General chemistry 12: electrochemistry
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
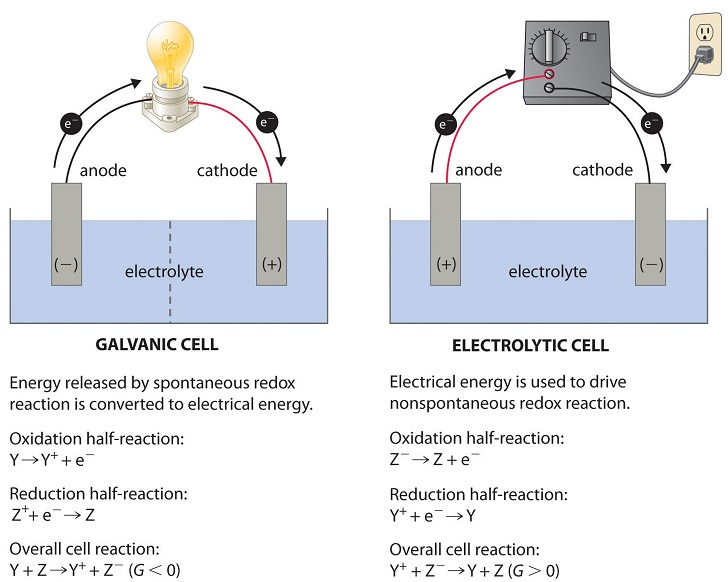
In an electrochemical cell, an anode attracts [anions or cations] and is always the site of [oxidation or reduction]
anions
oxidation
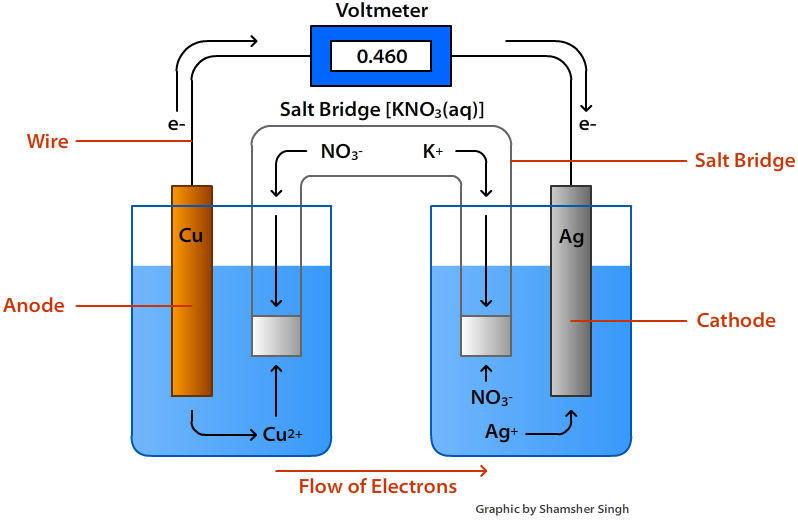
In an electrochemical cell, a cathode attracts [anions or cations] and is always the site of [oxidation or reduction]
cations
reduction

