INT ECON - Short run model of exchange rates; Complete model of exchange rates and trilemma
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
When PPP does not hold in the short run, economists have developed an alternative short-run explanatory theory based on the idea that
a) currency values are influenced in the short run because they serve as short-term assets.
b) currency values are different from other prices since currencies are not considered assets.
c) currency values will eventually result in PPP over time, so no short-run theory is needed.
d) currency values are set by government entities and the IMF so the value often does not result in PPP.
a) currency values are influenced in the short run because they serve as short-term assets.
Assume that the U.S. interest rate is 2%, the European interest rate is 7%, and the future expected exchange rate in one year is $1.224. If the spot rate is $1.18, then the expected dollar return on euro deposits is
a) 1.8%.
b) –1.8%.
c) 12.5%.
d) 10.7%.
d) 10.7%.
Assume that the U.S. interest rate is 2%, the European interest rate is 7%, and the future expected exchange rate in one year is $1.224. If the spot rate is $1.26, then the expected dollar return on euro deposits is
a) 0.4%.
b) 4.1%.
c) 8.9%.
d) –0.05%.
b) 4.1%.
If uncovered interest rate parity holds, the foreign interest rate is 8%, and the home currency is expected to depreciate by 5%, then the home interest rate is
a) 14%.
b) 13%.
c) 8%.
d) 3%.
b) 13%.
Using the UIP (uncovered interest rate parity) equation to determine the spot exchange rate, assume that the expected spot rate (after one year) for euros (in terms of dollars) equals $1.40, the current interest rate on euro deposits is 5.5%, and the current interest rate on dollar deposits is 4.5%. Which of the following current spot rates would satisfy the equation?
a) $1.335
b) $1.414
c) $1.541
d) $0.707
b) $1.414
When expected dollar-euro exchange rates fall, the foreign expected dollar return curve shifts
a) out.
b) not at all.
c) in.
d) Not enough information is provided to answer the question.
c) in.
Based on the graph, if i€ falls, the result is that
a) the dollar interest rate line shifts down and the spot rate rises.
b) the foreign return line shifts up and to the right and the spot rate rises.
c) the foreign return line shifts down and to the left and the spot rate falls.
d) the dollar interest rate line shifts up and the spot rate rises.
c) the foreign return line shifts down and to the left and the spot rate falls.
If domestic returns are greater than foreign returns, then
a) the spot rate is too high.
b) the spot rate is too low.
c) there is no opportunity for arbitrage.
d) expectations of future exchange rates will change in the long run.
a) the spot rate is too high.
Using the UIP equation, what will happen to the spot rate for euros if the interest rate on euro deposits rises, ceteris paribus?
a) The Federal Reserve will have to raise US short-term interest rates.
b) The spot rate to purchase euros will be unchanged.
c) The spot rate to purchase euros will rise (dollar depreciation).
d) The spot rate to purchase euros will fall (dollar appreciation).
c) The spot rate to purchase euros will rise (dollar depreciation).
Equilibrium, in the short run, is achieved when
a) inflation falls to zero.
b) traders adjust their expectations to match reality.
c) the government recognizes a problem and takes action to correct it.
d) differences in rates of return cause investors to purchase and sell currency and thereby change the spot rate of exchange.
d) differences in rates of return cause investors to purchase and sell currency and thereby change the spot rate of exchange.
Whenever there is an excess supply of real balances, the short-run adjustment occurs because
a) aggregate demand is decreased to restore equilibrium.
b) investors and borrowers sell bonds (convert to cash) and drive down their prices (drive up nominal rates of interest).
c) savers and investors buy bonds and drive up their prices (drive down nominal rates of interest).
d) the price level falls to restore real balances.
c) savers and investors buy bonds and drive up their prices (drive down nominal rates of interest).
When the public perceives that a monetary expansion will be temporary, what happens to nominal interest rates in the short run?
a) They will be unchanged.
b) They will overshoot their target.
c) They will fall.
d) They will rise.
c) They will fall.
