BOC: 155-247 Serology
1/92
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
93 Terms
In the anti-double-stranded DNA procedure, the antigen most commonly utilized is:
a. rat stomach tissue
b. mouse kidney tissue
c. Crithidia luciliae
d. Toxoplasma gondii
C
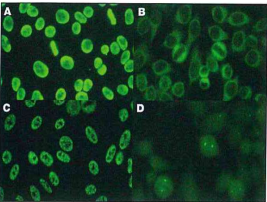
Which of these ANA patterns would be associated with high titers of antibodies to the Sm antigen?
a) image A
b) image B
c) image C
d) image D
C
Sera to be tested for IFA-ANA 6 days after drawing is best stored at:
a) room temperature
b) 5°C +/- 2°
c) -70°C in a constant temperature freezer
d) -20°C in a frost-free self-defrosting freezer
B
Antibodies directed at native DNA are most frequently associated with which pattern of fluorescence in the IFA-ANA test?
a) rim
b) diffuse
c) speckled
d) centromere
A
The technologist observes apparent homogenous staining of the nucleus of interphase cells while performing an IFA-ANA, as well as staining of the chromosomes in mitotic cells. This result is:
a) indicative of 2 antibodies, which should be separately reported after titration
b) expected for anti-DNA antibodies
c) inconsistent; the test should be reported with new reagent
d) expected for anti-centromere antibodies
B
The result of an anti-nuclear antibody test was a titer of 1:320 with a peripheral pattern. Which set of data best correlate with these results?
a) anti-dsDNA titer 1:80, and a high titer of antibodies to Sm
b) antimitochondrial antibody titer 1:160, and antibodies to RNP
c) anti-Scl-70, and antibodies to single-stranded DNA
d) high titers of anti-SS-A and anti-SS-B
A
A positive ANA with the pattern of anti-centromere antibodies is most frequently seen in patients with:
a. rheumatoid arthritis
b. systemic lupus erythematosus
c. CREST syndrome
d. Sjӧgren syndrome
C
In the indirect fluorescent anti-nuclear antibody test, a homogenous pattern indicates the presence of antibody to:
a. RNP
b. Sm
c. RNA
d. DNA
D
In the indirect fluorescent anti-nuclear antibody test, a speckled pattern may indicate the presence of antibody to:
a. histone
b. Sm
c. RNA
d. DNA
B
Rheumatoid factors are immunoglobulins with specificity for allotypic determinants located on the:
a) Fc fragment of IgG
b) Fab fragment of IgG
c) J chain of IgM
d) secretory of component of IgA
A
Rheumatoid factor in patients serum may cause a false:
a) positive test for the detection of IgM class antibodies
b) negative test for the detection of IgM class antibodies
c) positive test for the detection of IgG class antibodies
d) negative test for the detection of IgG class antibodies
A
Rheumatoid factors are defined as:
a) antigens found in the sera of patients with rheumatoid arthritis
b) identical to the rheumatoid arthritis precipitin
c) autoantibodies with specificity for the Fc portion of the immunoglobulin (IgG) molecule
d) capable of forming circulating immune complexes only when IgM-type autoantibody is present
C
False-positive rheumatoid factor in agglutination and nephelometric methods can be due to elevated levels of:
a. cryoglobulin
b. histidine-rich-glycoprotein
c. aspartame
d. C1q
D
Anti-RNA antibodies are often present in individuals having an anti-nuclear antibody immunofluorescent pattern that is:
a) speckled
b) rim
c) diffuse
d) nucleolar
D
Anti-extractable nuclear antigens are most likely associated with which of the following anti-nuclear antibody immunofluorescent patterns?
a) speckled
b) rim
c) diffuse
d) nucleolar
A
In an anti-nuclear antibody indirect immunofluorescent test, a sample of patient serum shows a positive, speckled pattern. Which would be the most appropriate additional test to perform?
a) antimitochondrial antibody
b) immunoglobulin quantitation
c) screen for Sm and RNP antibodies
d) anti-DNA antibody using C luciliae
C
Anti-phospholipid antibodies associated with autoimmune disorders tend to have immunoglobulin (IgG) that belongs to which of the following subclasses?