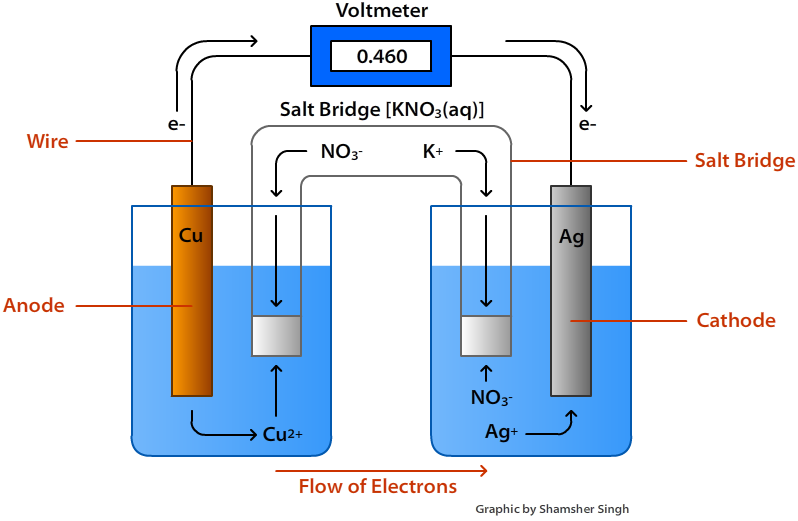
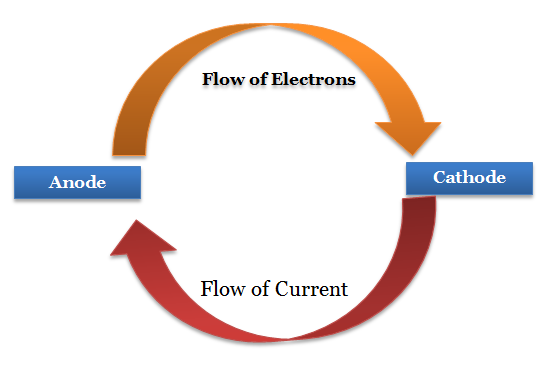
In an electrochemical cell, electrons flow from the [anode or cathode] to the [anode or cathode]
anode; cathode
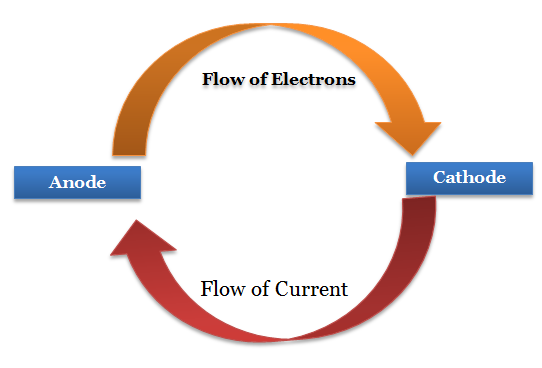
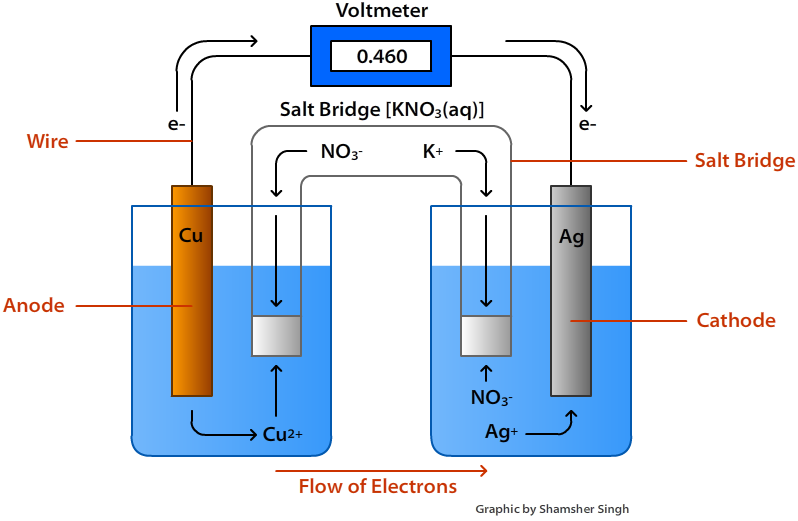
In an electrochemical cell, current flows from the [anode or cathode] to the [anode or cathode]
cathode to the anode
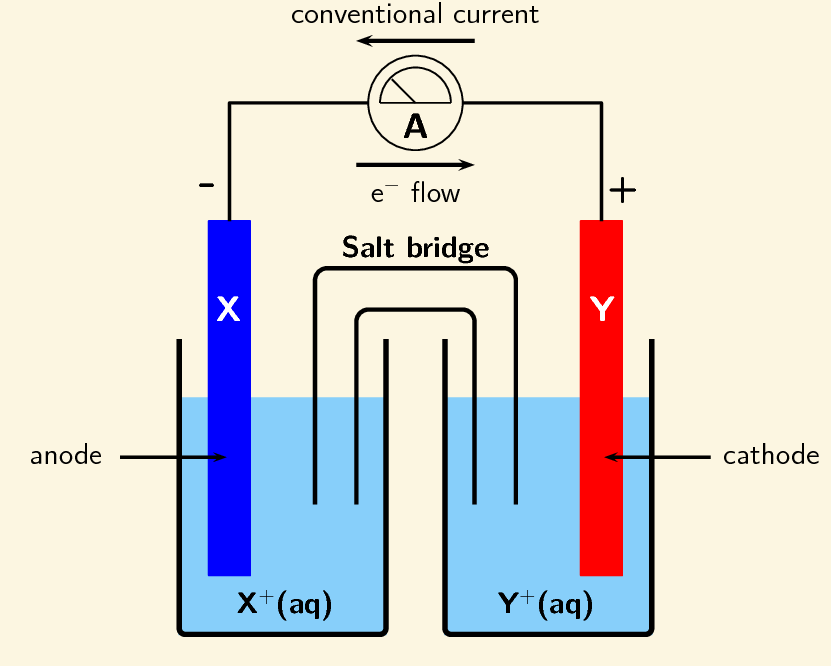
Galvanic cells are also known as [...]