A perceived permanent rise in the rate of money growth will cause what long-run effects in the economy?
a) a rise in the nominal rate of interest and a rise in real GDP by the same percentage
b) a fall in the nominal rate of interest and a fall in real GDP by the same percentage
c) a fall in the nominal rate of interest and a rise in inflation by the same percentage
d) a rise in the nominal rate of interest and a rise in inflation by the same percentage
d) a rise in the nominal rate of interest and a rise in inflation by the same percentage
An increase in real income _____ the demand for real money balances and thereby causes a ____ in the nominal rate of interest.
a) raises; fall
b) lowers; rise
c) lowers; fall
d) raises; rise
d) raises; rise
During the period 2001–04, the U.S. Federal Reserve lowered nominal interest rates on the dollar by more than the European Central Bank (ECB) did on the euro, a move that most market participants viewed as temporary. What was the effect on the dollar–euro exchange rate?
a) There was no change in the dollar–euro rate because real interest rates were unchanged.
b) The dollar appreciated against the euro.
c) The dollar depreciated against the euro.
d) There was no change in the dollar–euro rate because expectations adjusted.
c) The dollar depreciated against the euro.
When a country's central bank temporarily switches from an expansionary to a more conservative monetary policy, one would expect the exchange rate to:
a) depreciate in the short run, then return to its initial value.
b) appreciate in the short run, then return to its initial value.
c) depreciate in the short run and then stay higher.
d) appreciate in the short run and then stay lower.
b) appreciate in the short run, then return to its initial value.
If there is a temporary increase in the money supply in the Eurozone, ceteris paribus, what is the result for the United States?
a) The dollar appreciates against the euro.
b) The U.S. dollar nominal interest rate will increase, as the euro rate is unchanged.
c) The money supply in the United States must decrease by the same proportion.
d) Long-run expectations shift to expect a stronger euro.
a) The dollar appreciates against the euro.
A key assumption to ensure that domestic returns and foreign returns are in equilibrium is that:
a) there are perfectly flexible prices.
b) there are no capital controls preventing the movement of capital.
c) trade is not subject to any restrictions.
d) the quantity of money is fixed.
b) there are no capital controls preventing the movement of capital.
A nominal anchor is a commitment to keep nominal variables within limits, often tied to an external value or price. When nations do not incorporate such discipline into their monetary policy, exchange rates are often:
a) determined by political considerations rather than economic fundamentals.
b) less dependent on monetary variables.
c) extremely volatile, because traders consider monetary shocks to be permanent.
d) irrelevant to economic activity.
c) extremely volatile, because traders consider monetary shocks to be permanent.
If there is a permanent increase of 8% in the domestic money supply, then which of the following will be true in the long run?
a) The home country currency will depreciate by 8%.
b) Prices will decrease by 8%.
c) Prices will increase by 4%.
d) The home country currency will appreciate by 4%.
a) The home country currency will depreciate by 8%.
When the exchange rate depreciates in the short run and then depreciates slightly in the long run, it implies that the domestic money supply has:
a) permanently fallen.
b) temporarily risen.
c) permanently risen.
d) temporarily fallen.
c) permanently risen.
In the short run, the nominal interest rate is affected by changes in the money supply perceived to be temporary, but once ____ adjust(s), the nominal interest rate ____ in the long run.
a) expectations of interest rates; falls
b) the price level; will revert to its former level
c) real GDP; does not change
d) the supply of money; rises
b) the price level; will revert to its former level
Comparing the examples of Denmark and the United Kingdom in relationship to the European Monetary Union, the krone is pegged to the euro, whereas the British pound is not. What can be predicted then about their interest rates?
a) The United Kingdom can set its own interest rates and pursue an independent monetary policy, whereas Denmark's rates are virtually the same as those of the euro.
b) The United Kingdom will discover that it cannot lower its own interest rates after all, or the pound will depreciate so far that no investors will make investments in the United Kingdom.
c) Denmark gets the benefits of having fixed exchange rates as well as having an independent monetary policy and the ability to set its own rates of interest.
d) Denmark's price level in the long run will be much higher than in the Eurozone because it has to keep exchange rates fixed.
a) The United Kingdom can set its own interest rates and pursue an independent monetary policy, whereas Denmark's rates are virtually the same as those of the euro.
A country with a fixed exchange rate faces:
a) no monetary policy constraints in the long run.
b) no monetary policy constraints in the short run.
c) monetary policy constraints in the long run and the short run.
d) no monetary policy constraints in the long run and the short run.
c) monetary policy constraints in the long run and the short run.
