Cardiovascular system II: Major vessels
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
Pulmonary circuit (pulmonary/systemic circuits)
pulmonary trunk (from right ventricle)
pulmonary arteries-lungs
blood deoxygenated
gas exchange occurs within lungs
pulmonary veins to left atrium of heart
blood oxygenated
Arterial receptors
sensory structures in walls of major aa.
monitor bp & blood chemistry
transmit information to the brainstem
-regulates hr, bv diameters & respiration
baroreceptors in carotid & aortic sinuses
monitor bp from internal carotid aa. & aorta
transmit via glossopharyngeal & vagus nn.
baroreflex- keeps bp steady by rapidly adjusting cardiac output to match arterial bp
chemoreceptors (Arterical receptors)
Carotid bodies
monitor blood chemistry
transmit signals via glossopharyngeal nerve
adjust respiratory rate to stabilize pH, CO2 & O2
Aortic bodies (Arterical receptors)
similar to carotid bodies
interacted by vagus nerve
Major aa. include (Arteries)
aorta & its branches
arch, thoracic aorta & abdominal aorta
head/neck aa.
circle of willis
appendicular aa.
Aortic arch (Aorta & branches)
Brachiocephalic truck
right common carotid a. (right of head)
right subclavian a. (right shoulder/UL)
left common. carotid a. (left of head)
left subclavian a. (left shoulder/UL)
Are there different types of aortas?
yes 8
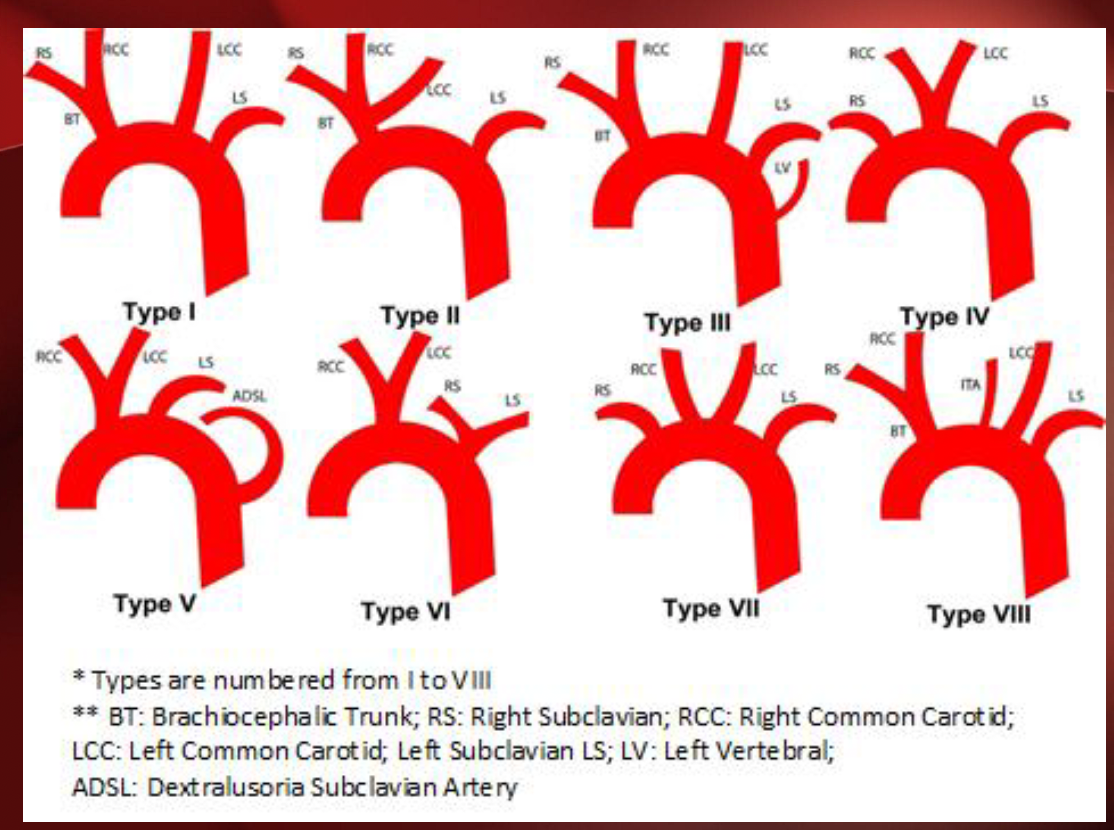
Ascending aorta (Aorta & branches)
right/left coronary aa.
