CH 22. Female reproductive system
1/89
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
90 Terms
How does the thyroid respond to pregnancy?
How does the thyroWhat initiates puberty in females?id respond to pregnancy?
What initiates puberty in females?
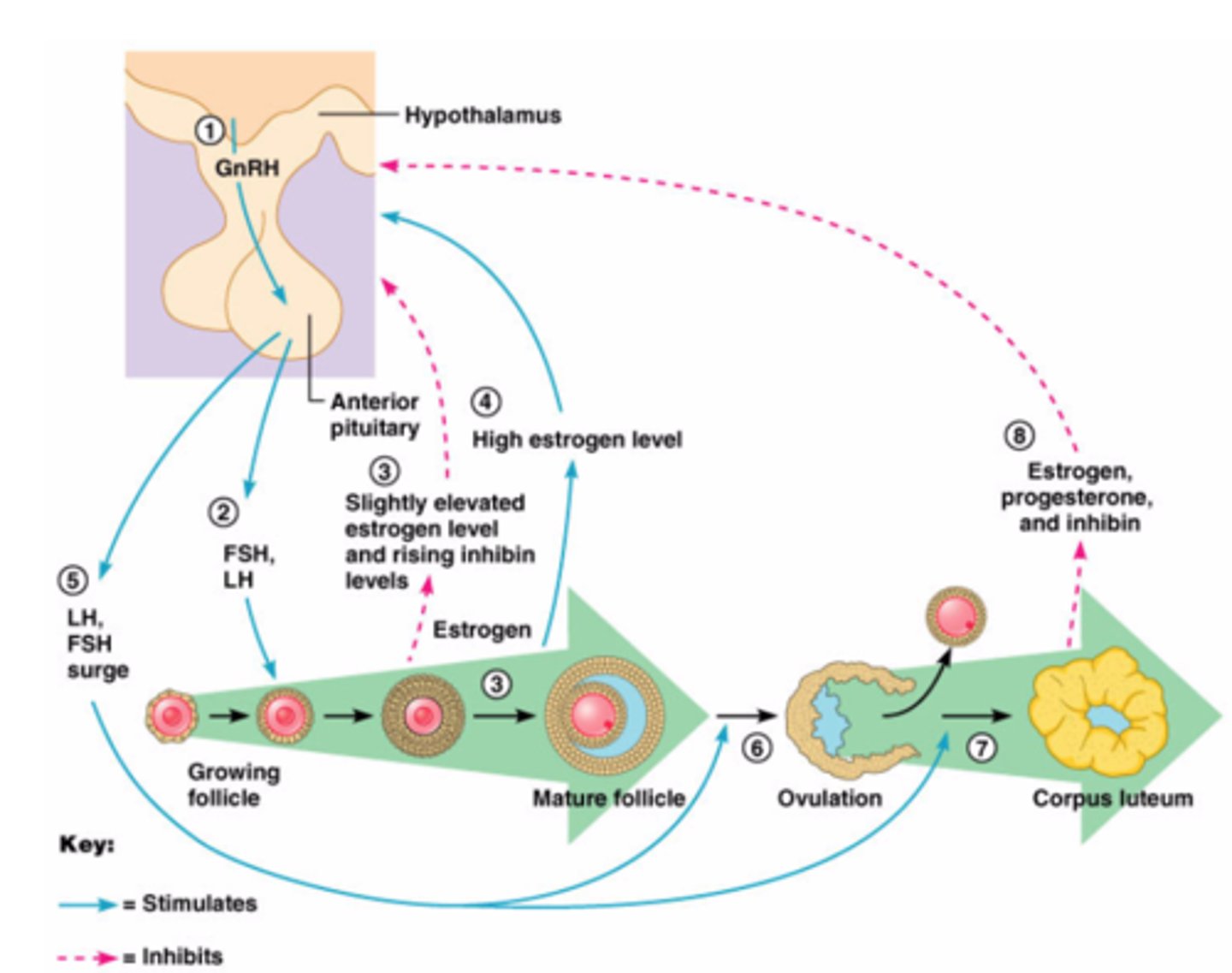
Rising levels of GnRH.
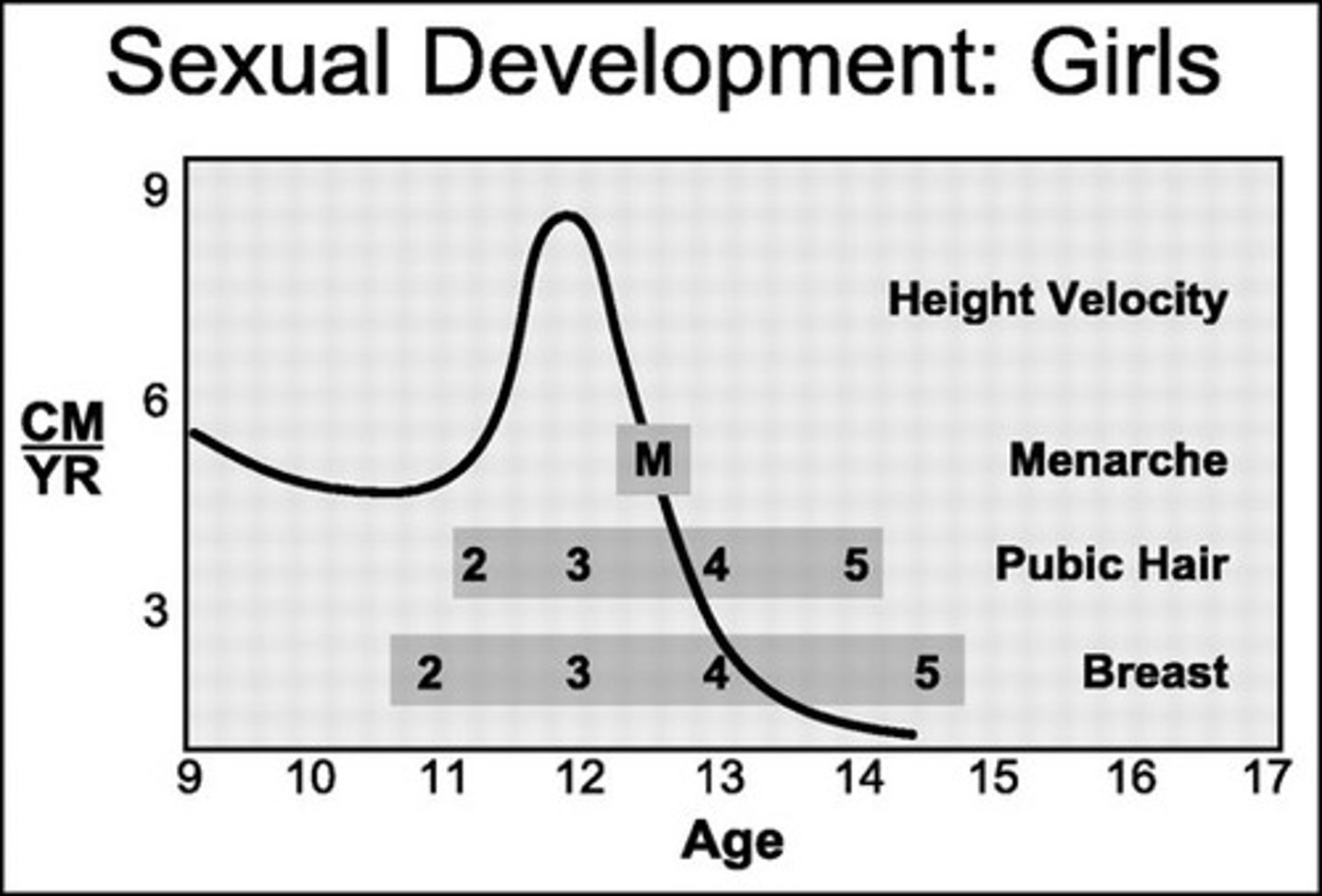
What does GnRH stimulate in the pituitary?
Secretion of FSH and LH.
What does FSH do in females during puberty?
Stimulates ovarian follicles.
What hormones are secreted by ovarian follicles at puberty?
Estrogen, progesterone, inhibin, and small amounts of androgen.
What is the most abundant estrogen in females?