voltaic cells

Galvanic cells house [spontaneous or non-spontaneous] reactions
spontaneous
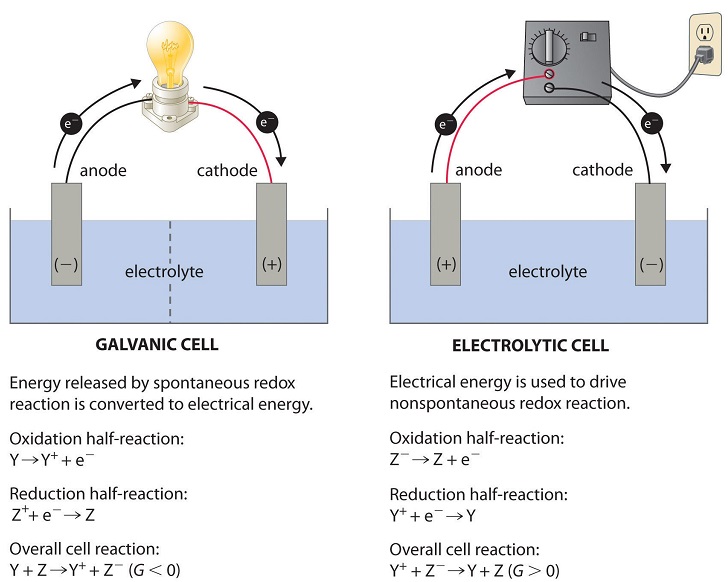
Electrolytic cells house [spontaneous or non-spontaneous]reactions
non-spontaneous
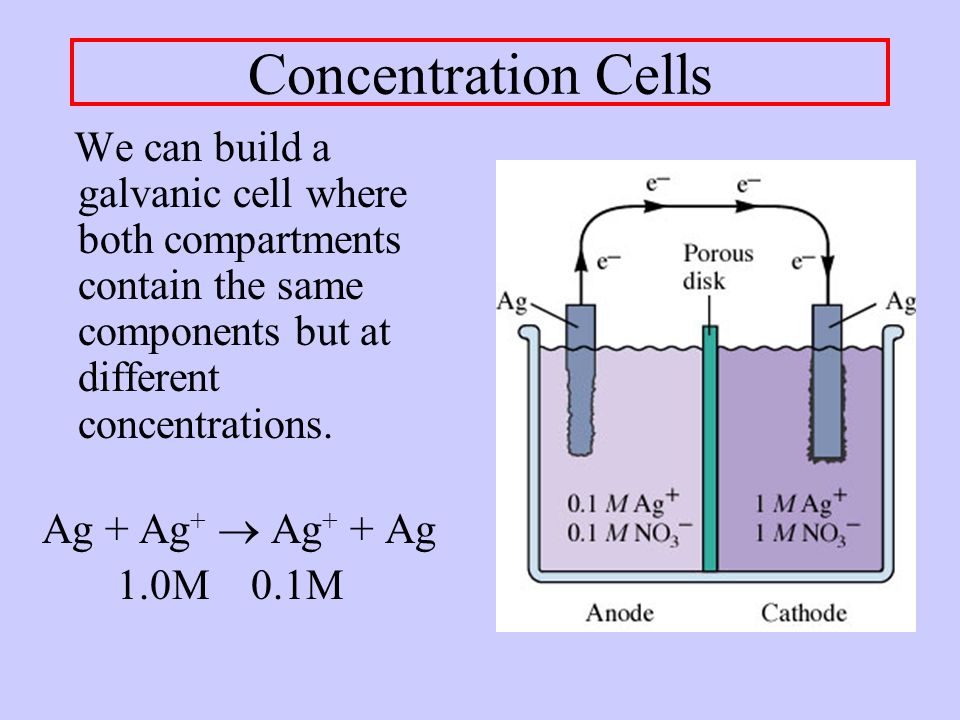
A/an [...] is an electrolytic cell that is comprised of two half-cells with the same electrodes, but differing in concentrations
concentration cell
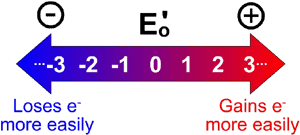
[...] is a measure of the tendency of a chemical species gain electrons and be reduced
reduction potential
a more positive Ered indicates a greater tendency to be reduced
The [...] is the tendency for a chemical species to be reduced, and is measured in volts at standard conditions