If Japan seeks to control its exchange rates so that ¥100 = $1, which of the following policies should it NOT maintain?
a) a willingness to raise interest rates when its currency begins to depreciate
b) a stable rate of price-level changes that will not cause currency depreciation or appreciation
c) interest rates that provide the same return as alternative international rates
d) a willingness to raise price levels
d) a willingness to raise price levels
Why would making a permanent change in a monetary aggregate have an effect on exchange rates in a nation?
a) A permanent change is never quite as permanent as policymakers claim—people form expectations on past performance rather than declarations.
b) The central bank is always aware of the effect on exchange rates as it formulates policy, so it is very careful to make small permanent changes that have no effect on exchange rates.
c) Traders form expectations of future exchange rates based on the anticipated long-run effects of monetary operations.
d) Permanent rates are mostly set by short-run fluctuations in the rate of interest caused by monetary instability.
c) Traders form expectations of future exchange rates based on the anticipated long-run effects of monetary operations.
If Belize, for instance, wishes to keep its exchange rate with the dollar fixed, what monetary policy options are available to lower unemployment in the short run?
a) Traders would realize that any monetary policy actions taken inside a nation would improve economic conditions without affecting international variables.
b) Belize's monetary action would restore confidence and help keep its currency stable.
c) Belize has all the options available to it, because domestic monetary policy is conducted inside the nation and has no bearing on its international variables.
d) Belize cannot use any monetary policy that would cause its short-run exchange rate to depreciate against the dollar.
d) Belize cannot use any monetary policy that would cause its short-run exchange rate to depreciate against the dollar.
With fixed exchange rates and capital mobility:
a) interest rates in the home country are higher.
b) monetary policy maintains its autonomy.
c) interest rates in the home country and in foreign countries are equalized.
d) interest rates in foreign countries are higher.
c) interest rates in the home country and in foreign countries are equalized.
Exchange rate interventions occur when a government:
a) buys and sells its own currency on forex markets.
b) buys and sells its own currency and other currencies on forex markets.
c) buys and sells other currencies on forex markets.
d) increases its interest rate.
b) buys and sells its own currency and other currencies on forex markets.
During the U.S. Civil War (1861–1865), the Confederate states printed their own currency. Events occurred during the war that affected the exchange value of the Confederate dollars. What evidence was there that supports the theory of long- and short-run exchange rate determination?
a) The Union soldiers burned Confederate dollars at every opportunity, making them more valuable than the Union dollar.
b) The Confederate dollar's value was closely linked to the difference in the deposit rates in Southern states' banks.
c) The Confederate dollar became worth more as it became clear that the South would lose, because the Confederacy's dollars would become collectibles.
d) Speculators traded for profit and based their valuation on the long-run expectation of the exchange rate, which tracked closely the probability of a victory for the South.
d) Speculators traded for profit and based their valuation on the long-run expectation of the exchange rate, which tracked closely the probability of a victory for the South.
What is the formula for dollar return?
In other words: if + (Se - S)/S
Where:
Se = Expected future spot rate
S = Spot rate
if = Interest rate in the foreign country
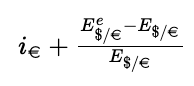
In the short-run, we assume prices are ______ and the ______ approach to exchange rates in valid.
sticky; asset
(In the asset approach, exchange rates are determined by the supply and demand of assets)
In the long-run, we assume prices are ______ and the ______ approach to exchange rates in valid.
flexible; monetary
(In the monetary approach, exchange rates are determined by money supply and price levels)
What happens to home interest rates and home exchange rates in the case of a temporary home monetary expansion?
Home interest rates fall and the home exchange rate depreciates. This temporary policy can be consistent with a nominal anchor in the long run.
What happens to home interest rates and home exchange rates in the case of a permanent home monetary expansion?
Home interest rates fall and the home exchange rate depreciates. In the short-run, it would also overshoot what will eventually be its long-run level. This permanent policy is inconsistent with a nominal anchor in the long run.
What is the essence of the trilemma?
In a fixed exchange rate regime, a country loses all monetary policy autonomy. The only way to recover it is to impose capital controls, but that would sacrifice capital mobility.
How are the short-run and long-run models of exchange rates connected?
The short-run equilibrium occurs when the uncovered interest parity (UIP) condition holds. However, the UIP needs a forecast of the long-run future expected interest rate to hold.