Estradiol; e2
estriol
e3; estrogen of pregnancy
estrone
e1; primarily secreted by the adrenal glands
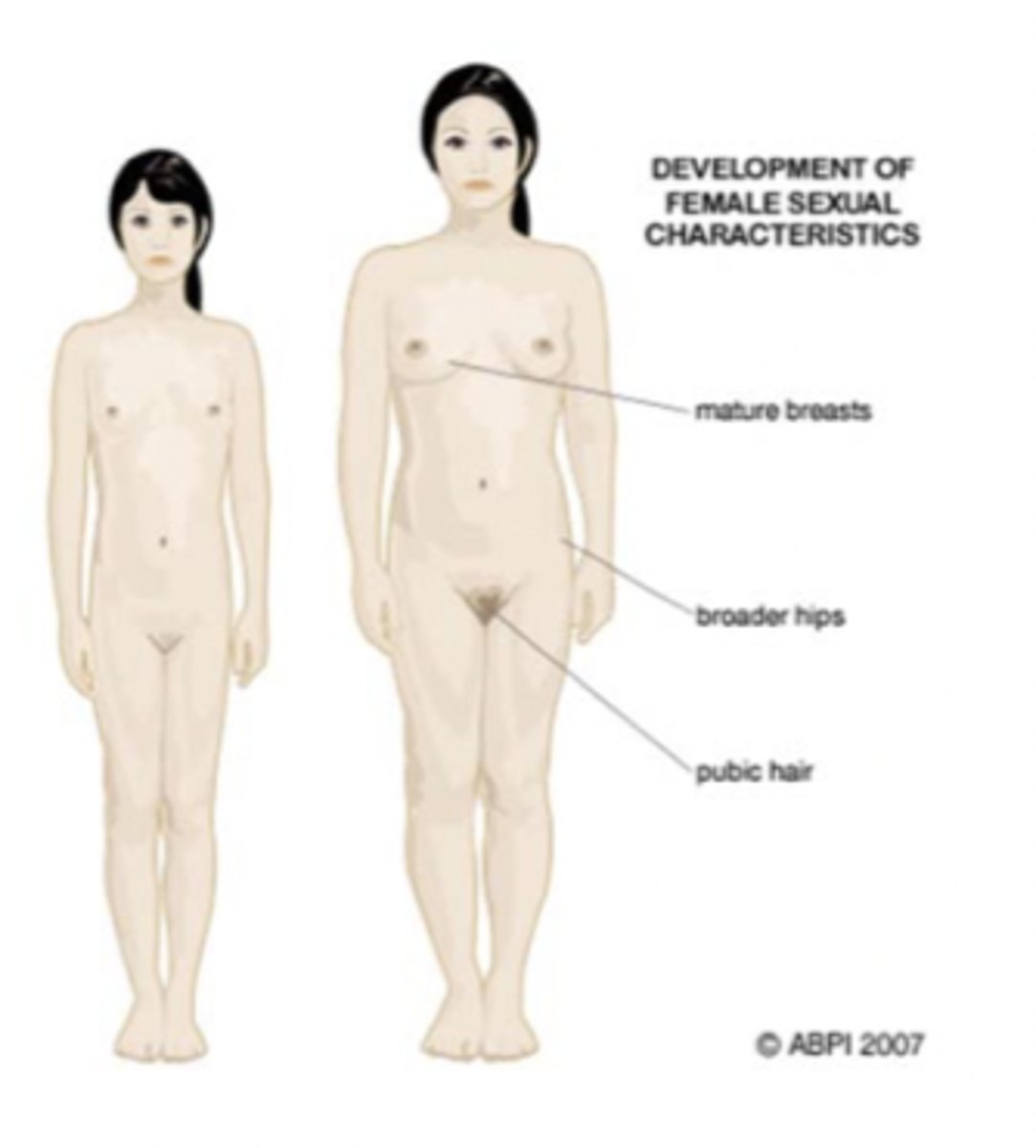
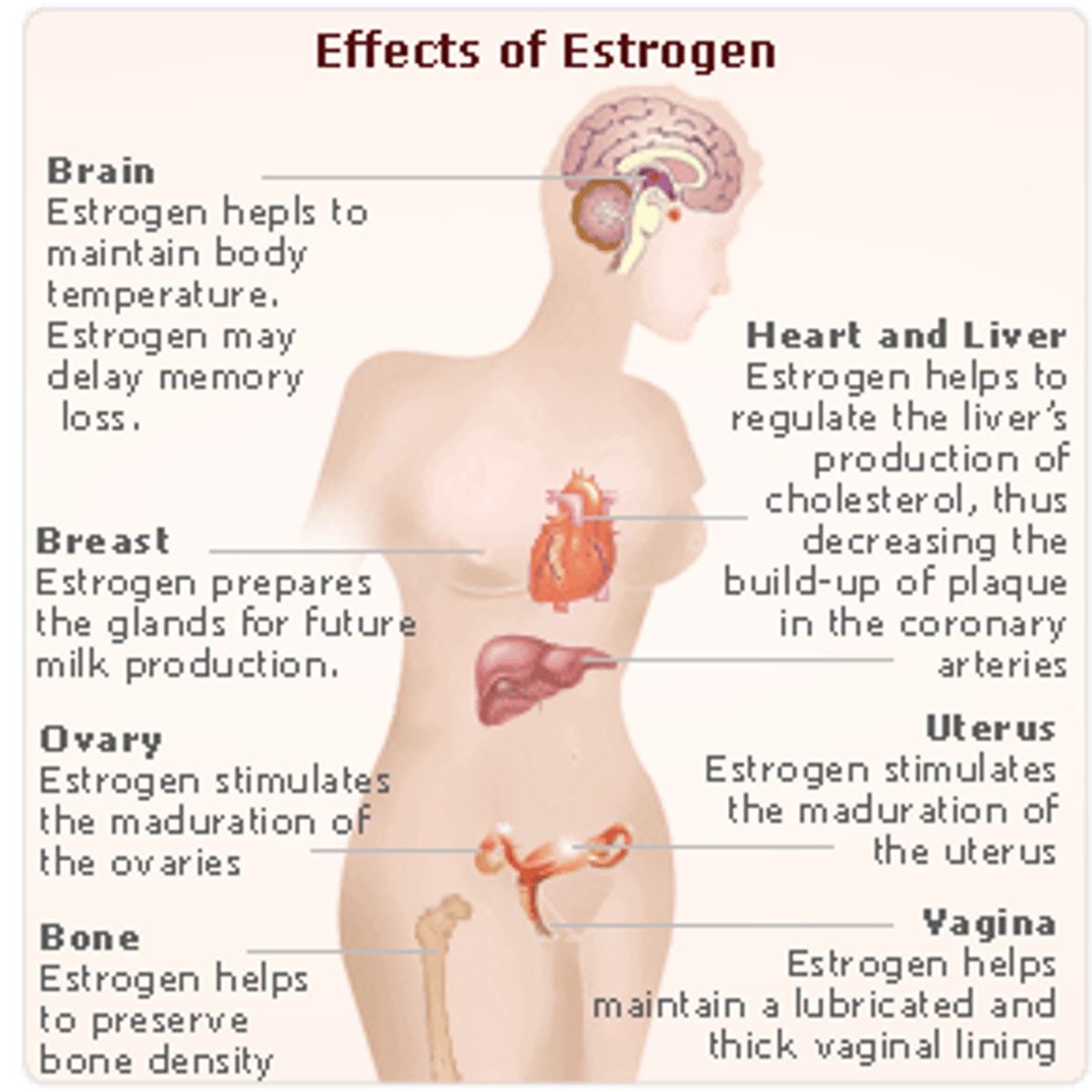
What are the effects of estradiol during puberty?
Stimulates vaginal metaplasia, growth of ovaries and sex organs, GH secretion, fat deposition, and skin thickening.
What does progesterone primarily act on?
The uterus, preparing it for pregnancy in the second half of the menstrual cycle.
How do estrogen and progesterone regulate FSH and LH?
They suppress FSH and LH through negative feedback.
What hormone selectively suppresses FSH secretion?
Inhibin.
What is unique about hormone secretion in the female cycle?
It is cyclic and follows a sequence.
What are the two major phases of the sexual cycle?
Follicular phase and luteal phase.
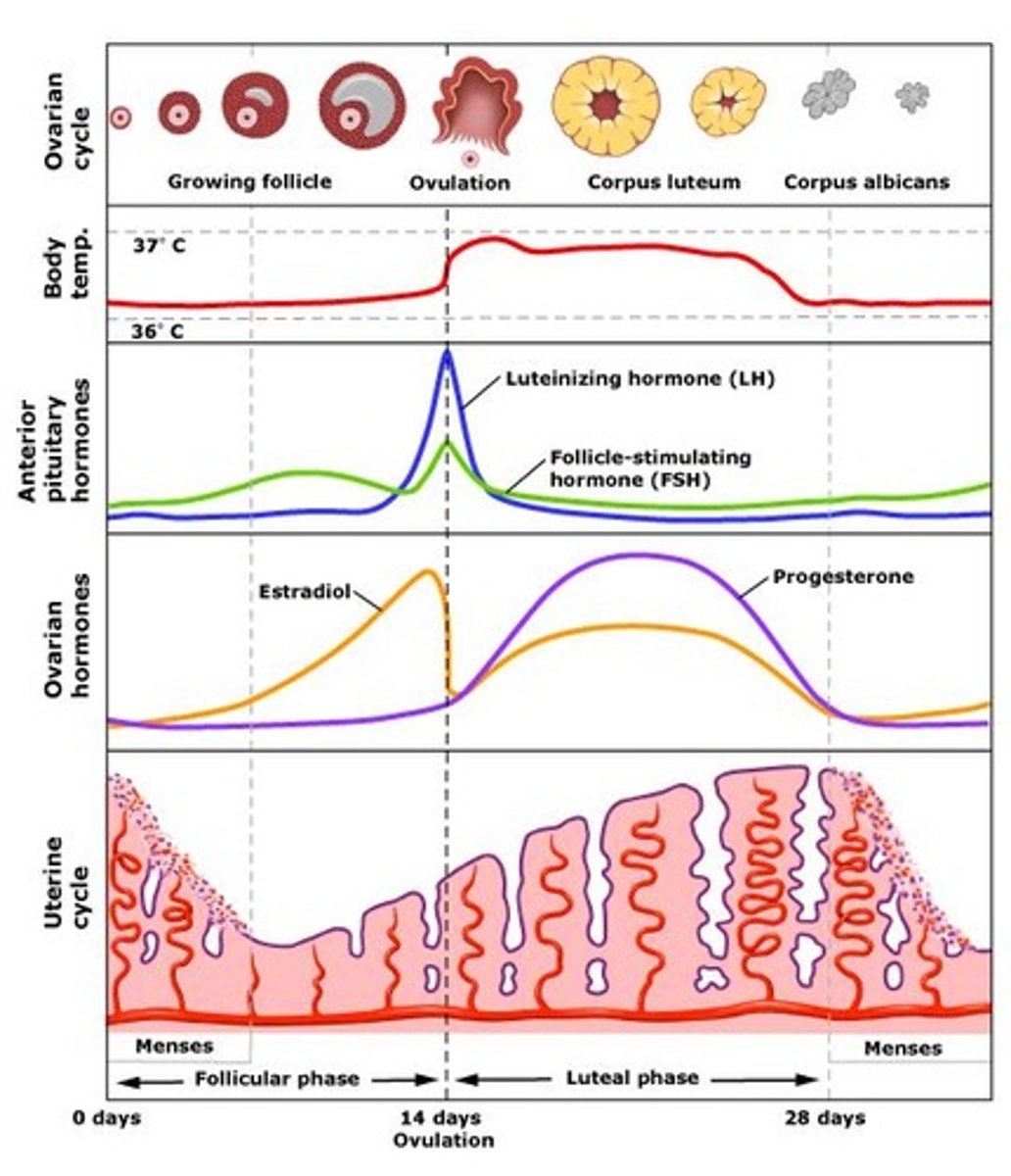
When does ovulation typically occur?
Around day 14 of the cycle.