a. IgG1 and IgG3
b. IgG2 and IgG4
c. IgG1 and IgG4
d. IgG2 and IgG3
B
The IIF staining pattern on ethanol-fixed leukocytes slides shows a perinuclear or nuclear staining pattern. This pattern is typically due to:
a. C-ANCA
b. LKM
c. P-ANCA
d. GBM
C
The specificity of an immunoassay is determined by the:
a. label used on the antigen
b. method used to separate the bound from free antigen
c. antibody used in the assay
d. concentration of unlabeled antigen
C
In the indirect immunofluorescence method of antibody detection in patient serum, the labeled antibody is:
a) human anti-goat immunoglobulin
b) rheumatoid factor
c) goat anti-human immunoglobulin
d) complement
C
A substrate is first exposed to a patient’s serum, then after washing, anti-human immunoglobulin labeled with a fluorochrome is added. The procedure described is:
a) fluorescent quenching
b) direct fluorescence
c) indirect fluorescence
d) fluorescence inhibition
C
Cholesterol is added to the antigen used in flocculation tests for syphilis to:
a) destroy tissue impurities present in the alcoholic beef heart extract
b) sensitize the sheep RBCs
c) decrease specificity of the antigen
d) increase sensitivity of the antigen
D
The presence of HbsAg, anti-HBc and often HbeAg is characteristic of:
a) early acute phase HBV hepatitis
b) early convalescent phase HBV hepatitis
c) recovery phase of acute HBV hepatitis
d) past HBV infection
A

From the test results, it can be concluded that patient #3 has:
a. recent acute hepatitis A
b. acute hepatitis B
c. acute hepatitis C (non-A/non-B hepatitis)
d. chronic hepatitis B
B
The disappearance of HBsAg and HBeAg, the persistence of anti-HBc, the appearance of anti-HBs, and often of anti-AHe indicate:
a. early acute HBV hepatitis
b. early convalescent phase HBV hepatitis
c. recovery phase of acute HBV hepatitis
d. carrier state of acute HBV hepatitis
C
An example of a live attenuated vaccine used for human immunization is:
a. rabies
b. tetanus
c. hepatitis B
d. measles
D
Flocculation tests for syphilis detect the presence of:
a) reagin antibody
b) antigen
c) hemolysin
d) Forssman antigen
A
Flocculation tests for syphilis use antigen composed of:
a) Treponema pallidum
b) reagin
c) cardiolipin and lecithin
d) charcoal
C
A serological test for syphilis that depends upon the detection of cardiolipin-lecithin-cholesterol antigen is:
a) FTA-ABS
b) RPR
c) MHA-TP
d) TPI
B
The serological test for syphilis recommended for detecting antibody in cerebrospinal fluid is:
a) non-treponemal antibody
b) CSF-VDRL
c) FTA-ABS
d) MHA-TP
B
In the direct fluorescent antibody test for primary syphilis, spirochetes are detected by addition of labeled antibody to:
a. Treponema pallidum
b. cardiolipin
c. human immunoglobulin
d. nonpathogenic treponemes
A
In the FTA-ABS test the presence of a beaded pattern of fluorescence along the treponeme indicates:
a. positive identification of Treponema pallidum
b. presumptive diagnosis of active syphilis
c. presence of nontreponemal antibody (NTA)
d. false-positive reaction
D
What assay would confirm the immune status of hepatitis B virus?
a) HBsAg
b) anti-HBs
c) IgM anti-HBcAg
d) hepatitis C Ag
B
The following procedure has been routinely used for detection of hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) because of its high level of sensitivity:
a) hemagglutination
b) counterimmunoelectrophoresis
c) radial immunodiffusion
d) ELISA
D
Which of the following is the best indicator of an acute infection with the hepatitis A virus?
a) the presence of IgG antibodies to hepatitis A virus
b) the presence of IgM antibodies to hepatitis A virus
c) a sharp decline in the level of IgG antibodies to hepatitis A virus
d) a rise in both IgM and IgG levels of antibody to hepatitis A virus
B
Biological false-positive VDRL reactions are frequently encountered in patients with:
a) lupus erythematosus
b) acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS)
c) gonorrhea
d) tertiary syphilis
A
Which serological marker of HBV infection indicates recovery and immunity?
a) viral DNA polymerase
b) HBe antigen
c) anti-HBs
d) HBsAg
C

The profile that matches the typical test profile for chronic active hepatitis due to hepatitis B virus is:
a. profile A
b. profile B
c. profile C
d. profile D
A
For diagnosis of late latent or tertiary syphilis, the most appropriate assay is:
a) RPR
b) VDRL
c) FTA-ABS
d) FTA-ABS IgM
C
A 26-year old nurse developed fatigue, a low-grade fever, polyarthritis and urticaria. Two months earlier she had cared for a patient with hepatitis. Which of the following findings are likely to be observed in this nurse?