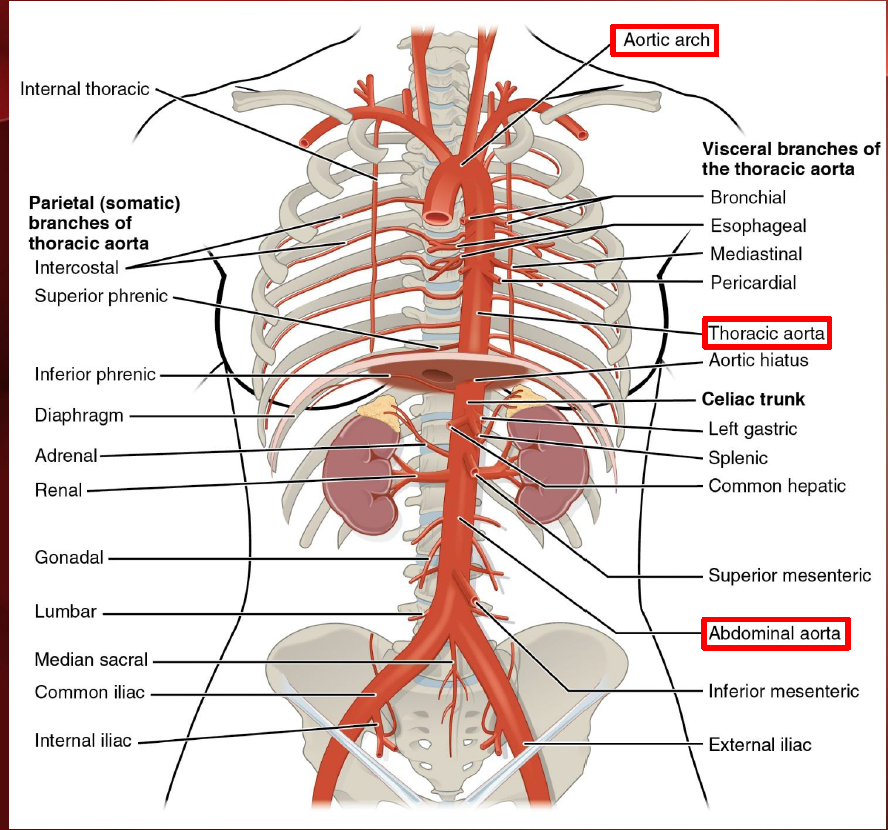
descending aorta (Aorta & branches)
thoracic aorta & abdominal aorta
arteries associated with esophagus, lungs, liver, spleen, kidneys, intestines, testes/ovaries & various muscles
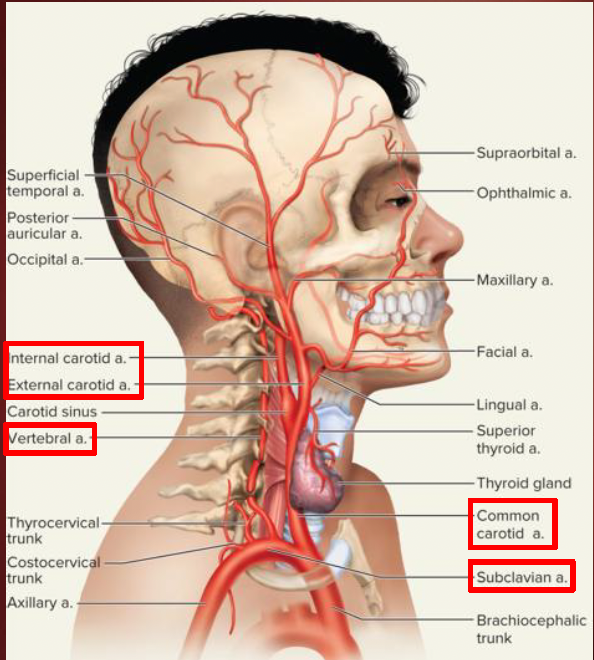
Head & Neck
Common carotids
internal carotid a.
external carotid a.