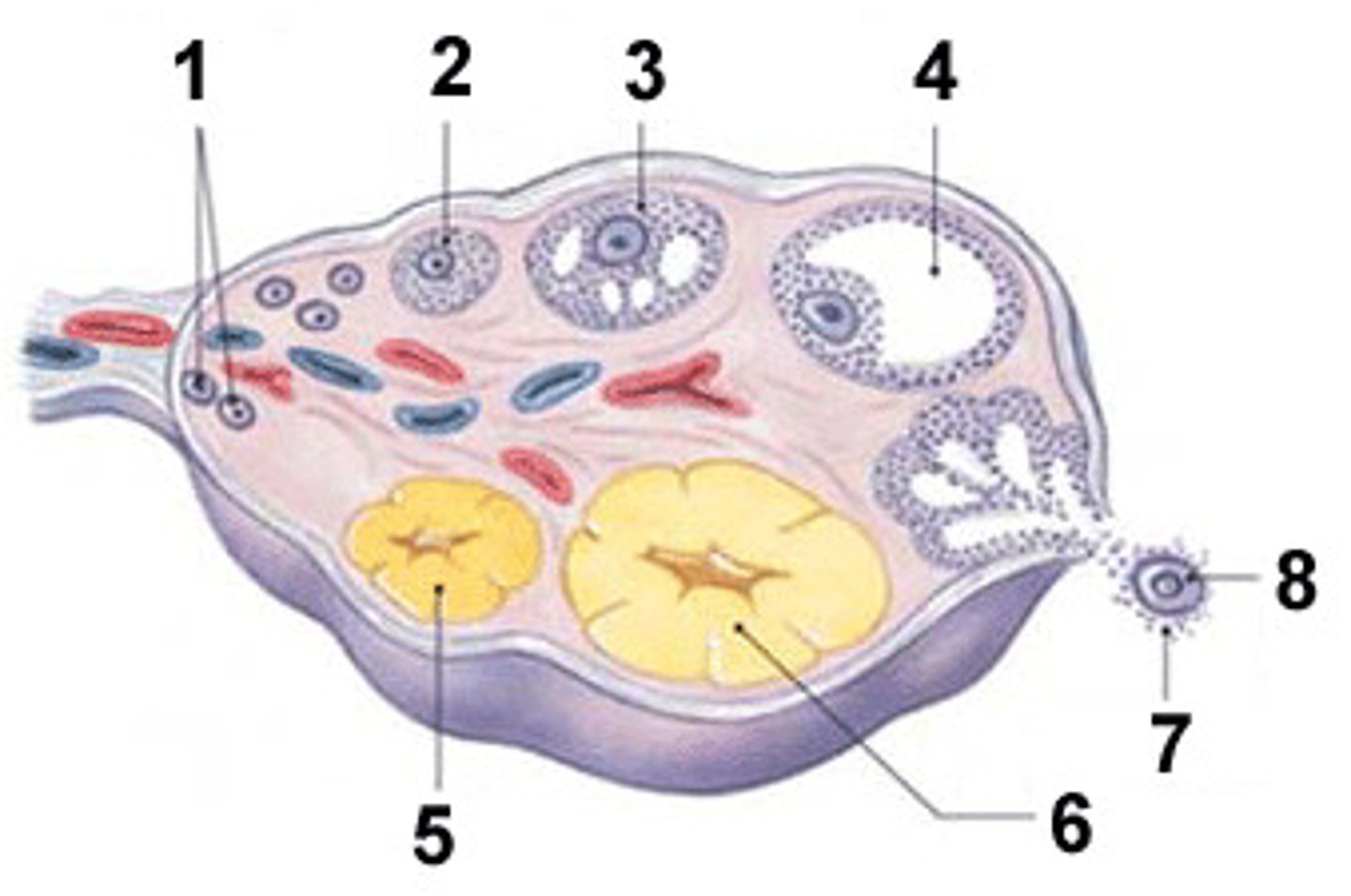
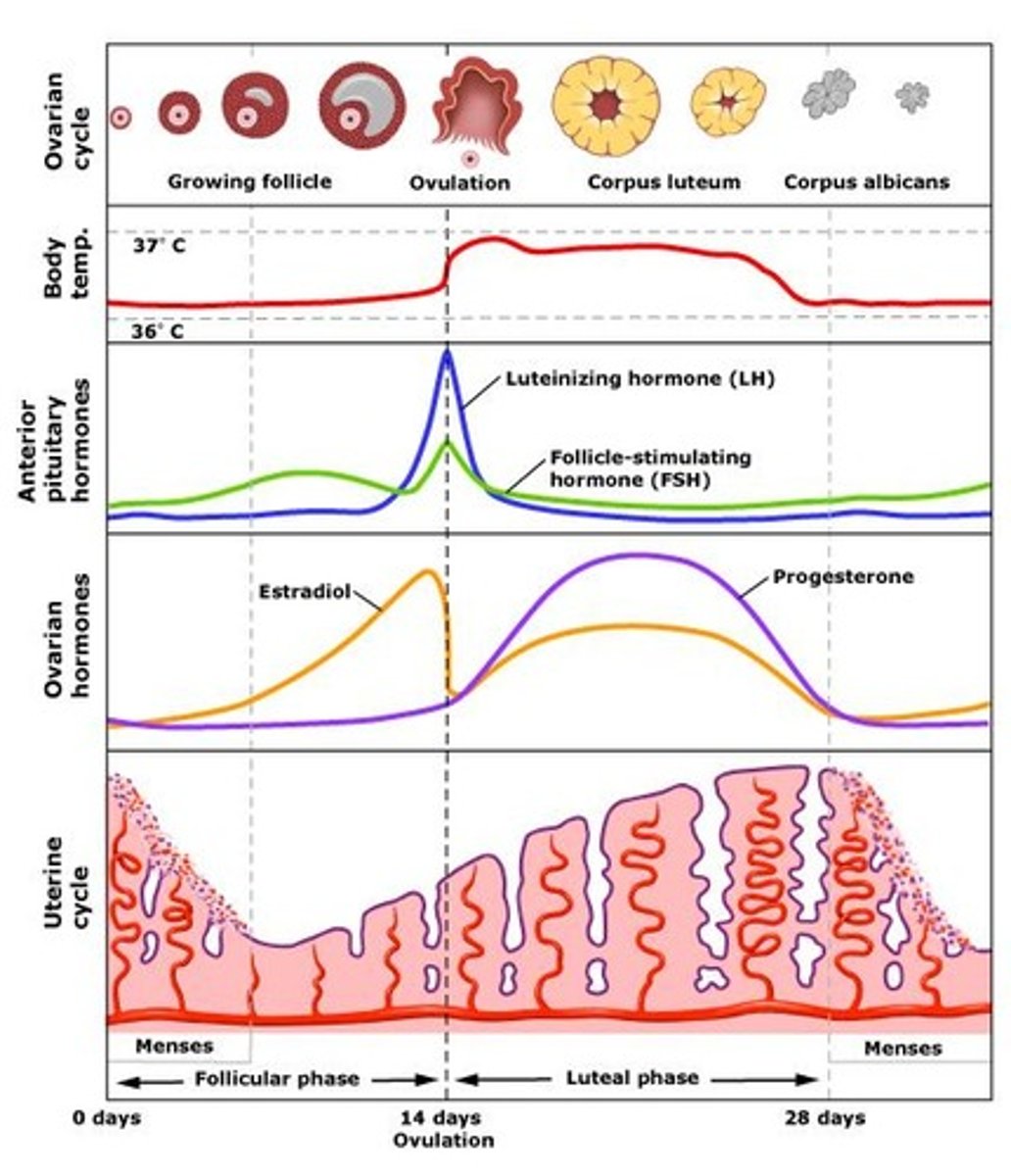
What happens during the follicular phase?
Menstruation occurs and follicles grow.
What is the role of FSH in the follicular phase?
Stimulates follicle growth and estradiol secretion.
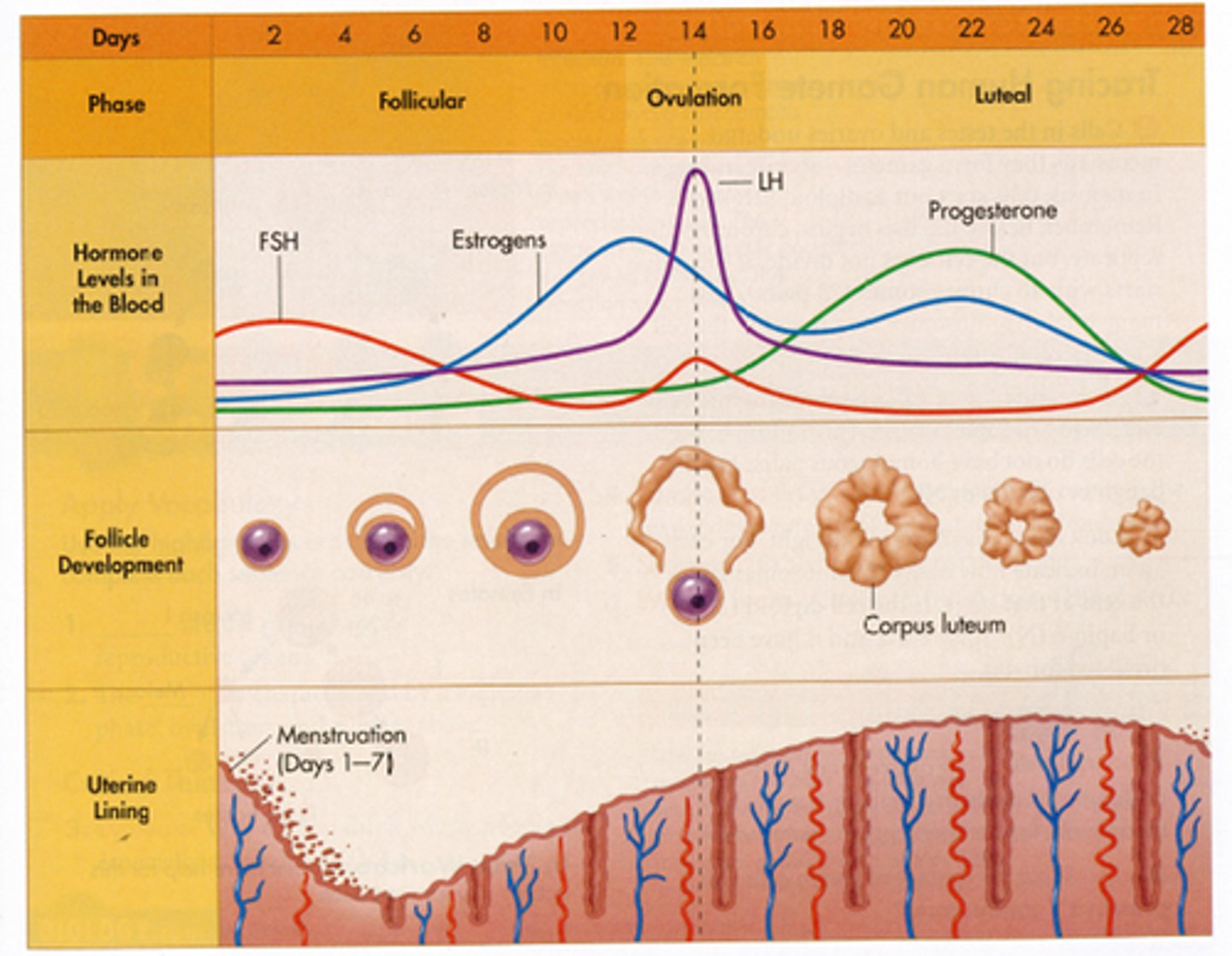
How is the dominant follicle selected?
It becomes increasingly sensitive to FSH, LH, and estradiol.
