Chap 19C - Solubility
1/6
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
7 Terms
When NH3 is gradually added to a solution of Zn2+ ions, a white precipitate is first formed. The white precipitate then dissolves on further addition of NH3 to form a colourless solution. Explain.
NH3(aq) + H2O(l) ⇌ NH4+(aq) + OH–(aq) ----- (1)
Zn2+(aq) + 2OH–(aq) ⇌ Zn(OH)2(s) ----- (2)
Zn2+(aq) + 4NH3(aq) ⇌ [Zn(NH3)4]2+(aq) ----- (3)
NH3 partially dissociates in water to produce OH-
In addition to NH3(aq), [OH–] increases, this causes the ionic product [Zn2+][OH–]2 to be greater than Ksp.
POE (2) shifts right to counteract the increase in [OH–] -> White precipitate of Zn(OH)2 is observed.
On further addition of NH3(aq), [NH3] increases and POE (3) shifts right to form colourless complex, [Zn(NH3)4]2+ -> decrease in [Zn2+]
POE (2) shifts left to counteract the decrease in [Zn2+]
When the ionic product, [Zn2+][OH–]2 is smaller than its Ksp, the white precipitate of Zn(OH)2 dissolves to give a colourless solution
State complex ion and equilibrium equation for AI3+, Ag+
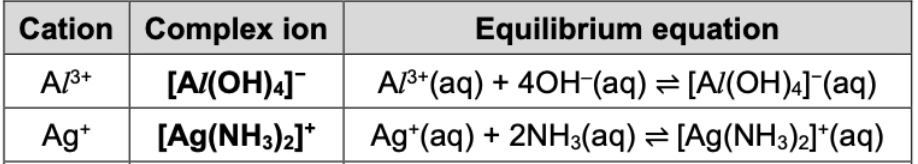
State complex ion and equilibrium equation for Cu2+, Cr3+
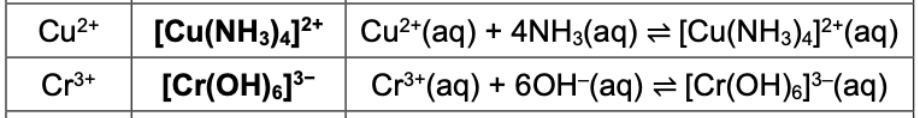
State complex ion and equilibrium equation for Zn2+ (both)
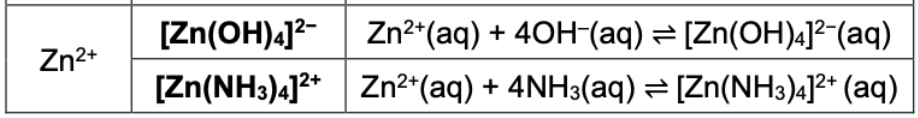
State which type of salt is affected by pH
Solubility of a sparingly soluble salt will be affected by pH changes if the anion of the salt is at least moderately basic
Solubility increases if solution becomes more acidic
Describe solubility of Ca3(PO4)2 in acid
Ca3(PO4)2 (s) ⇌ 3Ca2+ (aq) + 2PO43– (aq) ----- (1)
HCl (aq) → Cl– (aq) + H+ (aq) ----- (2)
H+(aq) + PO43– (aq) ⇌ HPO42– (aq) ----- (3)
PO43- is a conjugate base of a weak acid HPO42- -> PO43- undergoes hydrolysis
The H+ formed from the dissociation of HCl reacts with PO43– in equilibrium (3).
[PO43–] decreases and POE (1) shifts right to counteract the decrease in [PO43–]
When the ionic product [Ca2+]3[PO43–]2 is smaller than its Ksp, the Ca3(PO4)2 precipitate dissolves, resulting in an increase in solubility of Ca3(PO4)2 in acidic solution (low pH)
Describe solubility of Ca3(PO4)2 in base
Ca3(PO4)2 (s) ⇌ 3Ca2+ (aq) + 2PO43– (aq) ----- (1)
PO43- + H2O ⇌ HPO42- + OH- ----- (2)
PO43- is a conjugate base of a weak acid HPO42- -> PO43- undergoes hydrolysis
In basic solution, [OH-] is high -> POE in (2) shifts left to counteract increase in [OH-] -> [PO43-] increases
Ionic product [Ca2+][PO43-]2 > Ksp -> POE in (1) shifts left to counteract increase in [PO43-]
More Ca3(PO4)2 solid will be precipitated -> decrease in solubility in basic solution