Vertebral aa.
from subclavian aa.
come together to form basilar a.
circle of willis
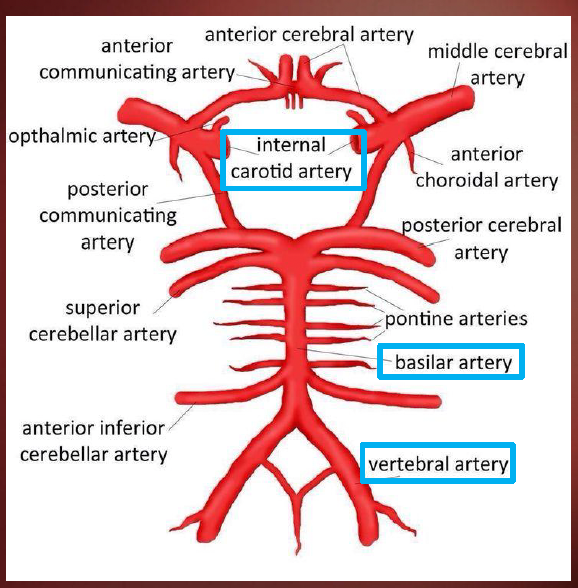
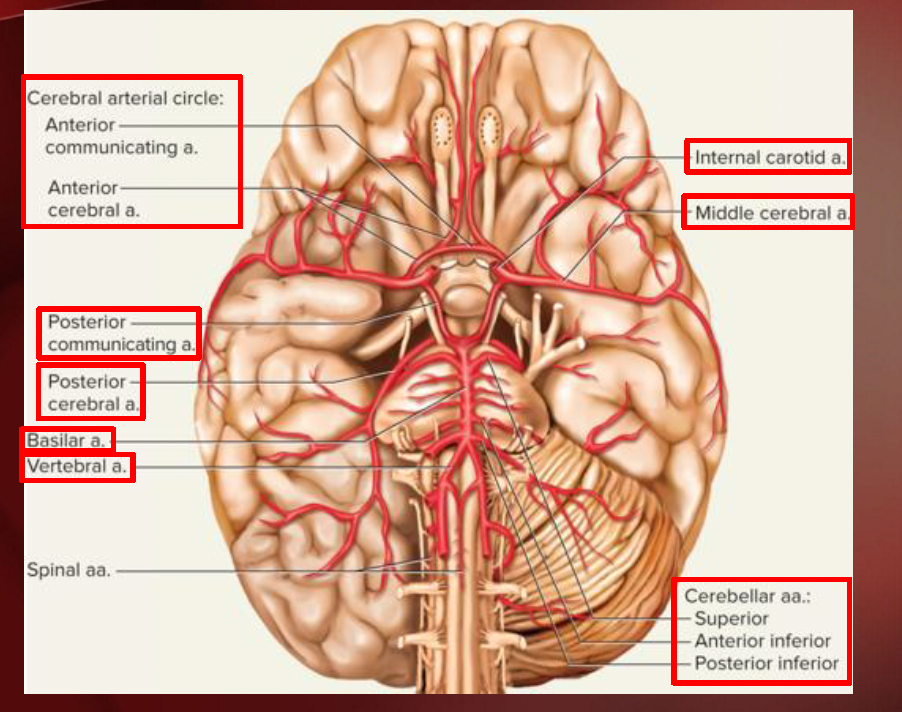
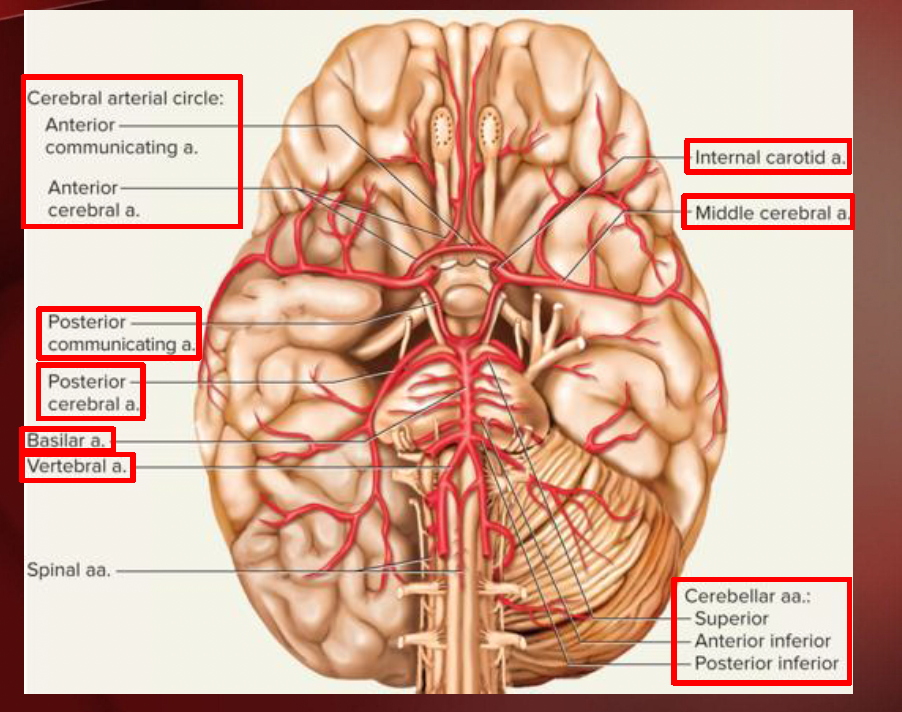
Circle of Willis (Head & Neck)
Internal Carotid aa.