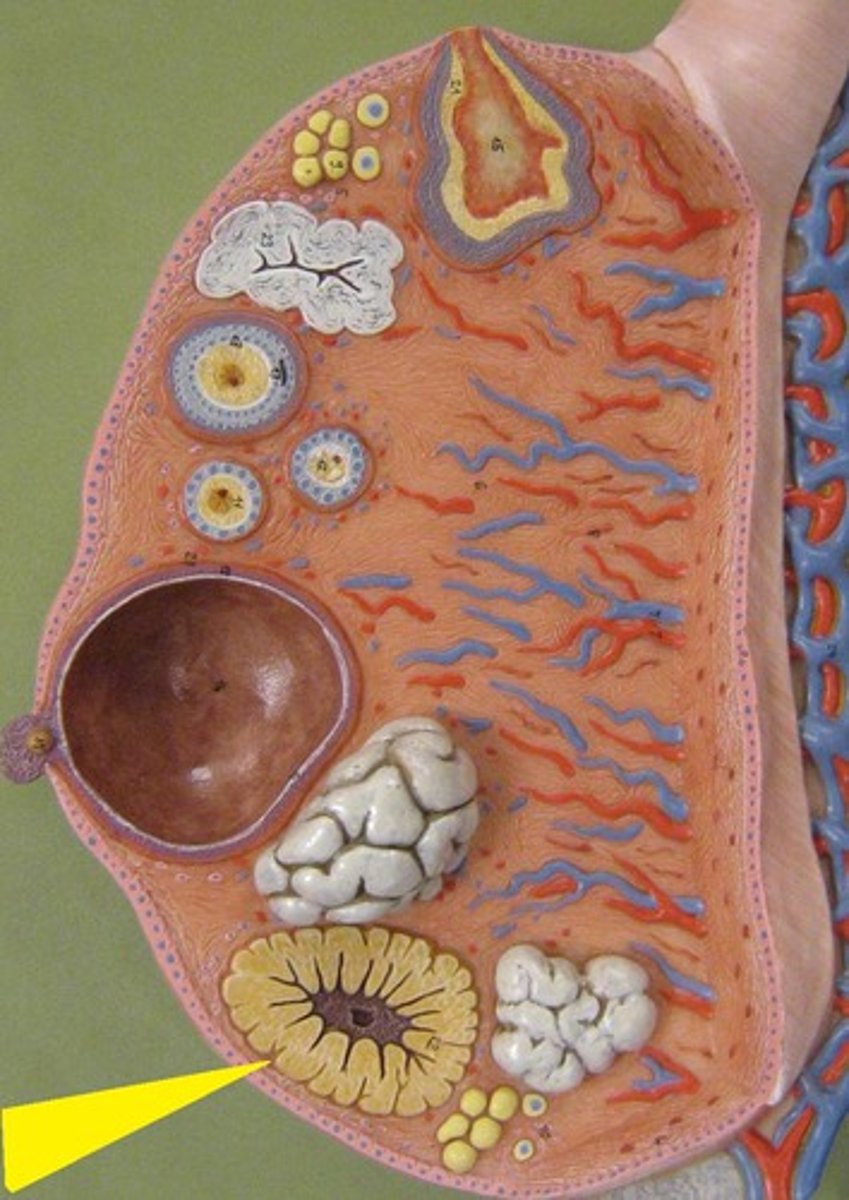
What is atresia?
Degeneration of non-dominant follicles.
What hormone surge causes ovulation?
LH surge (with a smaller FSH spike).
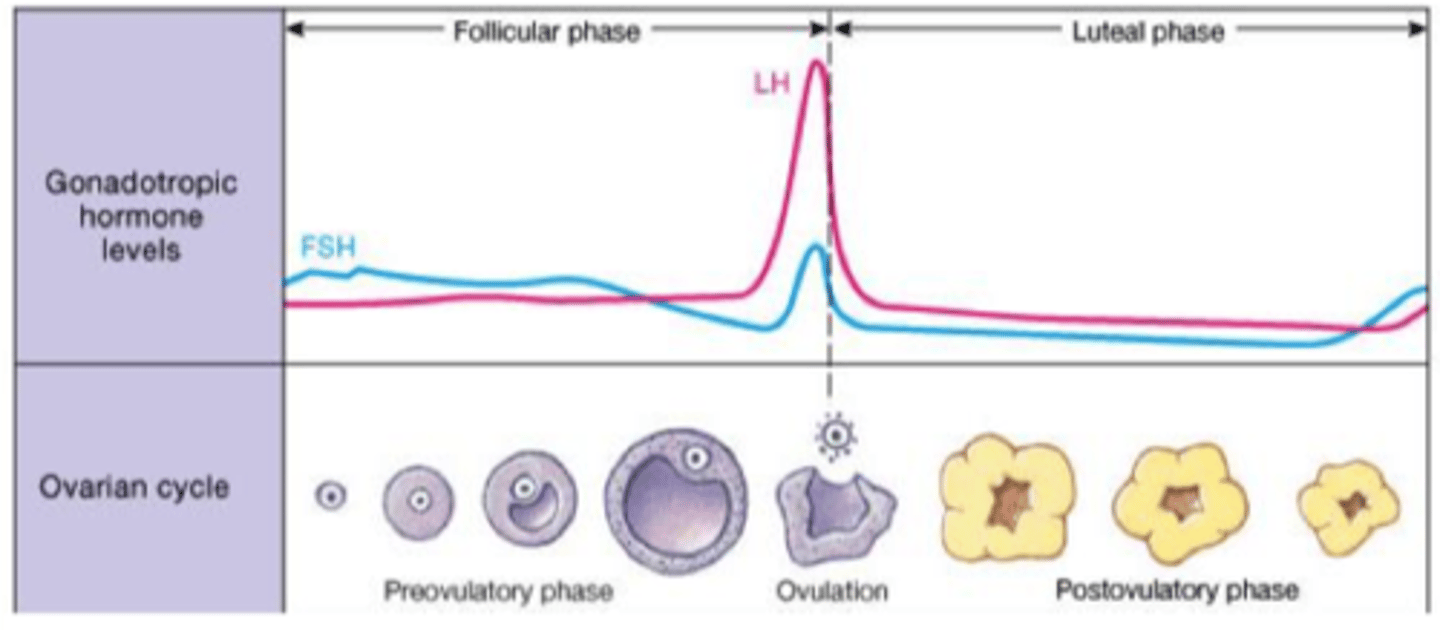
What is the role of LH in ovulation?
Stimulates oocyte to complete meiosis I and weakens the follicle wall for rupture.
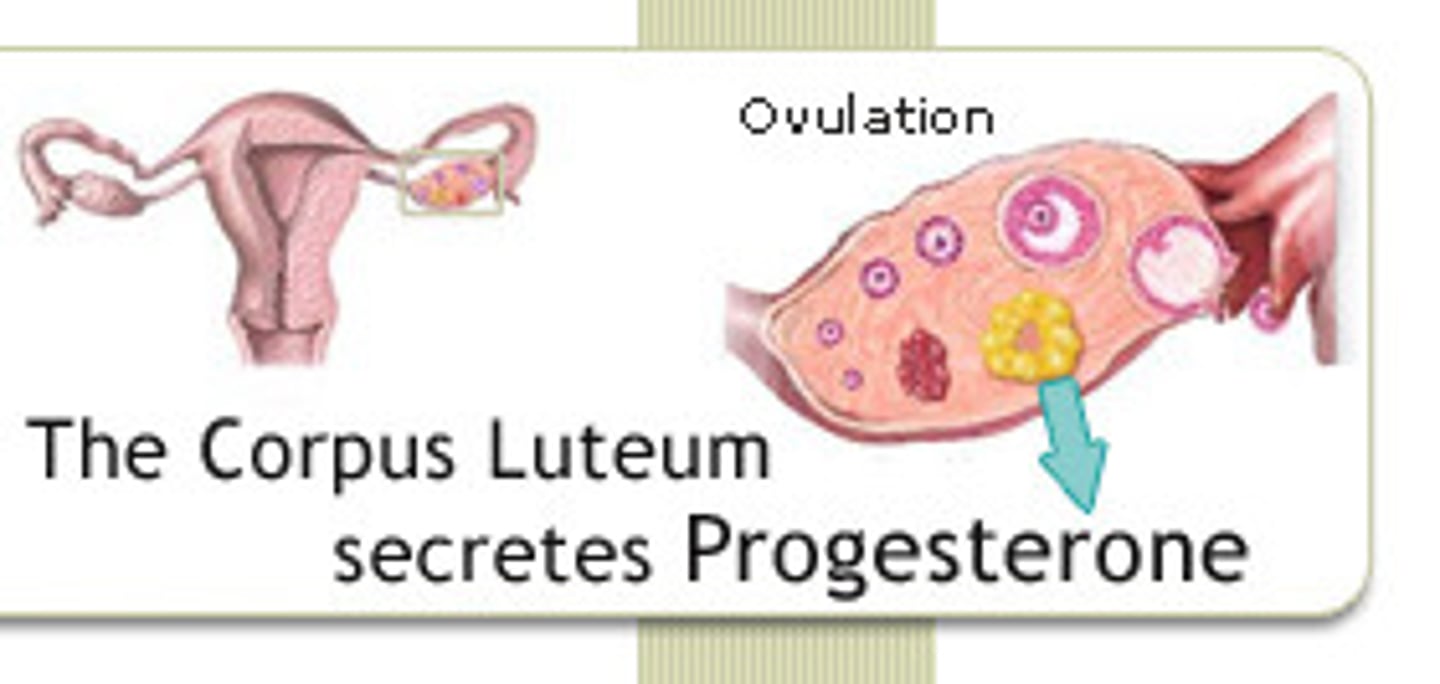
What is the corpus luteum?
Remnant of the follicle that secretes hormones during the luteal phase.
What happens if pregnancy does not occur in the luteal phase?
Endometrium breaks down and menstruation begins.
What marks the first day of the menstrual cycle?
Noticeable vaginal discharge.
What happens during the proliferative phase?
Functional layer of endometrium rebuilds under estrogen influence.
What happens to the endometrium by day 14?
It thickens to 2-3 mm.
What hormone prepares the endometrium to respond to progesterone?
Estrogen.