a) a negative hepatitis B surface antigen test
b) elevated AST and ALT levels
c) a positive rheumatoid factor
d) a positive Monospot test
B
The classic antibody response pattern following infection with hepatitis A is:
a) increase in IgM antibody → decrease in IgM antibody → increase in IgG antibody
b) detectable presence of IgG antibody only
c) detectable presence of IgM antibody only
d) decrease in IgM antibody → increase in IgG antibody of the the IgG3 subtype
A
The 20-nm spheres and filamentous structures of HBV are:
a. infectious
b. circulating aggregates of HBcAg
c. circulating aggregates of HBsAg
d. highly infectious when present in great abundance
C
The enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) technique for the detection of HBsAg:
a) requires radiolabeled C1q
b) is quantitated by degree of fluorescence
c) uses anti-HBs linked to horseradish peroxidase
d) uses beads coated with HBsAg
C
The antigen marker most closely associated with transmissibility of HBV infection is:
a) HBsAg
b) HBeAg
c) HBcAg
d) HBV
B
Chronic carriers of HBV:
a) have chronic symptoms of hepatitis
b) continue to carry HBV
c) do not transmit infection
d) carry HBV but are not infectious
B
Hepatitis C differs from hepatitis A because it:
a. has a highly stable incubation period
b. is associated with a high incidence of icteric hepatitis
c. is associated with a high incidence of the chronic carrier state
d. is seldom implicated in cases of posttransfusion hepatitis
C
The initial immune response following fetal infection with rubella is the production of which class(es) antibodies?
a) IgG
b) IgA
c) IgM
d) both IgG and IgA
C
The air temperature throughout the serology laboratory is 20°C. How will this affect VDRL and RPR results?
a) no effect -the acceptable test range is 20°C-24°C
b) weaken reactions so that false negatives occur
c) strengthen reactions so that positive titers appear elevated
d) increase the number of false positives from spontaneous clumping
B
Which laboratory technique is most frequently used to diagnose and follow the course of therapy of a patient with secondary syphilis?
a) flocculation
b) precipitation
c) complement fixation
d) indirect immunofluorescence
A
The most commonly used serological indicator of recent streptococcal infection is the antibody to:
a) streptolysin O
b) hyaluronidase
c) NADase
d) DNA
A
In laser flow cytometry, applying a voltage potential to sample droplets as they stream past the light beam and using charged deflector plates results in:
a. an emission of red fluorescence from cells labeled with fluorescein isothiocyanate
b. an emission of green fluorescence from cells labeled with rhodamine
c. a 90° light scatter related to cell size
d. the separation of cells into subpopulations based on their charge
D
Which of the following is true of the first stage of infection with Borrelia burgdorferi?
a. a generalized rash develops within 4-6 hours of a bite by a deer tick
b. the patient may be asymptomatic except for the rash
c. once developed, the rash persists for 7-10 days
d. serologic testing is often positive within 1 week after the tick bite
B
Which of the following is characteristic of the second stage of infection with Borrelia burgdorferi?
a. spread to brain and spinal cord via cerebrospinal fluid
b. spread to multiple organ systems via the bloodstream
c. 3-4 week latency after tick bite
d. involvement of the liver, gallbladder, and pancreas
B
Which of the following is characteristic of the late stage of infection with Borrelia burgdorferi?
a. spread to brain and spinal cord via cerebrospinal fluid
b. development in patients refractory to antibiotic therapy
c. arthritis, peripheral neuropathy, or encephalomyelitis
d. resistance to antibiotic therapy
C
Which of the following is consistent with CDC recommendations for confirmation of infection with Borrelia burgdorferi?
a. perform screening EIA with commercially-prepared antibody coated slides
b. if asymptomatic but screening positive, perform both IgM and IgG western blot
c. confirm diagnosis if 1 of 3 critical IgM bands reactive on nitrocellulose strip
d. confirm diagnosis if half of the 10 critical IgG bands reactive on nitrocellulose strip
D
Which of the following statements is most accurate regarding polymerase chain reaction (PCR) confirmation of infection with Borrelia burgdorferi?