Vertebral aa.
cerebellar aa.
pontine aa.
cerebral aa.
communicating aa.
parts
parts
Thorax & upper limb
subclavian aa.
axillary aa.
brachial aa.
radial aa.
deep/superfical palmar arches
ulnar aa.
interosseous aa.
deep/superficial palmar arches
abdominopelvic
Celiac trunk
common hepatic a.
splenic a.
left gastric a.
superior mesenteric a
renal aa.
gonadal aa.
ovarian/testicular aa.
inferior mesenteric a.
common iliac aa.
internal iliac a.
lower limb
common iliac aa.
internal iliac aa.
external iliac aa.
femoral aa.
deep femoral
popliteal aa.
posterior tibial aa
fibular aa.
anterior tibial aa.
dorsal pedal aa.
venous sinuses
some veins expand to form venous sinuses
thin walls, large lumens & no smooth muscle
not capable of vasomotor responses
e.g dural venous sinus & coronary sinus
superior vena cava (major veins)
jugular, vertebral & axillary vv. drain into the subclavian vv. which then drain into the brachiocephalic vv. - svc
inferior vena cava (major veins)
iliac, hepatic, renal & gonadal vv. drain here
Dural sinuses (Head & Neck)
internal jugular vv.
external jugular vv.
Dural sinuses
drain blood from brain into internal jugular vv,
also drain css via arachnoid granulations
5 unpaired sinuses: superior sagittal inferior saggital, straight, occipital & inter cavernous
Confluence of the sinuses
Dural sinuses (part 2)
5 paired sinuses: transverse, sigmoid, cavernous, superior petrosal & inferior petrosal
confluence of the sinuses
Thorax
Blood from the tissues & organs in the thorax drained by the intercostal veins % azygos vein
azygos v. formed by right lumbar v. & right subcostal v.
Azygos vein system drains to the svc
hemiazygos &accessory hemiazygos vv. drain into azygos v.
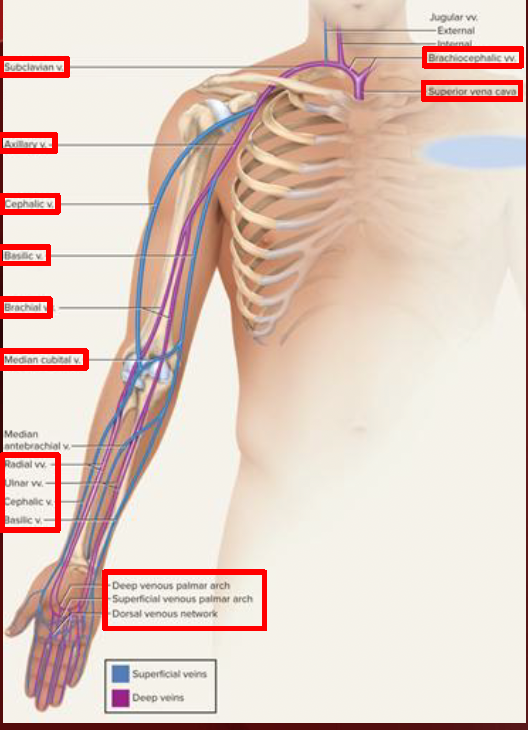
Upper limb
Deep & superficial veins
hand vv. drain into forearm
deep/superficial venous palmar arches/network
radial, ulnar, cephalic & basilic
forearm drains to arm
basilic, radial, ulnar vv. drain to the brachial vv.
cephalic, basilic & brachial vv. drain to the axillary vv.
median cubital vv.
between cephalic & basicli
arms to subclavian vv.- brachiocephalic vv- svc
Abdomen
Veins drain into the ivc
internal iliac & external iliac vv.
drain into the common iliac vv.
gonadal vv.
ovarian vv.
testicular vv.
renal vv.
hepatic vv.
phrenic vv.
lower limbs
foot drains to crural region - drains to leg
dorsal vv. superficial & drain to small saphenous vv.- great saphenous vv.
great saphenous vv. drains to femoral vv.
plantar vv. deep & drain to fibular, anterior tibial & posterior tibial vv.
popliteal vv. - femoral vv.
femoral vv. drain into the external liar vv.- ivc