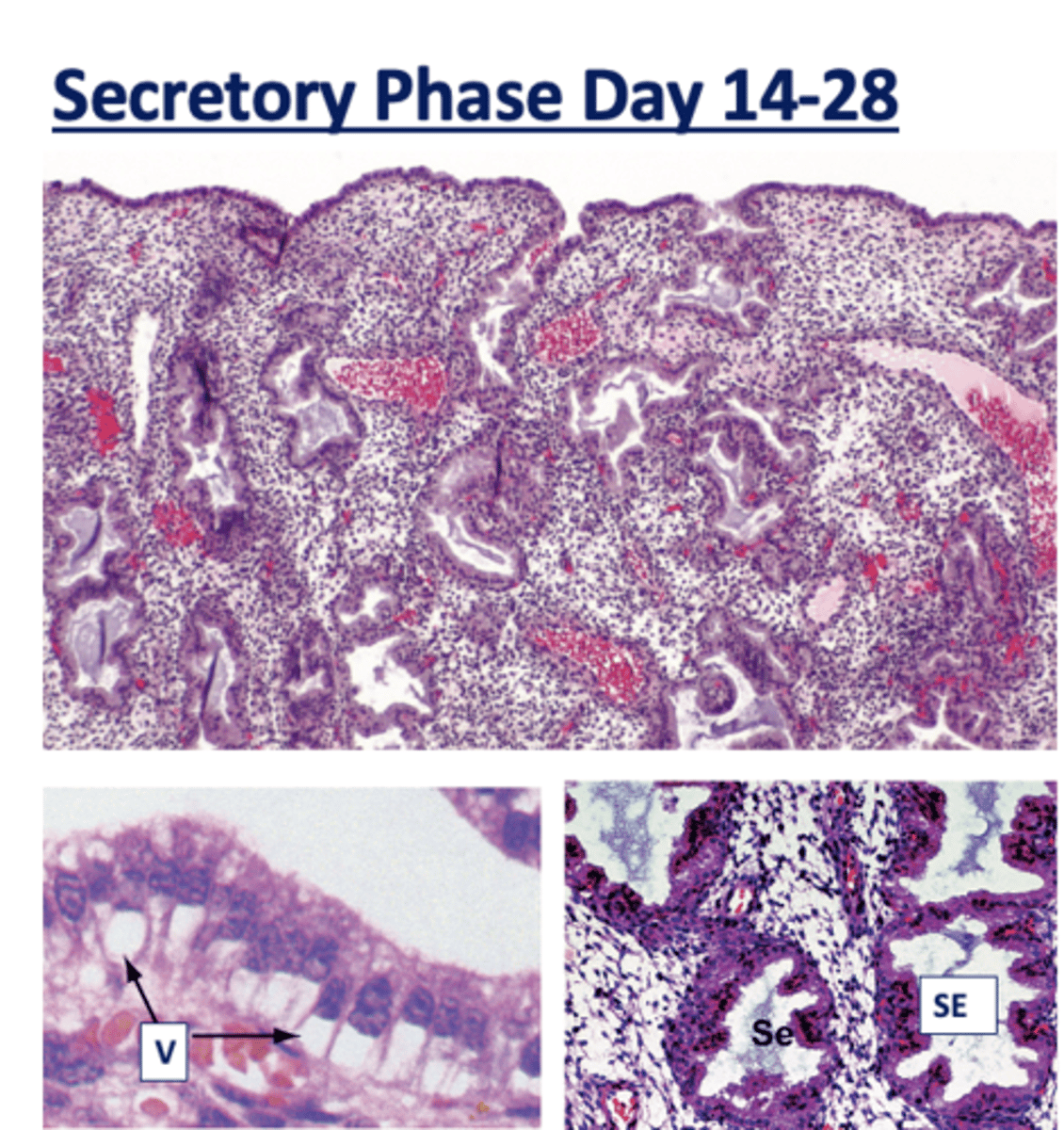
What is the secretory phase?
Endometrium thickens further due to progesterone from the corpus luteum.
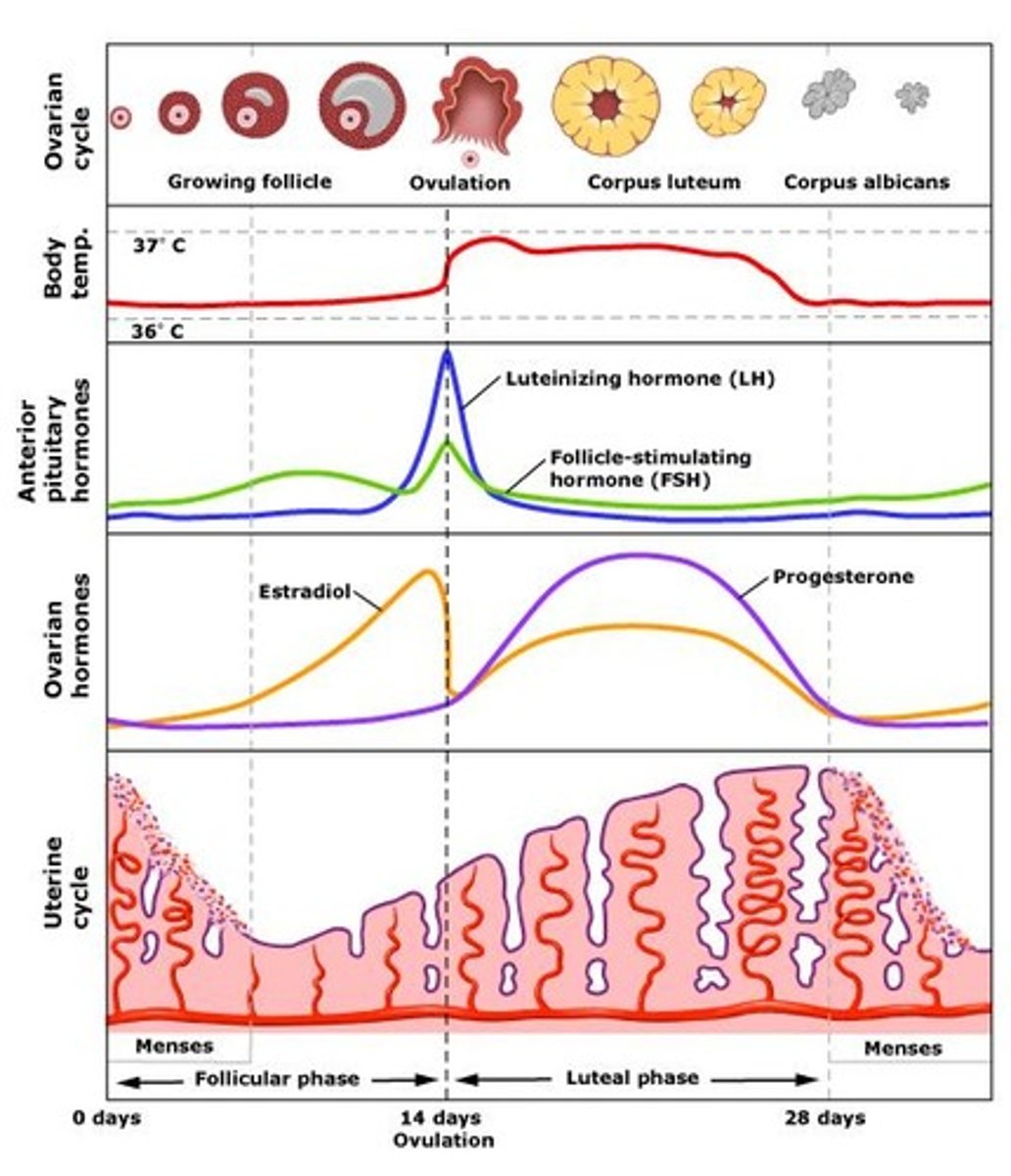
progesterone function
stimulates development and maintenance of endometrium that prepares it for implantation.
What occurs in the premenstrual phase?
Endometrial degeneration and ischemia.
What is the menstrual phase?
Shedding of the endometrial lining.
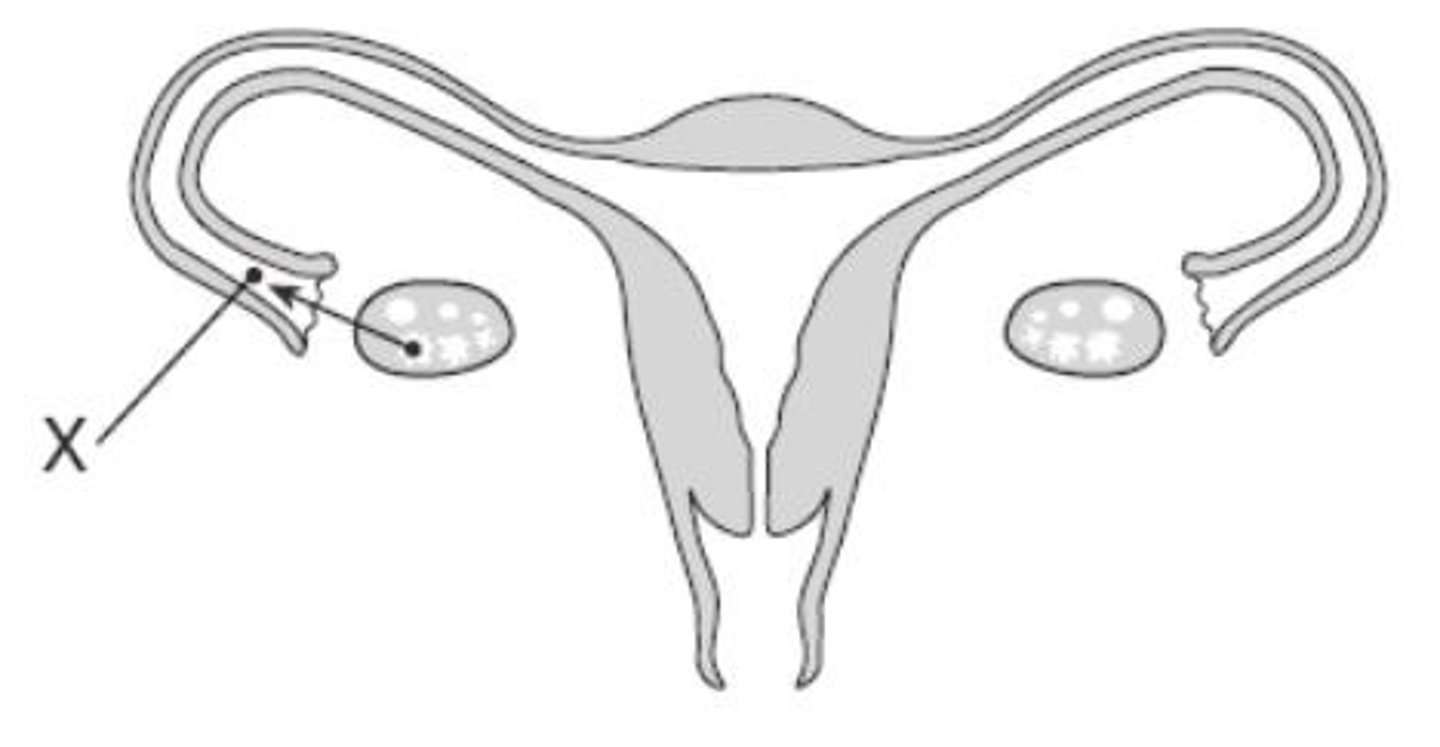
what is ovulation
The rupture of a mature follicle and release of an egg from the ovary
How long is gestation from conception to childbirth?
About 266 days.

How is gestational age typically calculated?
From the first day of the last menstrual period (LMP).
What is the term for all products of conception?
Conceptus.