standard reduction potential

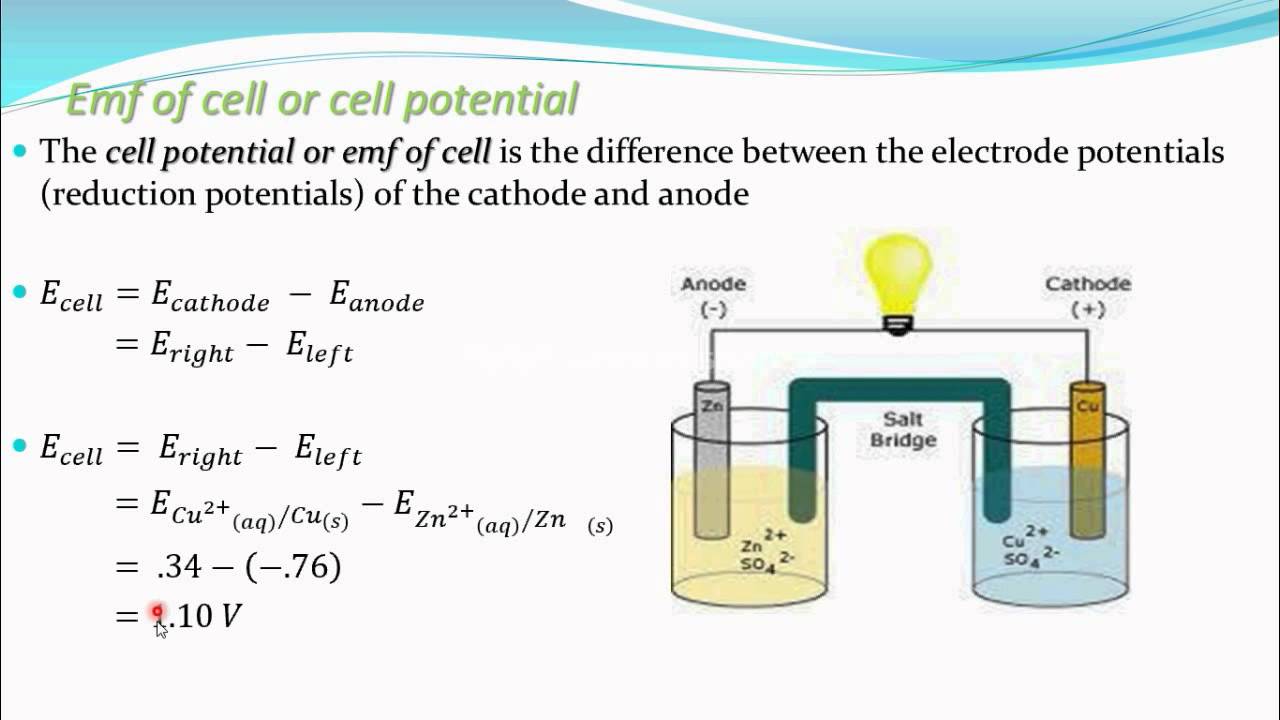
The [...] is the maximum potential difference between two electrodes of a galvanic or voltaic cell
electromotive force (EMF)
also known as the cell potential
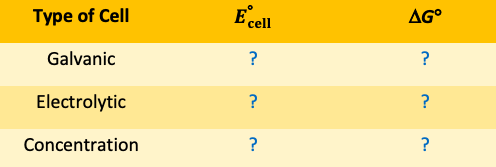
Complete the above table with the signs (+, -, or 0) for each type of electrochemical cell
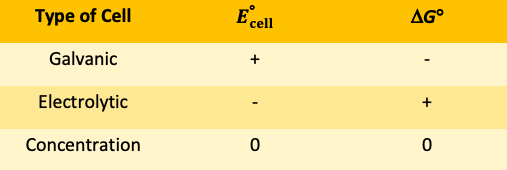
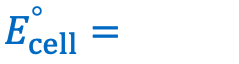
Give the equation for the cell potential (electromotive force) of an electrochemical cell:

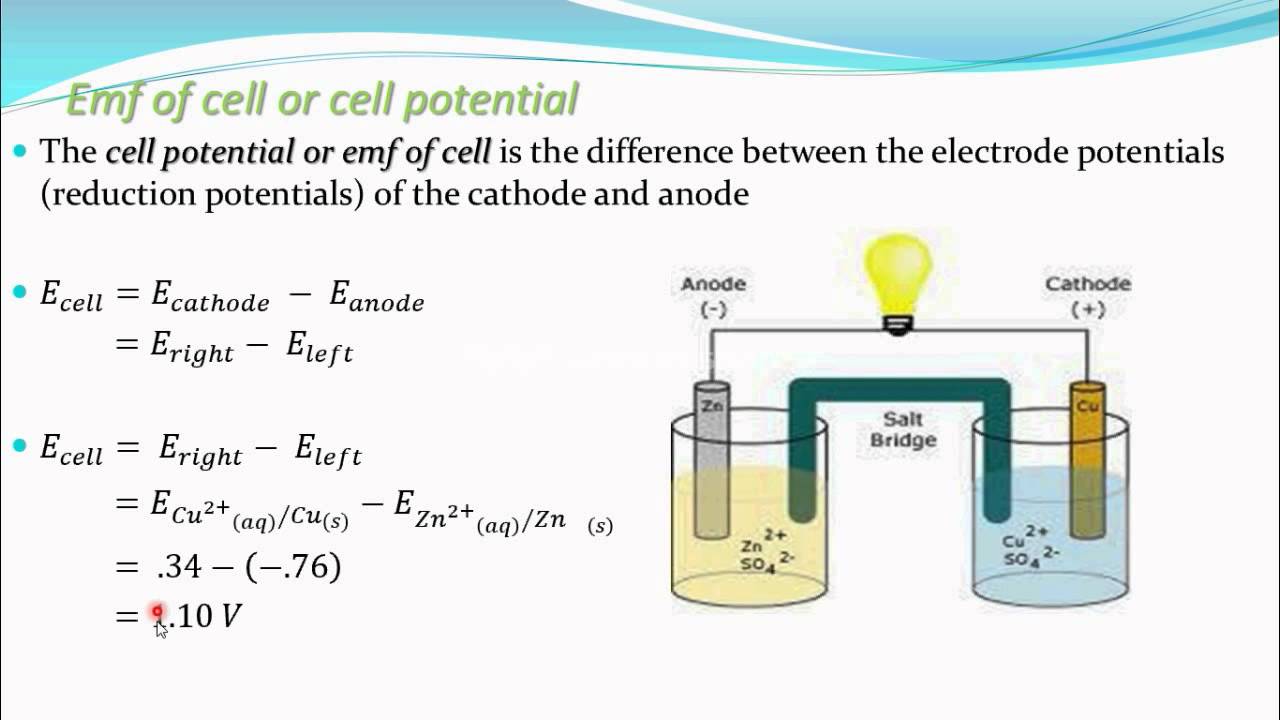

Give the equation for the change in Gibbs free energy during a REDOX reaction as a function of standard cell potential:
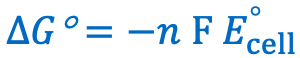
