CHAPTER 6 - Vision and Chemoreception
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
Light
A form of electromagnetic radiation, that can be conceptualized as a stream of tiny, massless packets of energy called photons
We see a continuum from________ to_______
400nm (purple)
700 nm (red)
Cornea
The clear, dome-shaped outer layer of the eye that covers the iris and pupil
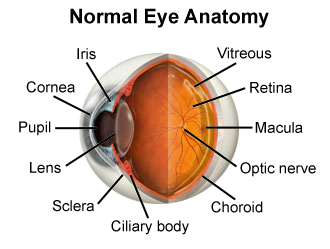
Pupil
The opening at the center of the iris through which light passes
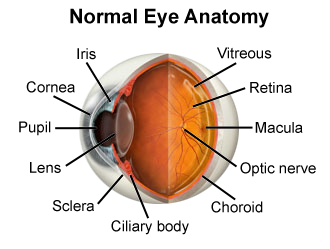
Lens
A clear, transparent, biconvex structure located behind the iris and pupil that focuses light rays onto the retina, enabling us to see clearly.
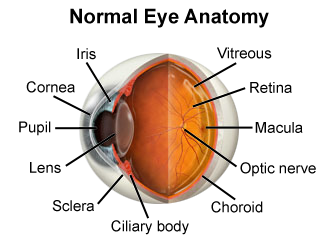
Retina
A clear, transparent, biconvex structure located behind the iris and pupil that focuses light rays onto the retina, enabling us to see clearly.
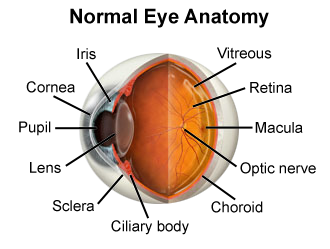
Ganglion cells
The projection neurons of the vertebrate retina, conveying information from other retinal neurons to the rest of the brain
Intermediate cells
Also known as bipolar or amacrine cells to process and transmit signals from photoreceptors (rods and cones) to ganglion cells
Photoreceptor cells
Specialized light-detecting cells (rods and cones) that convert light into electrical signals that the brain uses to form images.
Photopic (daytime) vision
Cones
Fovea
Cones
Photoreceptor cells in the retina that are responsible for color perception and high visual acuity in bright light conditions
Fovea
Where the human eye is able to best distinguish visual details.
Scotopic (night) vision
Rods
Retina Periphery
Rods
Photoreceptor cells in the retina that are highly sensitive to light and responsible for low-light vision
Retina Periphery
the area of the retina responsible for encompassing everything outside the central macula, including the edges of your vision.
Myopia
Also known as nearsightedness is a common eye condition where distant objects appear blurry while close objects remain clear due to the eyeball being too long or the cornea (the clear front cover of the eye) is too curved.
What kinds of lens is used for Myopia?
Biconcave lens used to correct
Hyperopia
Also known as Farsightedness is a common eye condition where close object appear blurry due to the Eyeball being too short or cornea being flatter than normal
What kinds of lens is used for Hyperopia?
Biconvex lens used to correct
Trichromatic theory
States that we perceive colors because we have three types of photoreceptor cells cones that each have photopigments sensitive to different wavelengths of light.
Blue (short)
Green (medium)
Red (long)
Opponent process theory
Ganglion cells in the retina and cells in the thalamus send different color signals depending on if they are excited or inhibited.
R+G– sends a signal for red when excited and green when inhibited.
R–G+ sends a signal for green when excited and red when inhibited.
Y+B– sends a signal for yellow when excited and blue when inhibited.
Y–B+ sends a signal for blue when excited and yellow when inhibited.
Visual Pathway
Axons from ganglion cells make up the optic nerve., which then travels to the LGN of the thalamus.
Primary visual cortex
The first area of the brain's visual cortex to receive and process visual information, relayed from the retinas.
Simple Cells
Sensitive to lines of specific orientation on their receptive fields
Complex cells
Sensitive to lines of specific orientation moving in a specific direction
Hypercomplex cells
Sensitive to lengths and angles of lines
Figure 6.14: Visual Pathways
Inferior Temporal Lobe
Part of the brain involved in complex visual processing, including recognition of objects and faces.
Primary Cells
Respond to simple shapes like squares, spots, and circles.
Elaborate Cells
Respond to complex shapes, textures, and shapes with specific colors. Damage to these cells can result in agnosia.
Face-Selective Cells
Respond to faces, faces of specific orientations, and specific people’s faces. Damage to these cells can lead to prosopagnosia (inability to recognize faces).
Figure 6.19: Olfactory System
Taste Sensation and Perception (_______)
Gustatory
Tastants
Chemicals associated with different flavors
Sweet, salty, sour, bitter, umami (taste of glutamate)
Taste Papillae
Bumps on the tongue that contain taste buds
Explain taste
Trenches around papillae collect saliva and tastants.
Papillae contain taste receptor cells where transduction takes place.
Supertasters have more…
more papillae and are more sensitive to bitter flavors.
According to the video describing features of the Human Genome Project, findings from this project have helped in the prevention of some diseases.
True
False
True
Genetically modified organisms only include food products.
True
False
False
Which of the following is NOT one of Darwin’s Postulates?
Over reproduction
Advantage
Nature vs nurture
Variation within the population
Modification through descent
Competition
Nature vs nurture
Where is the blind spot located within the eye?
Fovea
Lens
Optic nerve
Iris
Optic nerve
The fovea is where the most rods are located and supports peripheral vision.
True
False
False