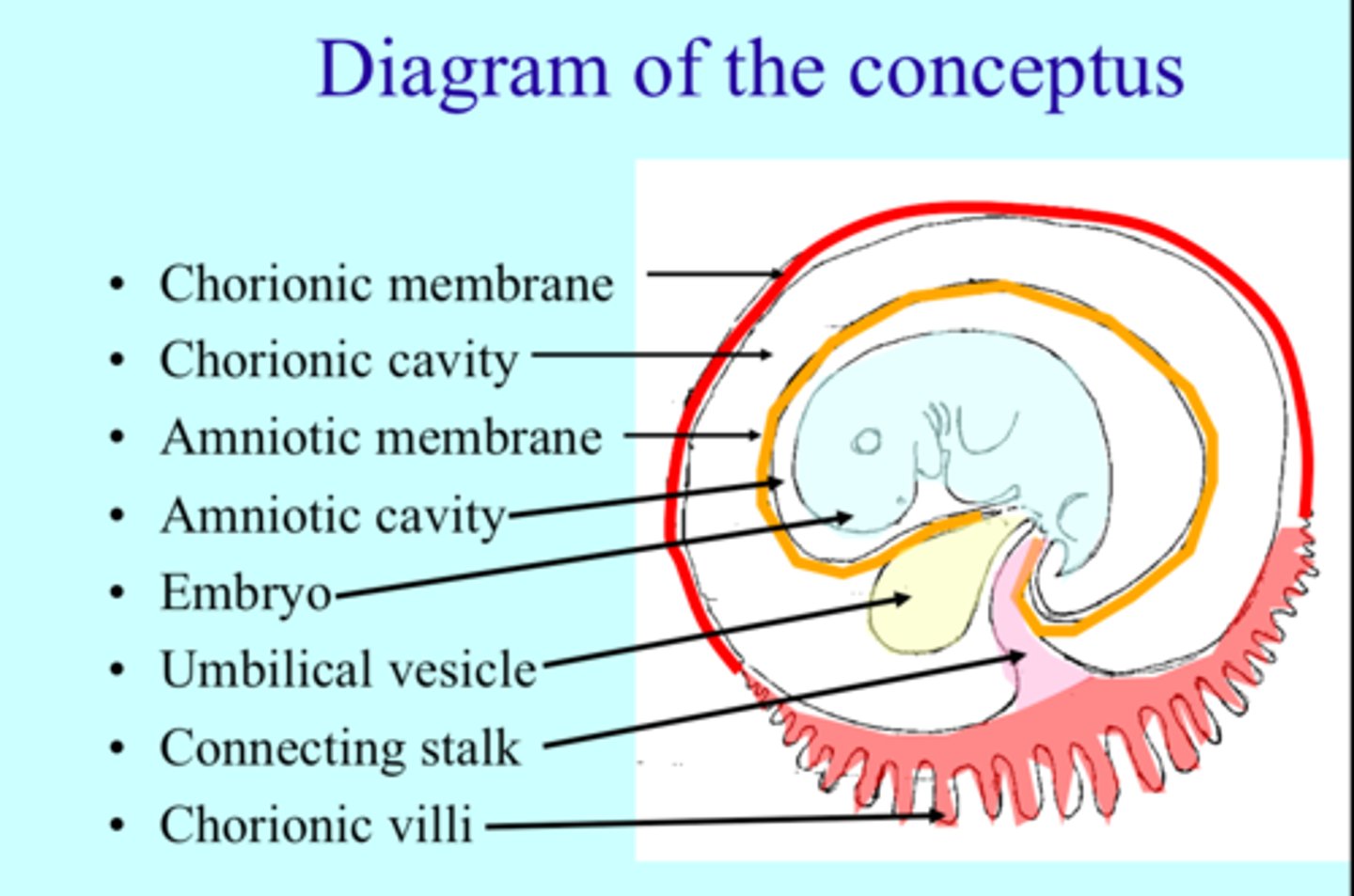
What is the developing individual called in the first 2 weeks?
Blastocyst.
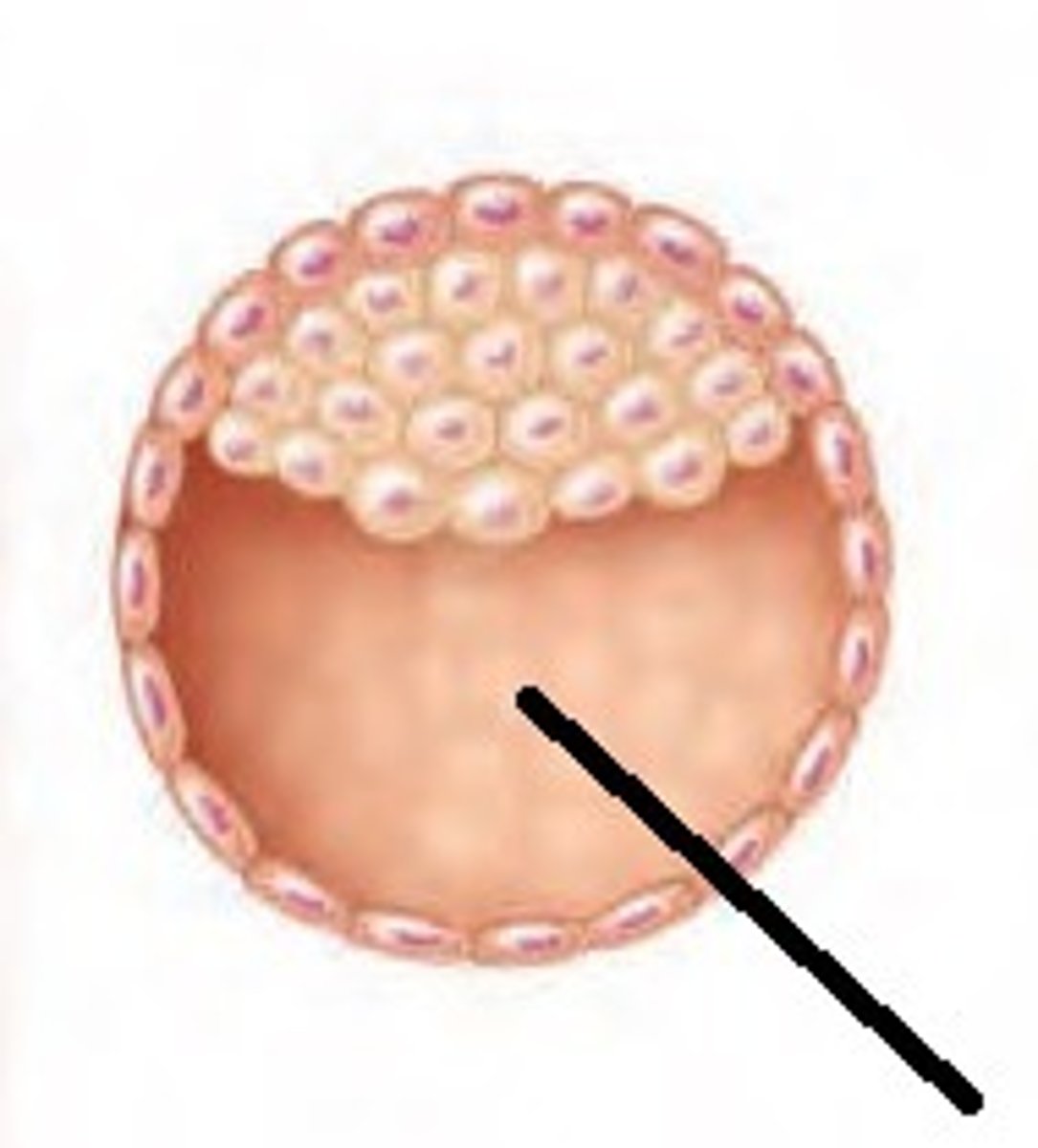
When is it called an embryo?
From day 16 through week 8.
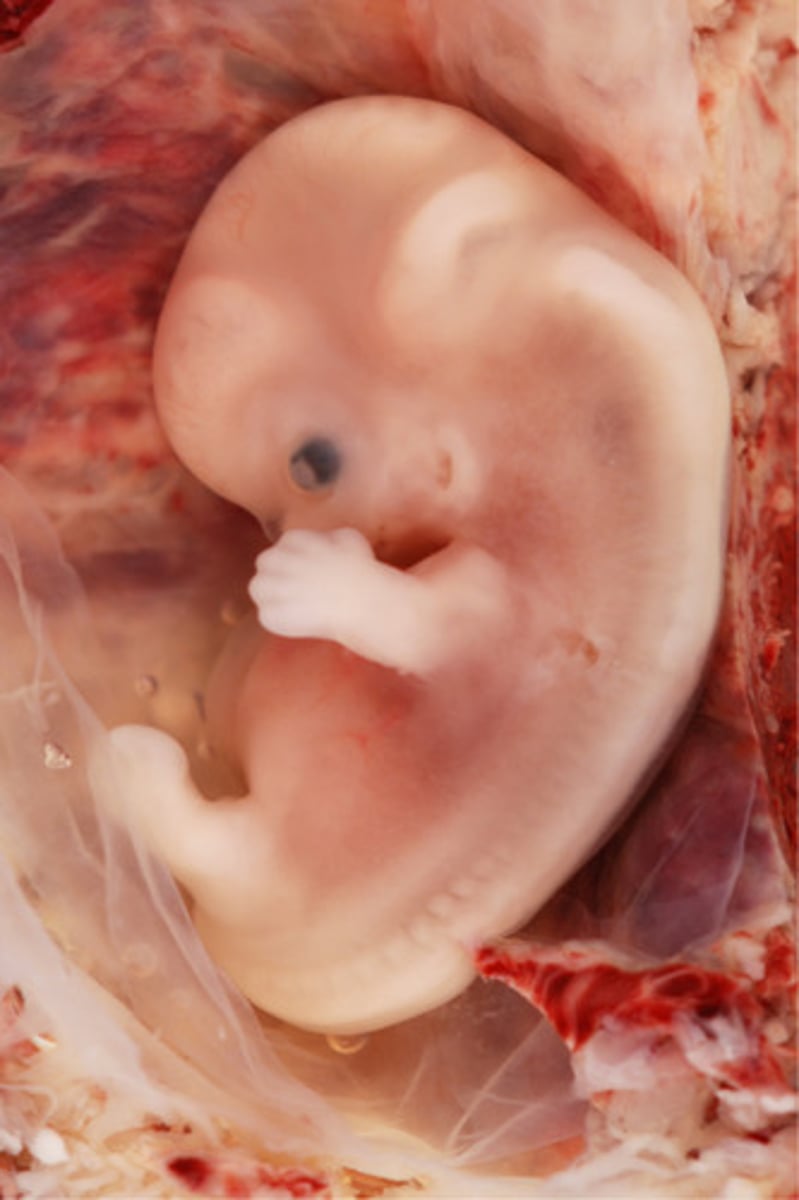
When is it called a fetus?