a. PCR detects specific Borrelia antibodies
b. no cross-reactivity issues exist with PCR because of its specificity
c. PCR is recommended to routine positive screening tests
d. PCR can utilize either a fluorescent or enzyme marker
C
Purified protein derivative is used to assess the presence of infection with Mycobacterium tuberculosis in the:
a. Mantoux test
b. RAST test
c. serum sickness test
d. Laurell test
A
The Mantoux test for Mycobacterium tuberculosis is based on a:
a. Type III hypersensitivity reaction
b. Type II hypersensitivity reaction
c. Type I hypersensitivity reaction
d. Type IV hypersensitivity reaction
D
The Mantoux skin test to identify infection with Mycobacterium tuberculosis is:
a. a cell-mediated response
b. an IgG response
c. an IgE response
d. an IgM response
A
The Quanti-FERON-T Gold In-Tube (QFT-GIT) test to support diagnosis of latent tuberculosis measures release of interferon gamma (IFNγ) by:
a. T cells
b. macrophages
c. neutrophils
d. B cells
A
A cytokine that is classically associated with Th1 cells is:
a. interleukin-4
b. interferon gamma
c. interleukin-5
d. interferon alpha
B
Anti-nuclear antibody tests are performed to help diagnose:
a. acute leukemia
b. lupus erythematosus
c. hemolytic anemia
d. Crohn disease
B
In the anti-nuclear antibody test, what are the fixed HEp-2 cells?
a. unlabeled antigen
b. labeled antigen
c. labeled antiglobulin
d. unlabeled antiglobulin
A
Which of the following is true of hashimoto thyroiditis?
a. it is more common in male patients
b. it is also known as chronic lymphocytic thyroiditis
c. anti-thyroid-stimulating hormone receptor (TRAb) is usually present
d. the goiter is firm rather than rubbery
B
Which of the following is true of Graves disease?
a. it is more common in male patients
b. it is also known as chronic lymphocytic thyroiditis
c. the presence of anti-thyroid-stimulating hormone receptor (TRAb) is diagnostic
d. the goiter is firm rather than rubbery
D
Which of the following thyroid antibodies causes hyperthyroidism by binding to the TSH receptor?
a. anti-thyroglobulin (Tg)
b. anti-thyroperoxidase (TPO)
c. anti-thyroid-stimulating hormone receptor (TRAb)
d. anti-thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH)
C
Rheumatoid factor is most often of which of the following classes:
a. IgE
b. IgA
c. IgM
d. IgG
C
Rheumatoid factor consists of antibodies that bind the:
a. Fc portion of the IgG molecule
b. Fab portion of the IgG molecule
c. Fc portion of the IgM molecule
d. Fab portion of the IgM molecule
A
Which of the following is not commonly associated with the effects of rheumatoid factor?
a. joint inflammation
b. immune complex deposition
c. capillary endothelial space widening
d. complement inhibition
D
In the direct immunofluorescence assay for Legionella pneumophila, patient sample affixed to the slide may be detected with:
a. primary antigen with fluorescent conjugate
b. primary antibody with fluorescent conjugate
c. secondary antigen with fluorescent conjugate
d. secondary antibody with fluorescent conjugate
B
An agglutination test wherein the antigen is a natural component of the infectious entity is a(n):
a. indirect agglutination procedure
b. direct agglutination procedure
c. passive agglutination procedure
d. reverse passive agglutination procedure
B
A suspected anthrax lesion is submitted to the lab for preparation and testing. The test of choice to perform on this sample is:
a. capture immunoassay
b. indirect immunoassay
c. direct immunoassay
d. sandwich immunoassay
C
The primary advantage of labeled immunoassays compared to unlabeled immunoassays is:
a. rapidity
b. quality
c. sensitivity
d. cost
C
Which of the following pairs of considerations do not pertain to ELISA testing?
a. competitive vs noncompetitive
b. heterogeneous vs homogeneous
c. luminescent vs fluorescent
d. radioactive vs colorimetric
D
A classic ELISA test is performed on a sample from a 67-year-old male patient who is suspected of having ingested large amounts of drug X. The ELISA procedure is performed as follows:
incubation of patient sample in antibody-coated microtiter plate wells
plate washing
addition of peroxidase-linked drug X conjugate
incubation followed by plate washing
addition of hydrogen peroxide
evaluation of color change
Which of the following is true regarding this procedure?
