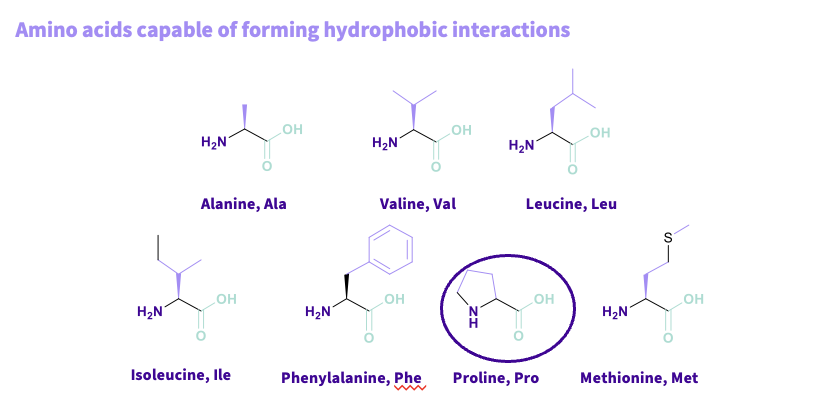
What are the amino acids that are capable of forming Hydrophobic interactions?
Alanine,ala
valine,val
leucine,leu
Isoleucine,ile
Phenylalanine,phe
Proline,pro- cyclic compound residue in a circle tertiary amine- provides more stability in a protein ,more rigid
Methionine ,Met
common- alky ,aryl chains
Note- WEAKEST
Not directional – multiple amino acids interacting so they have a hydrophobic surface
What bonds does Glycine form ?
Glycine - nothing , used for structure , spacer between other groups , no residue so no interactions
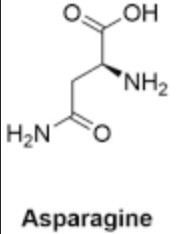
What type of bonds does Asparagine form
ionic, hydrogen,
DEPENDS ON THE PH