From week 9 until birth.
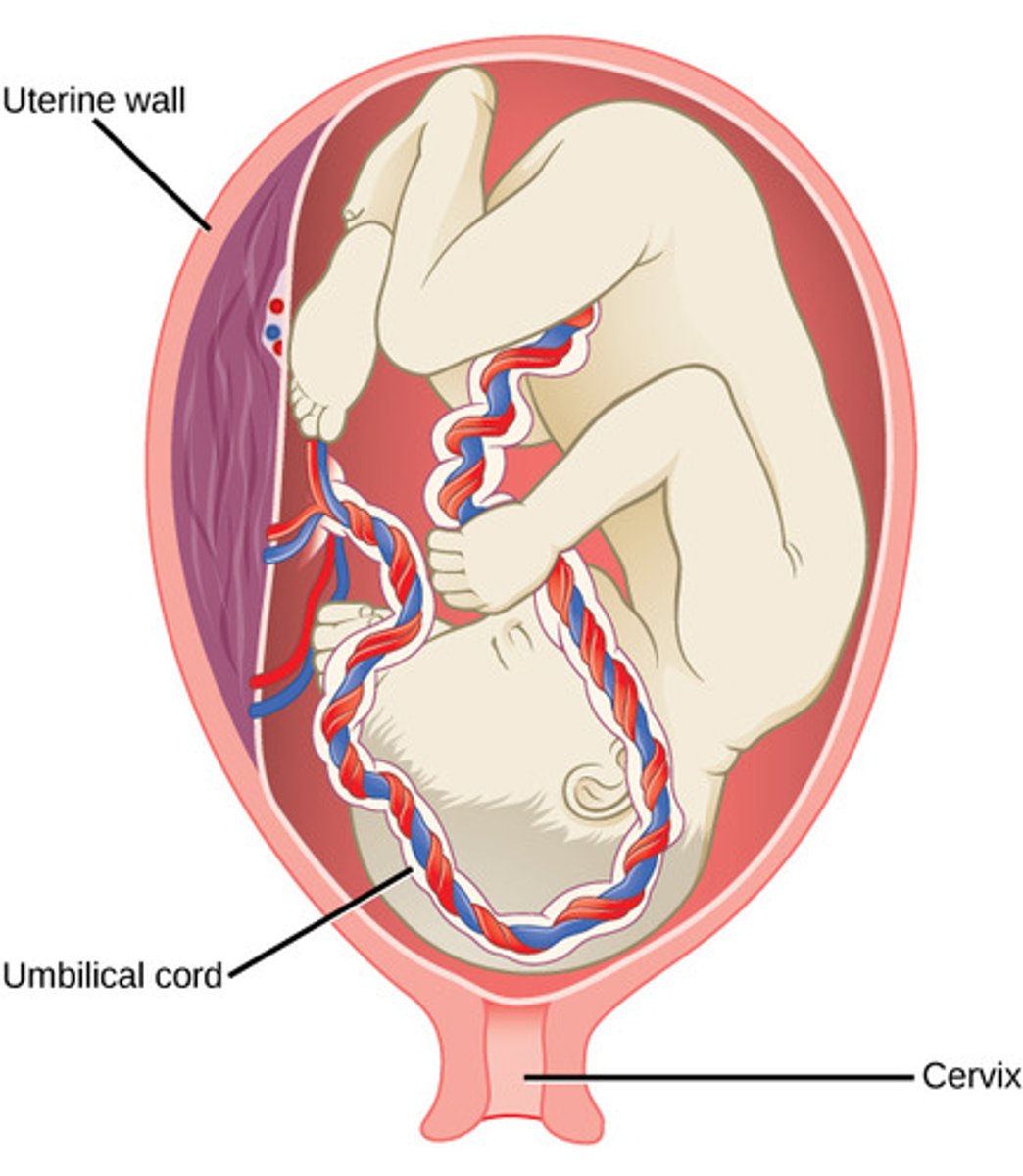
What is the function of the placenta?
Nutrition, waste removal, and hormone secretion for pregnancy.
What is the neonate period?
Newborn to 6 weeks after birth.

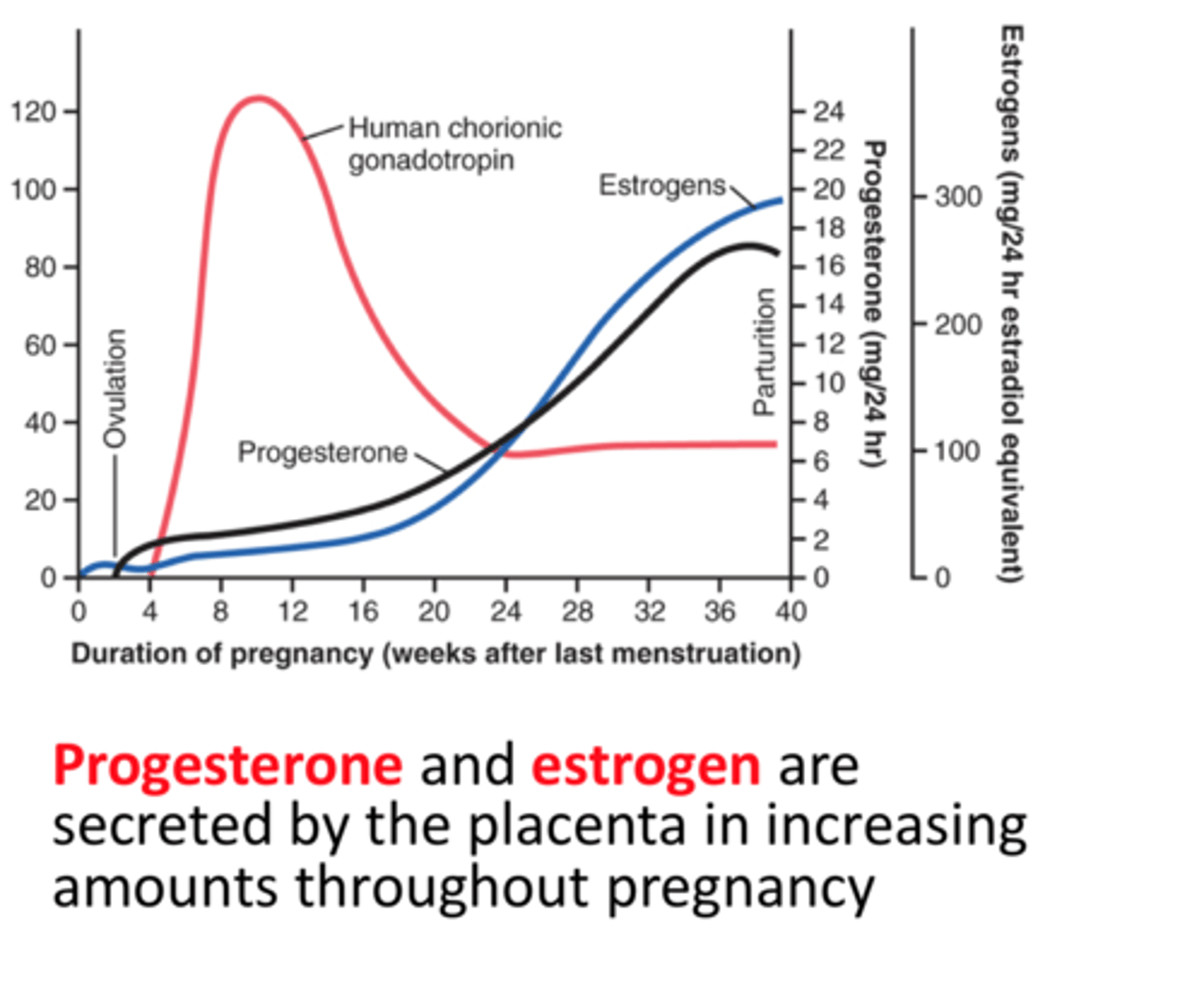
What hormones have the strongest influence during pregnancy?
Estrogens, progesterone, HCG, and HCS.

HCG
human chorionic gonadotropin
HCS
human chorionic somatomammotropin
What secretes human chorionic somatomammotropin?
Blastocyst and placenta.
What does HCG do?
Stimulates growth of corpus luteum which secretes increasing amounts of progesterone and estrogen
What secretes estrogen early and later in pregnancy?
Corpus luteum early, placenta later.
What are effects of estrogen during pregnancy?
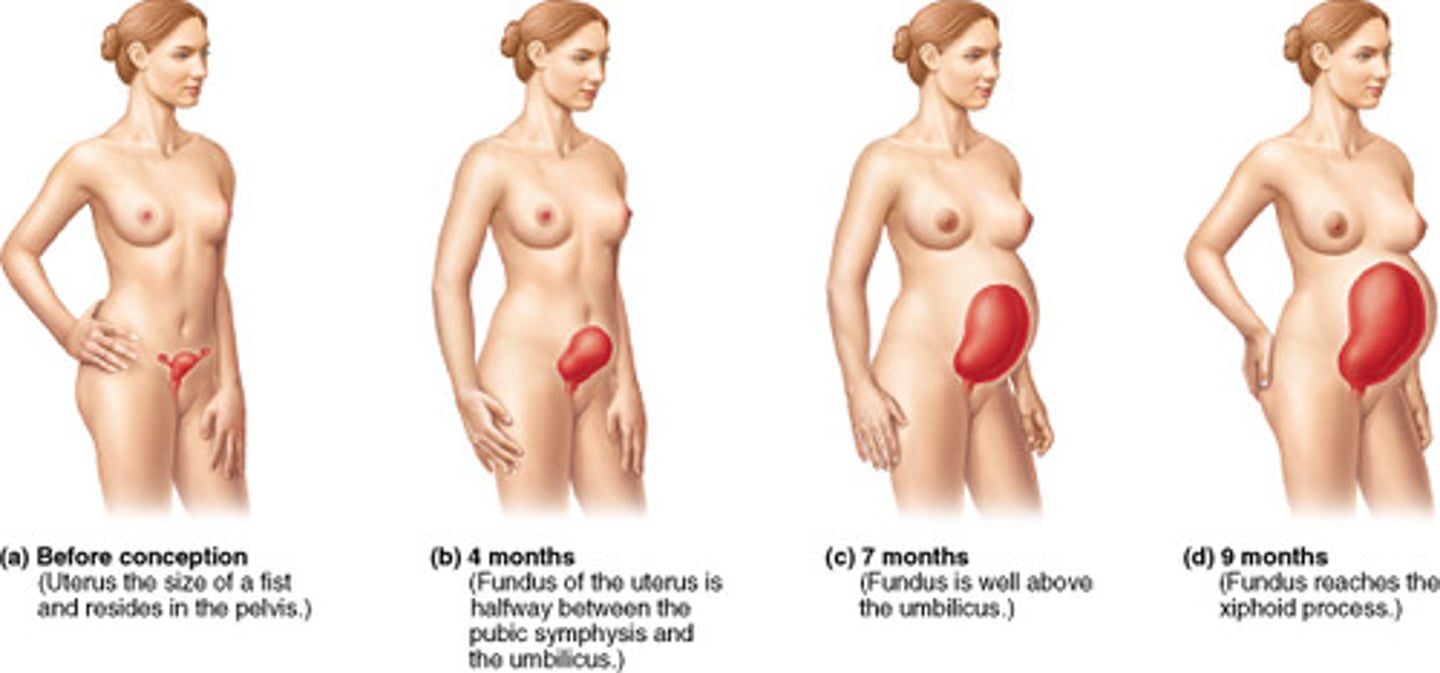
Growth of uterus, breasts, external genitalia, and pelvic relaxation.