a. hydrogen peroxide is the substrate
b. the conjugate contains the antibody
c. the test is homogeneous
d. the test is noncompetitive
A
A physician suspects the presence of anti-IFNγ autoantibodies in a patient. A serum sample is sent to your laboratory to measure the presence or absence of anti-IFNγ autoantibodies by an enzyme-immunoassay. Which of the following would be used as the detecting reagent in the kit?
a. horseradish peroxidase-conjugated recombinant human IFNγ
b. horseradish peroxidase-conjugated mouse Ab to goat Ab
c. horseradish peroxidase-conjugated goat Ab to human IFNγ
d. horseradish peroxidase-conjugated mouse Ab to human Ab
D
IL-4 can stimulate B cells to produce IgE, a major contributor to:
a. Type I hypersensitivity
b. Type II hypersensitivity
c. Type III hypersensitivity
d. Type IV hypersensitivity
A
Cytokines involved in innate immune regulation include all but:
a. IL-6
b. IL-3
c. IL-1
d. TNF-alpha
B
Multiplex bead assays for the detection of cytokines are efficient quantifiers of numerous cytokines at one time. One complication of such testing is:
a. the cross-reactivity of fluorescent probes
b. the short half-life of certain cytokines
c. the lack of test sensitivity
d. inadequate cytokine-specific antibodies
B
The procedure for compatibility testing in organ transplant medicine is very similar for the donor and the recipient. One additional procedure that the recipient must undergo that is not relevant to donor testing is:
a. ABO typing
b. HLA typing
c. CMV testing
d. anti-HLA antibody testing
D
PCR is extremely sensitive, but testing may be complicated by:
a. an inability to detect nucleic acids from nonviable organisms
b. poor quality amplification
c. contamination of samples yielding false-positive results
d. lack of specificity
C
Methods of target amplification in molecular testing include all but:
a. reverse transcriptase-based amplification
b. strand displacement amplification
c. signal amplification
d. primer amplification
D
What type of short read files with quality scores are used for storing next generation sequencing read data?
a. FASTA
b. FASTQ
c. RRBS
d. WGBS
B
In dideoxy chain termination sequencing (Sanger method), what does a heterozygous nucleotide position look like on an electropherogram?
a. 1 peak twice the height of those around it
b. 2 peaks in the same position, one twice the height of the other
c. 2 peaks of equal height at the same position
d. 3 peaks of equal height at the same position
C
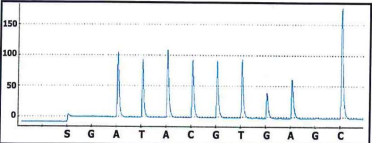
What is the sequence of the DNA shown on this pyrogram?
a. allele 1: ATACGTGCC allele 2: ATACGTGCC
b. allele 1: ATACGTGCC allele 2: ATACGTACC
c. allele 1: ATACGTGAGC allele 2: ATACGTGAGC
d. allele 1: ATACGTGACC allele 2: ATACGTGACC
B
Which condition has the highest stringency for DNA probe hybridization?
a. low temperature, low salt concentration
b. high temperature, low salt concentration
c. high temperature, high salt concentration
d. low temperature, high salt concentration
B
A heterophile antigen is best described as:
a. an auto-antigen
b. existing in an unrelated animal
c. resulting from an amnestic response
d. an adjuvant to increase immune response
B
What should be adjusted to make sure emission of fluorescence from a single fluorophore does not bleed into multiple channels?
a. compensation
b. threshold
c. voltage
d. fluid speed
A
What does light emitted as FSC measure?
a. cell granularity/complexity
b. cell size
c. cell surface marker fluorescence
d. nucleic acid marker fluorescence
B
What type of biological sample is best measured by flow cytometry?
a. single cell suspension
b. a piece of tissue
c. intact BM core biopsy
d. plasma
A
The process of centering the sample core within the sheath fluid is known as:
a. acoustic focusing
b. hydrodynamic focusing
c. liquid focusing
d. isoelectric focusing
B
To which filters do these definitions correspond:
transmit light in the specified wavelength
transmit light equal to or longer than specified wavelength
transmit light equal to or shorter than specified wavelength
a. longpass, shortpass, bandpass
b. shortpass, bandpass, longpass
c. bandpass, longpass, shortpass
d. bandpass, shortpass, longpass
C
The electronic signal produced by the detectors is proportional to:
a. the amount of light striking them
b. the speed of fluid flow
c. the presence of clumps in the sample
d. the viscosity of the fluid
A