n=number of moles of electrons transferred
F= faraday constant = 96485 c/mol
Ecell= standard cell potential
ive the equation for the change in Gibbs free energy in a REDOX reaction as a function of Keq and in standard conditions:

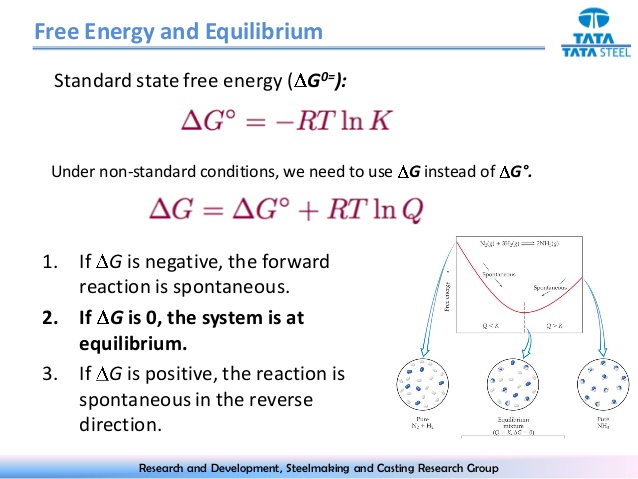
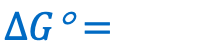
Give the equation for the change in Gibbs free energy in a REDOX reaction as a function of Keq and in non-standard conditions:
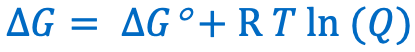

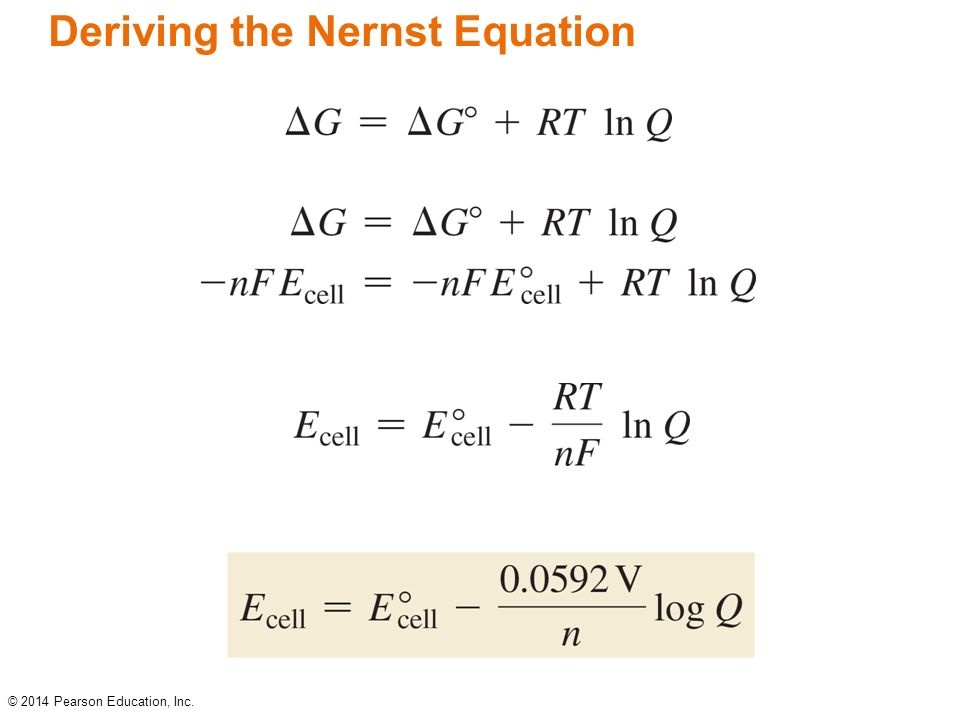
Give the Nernst equation:

he Nernst equation is used to calculate cell potential in non-standard conditions
Ecell = cell potential
Eºcell = standard cell potential
R = universal Gas Constant, 8.31j/kmol
T = temperature in Kelvin
n = number of moles of electrons transferred
F = Faraday's constant = 96485 c/mol`
Q = reaction quotient (equals K if reaction is at equilibrium)
MILEDOWN::GENERAL_CHEMISTRY::ELECTROCHEMISTRY

Give the Nernst equation with the constants simplified to a single value:
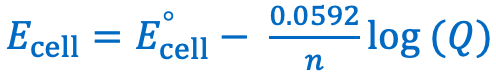
At the equivalence point, a solution of weak acid and strong base will have a pH [ <, >, or = ] 7
> 7
At the equivalence point, a solution with strong acid and strong base will have a pH [ <, >, or = ] 7
= 7
At the equivalence point, a solution with strong acid and weak base will have a pH [ <, >, =] 7
A/an solvent is a liquid that dissolves a solid, liquid or gaseous [...]
solute