What does progesterone do during pregnancy?
prevents ovulation, suppresses uterine contractions, and supports endometrium, premature childbirth and menstruation, devlops acini in breasts
What does HCS do during pregnancy?
Reduces maternal insulin sensitivity and glucose usage.
What change occurs in the pituitary during pregnancy?
Grows 50% larger and increased thyrotropin, prolactin, and ACTH output
What does relaxin do?
secreted by the placenta and corpus luteum promotes decidual cell growth and uterine blood vessels.
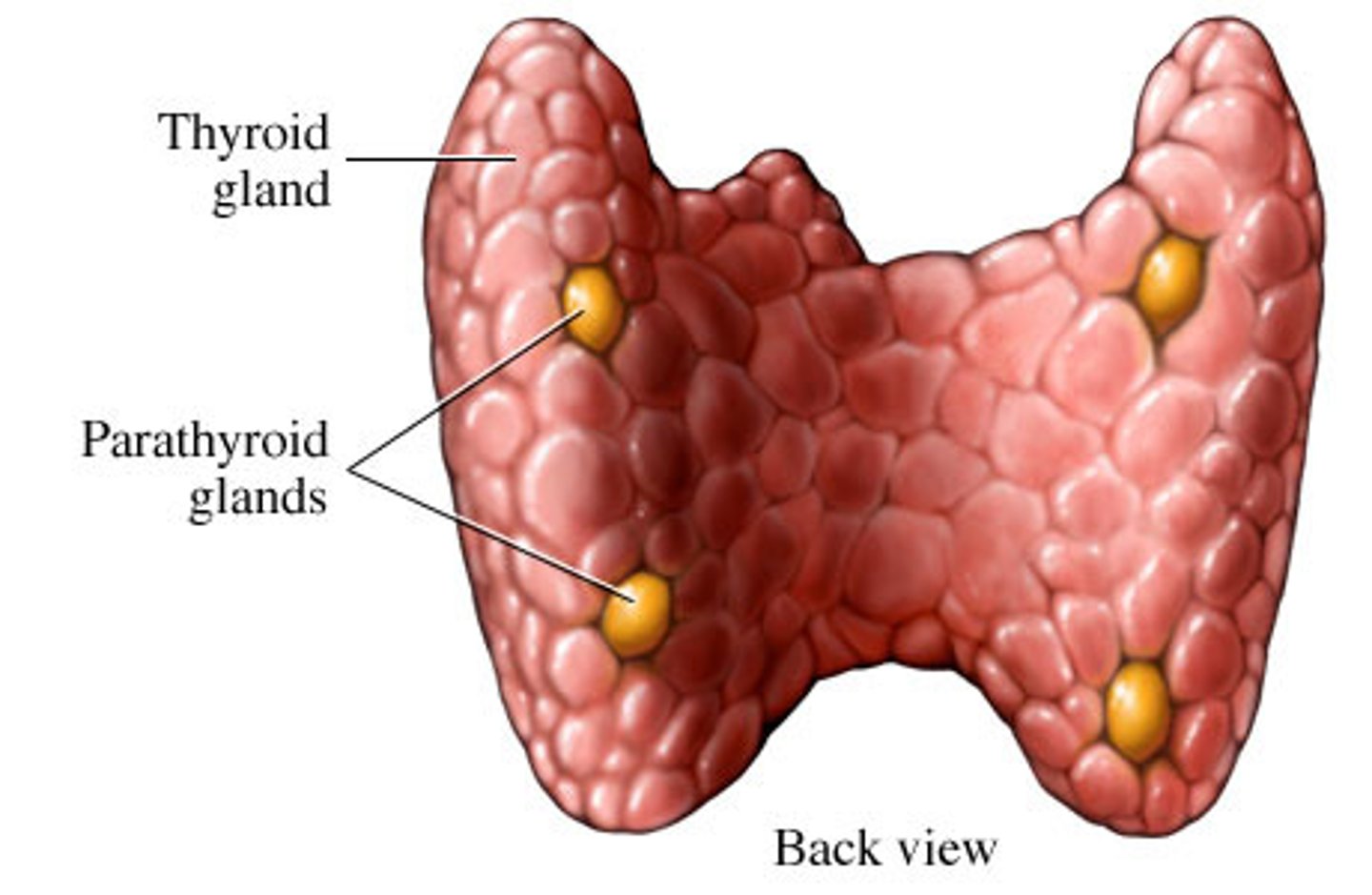
PTH in pregnancy
enlarge and increase osteoclast activity
What causes heartburn and constipation in pregnancy?
Reduced intestinal motility and gastric reflux.
How much does BMR increase during pregnancy?
About 15%.
Why is iron important in late pregnancy?
To prevent maternal anemia.
vitamins of pregnancy
vitamin K, D, and folic acid
vitamin k in pregnancy
minimizes neonatal hemorrhage

folic acid importance in pregnancy
reduces risk of fetal neural disorders like spina bifida, and anencephaly
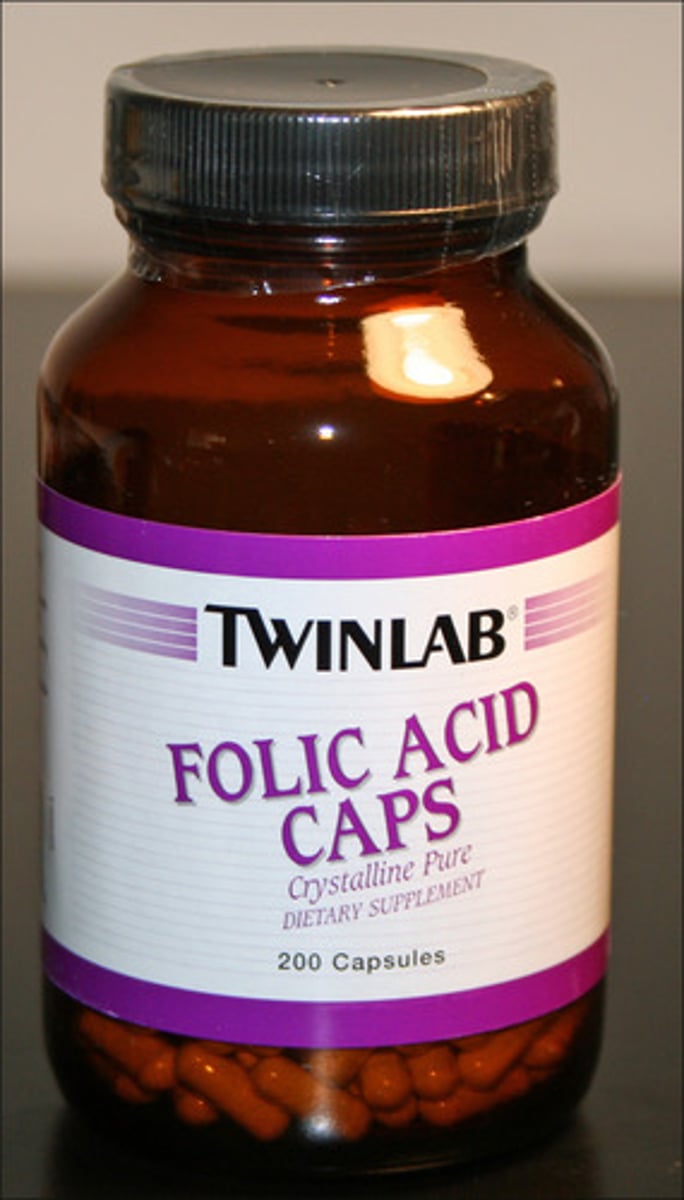
Folic acid.
How does blood volume change during pregnancy?
What causes varicose veins or edema in pregnancy?
Uterus pressure on pelvic veins.
By full term, how much blood does the placenta require?
625mL per min from mom
What initiates true labor?
Powerful uterine contractions.
What does oxytocin do during labor?
Stimulates uterine contractions and prostaglandin release.
How does the fetus contribute to initiating labor?
Produces cortisol and oxytocin, stimulating the placenta and uterus.
What is Braxton Hicks contraction?
Weak false labor contractions.
What happens to progesterone and estradiol near term?
Progesterone declines, estradiol rises.
Parturition
process of giving birth

Cervical stretch → oxytocin → contractions → more stretch.
What is the Valsalva maneuver during labor?
What causes early labor pain?
Ischemia of the uterine muscles.
What causes later labor pain?
Stretching and tearing of cervix and vagina.
Stages of Labor
dilation, expulsion, placental
What happens in the dilation stage?
Cervix dilates to 10 cm, membranes rupture, and loss of amniotic fluid
What is the expulsion stage?
Baby is pushed out through the vagina.
What happens in the placental stage?
Placenta detaches and is expelled.
Puerperium
First 6 weeks after birth for recovery.
What is uterine involution?
Shrinkage of uterus after birth.
What promotes uterine involution?
Breastfeeding via oxytocin release.
What is colostrum
first milk produced, contains 1/3 less fat, contains IgA, and a cloudy yellow think wattery fluid
What hormone stimulates milk synthesis?
prolactin
What happens to prolactin during nursing?
Spikes for an hour after nursing.
What other hormones support milk production?
GH, cortisol, insulin, and parathyroid hormone.
How long can lactation last?
As long as nursing continues.
How does breastfeeding suppress fertility?
Inhibits GnRH and reduces ovarian cycling.
What are behavioral methods of contraception?
Abstinence, rhythm method, and withdrawal.
barrier methods of contraception
Condoms, diaphragm, sponge, and spermicides.
What do hormonal contraceptives typically do?
Prevent ovulation by inhibiting FSH and LH.
What are the morning after pills?
emergency contraceptive pills

emergency contraceptive pill
high dose of estrogen and/or progestin that inhibit ovulation, movement of sperm and egg, and implanatation
What does RU-486 do?
Acts as a progesterone antagonist to induce abortion.
What is an IUD and how does it work?
A device that prevents implantation by irritating the uterus.